Content
- 1 Siberia and viticulture
- 2 Recommendations for the care of grapes
- 3 Features of caring for grapes on the site
- 4 Growing features
- 5 Greenhouse cultivation technology
- 6 Cultivation rules in open ground conditions
- 7 Tips & Tricks
- 8 How to plant grapes in Siberia (video)
- 9 Reviews and comments
- 10 Grape varieties for Siberia
- 11 Planting grapes in Siberia
- 12 Grape care in Siberia
- 13 Reviews and advice of Siberian winegrowers
- 14 Where to get quality planting material
- 15 Preparation of a plot for a vineyard
- 16 Planting vines
- 17 Vineyard care
- 18 Extreme situation
- 19 Conclusion
.
The grape plant is one of the plants that love moisture and warmth. The planting material has a negative attitude to temperature extremes. If southern grape varieties are planted in Siberian latitudes, they will not ripen and will not be able to yield a harvest. This is due not so much to the difference in climatic conditions as to the instability of the climate.

Srostinsky grapes - one of the varieties for cultivation in Siberia
Siberia and viticulture
Considering viticulture from the point of view of the abundance of diseases and pest activity, the Siberian region is more adapted to planting and growing grapes. For viticulture to be effective, you need to choose the right variety.
For the conditions of a quickly ending summer and a long harsh winter, early grape varieties are chosen. Providing them with care, it is necessary to insulate the planting material. Planting is carried out with grafted varieties, with the help of a rootstock, hardy varieties are planted.
There are certain recommended varieties for planting and growing grapes in Siberia. They were either bred locally, or they were created by breeders for harsh climatic conditions. Among the European and southern varieties, there are those that can grow in the regions of Siberia.
Species suitable for planting in Siberia:
- Siberian bird cherry, Muscat and Riddle.
- Katyr, Dubinushka and Srostinsky.
- Delight, Tukai and Dombovskoy.
The latter is a popular variety for the area. The grapes are small and harvest early and are highly resistant to cold weather. Southern varieties can be safely grown in Siberia, but they need shelter.
Known to all gardeners and beyond, Isabella and Lydia are great for planting and growing in cold climates. The cultivation of these varieties in Siberia is carried out in order to obtain wine, since they are not particularly appreciated fresh.

Katyr grapes give good yields in a harsh climate
Recommendations for the care of grapes
To plant grapes and grow them in cold climates, you need to prepare a hole that will be one meter deep. Gravel is poured at the bottom of the pit, other material can be used, followed by organic fertilizers.
The soil that you dug from the hole is mixed with fertilizers and sand, and returned to its original place. In order for the grapes to grow in the depression, an insignificant part of the land is harvested. This will create convenience for warming the planted plant. Along the slide on which the seedling is placed, the roots should be straightened and sprinkled with soil. The final stage of planting is abundant watering.
You can place a pipe in the dug hole, which will provide an inflow of water and oxygen to the root system of the plant. This action is carried out at will, but its effectiveness is so high that one should think and work hard to implement it.
The bottom of the excavated area is covered with a special material, where the bottom of the pipe is placed and the entire area is covered with stones, gravel is suitable. Further processing of the pit corresponds to the previous method. The pipe must be brought out in such a way that it can be covered to the cold.

The grape planting pit can be equipped with a tube for the inflow of water and air
Vineyard bush cleaning
Due to the peculiarities of the climate of the Siberian region, the period and quality of pruning is carried out in a special order. Vine pruning is done twice, dividing the pruning sequence in a couple of times. The first cleaning of the vineyard begins in August and ends in September. This period is notable for the harvested harvest and the presence of green vegetation in the vineyard. To be removed:
- A vine that has already yielded a harvest.
- Shoots characterized by weakness.
- Damaged branches and dry areas of the plant.
You need to leave those parts of the bush that create a replacement for the removed areas.
The second pruning is done before the grapes are sheltered for the winter. It is optimal to peel the grapes as late as possible to allow the plant to absorb the maximum nutrients from the soil.
Spring is not suitable for pruning grapes in Siberia. In this region, springtime is accompanied by an active flow of sap and flowering.
The rules for cleaning the bush are similar to the recommendations in other regions of the country. The reason for pruning is the formation of a replacement section of the vine.
The pruning is directed to control the density of the grape bush. The fruiting vine is pruned completely and a few shoots are left. One shoot is pruned more, the other less. When you grow grapes in Siberian latitudes, keep in mind that it is important to control the congestion of the bush. One bud is needed per eye for vegetation and yield, this is the optimal pruning of the grape bush.
The first twelve months after planting the grape bush grows and develops. The vine is formed and saturated with nutrients. At the time of fruiting, the vine is left with twenty eyes, from which future clusters will grow. In the second year of growth. The number of places for future bunches is doubled. Also done in the third year of growth. And in the fourth year after planting the seedling, the grapes should grow about eighty eyes.
By regulating the growth of the vine and the strength of the vineyard, the number of places under the bunch can reach one hundred and fifty. If the grapes are small, then there should be many eyes, and vice versa. The degree of congestion of a grape bush depends on its endurance and strength.

Pruning of grapes in Siberia is carried out in the fall
Features of caring for grapes on the site
To grow grapes in Siberia, you need to prepare the plant for the cold - harden it. Southern grape varieties need to be grown in Siberia by beginners and experienced gardeners under insulation material. Since they can fall prey to temperature extremes. Shelter is needed for young grapes and in an unstable spring.
Over time, the grapes will become more resistant to changes in climate and will calmly endure the winter. In caring for a vineyard in Siberia, it should be borne in mind that the planting material must be insulated for the winter. A huge role is played by feeding grapes and processing planting material with special preparations.
The pruned sections of the vine are removed from the mountings, and laid along the site where it is planted. Dry bushes are subject to shelter. The climate for landing should be windy and warm. It is necessary to cover the grapes so that moisture does not get onto the site at all. High humidity leads to disease.Cover the vine with a special material and sprinkle it with earth from all sides. The grapes need to be sprinkled with abundant snow so that the planting material is protected from excessive frost. If the snow is heavy, then you need to fence the vineyard from excessive rainfall. With the onset of spring, the upper part of the vineyard protection must be removed.
The insulation material is opened so that air can access the planted material. In the middle of spring, all the shelter is removed, greenhouse conditions are created for the planting material until the time when the period of probable frost is over.
For beginners, growing grapes in Siberia will not seem difficult if you follow the care of the plant consistently.
Subscribe Be aware of new products on our site
 Grapes in Siberia grow and ripen quite well, subject to the correct choice of the variety or hybrid form, as well as adherence to the cultivation technology. Every year, breeders and amateur winegrowers develop new varieties that are perfectly adapted to growing in the difficult climatic conditions of this region.
Grapes in Siberia grow and ripen quite well, subject to the correct choice of the variety or hybrid form, as well as adherence to the cultivation technology. Every year, breeders and amateur winegrowers develop new varieties that are perfectly adapted to growing in the difficult climatic conditions of this region.
Growing features
The cultivation of grapevine in Siberia has its own characteristics, which are due to a very short and often cold summer period for heat-loving crops. In the southern part of Western Siberia, especially on the territory of virgin regions, the continentality of the climate increases, and the formation of the climate of Eastern Siberia, in addition to the territorial location of the region, is influenced by the features of the relief.
However, the climatic conditions of Siberia also have their advantages for viticulture: there is a very low risk of damage to the vineyard by phylloxera or downy mildew.

The main difficulty for novice winegrowers is the cultivation of grapes in open field conditions. Many gardeners are abandoning this method in favor of growing in a greenhouse. The protected soil ensures good growth and development of the vine, and also allows you to get a bountiful and high-quality harvest.
Also read: Strawberry "Pineapple": description and useful properties of the variety
Novice winegrowers are advised to grow this thermophilic and rather capricious crop using own-rooted seedlings in protected ground conditions.

| Indoor variety name | Description of the plant | Description of the berry | Features of the variety |
| "Tukai" | Table variety of very early ripening period. The bush is vigorous. The flower is bisexual. The brushes are of medium density, large, cylindrical-conical, winged. Average weight 850 g | Berries are medium, round, white, with seeds | To mildew, oidium unstable |
| "Rusven" | Very early maturation. The bushes are vigorous. Medium-dense or dense brushes, large, cylindrical-conical, with an average weight of up to 550 g | The berries are large, round, matte pink. The pulp is juicy and sweet | Resistant to mildew, powdery mildew. Frost resistance up to -25 ° С. |
| "Amirkhan" | Canteen, early ripening. The bush is vigorous. The flower is bisexual. Brushes are dense, large, cylindrical-conical, weighing up to 850 g | The berries are large, oval, pink in color. The taste is simple, pleasant, with a slight nutmeg | Average frost resistance. The variety can be affected by gray mold |
|
"Delight" |
Canteen form of early ripening. The bush is medium-sized. The flowers are functionally feminine. Brushes are loose, large, conical in shape, weighing up to 830 g | The berries are very large, oval or ovoid, pink, reddish in the sun. The skin is thin. The pulp is fleshy. The taste is very pleasant and harmonious | Resistant to mildew, powdery mildew, gray mold. Frost resistance up to -25 ° С |
| "Kara jijigi" | The bush is vigorous. The flower is bisexual. Medium or loose brushes, medium, tapered | The berries are small, ovoid or round-oval, black. The skin is thick and firm. The pulp is fleshy, juicy | Frost resistance is insufficient. The variety is strongly affected by powdery mildew |
Greenhouse cultivation technology
Growing grapes in greenhouses is very promising and is especially in demand in areas where recurrent spring frosts are often observed, and the summer period is quite short. The technology of cultivating grapes in a greenhouse has a number of differences from cultivation in open ground. To obtain a good result, it is very important to strictly adhere to agricultural techniques, providing plants with an optimal temperature regime, timely feeding and watering, carrying out competent pruning of grape bushes.

- The greenhouse structure for growing grapes should be as high as possible, at least 3 m, and sufficiently spacious.
- It is recommended to give preference to durable structures equipped with high-quality lighting fixtures and heating equipment.
- When using powerful heating systems, it is required to strictly monitor the humidity indicators and carry out systematic ventilation.
- Despite the adaptation of some varieties to cultivation in indoor conditions, it is necessary to carry out manual pollination in a timely manner.
- Whether to carry out the chasing of shoots and to tear off the leaves that shade the bunches when grown in a greenhouse, each grower decides independently, based on the state of the plant and the load.
When cultivating grapes in greenhouses, the gardener needs to pay attention to the measures for feeding and replenishing the soil. Greenhouse grapes need good watering. If the inside of the greenhouse is dry enough and airing is carried out, then mildew affects the grapes extremely rarely. For the purpose of prevention, treatment with potassium permanganate or systemic drugs is carried out.

Cultivation rules in open ground conditions
When growing winter-hardy and early grape varieties, zoned for cultivation in Siberia, some agrotechnical requirements should be adhered to:
- an ordinary vineyard planting in open ground should be located in the direction from north to south;
- it is also recommended to place grape plantings along the southern walls of buildings or blank fences;
- the standard distance between the rows should be at least one and a half meters, but can be increased to two meters when the landings are located from east to west;
- it is necessary to adhere to the distance from the buildings to the vineyard in meter, which allows to increase the area of plant nutrition and facilitates the maintenance of the vineyard.

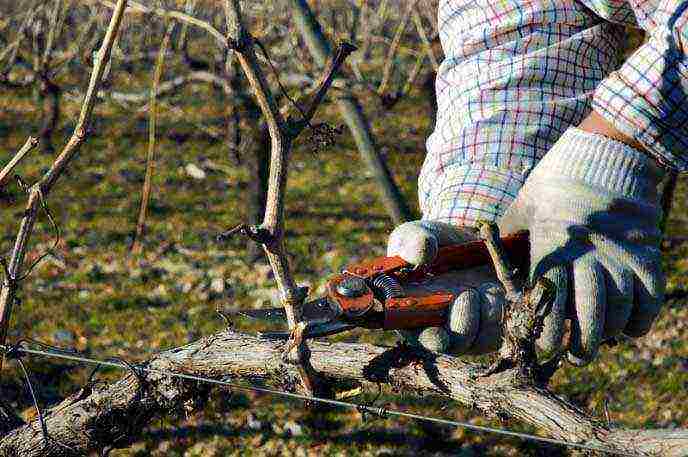
You should stock up on a film or non-woven covering material, as well as arcs that are installed over grape bushes with the threat of spring frosts.
Autumn pruning is carried out in two stages. The first pruning is done between mid-August and late September. During this period, the fruiting vine and the thinnest and weakest branches are removed. The second pruning allows you to create a fruit link or replacement knot.
After reading the corresponding article on our resource, you can learn how to properly prepare grapes for winter.

Tips & Tricks
Climatic and weather features of the Siberian region imply the observance of the following rules when growing grapes:
- it is very important to correctly calculate the load of plants with a crop and not to overload the grape bush;
- it is necessary to provide shelter for the overwintered vine that has not yet been tied to trellises for the period of the most severe spring frosts;
- correct agricultural technology involves the acclimatization of plants and excludes the introduction of a large amount of nitrogen-containing fertilizers.
How to plant grapes in Siberia (video)
Timely removal of the shelter in the spring will protect the vine from damping and will allow the plant to harden. The implementation of competent care makes it possible, even in conditions of risky farming, to receive guaranteed high and high-quality grape yields.
Attention, only TODAY!
Reviews and comments
Did you find a mistake in the text? Please select it and press Ctrl + Enter. Thank you!
Rating:
(
estimates, average:
out of 5)
Grapes, traditionally considered a southern crop, have long been successfully grown in Siberia. This opportunity appeared not because the harsh Siberian climate has softened, but thanks to breeders who have developed frost-resistant varieties. However, in a short summer, even unpretentious grapes need special care.
Grape varieties for Siberia
The opportunity to grow large and sweet grapes in Siberia is a good gift for gardeners in this region. Varieties have been developed that are adapted to a sharply continental climate with strong fluctuations in both daily and annual temperatures. The warm frost-free period here lasts three months: from early June to early September. Therefore, early varieties grow well in Siberia: Muromets, Solovyova-58, Tukai, Rusven, Kodryanka and other early ripening plants, in which 90-115 days pass from budding to full ripeness of berries.
Photo gallery: grape varieties suitable for growing in Siberia
Planting grapes in Siberia
The correct planting of vines is one of the important factors affecting a good harvest.
Seat selection
Choose a place that is sunny and protected from the wind. Grapes should not be planted in lowlands, where frost, fog and stagnant water are more common. On a personal plot, it is better to place grapes near a blank fence or wall of a house, facing south or southeast.
In one place, grapes can grow and give good yields for 15–20 years.
Video: choosing a place for grapes
Timing
The most favorable time for any planting in Siberia is spring. Autumn is very short here, snow can fall already in September, the seedlings, when planted in autumn, simply will not have time to take root. Plant grapes in May under cover (in a greenhouse, greenhouse) or in open ground when the threat of frost has passed. In some regions of Siberia, snowfalls occur in early June.
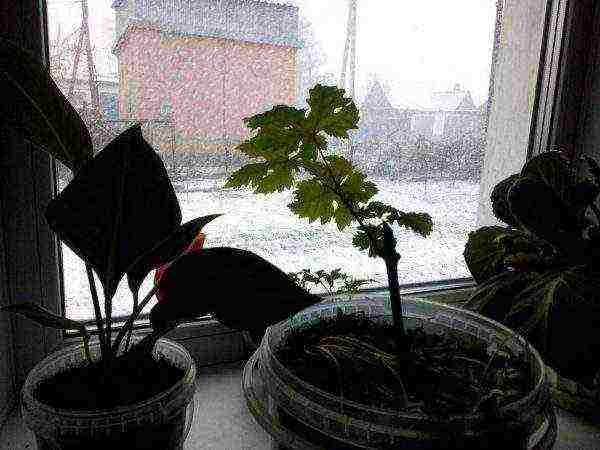

In Siberia, until June, there is a high probability of frosts and snowfalls, so the seedlings bought in the spring have to be kept on the windowsill before the arrival of heat
Pit preparation
During the growing season, grape shoots grow by 5-10 cm per day. Such an active growth requires good nutrition. If the grapes are planted in unprepared soil, then all nutrients are quickly consumed from the upper fertile layer. The bushes will not develop well and bear fruit. Therefore, at least 2-3 weeks before planting the seedlings in a permanent place, planting pits are prepared for them and filled with fertilizers.
Preparation of planting holes:
- Dig a trench 30 cm deep and 80 cm wide; towards the bottom it can taper to 60 cm. The length depends on the number of seedlings. The distance between the bushes should be 2 m. If you plan to plant in 2 rows, then the row spacing is 2-3 m.
- Put the top layer of soil (on the bayonet of a shovel) to one side, everything below - to the other.
- Under each seedling inside the trench, dig a planting hole 60 cm deep and wide, that is, the total depth at the planting sites should reach 90 cm from ground level.
- Pour ash and 200 g of superphosphate at the bottom of the planting pits. Lay a layer of twigs and rough weed stalks.
- Fill the pits with a mixture of humus, topsoil and river sand (1: 1: 0.5).
- It is not necessary to fill the trench itself; reinforce its walls with boards. Thus, the vine bed will be sunk into the ground, that is, from the planting level to the ground level, there should be 30 cm (trench depth).
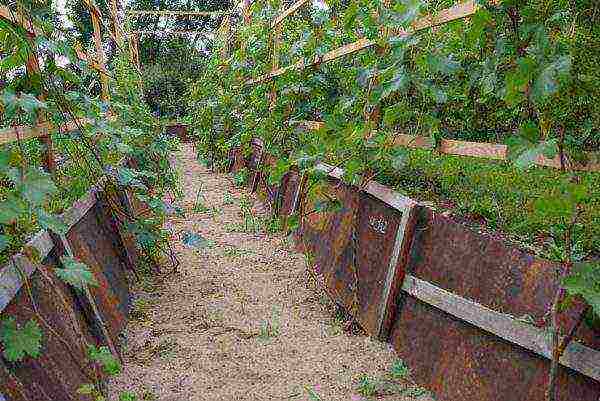

The grapes are planted below the soil level on the site, the walls of the trench are reinforced with shields
For Siberia, at a planting depth of 20–40 cm, the heat obtained over the summer is used to the maximum extent. The trench can be made wider, then it will be better illuminated by the sun. The planting hole is also often made larger. It is believed that a pit 1 m deep, filled with organic matter and mineral fertilizers, provides the grape bush with nutrition for 10-15 years, that is, no additional feeding is needed throughout the cultivation.
If you want to do without top dressing and not dig a huge hole, sow the soil under the bushes and in the aisles with siderates: alfalfa, mustard, clover, peas, lupins, wheat, oats. These plants contribute to the redistribution of nutrients between soil layers and the accumulation of humus. Grow siderata before flowering, then cut and place under the grapes as mulch.
Drainage system
There are recommendations to lay a drainage of stones and broken bricks at the bottom of the planting pit and install a pipe through which the grapes are watered. But there are also reviews of gardeners who did not see the difference between planting grapes in "smart" pits and in ordinary ones. When watering through the pipe, the roots stretch towards it, and do not develop evenly in depth and breadth. Drainage silts over the years, the roots can rot.
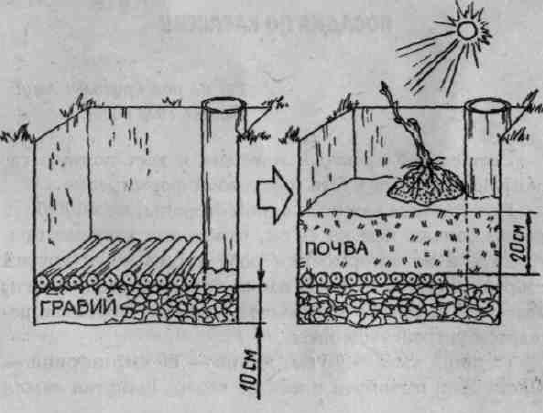
A smart pit in Siberia does not justify the effort required to build it
Many growers agree that "smart" pits are needed only in the first 1-2 years after planting, and then they lose their effectiveness, since the roots go beyond its boundaries. However, in the climatic conditions of Siberia, it is impractical to make drainage systems, since young non-fertile bushes rarely need watering - 2-3 times per season.
There are few hot days in the region; rainy weather is more common. In addition, the evaporation of leaves in young grapes is minimal, it has not yet developed into a strong bush. The best option is to put branches instead of stones at the bottom of the pit, which will eventually rot and turn into top dressing, and after planting, cover the soil with a layer of straw, hay, grass cuttings or green manure.
Seedling preparation and planting
Grape seedlings in Siberia are rooted cuttings with a closed root system. They are sold in plastic cups. Many buy them in early spring, while there is a choice and low prices are kept, so preparation for planting and the planting itself consists of the following stages:
- If you bought seedlings in early spring, then transplant them by transshipment from cups into larger pots and keep them until the end of the frost on the windowsill, glassed-in balcony or in the greenhouse. Use the soil for transplanting from your site, mixing it with humus (1: 1).
- On warm days (20⁰C and above), take the cuttings out under the open sky for an hour first, gradually increase the exposure to sunlight until daylight hours, be sure to bring them into heat at night.
- After June 5-7, you can start planting in open ground, the day before, water the seedlings well.
- For each seedling, dig a pot-sized hole in which the grapes grow in a pre-prepared planting hole.
- Take out the seedling along with a clod of earth and place it in the hole at an angle in the direction in which you will bend and lay the vine in the fall for shelter for the winter. Bury the seedling up to the first green petioles.
- Cover with earth taken out when digging a hole, pour a bucket of water and mulch.
Video: how to properly plant grapes in Siberia
Grape care in Siberia
Growing grapes is a complex of agricultural practices, which includes: irrigation, shaping and thinning, tying to trellises, providing heat, shelter for the winter. Diseases and pests of grapes have not yet reached Siberia, so there is no need to spray the plantings.
Watering
This solar crop is drought and heat tolerant. The soil under the grapes must be dry. The need for water is determined by the appearance of the plants - the leaves lose their elasticity in the heat, they hang. To water the seedling, make a groove 15–20 cm deep around the circumference, stepping back 30 cm from the stem, pour 5–15 liters of water into it. The rate depends on how well the soil absorbs. Use only sun-heated water.After watering, level the groove and mulch.
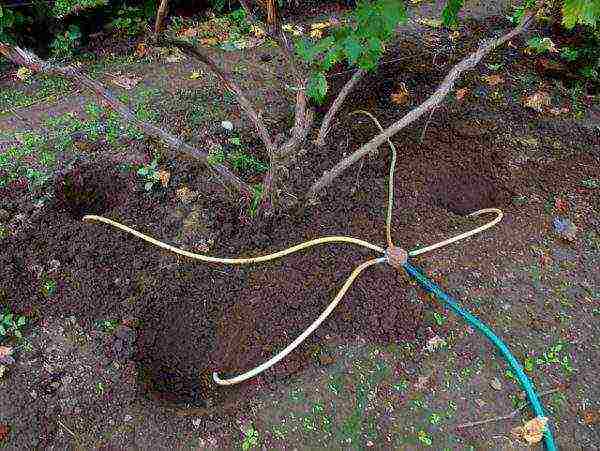

For watering the grapes, furrows or holes are dug
In the Siberian summer, after planting, seedlings will rarely have to be watered, especially if the vineyard is located in a place protected from the wind, and the ground is covered with mulch. A fruiting vine needs more water. But the frequency and rate of watering depends on the weather. The state of the grapes is still the signal. Pay special attention to it during periods:
- immediately after bud break;
- 2 weeks before flowering;
- 1-2 weeks after flowering;
- in front of the winter shelter.
If the weather is dry during these important phases of development, be sure to water the grapes, soaking the top 30-50 cm. Do not water during flowering! In August, watering is also undesirable, the vine will ripen better without them.
The importance of mulch
The mulch keeps the soil moist and loose, the lower layer gradually decays, and the upper one remains dry and does not allow fungi to develop. Thanks to the mulch, there are no sudden temperature changes in the root zone during rain; in the heat, the sheltered ground maintains a comfortable coolness. In addition, such a litter, rotting, releases carbon dioxide - one of the elements of photosynthesis.
Lay mulch in the spring only after the ground has warmed up. Rotted sawdust, grass cuttings, hay or straw are good choices. These natural materials will rot by autumn and enrich the earth with humus.
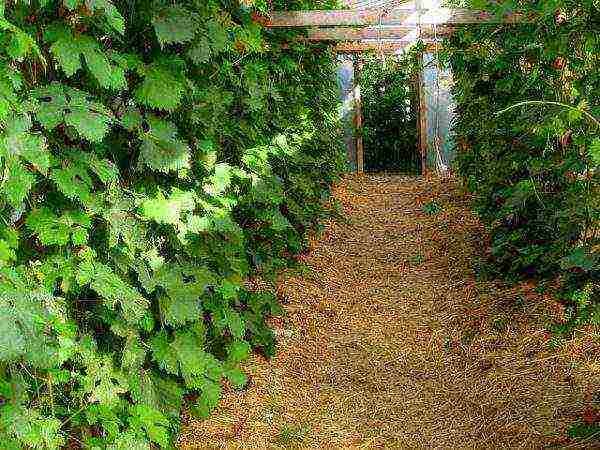

Mulch keeps the soil moist and loose, the lower layer gradually decays, and the upper one remains dry and does not allow fungi to develop
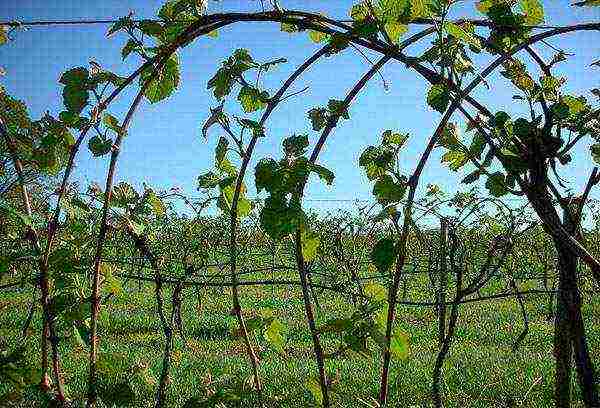
Bush formation
Start the formation in the first year with a garter, it is not necessary to build a trellis, it is enough to stick stakes or fittings 1.5 m high next to the seedlings. Leave the two strongest shoots on each cuttings, when they grow to 50-60 cm, tie each to your support in the form of the letter V. It happens that only one shoot grows on the handle, tie it up too.
All summer, stepchildren will grow from the axils of the leaves, they need to be pinched. Some growers recommend pinching stepchildren not at the base, but over the second leaf. In their opinion, additional leaves improve photosynthesis, the young vine receives more nutrition and strength. In August, emboss, that is, pinch the tops of the main shoots.
Stages of forming a bush from a seedling with two shoots (the simplest scheme):
- In autumn, after shedding the leaves, cut one shoot into 4 buds, and the other into 2. The first will become a fruit arrow, the second - a replacement shoot, and together they form a fruit link.
- In the spring of the second year, tie the arrow and the replacement shoot horizontally to the trellis, and direct the stepsons growing from the axils of the leaves vertically.
- In the fall of the second year, cut the long sleeve of 4 buds in half, that is, both sleeves will now have two vertical shoots. Then shorten these four shoots: those closer to the center of the bush by 2 buds (replacement shoots), and the distant ones by 4 (fruit arrows).
- In the spring of the third year, tie the fruit arrows horizontally, and allow the replacement knots to grow vertically. Over the summer, 12 stepchildren will grow up - tie them up vertically.
- In the fall of the third year, cut each of the two horizontal branches (fruit arrows) to a replacement knot together with the outer four shoots. Again, only four vertical shoots will remain in the bush. We cut them again according to the same principle: the ones closest to the center of the bush by 2 buds, the remaining two - by 4 buds.
- From the spring of the fourth year, continue the formation according to the given scheme.
Photo gallery: pruning grapes by year
If only one shoot grew on your seedling in the first year, then in the fall, cut it into two buds, of which by the next year form an arrow and a replacement shoot, then follow the given scheme. In Siberia, you can leave shoots with a large number of buds (5-6), that is, do not shorten the vine too much in case of freezing in winter. But in the spring, do not cut the main branches, but blind the extra buds and shoots. If you leave them, they will take up strength, thicken the bush, grapes in a short summer may not have time to ripen.
Pruning grapes in the spring is not recommended. At this time, sap flow begins, the wounds on the grapes do not heal well, the vine "cries", loses a lot of strength, will develop poorly, and may die.
On vertical shoots, clusters will be laid in June, leave only the lower, well-developed ones, pluck the upper ones. If you leave everything, then in a short summer they will not have time to ripen.
Having understood the principle of formation, experiment, leaving a different number of buds, shoots, inflorescences. So you will find out from your own experience under what conditions you can get the maximum yield.
How to provide extra warmth to grapes in Siberia (trellis device)
Trellis can be not only a support, but also a protection for grapes. Classic trellises consist of metal or wooden posts and a wire stretched between them.
Design features of trellises allowing heat accumulation:
- A visor over the trellis: at night, the cold air coming from above is cut off, and the heat rising from the ground is retained.
- The ends covered with a foil - protection from the wind.
- Reflective screens made of foil or aluminum sheets around the perimeter of the trellis - the effect of better illumination and also an additional source of heat.
Video: one-plane trellis for grapes
Shelter grapes for the winter
After harvesting (and young seedlings in late August - early September), the grapes must be protected from the first frost. To do this, cover the ground under the bushes with an old film, remove the vines from the supports, lay them on the film, and on top build a greenhouse in the form of a tunnel made of polycarbonate or arcs and film. As a result, when the temperature drops at night, the leaves will not freeze, and during the "Indian summer", when there are still warm days, photosynthesis and bud maturation will continue.
After leaf fall, with the onset of cold weather, remove the temporary shelter, and leave the film on the ground. On top, build something like a box with sides. It is necessary to make such a structure so that the grapes are in the air gap, and not sandwiched between the upper and lower shelters. Lay cardboard, foam sheets, agrofibre, burlap or other insulation on the sides of the box. Cover all this with a film on top, dig in its edges. Water should not get inside the shelter, otherwise the grapes will sop. For waterproofing, you can use slate, roofing felt and other materials.

The grapes are packed in boxes, insulated and protected from getting wet by slate
In a winter shelter, the grapes should not come into contact with metal (arcs, pins). Otherwise, the shoots in this place will freeze, the buds will die.
In the spring, when the snow melts, remove the shelter. In Siberia, this can happen in April and May. There is no need to wait for the soil to thaw. Do not lift the vines, but build, as in the fall, a greenhouse. It is possible to remove it and tie the shoots to the trellises only when the threat of frost has passed, that is, in June. On warm days, do not forget to open the ends and ventilate.
Reviews and advice of Siberian winegrowers
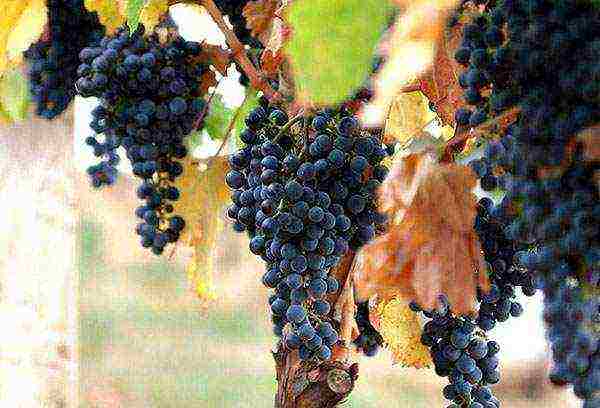
Growing grapes in Siberia is challenging but interesting. The main thing is to prevent the bushes from freezing in the winter and to provide the maximum amount of heat in the summer. If bunches of ripe grapes appear on the vines, it means that all your efforts were not in vain. You can assign you the honorary title of winegrower, because not every gardener can successfully cultivate this crop, even in the south of the country.
Living in a cold region is not a reason to eat only imported southern berries, and growing grapes in Siberia is not a fantasy, but a very real phenomenon. On the forums of gardeners, you can find complaints that a person spent time and money, but he was not able to care for a delicate culture. Indeed, the occupation is difficult, so it is better to accumulate experience gradually.Do not try to immediately start a huge plantation with many different varieties, start with the simplest. For a first try, try growing an ornamental girlish grape.

Where to get quality planting material
First of all, take care of the planting material. Do not buy seedlings on the market: unscrupulous sellers have noticed the interest of Siberians in exotic culture and are making good money on it. In the south, they buy the cheapest species for a pittance, which no care will help them survive the harsh winters. In cold regions, the vine is sold for a lot of money under the brand name of zoned varieties.
For quality material, check out your local nursery or specialty mall. Experienced consultants will advise you on which varieties are good for beginner winegrowers, give advice on planting and care. If your friends have already mastered the cultivation of grapes in the northern dacha, you can take seedlings from them.
Even if you know how to properly plant grapes in Siberia, but use the wrong material, you may not wait for the harvest. When choosing seedlings, pay attention first of all to frost resistance and early ripening of fruits.
The best varieties for Siberia:
- Thumbelina;
- Savraska white;
- Klyunevsky;
- Pinocchio;
- Siberian bird cherry;
- Sharov's riddle.
Maiden grapes are propagated by seeds, cuttings and layering. The easiest way is to cut off a part of the shoot with leaves in the fall and put it in a vessel with water. Spray the cutting from time to time. When roots appear, you can plant it in the ground.
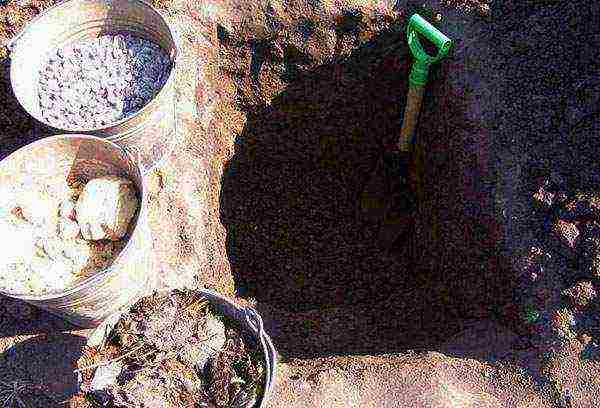

Preparation of a plot for a vineyard
To make the southern guest feel comfortable in unusual conditions, you need to provide him with the most convenient place and provide him with good care. The plant is accustomed to the sun - plant it where neither trees nor buildings will shade the vineyard. The vine needs a lot of moisture, but high groundwater will badly affect its root system. Cold northerly and northeasterly winds will also not like a heat-loving culture. To prevent grapes from freezing in winter, they need a snow cover at least 50 cm thick.
On a good bush, many long shoots grow annually, and in a short summer several kilograms of berries ripen on it. For such a rapid development, good nutrition is needed. The soil should be light and fertile.
In order for the plants to be spacious, the distance between them should be at least 2 m. You can dig a trench 0.5 m wide and 60 cm deep, or separate holes of the same volume. Place 10 cm of gravel at the bottom for drainage. Pour fertile soil in half with compost under the roots, add 50 g of superphosphate and 20 g of potash fertilizer to each pit. Mix the soil well, cover it with earth on top so that the root system does not come into contact with chemicals.
Maiden grapes are less picky about growing conditions. He also does not like high groundwater, but it can grow in the shade and on not very fertile soils. It is desirable that the ground be loose before planting - carefully dig up the site.
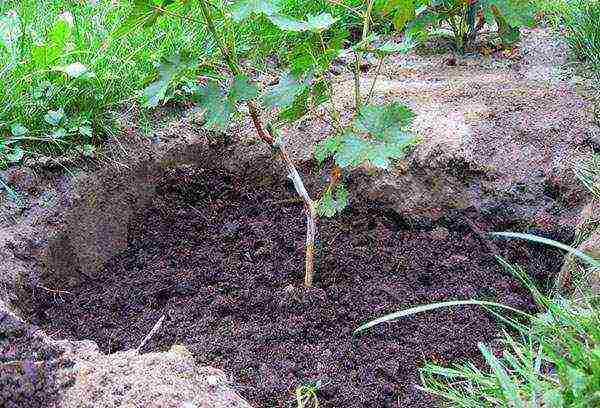

Planting vines
Grapes are planted in spring, when the temperature outside reaches + 15⁰. In Siberia, this weather usually occurs towards the end of May. Although the plant loves the sun, it will not like planting on a very clear day. Choose cloudy weather or an evening before sunset.
Both girlish and fruit grapes will take root faster if the root system is properly prepared. Before planting, treat the underground part with a growth stimulant and dip it in a clay mash. Spread out the roots of the plant and place it in the hole. The root collar should be buried a couple of centimeters into the ground. You do not need to fill the holes flush with the ground, leave a circle about 10 cm deep.
Stock up on trellises in advance and install them near the bushes. After planting, the shoots should only grow vertically. This position allows the plant to develop correctly and makes it easier to care for it.In the early days, the soil should be constantly moist. If you see that the top layer is dry, water the plantings.
When planting maiden grapes, calculate the depth and diameter of the holes according to the size of the root system of the seedling. All roots should be covered with soil, it is better to deepen part of the stem than to leave a fragment of the appendage on the surface. Planting is possible not only in spring, but also in September.

Vineyard care
The soil in the hole has been well fertilized, but the young roots cannot reach the nutrient-rich layer. Feed the plants several times with a manure solution: 1 liter per 10 liters of water. Since August, nitrogen is harmful to plants, it causes rapid growth of young shoots, and the bush will not have time to prepare for wintering. At the end of summer, water them with phosphorus-potassium fertilizers a couple of times. Girlish grapes can be watered with a superphosphate solution.
In Siberia, grapes usually do not get sick and are not affected by pests: all infections and insects hostile to it live in warm regions. Summer care comes down to watering, fertilizing, weeding and loosening. Cover the ground along the rows with a thick layer of mulch, then this work will be cut in half. Girlish grapes also do not require complex care, the methods are similar to those used in relation to fruit varieties.
When the bushes begin to bear fruit, you need to correctly calculate the number of buds from which clusters appear. If there are few of them, shoots will begin to develop vigorously, and the bush will not prepare for wintering. If the harvest is too abundant, young shoots will not develop.
In the fall, trim, leaving the required number of eyes.
- For the first two years, you don't need to cut anything.
- Third year - 20 fruit buds.
- The fourth year is up to 40.
- Fifth year - up to 60.
Do not let a young bush grow many shoots. In the first year, leave 1-2 of the strongest shoots, shorten the rest so that 2 leaves remain on each. In the fall, after the first frost, remove the vine from the trellis and trim off any unripe areas. Place the shoots on the ground and insulate them. There are many ways: you can dig shallow trenches and bury the vine or cover it with sawdust, pine needles, straw. The methods are laborious, and during the winter, some of the buds undergo heating. It is better to make a gutter about 25 cm deep from the boards and cover the laid shoots with wooden shields. Air and wood are excellent heat insulators, and a large snowdrift will not let even a strong cold down.
Advice
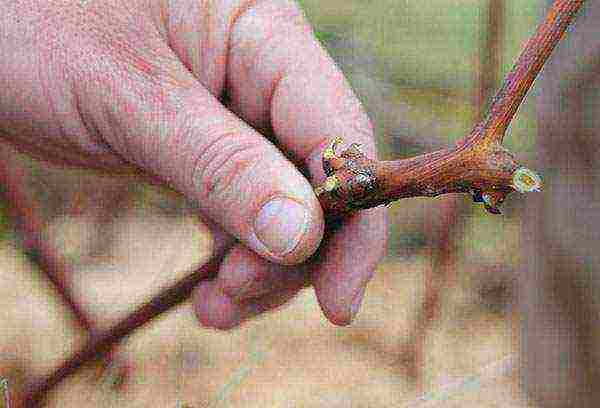
Bend the tip of the shoot to identify an immature area. If it bends well, the site did not have time to lignify. On the ripe fragment, a crunch is heard when bent.
In the spring, dig out the bushes or remove the cover from the gutter, but do not lift the vine, but arrange it with a film shelter. It is possible to fix the shoots on the trellises when the danger of spring frosts has passed.
Maiden grapes winters well outside, it does not need to be sheltered either from winter cold or from snowfall in May.

Extreme situation
If you decide to grow grapes in Siberia in the open field, be prepared for unpleasant surprises. At the beginning of summer, such frosts can hit that neither fires, nor fumigation with smoke, nor excellent care will save young shoots. You will have to say goodbye to this year's harvest, but the bushes themselves can be reanimated, and next year they will bear fruit.
First, cut out any frozen pieces. Then give the grapes extra nourishment, then the bush can survive.
Feed every week. The following scheme can be used.
- The first feeding is to take 30 g of complex fertilizers and 20 g of nitrogen-containing preparations for 10 liters of water.
- The second feeding - for 10 liters of water, 0.5 liters of poultry manure and 1.5 liters of manure.
- Until the end of July, alternate the 1st and 2nd feeding.
- When leaves appear, dissolve 50 g of nitrogen fertilizer in 10 liters of water and spray the bushes, repeat the procedure after 10 days.
- In August, for top dressing, put 30 g of potassium and phosphorus fertilizers per 10 liters of water, exclude nitrogen and organic matter.
In July, the shoots will release the stepchildren.Since the top has been cut off, many side shoots will appear on each vine. Leave the top shoot, and pinch all the rest, leaving 2 leaves each. Greens are involved in photosynthesis and provide the bush with additional nutrition. In the fall, unnecessary processes can be cut off.

Conclusion
If you want to grow southern plants in Siberia, start with the simplest - plant girlish grapes. It will not give edible fruits, but this unpretentious and very beautiful culture is perfect for landscape design. You can make a hedge, a green gazebo, a hut. This plant is a great workout for budding wine growers.
After you have learned how to grow girlish grapes, you can move on to fruit varieties. Planting and caring for them is more challenging, but fear not, you will succeed. The main task is not to be mistaken with the choice of a winter-hardy variety. For the first experience, plant 2-3 bushes, learn how to properly shape the vine to send it for the winter. Do not doubt your abilities, and in a few years you will be eating fresh berries, raisins and drinking compotes.


