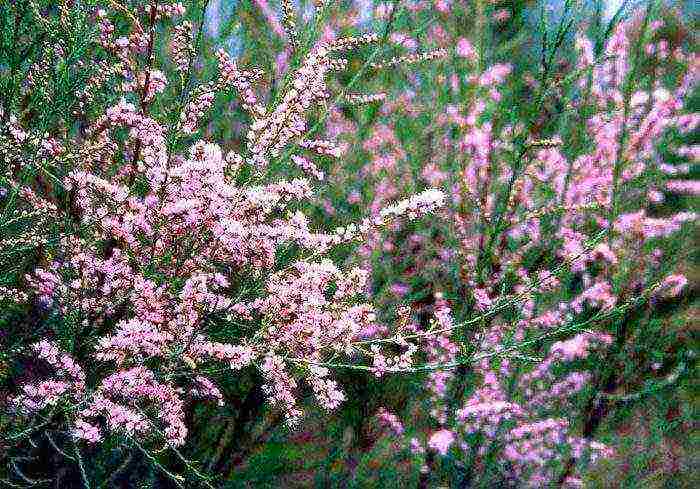More than 75 species of tamarix are known. Its other names are comb and bead, since the inflorescences look like small beads. The plant is used in landscape design in Mongolia, India, Kazakhstan and even in Siberia. With the right approach, the flower can be grown in the Moscow region, even as a hedge.
One of the unique varieties is the graceful tamarix. The northern regions of the country are suitable for him. The plant is characterized by thick branches, grayish or brownish bark. The most beautiful variety of this species is Mirikaria. It is distinguished by delicate pink inflorescences. Planting, caring for and breeding tamarix will not be difficult, but you still need to adhere to certain recommendations.
1 Landing rules
Before planting, you need to find a place for the tamarix. It should be well lit. It is recommended to avoid places where there are drafts or strong winds. The plant is resistant to cold, but it is better to protect it.
The soil should be loose and permeable. The humus should be added to the sandstone. But heavy clay soils are not at all suitable for this plant, especially if they are located in moist lowlands. In this case, it is necessary to make a thick drainage layer, and mix the soil itself with fertilizers.

It should be borne in mind that adult seedlings are not suitable for planting. It is better not to use them, since the likelihood that they will be able to fully take root and adapt is very small. Therefore, it is recommended to choose young shoots.
You can buy ready-made seedlings in specialized stores and nurseries. If you plan to grow in the Urals, in Siberia or in the Moscow region, then you should choose zoned varieties. When buying a seedling, you need to make sure that it is sold immediately with a container and soil. If the root system of the shrub is bare, then it will not take root well. Shoots must be healthy and branched.
Planting is carried out in early spring. You can also do this procedure in the fall. The algorithm of actions will be as follows:
- 1. Prepare the soil for the beads. It is recommended to choose clay-type soils, which additionally need to be fertilized with peat and humus.
- 2. Dig a pit. Its dimensions should be 2 times larger than the earthen lump, which is located in a container with a seedling. In depth, it should be 0.6 m.
- 3. Place drainage on the bottom of the pit.You can use small stones, crushed stone, gravel, expanded clay, broken slate and bricks. You can also pour coarse river sand in this place. Thanks to this, the root system will not be constantly in the water and will not rot.
- 4. Add wood ash and other organic fertilizers. The soil from the pit can be mixed with compost.
- 5. Remove the bush from the container.
- 6. Carefully place the roots in the hole, spread them out and sprinkle with substrate. Then lightly tamp the soil in this place so that there are no voids left.
- 7. Form a watering circle.
- 8. Water the bush.
- 9. Then make a layer of mulch. You can use shredded bark.

It is recommended to darken a young seedling that has just been transplanted so that direct sunlight does not leave burns on the weakened bush. Watering should be monitored after planting. It should be abundant, but overflow should not be allowed.
Tamarix does not tolerate moisture stagnation. Its trunk absorbs and accumulates water, therefore, when a sharp cold snap comes, it will simply die. It is most convenient to plant tamarix with a seedling. Under the right conditions, it quickly adapts to a new location.
2 Reproduction
You can not only plant seedlings of beads: in addition, there are several methods of propagation of this culture. The first option is to use seeds, but this method is ineffective. In addition, a long time will pass from the moment of sowing to the full development of the bush.
You can also use cuttings. This method is considered simple and convenient. There are a few key points to keep in mind:
- 1. Cuttings should be prepared in winter - their length should be 10 cm. For harvesting them, you should choose branches with a thickness of 10 mm. They must be hard.
- 2. When the cuttings are cut, they must be tied into a bunch, and then wrapped in cheesecloth, which was previously moistened.
- 3. Then put everything in a plastic bag where the cuttings can be stored until spring. The temperature should be 3-40 C.

Before planting, you must carefully examine the cuttings. Any dried or moldy ones should be destroyed. All the rest to plant. The algorithm of actions will be as follows:
- 1. Prepare the place where the cutting will be located. The soil must be loosened. Be sure to add humus.
- 2. Sprinkle the ends of the cuttings with a stimulating agent (for example, Kornevin). Also, some people prefer to just hold the branches in the water so that they have small roots.
- 3. Make a hole in the ground. It needs to be filled with earth, peat and sand. The depth of the pit should be no more than 20 cm.
- 4. Place the seedling in the pit and compact it around the ground. Cover with a glass jar or plastic bottle.
- 5. You can mulch the soil around. Water periodically to keep the ground always moist.
3 Care
The Grebenshik is completely unpretentious in terms of care. But experts still advise to follow some rules:
- 1. In a dry season, be sure to water the bush. Stagnation of moisture should not be allowed so that it does not die. If the summer is rainy, then there is no need for watering.
- 2. When the flowering time is over, it is necessary to cut off the inflorescences that have dried up. Then the shrub will look neat and beautiful.
- 3. In the summertime, it is recommended to use fertilizers. As a top dressing, mixtures that contain potassium and phosphorus are suitable. If they were used as foliar feeding, then the shrub will absorb and assimilate them much better. When planting, it is recommended to pour superphosphate in granular form into the flower pit. As for the spring time, it is better to use organic fertilizers for vegetative growth and development. Also at this time, formulations that contain nitrogen are required. They will help the plant grow green mass.
- 4. Periodically pruning is required.Thanks to this procedure, the plant will look neat. Pruning will help prevent the development of various diseases that are characteristic of this particular bush. If branches appear on which the bark has begun to darken, then they must be immediately cut off and burned. The same applies to those shoots on which mold has developed. Experts also advise to shorten the branches in the spring so that they do not break and freeze. Some people prefer to prune the shoots so that the bushes become more branched the next year. You can use a universal technique: cut one branch completely, and the other - only half.
- 5. In regions where the temperature reaches -280 C and even lower, it is necessary to prepare the shrub for wintering. It is recommended to close the area around the trunk with spruce branches. The crown needs to be covered with burlap or other materials with thermal insulation properties (agryl is suitable). The larger and higher the snowball that covers the tamarix, the better the plant will survive the cold. But even if the comb is completely frozen, then in spring new branches will grow from the root system, and the bush will be able to recover over time.

Tamarix is not susceptible to diseases and pests. But if the conditions of detention are incorrect (with frequent overflow), then diseases will develop that are caused by fungal infections. As a result, brownish wet spots appear on the plant. Such branches should be cut and burned immediately so that the infection does not spread throughout the bush and does not spread to other plants.
For various fungal diseases, you should use fungicidal preparations: Ridomil Gold, Skor, Quadris and Maxim. Insecticidal agents save from parasitic insects. You can use Aktelik, Aktara and Match.
 Tamariks, or Grebenshchik, or Bisernik (there are other unofficial names, but these are perhaps the most common). This is a sprawling, perennial, multi-stemmed bushy tree loved by landscape designers.
Tamariks, or Grebenshchik, or Bisernik (there are other unofficial names, but these are perhaps the most common). This is a sprawling, perennial, multi-stemmed bushy tree loved by landscape designers.
Its dimensions are not the largest. As a rule, it reaches no more than 1.5 m in height, less often it grows up to 3-5 m.
In nature, in some regions there are specimens that grow up to 12 m.
Tamarix: planting and care in the open field
However, when growing a shrub in central Russia and in garden conditions (for example, in the Moscow region), you should not count on the fact that it will stretch more than 1.5-2 m, because, alas, it does not differ in special winter hardiness and does not live for a long time. But it has excellent drought resistance... The thickness of the plant stem is no more than half a meter.
Despite its modest dimensions, the tamarix plant looks usually pretty impressive anyway, as it blooms unusually violently and has a lot of branches, which together form something like a large fluffy hat, especially from afar. In general, the spectacle is impressive. Because of its special appearance, the bush got among the people one of the most accustomed names of its own - "seed beads", and under this name it is much better known than under the scientific Latin "Tamarix". And it was named tamarix in honor of the Tamariz River, which flows in the Pyrenees, where this plant takes its roots.
 By sight, a tamarix shrub it is quite (and even too) graceful, delicate and beautiful, and indeed - very much resembles jewelry made of fine beads, so it got its popular name for a reason. The plant especially corresponds to it when it has not yet blossomed completely, but the buds resembling small crumbly beads are already there. At the same time, the plant acquires its most decorative appearance.
By sight, a tamarix shrub it is quite (and even too) graceful, delicate and beautiful, and indeed - very much resembles jewelry made of fine beads, so it got its popular name for a reason. The plant especially corresponds to it when it has not yet blossomed completely, but the buds resembling small crumbly beads are already there. At the same time, the plant acquires its most decorative appearance.
Thin long branches are covered with small, scaly emerald green foliage, about six mm in length. Saline glands are formed on the leaves. These leaves very much resemble needles, but, nevertheless, they are not.Tamarix flowers most often have various pinkish-whitish shades, but lilac and red are also not the rarest for this type of shrub. A tree or shrub blooms from May to September, depending on the specific species.
Tamarix species
There are a huge variety of plant species., somewhere around seventy pieces. In the wild, all of these species can be found growing somewhere between India and the southern border of Europe. The most famous of them:
- branched tamarix
- tamarix graceful
- four-pointed tamarix
- loose tamarix
 Branched tamarix is a short, upright (that is, growing straight and elongated in length) shrub with thin branches and narrow leaves bent downwards. As a rule, it grows up to two m and stops there. In comparison with other species, it loves water quite strongly and is often found on the shores of water bodies. Blooms from June to September.
Branched tamarix is a short, upright (that is, growing straight and elongated in length) shrub with thin branches and narrow leaves bent downwards. As a rule, it grows up to two m and stops there. In comparison with other species, it loves water quite strongly and is often found on the shores of water bodies. Blooms from June to September.
Tamarix graceful is already much larger, reaches a height of up to four m and, with all this, rushes in breadth rather than in height. Its branches are thick and drooping, covered with gray or brown bark, and the foliage is lanceolate or subulate. It begins to bloom in May, with bright pink flowers. Grows in Siberia, China, Mongolia, Kazakhstan.
Four-pointed - the largest comrade of these three, grows up to ten m. The branches are arcuate, the bark on them has a color, usually reddish, the leaves are elongated and refined in shape, bright green in color. Blooms in April and May, flowers are usually white or light pink, with round petals and club-shaped stamens. Grows in Russia, Western Transcaucasia, Greece, Crimea.
Last, loose, has oval leaves, blooms in June and reaches a height of five m. Pink inflorescences are collected in panicles, flowering lasts two months. Iran, Afghanistan, China, the lower Volga are the natural habitats of this species.
Tamarix: planting and care
 Regardless of the type, planting seedlings is best done early spring, in March or April... But some people prefer to plant them in the fall, although this is a less desirable period, but quite normal. Both clay content and soil salinity are not an obstacle for this shrub, but the preferred conditions.
Regardless of the type, planting seedlings is best done early spring, in March or April... But some people prefer to plant them in the fall, although this is a less desirable period, but quite normal. Both clay content and soil salinity are not an obstacle for this shrub, but the preferred conditions.
What the shrub does not tolerate is too much water and a lack of light. But in general, the plant is very, very picky about the soil. It is best to choose young seedlings for planting, adults can easily not adapt and not survive.
You can use for planting:
- the seeds
- cuttings
- seedlings
But now we will consider exactly shrub propagation method... First, you need to prepare the soil for planting. A pit is dug - a planting hole about half a meter deep and at least twice as wide as the lump of earth supplied with the seedling. Drainage is poured at the bottom of the planting pit - gravel, pebbles, expanded clay, crushed stone.
After pulling out and falling asleep, all this must be organically fertilized, before starting the seedlings there (first of all, with wood ash). Sapling roots - place in a hole, spread and tamp with earth and water. It will not be superfluous to darken the seedling a little after planting and thereby protect it from burns, which can leave direct sunlight falling on the bush.
But vegetative way got much more widespread. Cuttings 10-15 cm long are cut in the autumn season and placed in warm water. As soon as the first roots are visible, they are planted in some warm and sufficiently lit room in the peat soil. They are planted in open ground somewhere around May.
With seeds, everything is very, very ambiguous.... You will have to make a lot of effort, as well as be patient in order for something acceptable to come out of this.First, they need to be planted as quickly as possible, otherwise they will lose their fertility. Secondly, for them you need to prepare special containers filled with loose sandy soil. The planted seeds are kept indoors for the next two years, taking the containers outside in the spring and summer, and taking them back for the winter. And only at the end of this period they are planted in open ground.
How to care
 Care for each type is selected with appropriate remarks. But, of course, it is possible to single out some general rules of care.
Care for each type is selected with appropriate remarks. But, of course, it is possible to single out some general rules of care.
The plant is quite unpretentious, and does not require special efforts in the process of care and maintenance.
Firstly, you should not overdo it with watering the shrub, otherwise it can easily bend and pick up the fungus. In general, tamarix is highly prone to moisture accumulation in its stems. Often he can do without watering at all, especially during rainy periods.
But in dry times, this must, on the contrary, be monitored very carefully. And at first after planting, it also requires abundant watering, after a while it is better to cut it.
The next point of care is pruning.... The plant is not at all afraid of pruning, they prevent the appearance of many different diseases and give the plant a neat shape. Dried inflorescences, when the flowering time of the bush comes to an end, everything must be cut off. All moldy, darkened, frozen branches should be removed immediately. In addition, if there is a desire to achieve more branching next year, it is worth pruning the shoots a little.
As fertilizers for feeding the plant, mineral fertilizers are ideal - potassium and phosphorus. Care will be incomplete without them.
For the plant to survive the winter, at the end of autumn it will be best to cover it with a film. It is also necessary to mulch the soil to protect the plant from cold weather.
iv class = "dacha-adapt3" id = "dacha-1346620034">
Tamarix shrub
The type genus Tamarix, also called comb, or tamarisk, belonging to the Tamarisk family, is represented by shrubs and small trees. This genus unites more than 75 species. Such a plant is also called bead, gidovilnik, jengil, divine tree, comb and Astrakhan lilac. The scientific name tamarix comes from the toponym of the river Tama-riz, which is located in the Pyrenees, at the moment it is called Timbra. In nature, tamarix can be found in Asia, Africa and in the southern part of Europe, while it prefers to grow in deserts and semi-deserts, in dune sands, and also on salt licks and salt marshes. For example, in the tugai forests of Central Asia there are 15 species of such a plant, in the mountains of Central Asia it is found at an altitude of about 2000 meters above sea level, while in the Caucasus, tamarix rises to a height of no more than 600 meters.
The tamarisk shrub is cultivated by gardeners as an ornamental and sand-fixing plant.
Features of the tamarix shrub
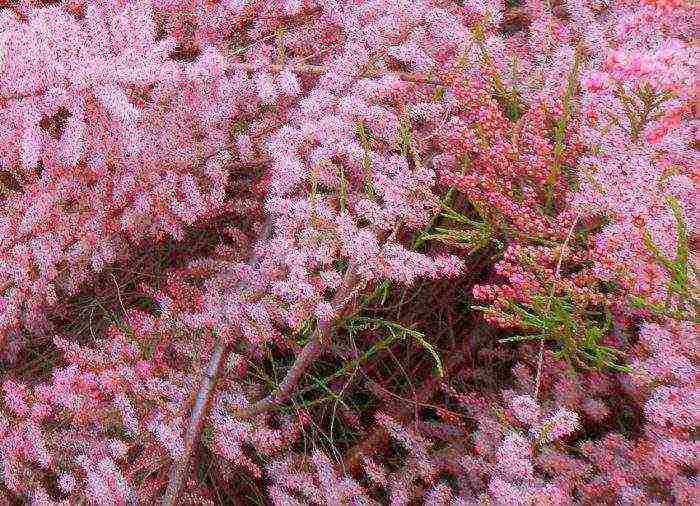

The graceful tamarisk shrub can be deciduous or evergreen. In addition to shrubs, trees are often found that grow bush-like, they have a height of 1.5-12 meters, and their trunk is not thicker than half a meter. The crown consists of rod-shaped stems, on which there is a huge number of alternately located small leaf plates similar to scales, their color can be emerald, greenish-blue or dark green. Large panicle or racemose inflorescences consist of small white or pink flowers. Before flowering, when the bush is strewn with many unopened buds, it may seem as if it was decorated with beads. This plant is an excellent melliferous plant, therefore, during the flowering period, it attracts bees to the garden. The fruit is a pentahedral-pyramidal box, which is polyspermous, inside it has small seeds.
Tamarisk is a very tenacious plant that is highly drought tolerant.This shrub can be grown even in a large city, because it is resistant to gas pollution. Growing such a plant is not troublesome and very pleasant.
Planting tamarix in open ground
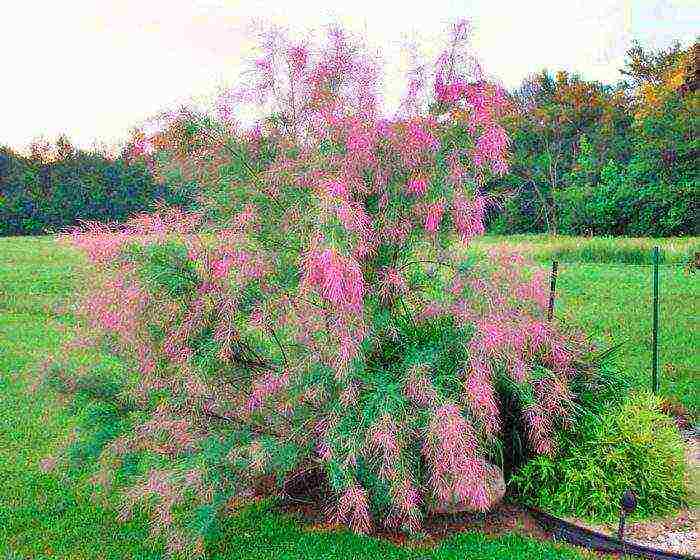

What time to plant
It is recommended to plant tamarix seedlings in open soil in the autumn during the fall of leaves, but it is better to do this at the very beginning of spring. The soil for such a shrub needs a well-drained one, while its composition can be of any kind. It can be grown even in heavy clay soil, but only in this case humus and peat must be added to the soil during planting. You can grow tamarisk in the shade, but it is better to choose a well-lit area for planting it.
The choice of a site for planting such a shrub must be done very carefully, because because of the long thin roots that are easy to damage, it suffers a rather painful transplant.
How to plant correctly
The size of the landing pit should be 0.6x0.6x0.6 meters. At the bottom of the finished pit, you need to make a good drainage layer, the thickness of which should be about 20 centimeters, for this you can use broken brick, crushed stone, expanded clay or pebbles. A mixture of humus and wood ash must be laid on top of the drainage. Then the pit should be filled with soil mixture by 2/3, which contains sand (1 part), fertile soil (2 parts) and peat (1 part).
Before planting, you should trim the stems of the seedling, while the remaining segments should not exceed 30-50 mm in length. Then the plant must be placed in a pit, which should be covered with soil mixture (the composition is described above), but only after the roots of the seedling are carefully straightened. Tamp the surface of the soil around the planted plant, and then water it well. When planting, it should be borne in mind that after the seedling is watered, its root collar should be at the level of the surface of the site.
Caring for tamarisk in the garden
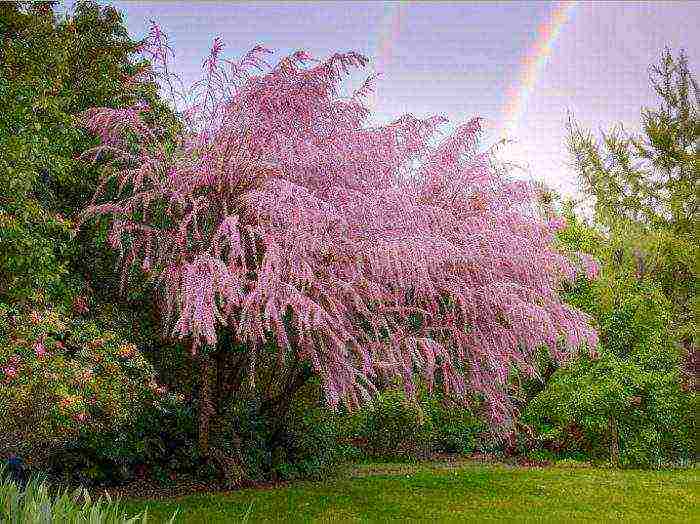

A tamarix seedling planted in open soil needs protection from direct sunlight and systematic watering during the first 15–20 days. After the leaves appear on the plant, they stop protecting it from the sun's rays, and also reduce the number of watering. In order for the water from the soil not to evaporate so quickly, its surface must be covered with a layer of mulch, for this you can use any organic material. Adult shrubs need watering only during a long dry period, but if it rains regularly in the summer, then there is no need to water the tamarix at all. After the rain has passed or watering has been carried out, the surface of the trunk circle should be slightly loosened, while pulling out all the weeds.
Top dressing of the shrub is carried out in the spring, as soon as the growing season begins, for this they use organic fertilizer. In the summer, it should be sprayed over the foliage with a solution of phosphorus and potassium fertilizers.
Tamarix is highly winter-hardy, therefore it can be cultivated in regions with not very warm climates. So, in the Urals and in the Moscow region, this plant is today widespread quite widely. This shrub without shelter is able to withstand temperatures as low as minus 28 degrees. If the winters are very cold, then such a shrub simply needs shelter. To do this, the root zone should be covered with a thick layer of sawdust or covered with spruce branches, the trunk should be wrapped with a dense cloth or polymer film.
Pruning tamarix
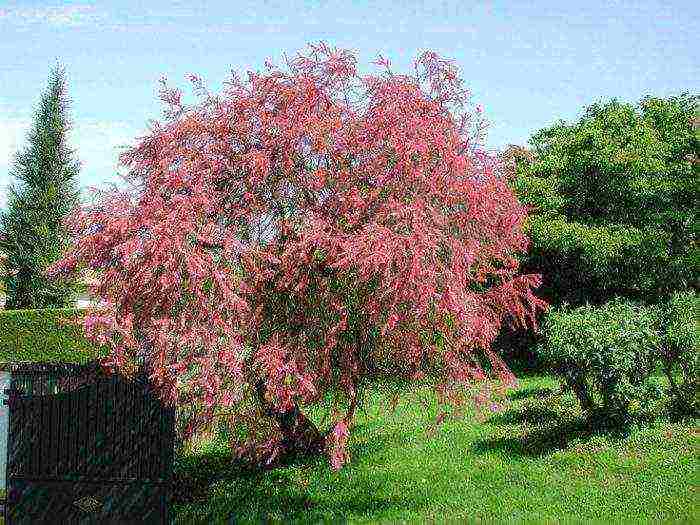

Tamarix needs shaping scraps, which he transfers easily enough. The best time to trim the crown is early spring, and you need to be in time before the buds swell. Old branches with short growths need to be cut into a ring, after only 4 weeks they will give young shoots, and the shrub will again become lush and beautiful. Such a plant needs rejuvenating pruning.They are made on a strong branch, which is placed as close to the base of the bush as possible. Remember that the growth of the stems should not diminish as this will reduce the number and length of the inflorescences. With the beginning of the growing season, branches and stems damaged by frost can be identified, which will need to be trimmed to healthy wood.
You can also prune the shrub at the end of flowering. In order for the crown to remain spectacular and well-groomed, it is necessary to cut off excessively elongated stems, as well as inflorescences that have begun to fade. When pruning the shrub, try to make it more stable, otherwise its branches will need to be tied to the supports.
In tamarisk, the crown thickens very quickly, in this regard, its thinning should be carried out systematically, cutting out part of the branches for this.
Diseases and pests
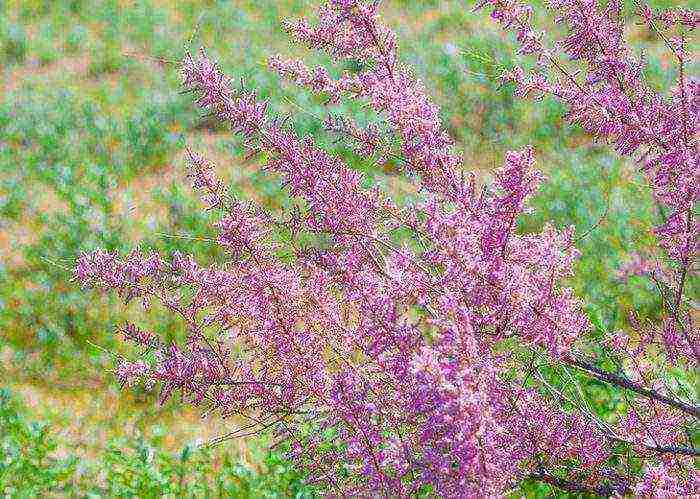

This shrub is highly resistant to pests. They can settle on it only if any of the neighboring plants is infected. To get rid of pests, it will be enough to spray the plant with an insecticide solution only once.
During the rainy season, tamarix can easily contract a fungal disease. Infected stems and branches should be cut and destroyed, and the bush itself and the soil around it should be sprayed with a fungicide solution.
Reproduction of tamarix in the garden
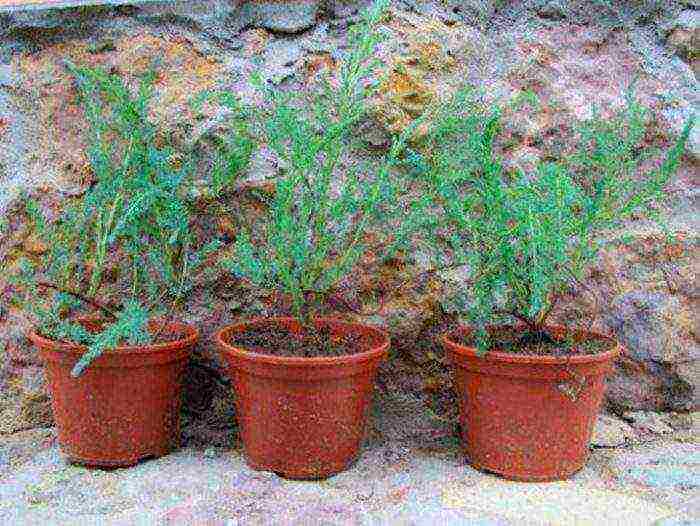

It is quite possible to grow tamarix from seeds, however, experienced gardeners do not advise spending their time on this, since cuttings are a more reliable and faster way of propagating such a plant.
The shrub can be propagated by cuttings at the beginning of the spring. To do this, you need to prepare semi-lignified cuttings 10 millimeters thick and 7-10 centimeters long. The lower cut should be treated with a solution of an agent that stimulates the growth of roots, then they should be planted at an angle in a container filled with a light soil mixture consisting of sand and garden soil (1: 1). On top of the box, it is imperative to put on a dome, which must be transparent. Instead, you can cover each stalk with a glass jar on top. After the cuttings take root, young leaves will begin to grow. Such cuttings are planted in open soil in May, and do not forget that they need mandatory shelter for the winter. With the onset of the next spring period, the plants that have survived the winter can be transplanted to a permanent place.
You can resort to another method of rooting; for this, the cuttings are placed in a container filled with water. When roots appear on the cuttings, they will need to be planted in the garden and covered with glass jars.
When propagating tamarisk by the generative (seed) method, remember that its seeds retain good germination for a short time, and when growing a shrub in middle latitudes, they rarely ripen. There is no need to stratify the seeds before sowing. They are simply evenly distributed over the surface of the soil mixture, without deepening or sprinkling with earth. Then the container must be placed on a pallet that is filled with water. Strengthened and grown plants must be planted in school for growing. Seedlings need good shelter for the winter. After 1 or 2 years, the plant can be planted in a permanent place.
Types and varieties of tamarix with photos and names
There are more than 70 species of tamarix in nature. However, most often cultivated are those that have high frost resistance.
Tamarix tetrandra
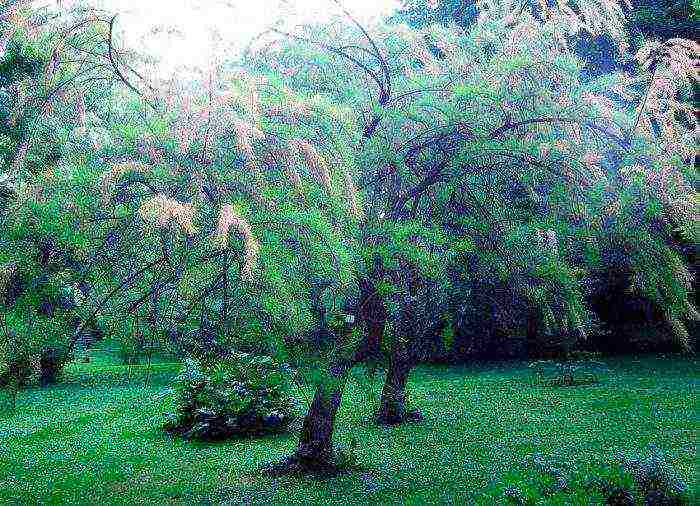

In nature, this species is found in Greece, Crimea, Asia Minor, as well as in the southeast of the European part of Russia. This shrub is relatively large and reaches a height of 5-10 meters. Arcuate curved branches are painted red-brown. Green-emerald leaf plates have an ovate-lanceolate or lanceolate shape, they taper towards the base, and at their top there is a beak-shaped sharpening.On the lateral shoots are racemose inflorescences, consisting of flowers, painted in various shades from pale pink to white. The plant blooms in April or May. This shrub is drought tolerant and durable (it can live for about 75 years).
Loose tamarix (Tamarix laxa)
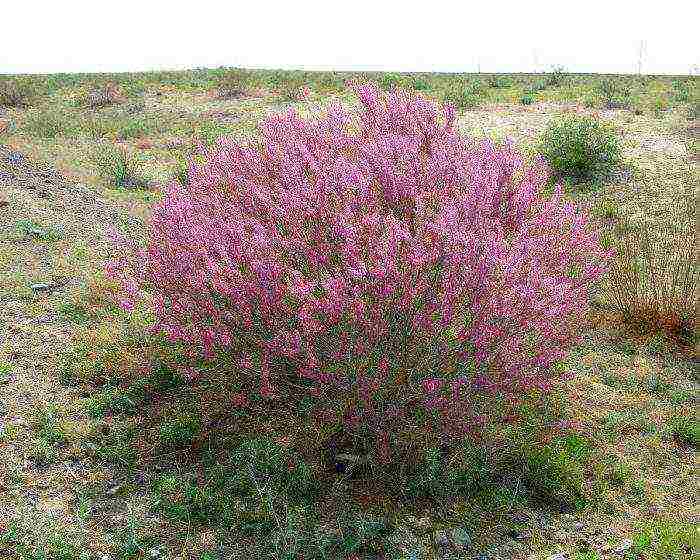

Under natural conditions, such a plant is found in northwestern China, northern Iran, Mongolia, Afghanistan and in the lower reaches of the Volga. This species is represented by a large branched shrub or a medium-sized tree, its height is about 5 meters. The bare, spreading branches are colored gray or green. Directly spaced leaf plates of an oval-rhombic or ovoid shape taper towards the base and sharpen towards the apex. The apical panicles are formed by lush racemose inflorescences consisting of pink flowers. This plant blooms for about 8 weeks. This species is distinguished by its drought and frost resistance, it is not picky about the soil and normally tolerates its salinity.
Tamarix graceful (Tamarix gracilis)
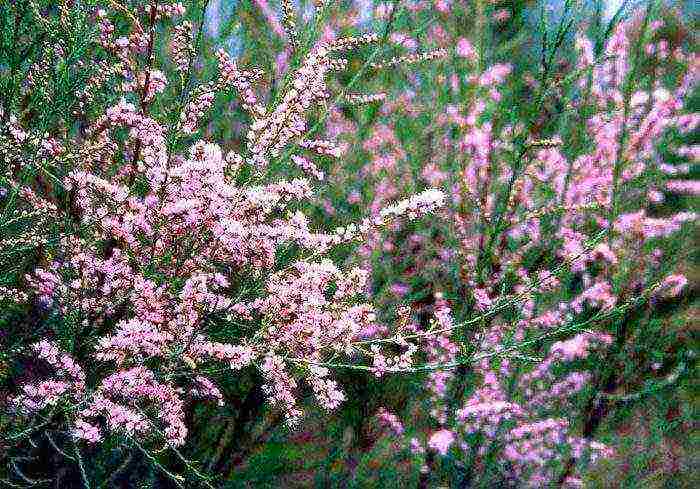
Under natural conditions, such a tamarisk is found in China, Ukraine, Kazakhstan, Siberia, in the west of Mongolia and in the south of the European part of Russia. The height of the shrub does not exceed 4 meters. On the surface of thick, concatenated branches, there are pale fawn specks of cork in the leaf axils and along the shoot. The color of the bark is greenish gray or chestnut brown. Pointed leaf plates on green shoots are tiled. On one-year-old branches, leaf plates of larger size grow, and they have a lanceolate shape and a fawn color. Simple spring racemose inflorescences are about 50 mm long and consist of deep pink flowers. Summer flower clusters are part of large paniculate inflorescences, and they reach 70 mm in length. This type is frost-resistant and beautifully flowering, it is often used by landscape designers.
Branched tamarix (Tamarix ramosissima), or five-headed tamarix (Tamarix pentandra)
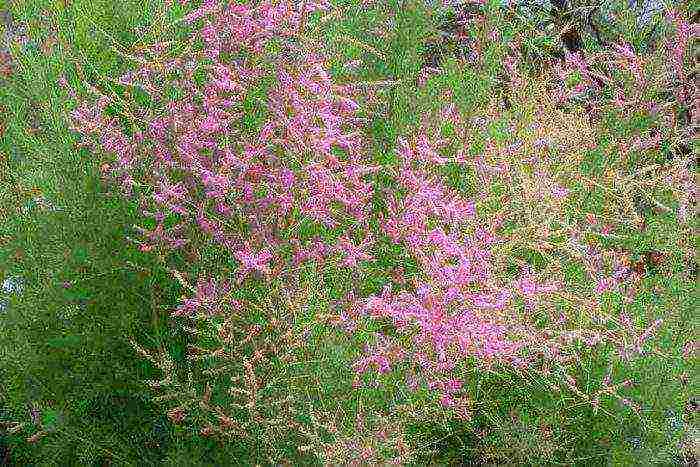

In the wild, such a plant can be found in Iran, Mongolia, Moldova, China, Central Asia, Ukraine and the Balkans. It prefers to grow on river banks, pebble shoals and on the terraces of river valleys. The height of such an upright shrub is about 2 meters. Thin branches are light gray or pale green, and annual shoots are pale red. Narrow awl-shaped leaf plates have curved tips. Dense complex racemose inflorescences reach 50 mm in length, they consist of pink flowers. Flowering is observed in June – September. Such a shrub is not picky about the composition of the soil, it quickly adapts to the conditions of the city, after freezing it is easily restored, but it must be covered for the winter. Popular varieties:

- Pink Cascade... This variety blooms very luxuriantly.
- Rubra... The color of the flowers is red-violet.
- Summare Glow... The color of the flowers is rich crimson.
Tamarisk in landscape design

Tamarisk is used in landscaping for group compositions and trimmed hedges. This plant is also used as a tapeworm, for example, as a flowering "fountain" in the center of a green lawn. It is recommended to combine not very tall trees and shrubs of this genus with conifers, namely: thuja, juniper and dwarf spruce. Also, this plant is in harmony with lilac, barberry and jasmine.
Certain evergreen tamarisk species are cultivated at home. Tamarix is also grown on saline soils, in forest plantations, in deserts and semi-deserts, and is also used to fix moving sands and slipping banks.
Tamarix is a representative of the Tamarix family; it is an elegant, spreading shrub or a short tree. Its thin branches are covered with many multi-colored tiny flowers, which gives the crown lightness, airiness. Tamarix will be a real decoration for hot sunny gardens.
The comb is hardy in severe drought, and its lace shoots are pleasing to the eye and fills the air with a pleasant aroma. The plant is popularly called "Astrakhan lilac", "bead", "comb", "jengil". A drought-resistant tamarix native to the deserts and steppes of southern Europe, Asia Minor and Africa, it is not afraid of sandy and saline soils.
Botanical description of tamarix
Tamarix is a deciduous or evergreen perennial plant. The roots are powerful: like thick vines, they spread in different directions underground in search of moisture and nutrients. On average, the plant reaches a height of 3-5 m, there are specimens up to 12 m high. The form of vegetation is shrub or tree-like. The trunk has a maximum diameter of 50 cm. Numerous thin processes extend from the main shoot and skeletal lateral branches.
Leaves 1-7 mm long resemble small scales, tightly attached to the stem, the leaves are covered with salt-secreting glands. The color of the foliage is dark green, bluish green, emerald.
When does tamarix bloom?
The flowering stage occurs at different times depending on the type of tamarix. For example, the four-stalked tamarix blooms in May, while the loose tamarix blooms throughout August and September. Flowers on short stalks are collected in racemose or paniculate inflorescences. Even before blossoming, the buds have a high decorative effect, they cover the branches like small beads of pastel, delicate tones.
Flowers are bisexual, 1.5-5 mm long, bracts with a blunt edge, ovoid or linear in shape. Under the bract there are 4-7 rounded petals of white, pink, purple, scarlet or purple. Stamens filiform, located in the center of 4-6 pcs., Thickened at the base, heart-shaped anthers, oblong ovary with a trihedral column. Only the dioecious tamarix Tamarix dioica has heterosexual flowers.
After pollination, small fruits are formed in the form of multifaceted pyramidal capsules filled with many seeds. Each seed has a tuft. Ripe bolls open and paniculate seeds are carried by the wind over long distances.
Growing tamarix from seeds at home

Tamarix seeds photo
Seeds remain viable for only 4 months after ripening, plant them fresh.
- Prepare a container with fertile, loose soil mixed with a fair amount of sand. there must be drain holes in the bottom of the container.
- Plant the seeds shallowly, up to 1 cm. Sow as little as possible, so as not to break later: the distance between the plants should be at least 3-4 cm.

Tamarix from seeds photo shoots
- When the seedlings grow up to 5-6 cm in height, plant them in separate cups.
- Grow your seedlings at room temperature and keep them moderately humid. This should be done for two years.
- In the spring-summer period, take the pots with the plant outside, and in the winter, be sure to return it to the warmth.
- Tamarix is planted in open ground along with a lump of earth in the third year of life in the spring.
Vegetative propagation of tamarix is the most popular: cuttings take root easily, giving 100% survival rate.
Reproduction of tamarix by cuttings

Tamarix cuttings with roots photo
- It is better to carry out the cuttings procedure in the fall, but before the first frost begins.
- Preferably from young, but lignified branches, cut the cuttings 10-15 cm long, place them in a container with warm water and wait for the rudiments of the first roots to appear.
- To accelerate root formation, the first few days, you can keep the cuttings in a solution of heteroauxin or root.
- Then plant in a sand-peat mixture, cover with a cap, keep in a warm place with good lighting.
- It can be planted in the soil in May-June.
- It is imperative that after disembarkation, before the first wintering, the soil around the tamarix is thoroughly mulched with fallen leaves or peat.
Reproduction of tamarix by layering
To do this, select a lignified, strengthened branch, dig it into the ground to a depth of about 20 cm, and fix it carefully. Better do it in the spring and by the end of summer you will have good, strong roots. Separate the shoot and transplant to a permanent location.
Planting and caring for tamarix outdoors
Tamarix is a tenacious, undemanding culture. The plant is very light-loving, choose open, well-lit areas for it. In the shade or even slight partial shade, growth will slow down significantly, and the death of the plant may occur.
Landing
Plant in spring. Beads do not tolerate wet, heavy soils. Sand and peat are added to very dense soils; lime is recommended to be added to acidic soil. Make a planting hole deep enough, be sure to place a gravel or pebble drainage pad on the bottom. In order for the plant to take root better, immediately after planting it is necessary to fertilize with a solution of humus and ash.
Watering
Water abundantly in the early days, then reduce watering. The grown tamarix does not require constant watering, it can even harm it. You can leave the plant unattended and water it only with prolonged sweltering heat, especially at the flowering stage. The rest of the time the plant is content with natural precipitation.
High humidity is contraindicated. It will increase the likelihood of being affected by rot and other fungal diseases.
Air temperature
The plant is also undemanding to the temperature regime. It will not burn in direct sunlight, and will also withstand a fairly severe frost down to -28 ° C. For the winter, it is enough to cover the base of the trunk and the soil with fallen leaves and spruce branches. Even if the ends of the shoots freeze, new shoots will quickly appear in their place.
Top dressing
If the tamarix is planted in fertile soil, it is sufficient to feed it once in mid-spring. Use a mixture of ash and chicken droppings or mullein as fertilizer.
Pruning
Prune your plant regularly for extra attractiveness. Pruning is carried out in early spring, before active sap flow begins. Cut off dried or frozen old branches in a ring - in a month they will be covered with new young shoots, and the flowering forms a lush spherical cap. In shrubs, the middle branches must also be partially removed so that the bush is not too thick.
Pests and diseases
Tamarix pests practically do not bother. They can move to the bead branches only from a nearby heavily infested plant. In dampness, from regular flooding, fungal diseases can appear. Better not to let this happen. Affected vegetation should be trimmed and burned. Treat with a fungicide, you can periodically process it for prevention.
Preparing tamarix for winter in the Moscow region and northern regions
Frost-resistant species of tamarix can withstand prolonged temperature drops down to -40 ° C. But it is better to protect young bushes: carefully cover the near-trunk zone with a layer of leaves, and tie the branches, gently bend them to the ground and pin them with metal pins, cover with lutrasil. In winter, scoop up more snow from above so that the branches are under it.
Types of tamarix with photos and descriptions
The Tamarix genus consists of more than 60 plant species. The most popular are described below.
Branched tamarix Tamarix ramosissima
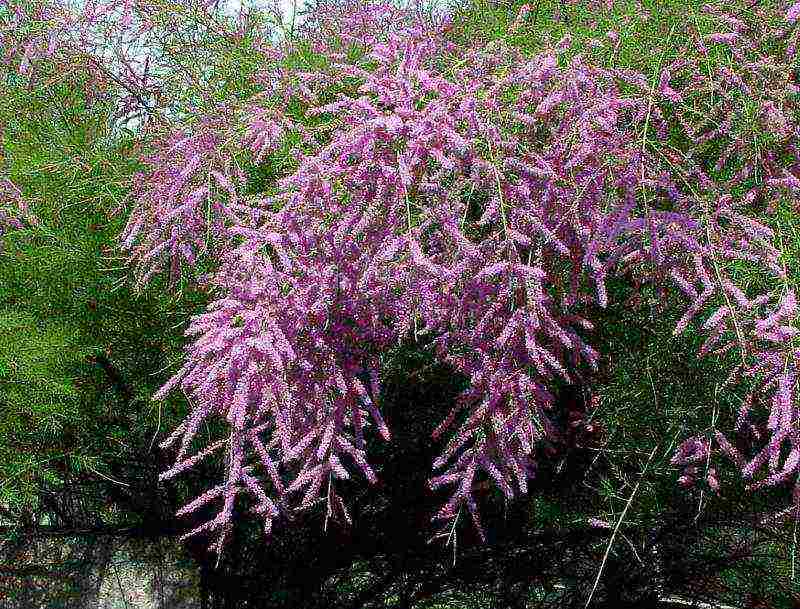

Tamarix branching Tamarix ramosissima ‘Pink Cascade’ photo
It is a shrub no more than 2 m tall with a slender, vertical crown. The branches end with thin green shoots covered with narrow subulate leaves only 1.5 mm long. Pink flowers, collected in racemose inflorescences, delight with their appearance in June-September.
Varieties:
- Rubra - flowers are painted in a bright purple-red color;
- Pink Cascade - light pink flowers densely cover the branches;
- Summer Glow - dense, raspberry-colored inflorescences.
Tamarix graceful or slender Tamarix gracilis
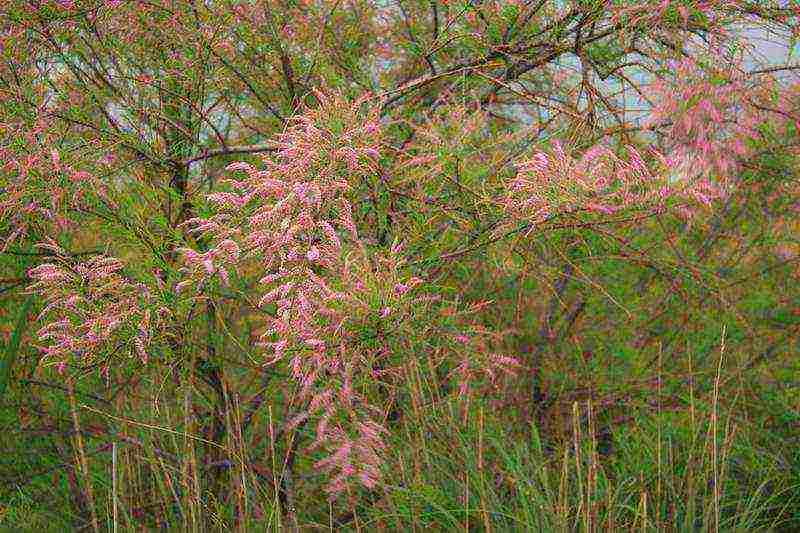

Tamarix graceful Tamarix gracilis Willd photo
Sprawling large shrub, reaches a height of about 4 m, branches are thick, drooping. Smooth bark of a brown-chestnut color with light brown spots covers the branches. The leaves are subulate or lanceolate, adjoining tightly to the branches. Flowers are bright pink in color. The racemose inflorescences, 5-7 cm long, bloom in May and bloom all summer.
Tamarix four-stalked or small-flowered Tamarix parviflora
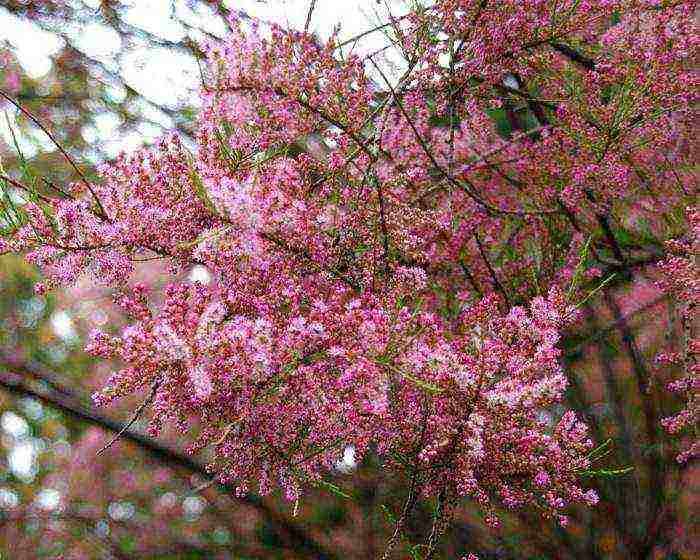

Small-flowered tamarix Tamarix parviflora photo
A large shrub, similar to a tree with several trunks, reaches a height of 5-10 m. Brown-red bark covers the shoots. The light pink flowers are composed of long, club-shaped stamens, framed by round petals. Bulky loose brushes bloom in April-May. The leaves are thin, long, bright green.
Tamarix Meyer Tamarix meyeri

Tamarix Meyer Tamarix meyeri photo
Suitable for growing only in the southern regions, since it absolutely does not tolerate frost. This is a sprawling shrub 3-4 m high, the branches are covered with reddish bark. Leaves are bluish-green, scaly, adjacent to the branches. Small lush pink flowers gather in dense inflorescences up to 10 cm long. Flowering begins in May.
Tamarix dioecious Tamarix dioica

Tamarix dioecious Tamarix dioica photo
A very beautiful shrub, especially in bloom, this species has male and female plants and it will take both to get seeds for pollination to take place.
Tamarix loose Tamarix laxa Willd
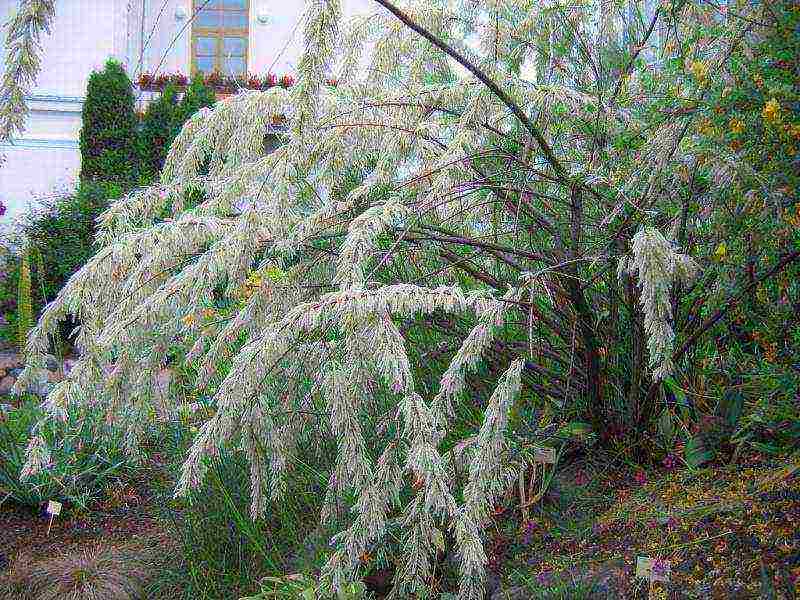

Tamarix loose Tamarix laxa Willd photo
Reaches a height of 5 m and is found in the wild in Central Asia, China, Mongolia, Afghanistan, grows in the lower reaches of the Volga. Absolutely not picky about the soil, resistant to diseases and pests, requiring absolutely no care. It propagates well by cuttings and seeds.
Tamarix in landscape design
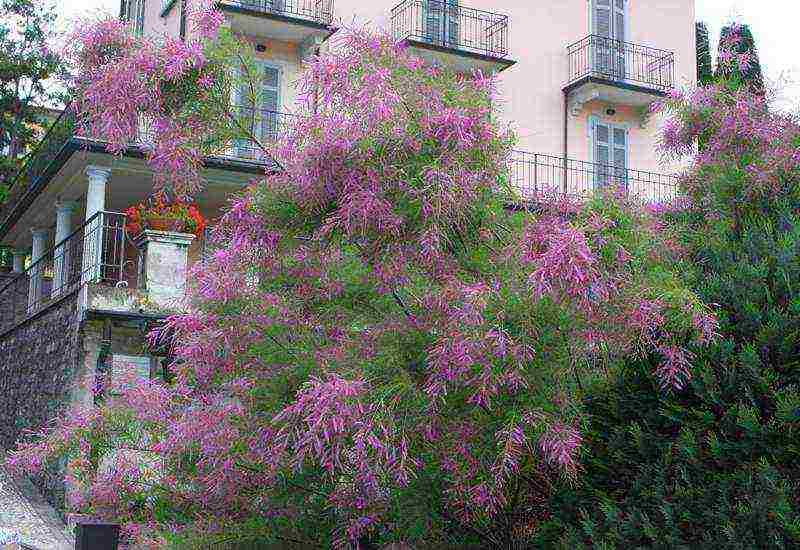

Tamarix in landscape design photo
Tamarix with its fabulous lace thickets is perfect for landscaping a garden. Plant solo near recreation areas or in loose groups. You can create a bright, lush fountain of flowering branches in the center of the composition or a hedge.

Tamarix in urban landscape photo
Trees and bushes with weightless branches will go well with junipers and any other conifers. You can plant tamarix near lilac, jasmine or barberry. The plant's strong roots hold the soil together so it can be planted on slopes to prevent landslides. Also, the plant is an excellent honey plant.
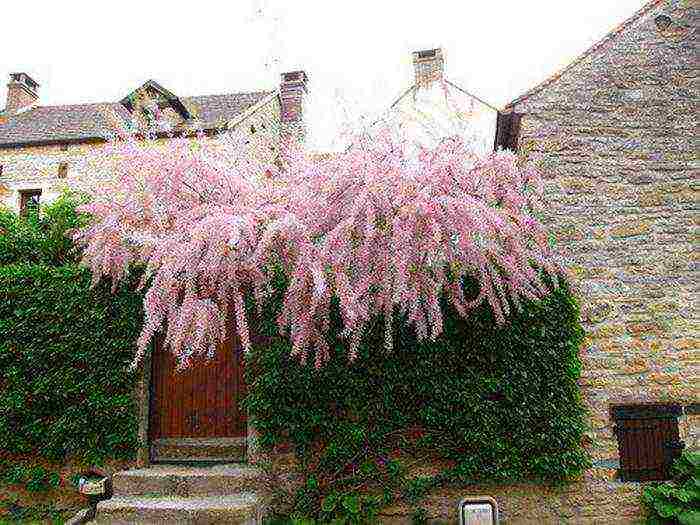

Tamarix in the landscape design of the city photo
Useful properties of tamarix
The medicinal properties of tamarix are also known.
- The bark and leaves contain polyphenols, tannins, coloring pigments, tannins.
- Young twigs, leaves and inflorescences are harvested in summer.
- They are used to prepare decoctions, alcoholic tinctures, which are taken as a diuretic, diaphoretic, analgesic, astringent and hemostatic agent.
- They help relieve an attack of rheumatism, diarrhea, and symptoms of stomach inflammation.




 Tamariks, or Grebenshchik, or Bisernik (there are other unofficial names, but these are perhaps the most common). This is a sprawling, perennial, multi-stemmed bushy tree loved by landscape designers.
Tamariks, or Grebenshchik, or Bisernik (there are other unofficial names, but these are perhaps the most common). This is a sprawling, perennial, multi-stemmed bushy tree loved by landscape designers. By sight, a tamarix shrub it is quite (and even too) graceful, delicate and beautiful, and indeed - very much resembles jewelry made of fine beads, so it got its popular name for a reason. The plant especially corresponds to it when it has not yet blossomed completely, but the buds resembling small crumbly beads are already there. At the same time, the plant acquires its most decorative appearance.
By sight, a tamarix shrub it is quite (and even too) graceful, delicate and beautiful, and indeed - very much resembles jewelry made of fine beads, so it got its popular name for a reason. The plant especially corresponds to it when it has not yet blossomed completely, but the buds resembling small crumbly beads are already there. At the same time, the plant acquires its most decorative appearance. Branched tamarix is a short, upright (that is, growing straight and elongated in length) shrub with thin branches and narrow leaves bent downwards. As a rule, it grows up to two m and stops there. In comparison with other species, it loves water quite strongly and is often found on the shores of water bodies. Blooms from June to September.
Branched tamarix is a short, upright (that is, growing straight and elongated in length) shrub with thin branches and narrow leaves bent downwards. As a rule, it grows up to two m and stops there. In comparison with other species, it loves water quite strongly and is often found on the shores of water bodies. Blooms from June to September. Regardless of the type, planting seedlings is best done early spring, in March or April... But some people prefer to plant them in the fall, although this is a less desirable period, but quite normal. Both clay content and soil salinity are not an obstacle for this shrub, but the preferred conditions.
Regardless of the type, planting seedlings is best done early spring, in March or April... But some people prefer to plant them in the fall, although this is a less desirable period, but quite normal. Both clay content and soil salinity are not an obstacle for this shrub, but the preferred conditions. Care for each type is selected with appropriate remarks. But, of course, it is possible to single out some general rules of care.
Care for each type is selected with appropriate remarks. But, of course, it is possible to single out some general rules of care.