Content
- 1 Spirea: types and varieties
- 2 Spirea: features of cultivation
- 3 Shrub propagation
- 4 Landing in open ground
- 5 Outdoor care for spirea
- 6 Plant diseases and pests
- 7 The nuances of growing in Siberia, in the Urals, in the Moscow region
- 8 Spirea: types and varieties
- 9 Spirea: features of cultivation
- 10 Shrub propagation
- 11 Landing in open ground
- 12 Outdoor care for spirea
- 13 Plant diseases and pests
- 14 The nuances of growing in Siberia, in the Urals, in the Moscow region
- 15 Spirea varieties for Siberia with a description
- 16 Spyria breeding methods
- 17 Planting spirea in the spring in open ground
- 18 Planting spirea in the fall
- 19 Watering and feeding spirea
- 20 Spirea pruning
- 21 Shelter spirea for the winter
- 22 Description of the plant and species
- 23 Planting spirea
- 24 Care rules
- 25 Reproduction
- 26 Planting and caring for spireas
- 26.1 Selection and preparation of a seedling
- 26.2 Selecting and preparing a landing site
- 26.3 Planting spirea in spring
- 26.4 Planting spirea in the fall
- 26.5 Care: watering, fertilizing, pruning, sheltering
- 26.6 Spirea pruning
- 26.7 Reproduction of spirea
- 26.8 Shelter spirea for the winter
- 26.9 Types and varieties
- 26.10 Garden use and partners
- 26.11 Video about the reproduction of spirea
- 27 Features of planting spirea
- 28 Planting spirea: site selection and planting pit depth
- 29 Spirea care secrets
- 30 How to trim spirea
- 31 Pest control
- 32 Types and varieties
- 33 Planting in spring and autumn
- 34 How to care for a bush
- 35 Reproduction
- 36 Planting and caring for spireas
- 36.1 Selection and preparation of a seedling
- 36.2 Selecting and preparing a landing site
- 36.3 Planting spirea in spring
- 36.4 Planting spirea in the fall
- 36.5 Care: watering, fertilizing, pruning, sheltering
- 36.6 Spirea pruning
- 36.7 Reproduction of spirea
- 36.8 Shelter spirea for the winter
- 36.9 Types and varieties
- 36.10 Garden use and partners
- 36.11 Video about the reproduction of spirea
- 37 Content
- 38 Listen to the article
- 39 Spirea shrub - description
- 40 Types and varieties of spirea
- 41 Growing spirea - features
- 42 Planting spirea
- 43 Spirea care
- 44 Spirea after flowering
- 45 Botanical features of spirea
- 46 How to grow spirea (video)
- 47 Variants of using spirea in landscape design
- 48 Description of shrub varieties
- 49 Features of planting and transplanting spirea in the open field
- 50 Types and varieties of spirea (video)
- 51 Haircut and other types of spirea care
- 52 Reproduction of spirea by dividing the bush, cuttings, seeds and layering
- 53 How to plant a spirea (video)
- 54 Some features of planting and caring for spirea in the Urals
- 55 And a little about the secrets.
Among the ornamental shrubs, spirea occupies a special place. She is surprisingly unpretentious and easily forgives the gardener even the most unobtrusive care. A wide variety of shapes and types allows you to choose the plant to decorate the site that will best fit into the surrounding landscape. Planting and caring for a spirea is not difficult, even a novice gardener can handle it.
Spirea: types and varieties
The genus spirea belongs to the pink family and is quite numerous, it includes more than 70 species. The distribution area of this deciduous shrub is wide. It can be found in the northern hemisphere in most climatic zones. Spirea rarely has single flowers, most often they are collected in a corymbose inflorescence, sometimes in a panicle. The color of flowers depends on the flowering time of the species. Plants blooming in spring have white flowers that bloom on last year's shoots, in species blooming in summer pink-crimson gamut prevails, flowers are located on annual growths.

The most common types.
- Medium spirea - an inhabitant of Siberian and Far Eastern forests, a tall shrub - above 2 m with white corymbose flowers that open in May and do not fall for 3 weeks, frost-resistant and drought-resistant, used in landscaping, suitable for northern regions.
- Spiraea birch-leaved - grows in Siberia, from 1 to 2 m in height, white flowers are collected in huge shields - up to 10 cm in diameter, blooms at the end of May and blooms throughout June.
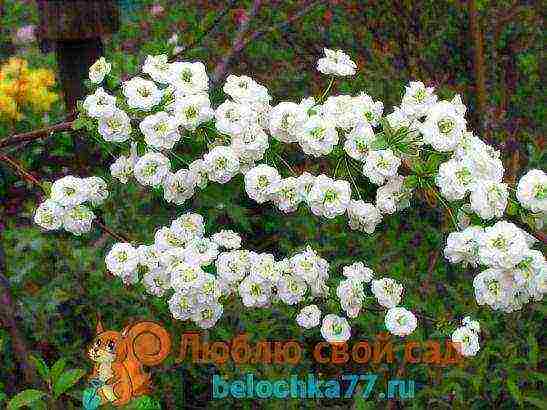
- Spirea crenate - has been used in landscaping for 200 years, there are cultural hybrid varieties. In nature, it is a low, up to 1 m shrub that blooms at the end of May. Quite large flowers are collected in corymbose inflorescences, due to the large number of long yellow stamens, it seems that they have a golden hue. This type of spirea is drought-resistant and frost-hardy, can be used to strengthen floating soils.
- Spirea St. John's wort is a shrub up to 1 m high, flowering - May-June, white flowers, is used to obtain new forms of the plant.
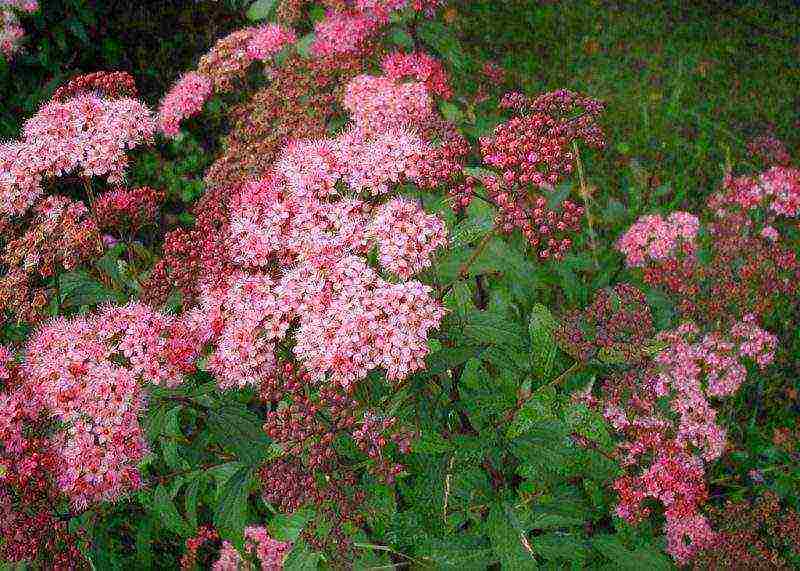
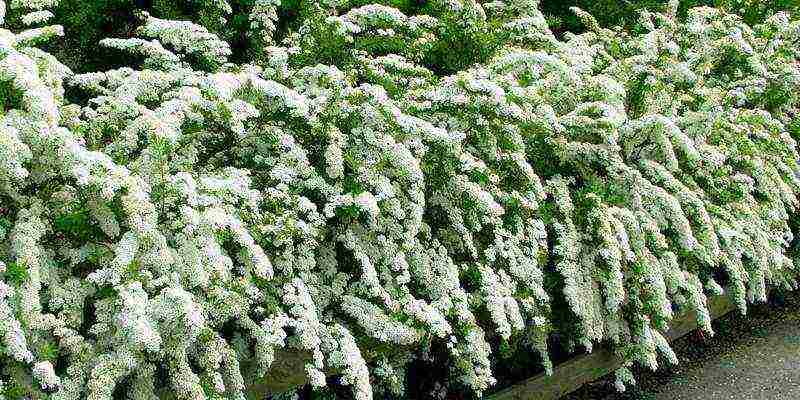
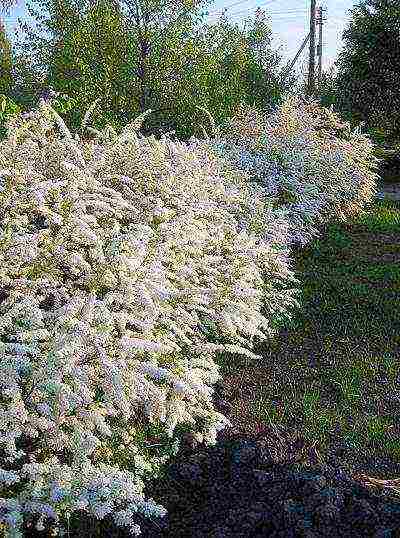
- Gray spirea - the result of crossing the previous species and whitish-gray spirea, has highly decorative varieties that bloom in spring. The most beloved variety of this species by flower growers is Spirea Grefsheim. The shoots of the tall bush bend towards the ground under the weight of flowers that completely cover the bush. The flowering is so abundant that the leaves are almost invisible.
- Spiraea is oak-leaved - blooms with umbrella-shaped inflorescences of white flowers with a large number of protruding stamens for 25 days, flowering occurs in May-June. The species is used in culture, it tolerates a haircut well.
- Spirea Nipponskaya came to us from Japan - this highly ornamental shrub 1-2 m high is decorated with yellowish-white inflorescence shields that appear in June. It does not differ in frost resistance; in severe winters, the tops of the shoots freeze slightly, but quickly recover. The most famous variety is Snowmound. A huge number of flowers on a bush up to 1.5 m high makes it very decorative at the time of flowering. The width of the bush is 2 times the height.
- No less decorative and spirea Wangutta is a hybrid species that blooms very profusely in June-July with white flowers collected in shields. The bush has an average height and can freeze slightly in frosty winters.
- Japanese spirea is quite thermophilic, but due to the low height of the bush - up to 1 m it winters without loss, covered with snow. The most interesting varieties are Little Princesses and Shirobana.Little princesses - a bush up to 80 cm high and up to 1.2 m wide blooms very profusely in June-July with pink flowers collected in medium-sized shields, grows slowly. Shirobana is a bush up to 0.8 m high and up to 0.6 m wide, blooms in mid-summer. Flowers in corymbose inflorescences have three colors - white, pink and crimson, if you cut off faded inflorescences, new ones will decorate the bush for another month.
- The adorable spirea stands out among other species by double flowering: in June on last year's shoots and in July and August on newly regrown ones. Flowers are collected in complex shields, can be white or pale pink. The species does not differ in frost resistance - up to -18 degrees, so in the middle lane it hibernates under cover.
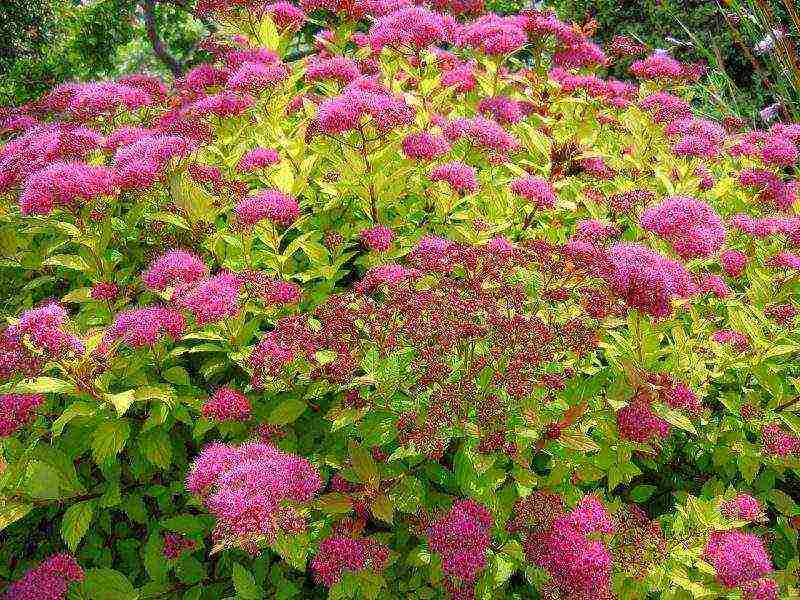
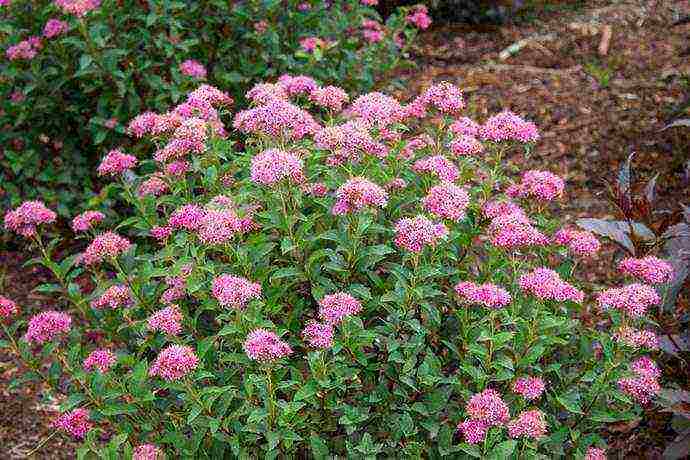
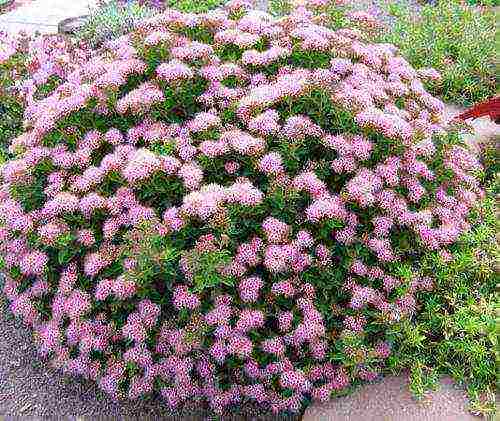
- Spirea Bumald is a decorative hybrid species, it also has a yellow-leaved form. The bush is low - up to 0.8 m in width and height. It blooms for more than 3 months with bright pink flowers in large shields. The most famous variety is Antoni Vaterer.
- Willow spirea grows wild in Siberia. The tall bush blooms in July and August with bright pink flowers collected in pyramidal panicles.
- Spirea Douglas grows above 2 m.In the second half of summer, it is decorated with pink flowers, collected in a paniculate inflorescence.
- When crossing the previous species and spirea willow leaf we got Billard's spirea. A tall, frost-resistant shrub blooms in the second half of summer and is decorated with large pink paniculate inflorescences until the very frosts.
- Also, the hybrid spirea is lilac-colored for a long time, only paniculate inflorescences, in accordance with the name, have a lilac-pink color. The bush can grow up to 2 m.
Spirea: features of cultivation
Spireas are unpretentious, but with proper careful care they give abundant flowering. Different flowering times dictate different pruning times. Some species and varieties have special soil and maintenance preferences. Most spirits prefer humus-rich, but not heavy soil without stagnant water, but they will feel good even on not very fertile soil. To keep the roots from getting wet, they need drainage. But before you plant a plant, you need to propagate it.
Shrub propagation
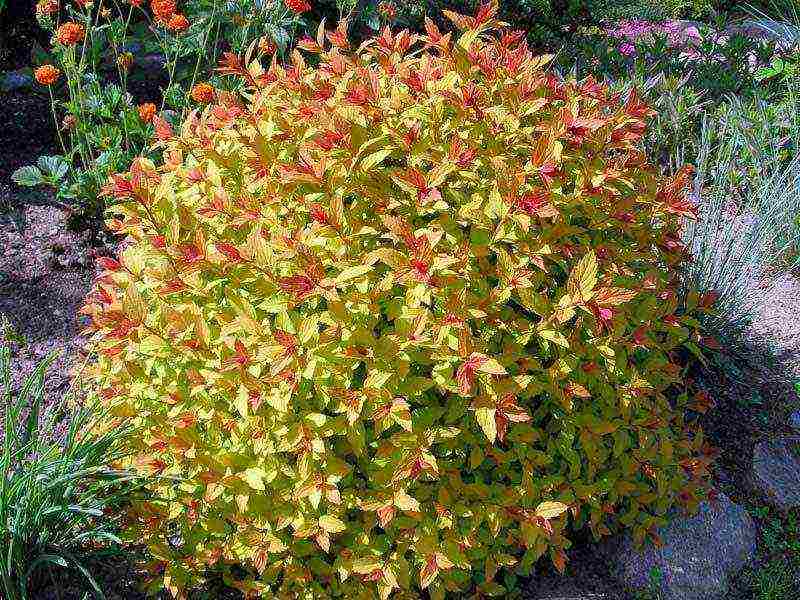

Spirea is very easy to propagate. Some species produce root shoots that can be transplanted. Parts of a divided bush take root well. Flexible shoots allow cuttings to be rooted. For propagation of all species, cuttings can be used, and for non-hybrid forms and varieties, seeds can also be sown.
Cuttings
When rooting the cuttings, you will get an exact copy of the parent plant. Green cuttings in early flowering varieties are cut at the beginning of June, and in late flowering varieties at the end of the month. For already lignified cuttings, the best rooting time is autumn, September or October.
- The annual green shoot is cut and cut into pieces with 5-6 leaves.
- Remove the bottom pair of leaves, cut the rest by half.
- The lower cut is placed in a vessel with an epin solution for 12 hours.
- It is treated with a powdery root stimulant.
- They are planted in a container with loose soil, sprinkled with a layer of sand at an angle of about 40 degrees to stimulate root formation.
- Cover with a film or glass jar and put in a lacy shade under the trees.
- They moisten the soil in the cuttings, preventing it from drying out, and the cuttings themselves are sprayed several times a day.
- In the fall, the container is dropped into the soil, mulched with fallen leaves and covered with a wooden box.
- In the spring, the shelter is removed. After the appearance of young shoots, the plants are planted in the garden in a permanent place.
Seed propagation
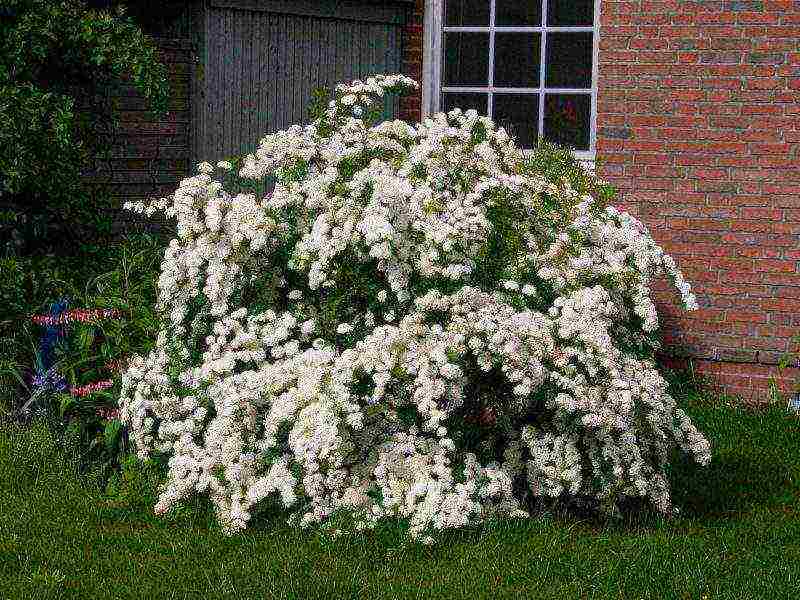

In non-hybrid varieties and species, seed germination reaches 80%. Collect them when the boxes turn brown, but have not yet opened. Dose in the room for 2 weeks. You can sow both before winter and in spring. Seeds do not require stratification. Seedlings dive when 2 true leaves are formed. Further care: watering as needed, 2 dressings with full mineral fertilizer.In the fall, seedlings are planted in a seedling bed, and next year in a permanent place. They begin to bloom for 3 years.
Landing in open ground
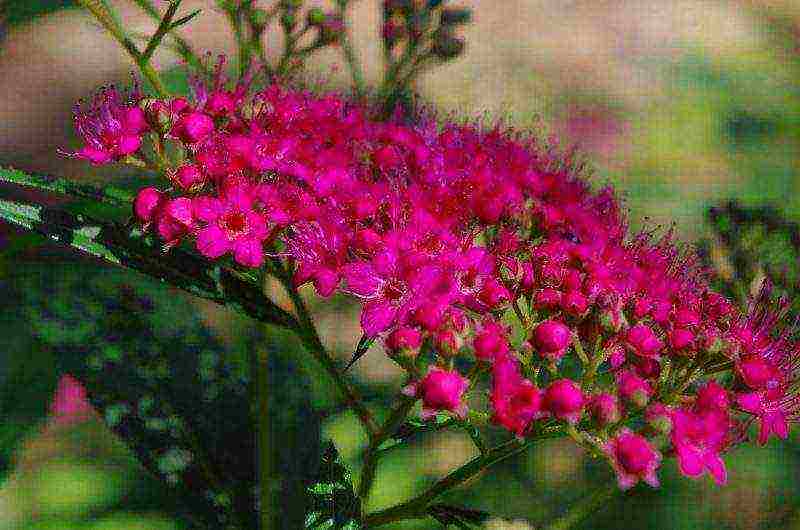

Proper planting is the key to abundant flowering and plant health. It is very important to maintain the optimal distance between the plants in order to provide them with the necessary nutritional area. When laying a hedge, it is enough to plant spireas 30 cm apart, for a normal planting the distance should be greater, since the bushes grow strongly in width: for tall varieties - about 1 m, for undersized varieties - 0.8 m.
The choice of planting material

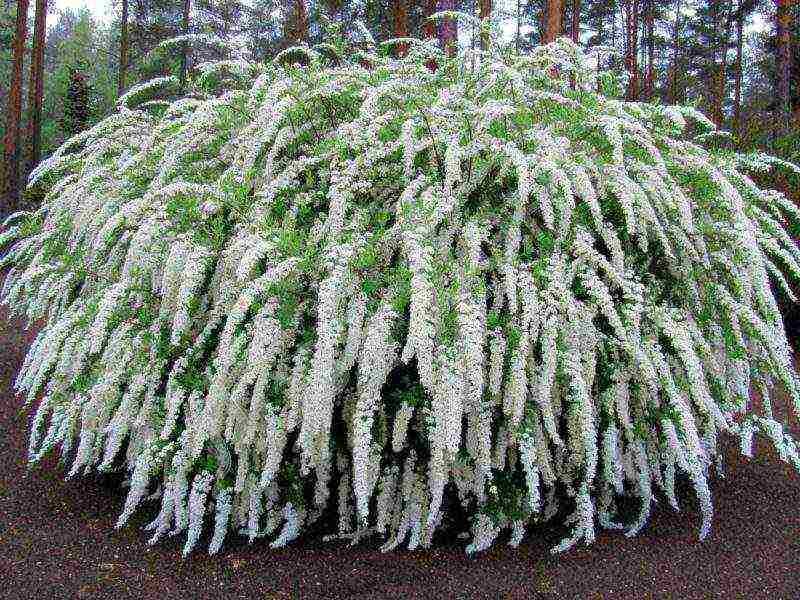
Now on sale there are many varieties and hybrids of spirea. The choice of a plant depends, first of all, on what place the spirea will occupy in the landscape design of a particular site. A hedge will require many plants of the same species, it is better if they are tall. As a tapeworm, you can plant an openwork bush with long flowering. On an alpine slide, undersized compact varieties will be appropriate. But whichever variety you choose, the plant should have a developed and healthy root system, consisting of 3 taproots and a well-developed lobe covered with a clay mash. With spring planting, not swollen buds, and with autumn planting, already flown leaves. It is best to choose a container-grown seedling that can be planted throughout the growing season.
How and when to plant?
Spirea is planted in pre-dug holes. Their size should be slightly larger than the root system of the plant. Usually the depth is about 70 cm, 20 of which falls on the drainage of expanded clay or brick fragments. The diameter of the hole is determined by the size of the roots.
Landing Algorithm:
- a plant is placed on a mound of earth poured in a hole, spreading the roots;
- fill up the earth, taking into account that the root collar is strictly at the level of the soil;
- watered in the planting circle using 2 to 3 buckets of water;
- mulch the soil around the bush with a layer of peat 7 cm thick.
Planting time depends on the selected variety: late flowering plants are planted in spring, early flowering ones - in autumn, but no later than 3-4 weeks before the onset of frost.
Soil preparation and site

The planting site should be well lit by the sun, a little shading is allowed during the day. It must be remembered that in the shade of the spirea it blooms badly.
This plant is undemanding to the soil. The preferred soil for spirea is light sod or leafy, with a neutral or slightly acidic soil reaction. Heavy clay soils are improved by the addition of sand and peat; a little clay should be added to light sandy soils. From fertilizers, you can add Art. tablespoons of long-acting ABA fertilizer for each bush. This amount will be enough for the plant for several years.
The nuances of planting in spring, autumn

If the variety blooms in summer, it is better to plant it in spring, early flowering varieties are planted in autumn, but so that the bushes take root before the onset of frost. In both cases, the plants must be dormant. In the spring, the buds should not yet swell, and in the fall, the leaf fall should already end.
Outdoor care for spirea
An unpretentious plant does not require special care measures, but top dressing and watering made on time will provide it with maximum decorative effect.
How to water properly?

Spirea is a drought-resistant plant, but in extreme heat and in the absence of rain for a long time, it must be watered. This is especially true for recently planted bushes. For an adult plant, the watering rate is 1.5 buckets per bush. For undersized species and varieties, one bucket is enough. Watering is sufficient once every 2 weeks, well soaking the root layer.
Fertilization and feeding
In order for the spireas to grow and bloom well, they should be fed regularly.

You can choose the following power plan:
- in spring, nitrogen mineral or organic fertilizer; for early flowering varieties, additional feeding with complete mineral fertilizer with microelements is needed;
- in June, plants are fed with full mineral fertilizer;
- at the end of August, fertilizing with phosphorus and potassium salts is needed so that the spireas are better prepared for winter.
At the end of summer, spireas cannot be fed with any fertilizers containing nitrogen, this can provoke the growth of new shoots that do not have time to ripen and freeze in winter.
All dressings can be applied both dry and liquid, combining them with watering. The next day, the soil around the plant must be loosened.
Spirea pruning
It is held on several dates, depending on the destination.
- Spring pruning is sanitary. Only dry and frost-damaged shoots are removed.
- Formative. Spireas blooming in the summer on the shoots of the current year are pruned in the spring immediately after the snow melts, combining formative pruning with sanitary pruning. Thin branches thickening the bush are removed - they will not give a good flowering. Different types of spirea have their own subtleties in pruning. Douglas and Boomald spire pruning begins only in the fourth year of life. Miniature varieties not exceeding 40 cm in height are cut into 2 buds. Cut out shoots with foliage that does not match the color of the variety. After flowering, the seed pods are removed, if there is no need for seeds - this contributes to the re-blooming of the inflorescences. It is enough to cut off a third of the shoot. The green hedge is trimmed to give the desired shape. Spring-flowering spireas form after flowering, cutting off shoots at the level of a strong young growth. The crown of the bush should be symmetrical.
- Anti-aging pruning. It is carried out in adult bushes, starting from the 7th year of life. All old shoots are removed, leaving no more than 5-7 young ones, while maintaining the symmetry of the bush. This pruning is best done in several stages, so as not to greatly weaken the bush.
Preparing for winter
The first wintering at a recently planted bush is a serious test. But adult plants, despite the frost resistance of most varieties, and species also need to be prepared for winter. For many of them, it is enough to feed the plants in August with potash and phosphorus fertilizers, to carry out moisture-charging irrigation after leaf fall and to mulch the trunk circle with humus.
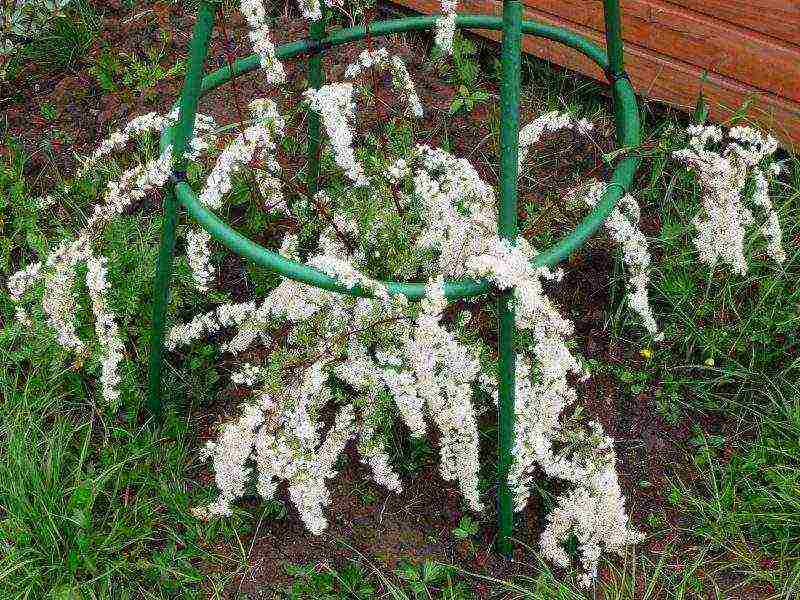

For less frost-resistant varieties, you will have to build a shelter:
- tie the branches into a bunch;
- bend the beam to the ground, fixing it with special fasteners;
- fall asleep with dry leaves;
- additionally throw in snow.
Plant diseases and pests
Spiraea rarely suffers from disease, but in a damp summer it can be damaged by powdery mildew and gray mold. To eliminate them, copper-containing fungicides, Fitosporin, colloidal sulfur are used.

Among the most common pests are aphids, blue meadow sawfly, whitefly and spider mites. Insecticides are effective against the first three: Fitoverm, Actellik. Insectoacaricides are suitable against the tick: Metaphos.
The nuances of growing in Siberia, the Urals, in the Moscow region
Almost all varieties and types of spirea are suitable for growing in central Russia. Shrubs such as Japanese Spirea and Nippon Spirea need additional winter shelter.
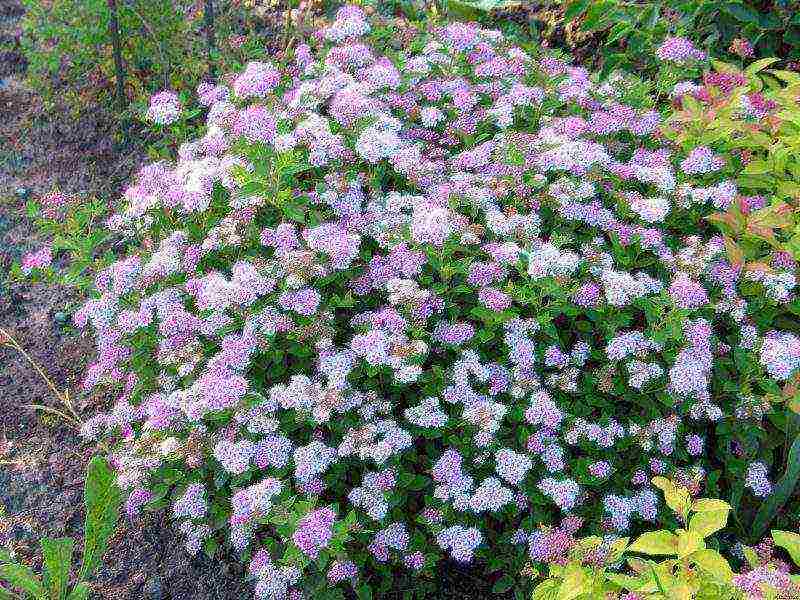

In the Urals, the climate is more severe. In its southern part, almost all types of spirits will grow well. In the middle lane and, especially in the north, frost-resistant shrubs should be preferred. The same can be said for spirea in Siberia. Only undersized varieties are able to overwinter under the snow without much loss. If medium and tall plants are not covered, then constant frosting in winter is guaranteed to them, decorativeness and abundant flowering cannot be achieved in such conditions.
Correctly selected varieties of spirea are able to create a flowering conveyor throughout the growing season and will be a real decoration of any garden.
Among the ornamental shrubs, spirea occupies a special place. She is surprisingly unpretentious and easily forgives the gardener even the most unobtrusive care.A wide variety of shapes and types allows you to choose the plant to decorate the site that will best fit into the surrounding landscape. Planting and caring for a spirea is not difficult, even a novice gardener can handle it.
Spirea: types and varieties
The genus spirea belongs to the pink family and is quite numerous, it includes more than 70 species. The distribution area of this deciduous shrub is wide. It can be found in the northern hemisphere in most climatic zones. Spirea rarely has single flowers, most often they are collected in a corymbose inflorescence, sometimes in a panicle. The color of flowers depends on the flowering time of the species. Plants blooming in spring have white flowers that bloom on last year's shoots, in species blooming in summer pink-crimson gamut prevails, flowers are located on annual growths.
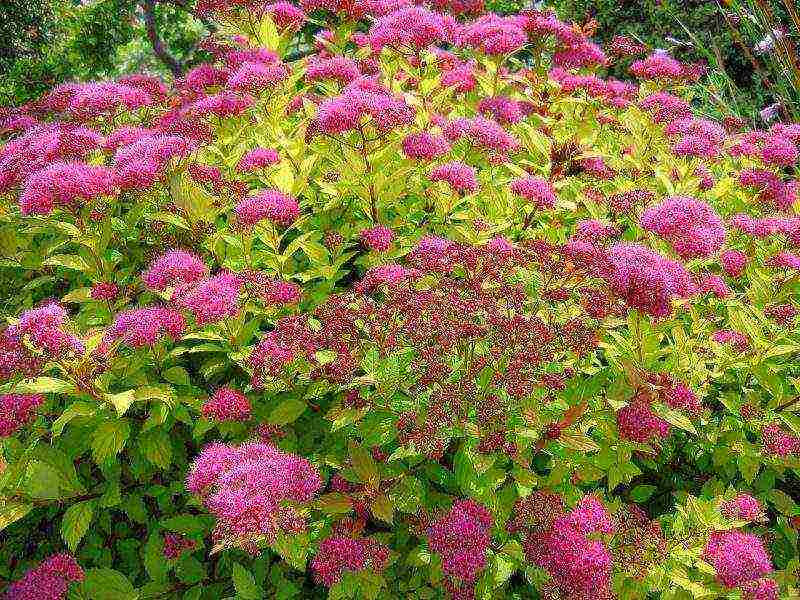

The most common types.
- Medium spirea - an inhabitant of Siberian and Far Eastern forests, a tall shrub - above 2 m with white corymbose flowers that open in May and do not fall for 3 weeks, frost-resistant and drought-resistant, used in landscaping, suitable for northern regions.
- Spiraea birch-leaved - grows in Siberia, from 1 to 2 m in height, white flowers are collected in huge shields - up to 10 cm in diameter, blooms at the end of May and blooms throughout June.
- Spirea crenate - has been used in landscaping for 200 years, there are cultural hybrid varieties. In nature, it is a low, up to 1 m shrub that blooms at the end of May. Quite large flowers are collected in corymbose inflorescences, due to the large number of long yellow stamens, it seems that they have a golden hue. This type of spirea is drought-resistant and frost-hardy, can be used to strengthen floating soils.
- Spirea St. John's wort is a shrub up to 1 m high, flowering - May-June, white flowers, is used to obtain new forms of the plant.
- Gray spirea - the result of crossing the previous species and whitish-gray spirea, has highly decorative varieties that bloom in spring. The most beloved variety of this species by flower growers is the Grefsheim spirea. The shoots of the tall bush bend towards the ground under the weight of flowers that completely cover the bush. The flowering is so abundant that the leaves are almost invisible.
- Spiraea is oak-leaved - blooms with umbrella-shaped inflorescences of white flowers with a large number of protruding stamens for 25 days, flowering occurs in May-June. The species is used in culture, it tolerates a haircut well.
- Spirea Nipponskaya came to us from Japan - this highly ornamental shrub 1-2 m high is decorated with yellowish-white inflorescence shields that appear in June. It does not differ in frost resistance; in severe winters, the tops of the shoots freeze slightly, but quickly recover. The most famous variety is Snowmound. A huge number of flowers on a bush up to 1.5 m high makes it very decorative at the time of flowering. The width of the bush is 2 times the height.
- No less decorative and spirea Wangutta is a hybrid species that blooms very profusely in June-July with white flowers collected in shields. The bush has an average height and can freeze slightly in frosty winters.
- Japanese spirea is quite thermophilic, but due to the low height of the bush - up to 1 m it winters without loss, covered with snow. The most interesting varieties are Little Princesses and Shirobana. Little princesses - a bush up to 80 cm high and up to 1.2 m wide blooms very profusely in June-July with pink flowers collected in medium-sized shields, grows slowly. Shirobana is a bush up to 0.8 m high and up to 0.6 m wide, blooms in mid-summer. Flowers in corymbose inflorescences have three colors - white, pink and crimson, if you cut off faded inflorescences, new ones will decorate the bush for another month.
- The adorable spirea stands out among other species by double flowering: in June on last year's shoots and in July and August on newly regrown ones. Flowers are collected in complex shields, can be white or pale pink.The species does not differ in frost resistance - up to -18 degrees, so in the middle lane it hibernates under cover.
- Spirea Bumald is a decorative hybrid species, it also has a yellow-leaved form. The bush is low - up to 0.8 m in width and height. It blooms for more than 3 months with bright pink flowers in large shields. The most famous variety is Antoni Vaterer.
- Willow spirea grows wild in Siberia. The tall bush blooms in July and August with bright pink flowers collected in pyramidal panicles.
- Spirea Douglas grows above 2 m. In the second half of summer, it is decorated with pink flowers, collected in a paniculate inflorescence.
- When crossing the previous species and spirea willow leaf we got Billard's spirea. A tall, frost-resistant shrub blooms in the second half of summer and is decorated with large pink paniculate inflorescences until the very frosts.
- Also, the hybrid spirea is lilac-colored for a long time, only paniculate inflorescences, in accordance with the name, have a lilac-pink color. The bush can grow up to 2 m.
Spirea: features of cultivation
Spireas are unpretentious, but with proper careful care they give abundant flowering. Different flowering times dictate different pruning times. Some species and varieties have special soil and maintenance preferences. Most spirits prefer humus-rich, but not heavy soil without stagnant water, but they will feel good even on not very fertile soil. To keep the roots from getting wet, they need drainage. But before you plant a plant, you need to propagate it.
Shrub propagation
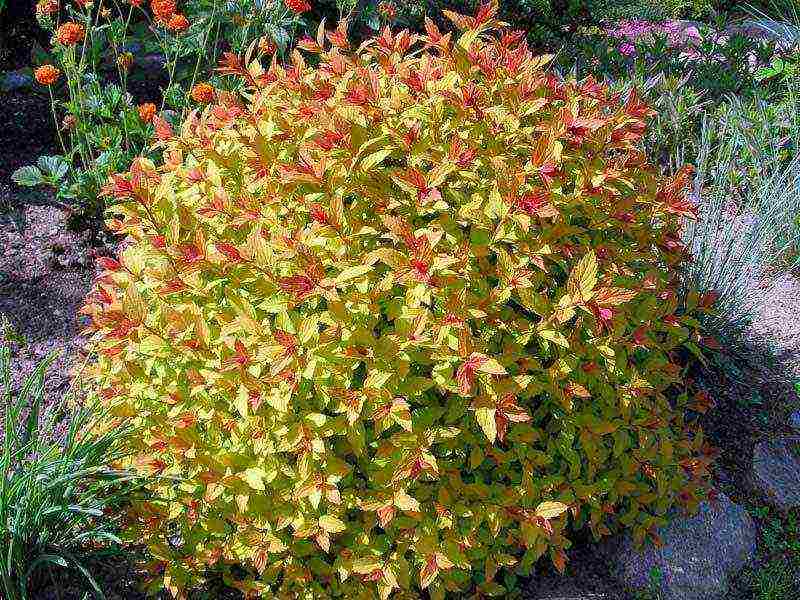

Spirea is very easy to propagate. Some species produce root shoots that can be transplanted. Parts of a divided bush take root well. Flexible shoots allow cuttings to be rooted. For propagation of all species, cuttings can be used, and for non-hybrid forms and varieties, seeds can also be sown.
Cuttings
When rooting the cuttings, you will get an exact copy of the parent plant. Green cuttings in early flowering varieties are cut at the beginning of June, and in late flowering varieties at the end of the month. For already lignified cuttings, the best rooting time is autumn, September or October.
- The annual green shoot is cut and cut into pieces with 5-6 leaves.
- Remove the bottom pair of leaves, cut the rest by half.
- The lower cut is placed in a vessel with an epin solution for 12 hours.
- It is treated with a powdery root stimulant.
- They are planted in a container with loose soil, sprinkled with a layer of sand at an angle of about 40 degrees to stimulate root formation.
- Cover with a film or glass jar and put in a lacy shade under the trees.
- They moisten the soil in the cuttings, preventing it from drying out, and the cuttings themselves are sprayed several times a day.
- In the fall, the container is dropped into the soil, mulched with fallen leaves and covered with a wooden box.
- In the spring, the shelter is removed. After the appearance of young shoots, the plants are planted in the garden in a permanent place.
Seed propagation
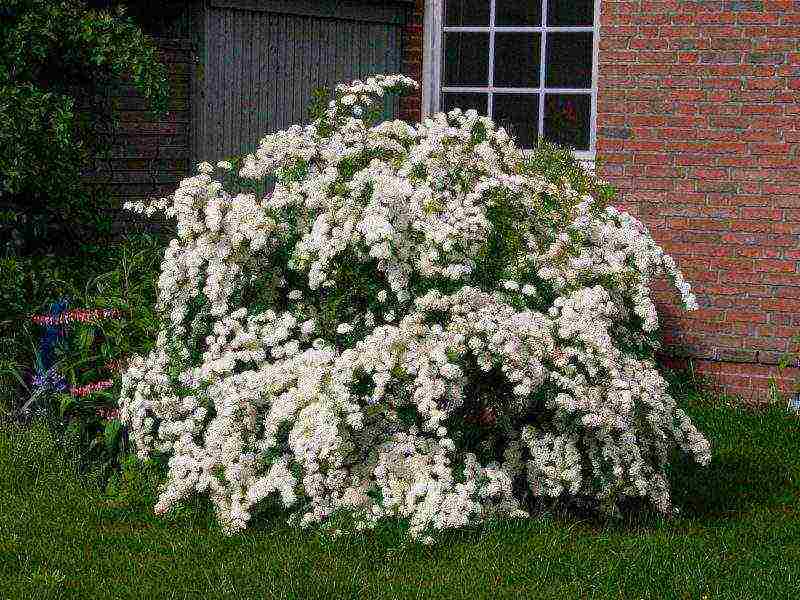

In non-hybrid varieties and species, seed germination reaches 80%. Collect them when the boxes turn brown, but have not yet opened. Dose in the room for 2 weeks. You can sow both before winter and in spring. Seeds do not require stratification. Seedlings dive when 2 true leaves are formed. Further care: watering as needed, 2 dressings with full mineral fertilizer. In the fall, seedlings are planted in a seedling bed, and next year in a permanent place. They begin to bloom for 3 years.
Landing in open ground
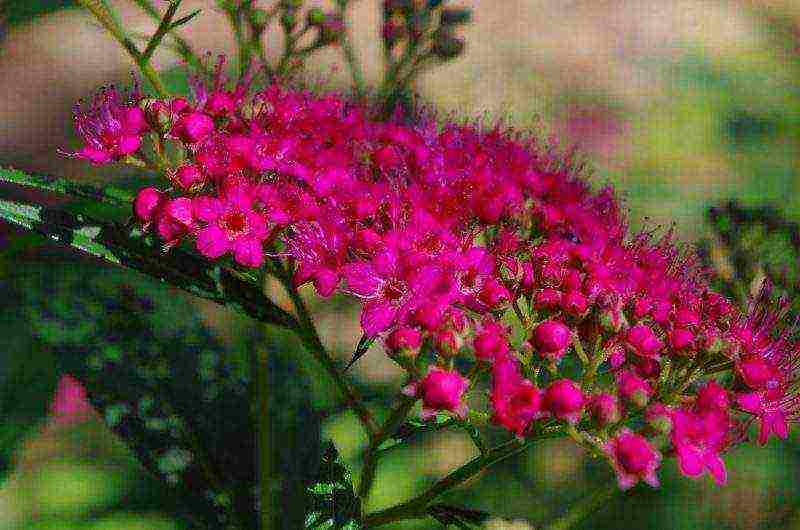

Proper planting is the key to abundant flowering and plant health. It is very important to maintain the optimal distance between the plants in order to provide them with the necessary nutritional area. When laying a hedge, it is enough to plant spireas 30 cm apart, for a normal planting the distance should be greater, since the bushes grow strongly in width: for tall varieties - about 1 m, for undersized varieties - 0.8 m.
The choice of planting material
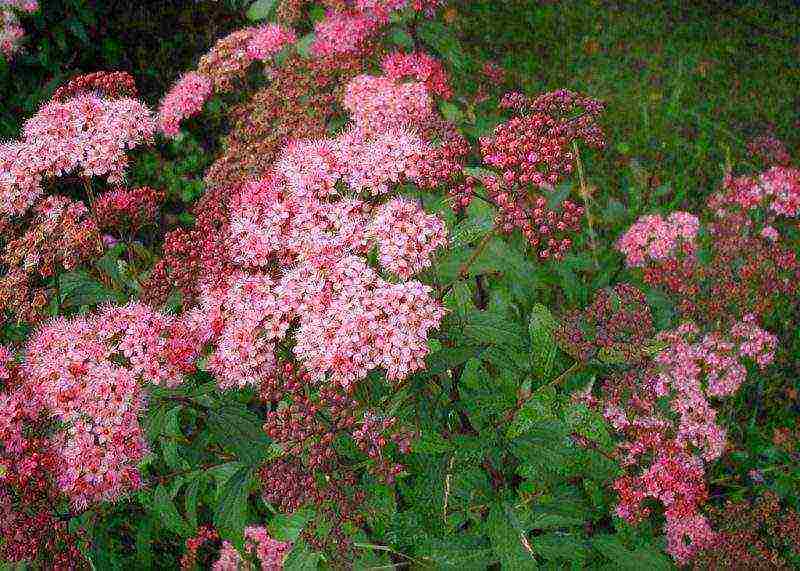

Now on sale there are many varieties and hybrids of spirea. The choice of a plant depends, first of all, on what place the spirea will occupy in the landscape design of a particular site. A hedge will require many plants of the same species, it is better if they are tall. As a tapeworm, you can plant an openwork bush with long flowering. On an alpine slide, undersized compact varieties will be appropriate. But whichever variety you choose, the plant must have a developed and healthy root system, consisting of 3 taproots and a well-developed lobe covered with a clay mash. With spring planting, not swollen buds, and with autumn planting, already flown leaves. It is best to choose a container-grown seedling that can be planted throughout the growing season.
How and when to plant?
Spirea is planted in pre-dug holes. Their size should be slightly larger than the root system of the plant. Usually the depth is about 70 cm, 20 of which falls on the drainage of expanded clay or brick fragments. The diameter of the hole is determined by the size of the roots.
Landing Algorithm:
- a plant is placed on a mound of earth poured in a hole, spreading the roots;
- fill up the earth, taking into account that the root collar is strictly at the level of the soil;
- watered in the planting circle using 2 to 3 buckets of water;
- mulch the soil around the bush with a layer of peat 7 cm thick.
Planting time depends on the selected variety: late flowering plants are planted in spring, early flowering ones - in autumn, but no later than 3-4 weeks before the onset of frost.
Soil preparation and site

The planting site should be well lit by the sun, a little shading is allowed during the day. It must be remembered that in the shade of the spirea it blooms badly.
This plant is undemanding to the soil. The preferred soil for spirea is light sod or leafy, with a neutral or slightly acidic soil reaction. Heavy clay soils are improved by the addition of sand and peat, a little clay should be added to light sandy soils. From fertilizers, you can add Art. tablespoons of long-acting ABA fertilizer for each bush. This amount will be enough for the plant for several years.
The nuances of planting in spring, autumn

If the variety blooms in summer, it is better to plant it in spring, early flowering varieties are planted in autumn, but so that the bushes take root before the onset of frost. In both cases, the plants must be dormant. In the spring, the buds should not swell yet, and in the fall the leaf fall should already end.
Outdoor care for spirea
An unpretentious plant does not require special care measures, but top dressing and watering made on time will provide it with maximum decorative effect.
How to water properly?

Spirea is a drought-resistant plant, but in extreme heat and in the absence of rain for a long time, it must be watered. This is especially true for recently planted bushes. For an adult plant, the watering rate is 1.5 buckets per bush. For undersized species and varieties, one bucket is enough. Watering is sufficient once every 2 weeks, well soaking the root layer.
Fertilization and feeding
In order for the spireas to grow and bloom well, they should be fed regularly.

You can choose the following power plan:
- in spring, nitrogen mineral or organic fertilizer; for early flowering varieties, additional feeding with complete mineral fertilizer with microelements is needed;
- in June, plants are fed with full mineral fertilizer;
- at the end of August, fertilizing with phosphorus and potassium salts is needed so that the spireas are better prepared for winter.
At the end of summer, spireas cannot be fed with any fertilizers containing nitrogen, this can provoke the growth of new shoots that do not have time to ripen and freeze in winter.
All dressings can be applied both dry and liquid, combining them with watering. The next day, the soil around the plant must be loosened.
Spirea pruning
It is held on several dates, depending on the destination.
- Spring pruning is sanitary.Only dry and frost-damaged shoots are removed.
- Formative. Spireas blooming in summer on the shoots of the current year are pruned in the spring immediately after the snow melts, combining formative pruning with sanitary pruning. Thin branches thickening the bush are removed - they will not give a good flowering. Different types of spirea have their own subtleties in pruning. Pruning of Douglas and Boomald spirits begins only in the fourth year of life. Miniature varieties not exceeding 40 cm in height are cut into 2 buds. Cut shoots with foliage that does not match the color of the variety. After flowering, the seed pods are removed, if there is no need for seeds - this contributes to the re-blooming of the inflorescences. It is enough to cut off a third of the shoot. The green hedge is trimmed to give the desired shape. Spring flowering spireas form after flowering, cutting off the shoots at the level of a strong young growth. The crown of the bush should be symmetrical.
- Anti-aging pruning. It is carried out in adult bushes, starting from the 7th year of life. All old shoots are removed, leaving no more than 5-7 young ones, while maintaining the symmetry of the bush. This pruning is best done in several stages, so as not to greatly weaken the bush.
Preparing for winter
The first wintering at a recently planted bush is a serious test. But adult plants, despite the frost resistance of most varieties, and species also need preparation for winter. For many of them, it is enough to feed the plants in August with potash and phosphorus fertilizers, to carry out moisture-charging irrigation after leaf fall and to mulch the trunk circle with humus.
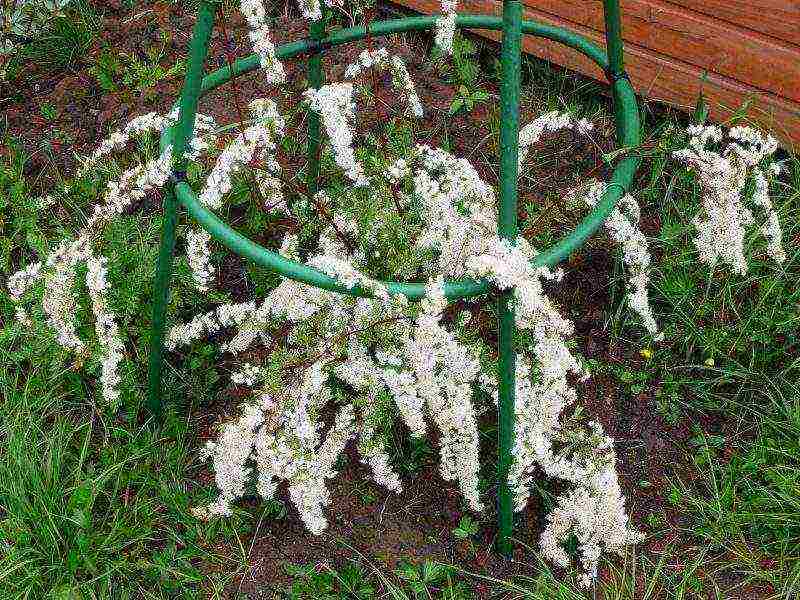

For less frost-resistant varieties, you will have to build a shelter:
- tie the branches into a bunch;
- bend the beam to the ground, fixing it with special fasteners;
- fall asleep with dry leaves;
- additionally throw in snow.
Plant diseases and pests
Spiraea rarely suffers from disease, but in a damp summer it can be damaged by powdery mildew and gray mold. To eliminate them, copper-containing fungicides, Fitosporin, colloidal sulfur are used.

Among the most common pests are aphids, blue meadow sawfly, whitefly and spider mites. Insecticides are effective against the first three: Fitoverm, Actellik. Insectoacaricides are suitable against the tick: Metaphos.
The nuances of growing in Siberia, in the Urals, in the Moscow region
Almost all varieties and types of spirea are suitable for growing in central Russia. Shrubs such as Japanese Spirea and Nippon Spirea need additional winter shelter.
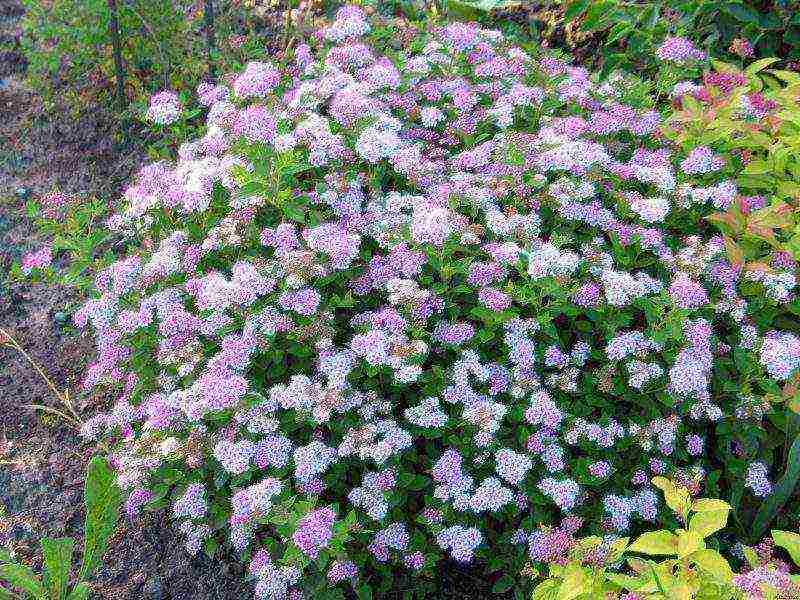

In the Urals, the climate is more severe. In its southern part, almost all types of spirits will grow well. In the middle lane and, especially in the north, frost-resistant shrubs should be preferred. The same can be said for spirea in Siberia. Only undersized varieties are able to overwinter under the snow without much loss. If medium and tall plants are not covered, then constant frosting in winter is guaranteed to them, decorativeness and abundant flowering cannot be achieved in such conditions.
Correctly selected varieties of spirea are able to create a flowering conveyor throughout the growing season and will be a real decoration of any garden.
Spirea, volzhanka or meadowsweet is a plant from the genus of the Rosaceae family. Such a variety as that of a spirea is very rare - there are dwarfs less than 20 cm in height and giants up to 2.5 meters in height. Branches can be upright, recumbent, or outstretched. They also differ in shape and color shades. Since spiria tolerates severe winters well, cultivation is practiced in Siberia and other northern regions.
Well on one site, several types of perennial crops are combined. Budleya and spirea will decorate your garden together.
Spirea varieties for Siberia with a description
Although many species tolerate frost well, they still prefer the most frost-resistant plants. Let's consider the most popular ones.
Gray spiria Greifsheim - densely branched, arched shrub more than one meter high.The lower leaves are light green, and the upper part of the foliage is gray-green. Flowers of a white shade are located throughout the shoot. The first leaves bloom in May, and already at the end of June the fruits ripen. Spiraea gray refers to hybrids - it was obtained by crossing whitish-gray and St. John's worm spirea. It is popular with gardeners in the northern regions, as graveshame tolerates frosty winters well.
Spiria willow Is a cold-resistant plant that tolerates severe winters well. This species became widespread in Europe, Siberia, Japan, North America and China. In nature, it is found in shrubs near water bodies. A bush with reddish-brown shoots, reaches a height of two meters. The upper leaves are dark green in color, and the lower ones are slightly lighter. Short peduncles are collected in short panicles. The flowers are pink and white.
 Spirea willow. Photo
Spirea willow. Photo
Spirea Rosea (pink) - bush up to 1.5 meters high, with beautiful pink flowers. Small flowers, collected in paniculate inflorescences. The shape of the leaves is elongated, up to 10 cm long. In diameter, the bush grows up to 1.5 meters. A distinctive feature of the species is its high resistance to severe winter frosts.
Spyria breeding methods
Four types of propagation of this culture are used - seeds, division of the bush, layering and cuttings. Let's take a quick look at each of them.
Layers - the branches easily bend to the ground, so this breeding method is very popular with gardeners. In the spring, the one-year-old shoot is bent to the ground in the prepared hole and covered with nutritious soil. Sprinkle abundantly with water. Maintain moderate soil moisture throughout the season.
In order for the roots to appear faster, it is recommended to cut the bark on the shoot where it touches the ground.
Dividing the bush - in the fall, carefully dig out a bush. Shake off the ground and divide into several bushes. When dividing, make sure that a sufficiently large root lobe and 2 strong shoots remain. The separated bushes are planted in a new place.
Cuttings - with the correct preparation of cuttings, 7 out of 10 take root and give roots. The time for harvesting cuttings depends on the variety - for summer-flowering spirits, cuttings are harvested in July, and for spring-flowering ones - at the beginning of June. Young shoots are cut off at the base, the bark is scratched in several places and buried in the ground to the leaves. Sprinkle abundantly with water. Before rooting, maintain a moderate soil moisture.
More information about this breeding method is described in the video:
Seeds - this method of reproduction is practiced by breeders to develop new varieties. In rare cases, it is used by gardeners. With this method, the varietal qualities of hybrid spirits are not inherited.
Planting spirea in the spring in open ground

In the spring, it is recommended to plant summer-flowering spirea species. Planting is carried out before the leaves bloom (approximately in May). Planting technology for seedlings:
- Dig a hole of the right size. A distance of at least 70 cm is left between the holes. For tall varieties, even more - up to 1 meter.
- The soil from the planting pit is mixed with organic fertilizers. If the soil on the site is clayey, then it is advisable to loosen it by adding a little sand and peat.
- Expanded clay or broken brick is poured as drainage with a layer of at least 15 cm.The larger the layer, the better - it can be increased to 20 cm.
- Shoots and long roots are shortened at the seedling. If necessary, pruning of dried roots is carried out.
- A little fertile soil is poured into the planting hole. They make a small mound, pour water to moisten the lower soil layer.
- They put the seedling in the hole and cover it with the rest of the earth. Around the bush, the earth is lightly tamped and an earthen rampart is formed.
- Water the seedling with water and mulch with peat, old sawdust or straw to retain moisture in the soil.
Planting spirea in the fall
If purchased seedlings are planted in the spring, then in the fall they practice dividing the bush.It is important to finish planting before the end of the leaf fall.
Important. Propagated by the method of division, young bushes up to 4 years old. They have a small root system, so it is easy to divide and extract from the ground.
A spirea bush is dug out, cleaned of the ground and lowered into a large container of water. The roots are washed and removed from the water. Lightly dry and divide the bush with pruning shears, leaving two summer shoots and a lobe of roots. Divided bushes are planted on a plot according to a 70x70 cm scheme.
Watering and feeding spirea
The cultivated plant needs regular watering, especially on hot and sunny days. Abundant watering is carried out (1.5 buckets of water each) twice a month. If the soil around the plants is mulched, then the frequency of watering is slightly reduced.
Spirea grows well without feeding. But it will not be superfluous to apply fertilizers before flowering and after pruning. Apply nitrogenous fertilizers for each bush in the spring (for example, mullein). In the fall, they are fed only with phosphorus-potassium fertilizers.
Spirea pruning
 Pruning summer blooming spirea
Pruning summer blooming spirea
In the first years of growth, plants do not need pruning. Only remove dried, frozen and damaged shoots. After 7-14 years, old branches are cut out at ground level, and 5 young ones are left for future flowering. Then, a year later, old shoots more than 7 years old are cut off and young ones are left again, etc. Any pruning is carried out in the fall or early spring.
The average life span of a spirea bush is 20 years. After this age, there is no need to wait for abundant flowering. New seedlings are planted on the site by grafting or dividing the bush.
Shelter spirea for the winter
Under a thick layer of snow, the cultivated plant tolerates frosty winters well. Therefore, it does not need additional shelter. But in order to protect the planted young plants, they tie the shoots into a bunch and bend them to the ground. Cover with a layer of dry leaves about 15 cm, then branches and cover with snow as soon as it falls. Such a shelter protects the spirea from freezing.
With proper care, you can enjoy the beautiful meadowsweet blooms from late spring to mid-summer.
 Spirea (Spiraea) is a deciduous type of ornamental shrub belonging to the pink family (Rosaceae). This plant is represented by nine dozen species common in forest-steppe and semi-desert zones, as well as in the subalpine mountainous zone in the Northern Hemisphere.
Spirea (Spiraea) is a deciduous type of ornamental shrub belonging to the pink family (Rosaceae). This plant is represented by nine dozen species common in forest-steppe and semi-desert zones, as well as in the subalpine mountainous zone in the Northern Hemisphere.
Botanical features of spirea
The height of the aboveground part, depending on the species characteristics, can vary within 15-250 cm. The root system of the decorative perennial is of the fibrous type, not deeply located. Erect and spread, recumbent type, ascending or creeping branches, have a light brown or dark brown bark, which can flake off. Young branches are characterized by light green, yellowish-reddish or brownish coloration, as well as the presence or absence of pubescence.
Small buds. The foliage is alternate, petiolar, without stipules, narrow lanceolate-linear or rounded. The racemose inflorescences of early flowering species are sessile or practically sessile, umbellate or corymbose type, with a leaf rosette at the base. Flowers are bisexual, less often dioecious, white, pink-red or purple in color. The fruits are multi-seeded leaflets, with flat, lanceolate winged brown seeds.
How to grow spirea (video)
Variants of using spirea in landscape design
The variety of types of spirea makes it easy to choose a shrub that will be ideal for decorating a backyard area. Undersized and miniature species are widely used., which are optimal when creating rockeries.
Varieties with different flowering periods can be combined to zone the area. Spireas are widely used in the creation of mixborders, as well as green hedges.They harmonize very well with scumpia, dahlias, turf and actions, and also look attractive and original with conifers, including spruces, thuja, pines and junipers.
Description of shrub varieties
On the territory of our country, several varieties of a shrub plant are quite successfully grown. All of them differ not only in appearance, but also in terms of flowering. Paniculata spirea, as well as varieties Junia Bright and Little Princesses.
Spirea hybrid Billard Triumfans
Billard's spirea is a hybrid form obtained by crossing the willow and Douglas spirea. The two-meter shrub has spreading branches and foliage of a wide lanceolate shape with a grayish-tomentose lower part.
Variety "Triumfans" has purple-pink spike-shaped inflorescences a quarter meter high, as well as green or reddish-brown young shoots with pubescence and ribbed bare old shoots, which gradually dry out. By the sixth year of life, there is a loss of shape by a shrub, so it is necessary to properly prune.

Spirea willow
Under natural conditions, the species grows in Siberia and Europe, as well as in the northern part of America, in Japan and China, where it forms thickets near lakes, along river floodplains. This is an upright shrub plant no more than two meters high, with very characteristic red-yellowish shoots and pointed foliage of an elongated lanceolate shape.
The base of the leaves is sharp, serrate. The surface of the plate is dark green in color, and the bottom has a lighter color. The flowers are white or pink in color, located on short pubescent peduncles, which are collected in inflorescences of the pyramidal or cylindrical paniculate type. The variety is frost-resistant, blooms in the fourth or fifth year.

White-flowered spirea argut
One of the most spectacular spring blooming varieties. A tall culture with a two-meter aboveground part, a spreading crown, and also narrow lanceolate foliage with strong serrated.
Snow-white flowers gather in numerous, umbrella-shaped inflorescences that densely cover the shoots. Flowering is observed on the shoots of the last year. The species is slow growing and needs to be pruned after flowering. The branches are quite thin and spreading, with small and relatively narrow leaves of a characteristic green color.
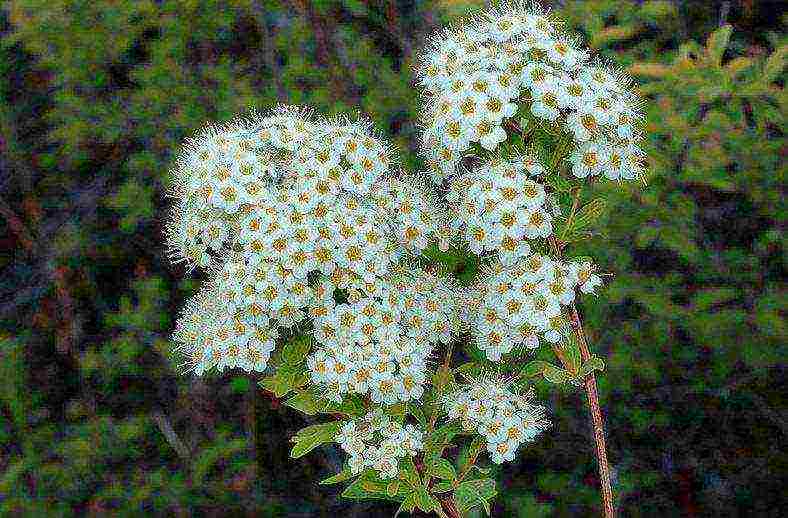

Spirea gray
A large and fairly frost-resistant plant with a height of the aerial part of up to two meters and numerous shoots, which are covered with pointed leaves of a grayish-green color. Flowers are formed in May, white, collected in corymbose inflorescences. The most popular variety in home gardening is "Grefsheim" with very characteristic drooping arcuate branches.
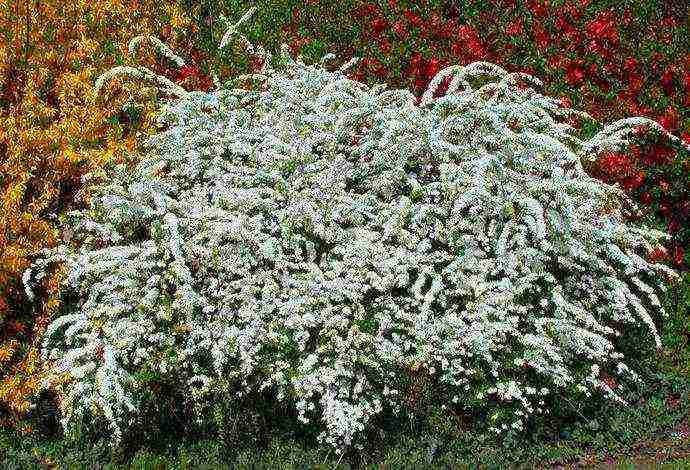

Japanese spirea
One of the most famous and very common species in our country, represented by a variety of varieties, excellent for use in modern backyard landscape design. Under natural conditions, the Japanese variety grows in China and Japan, as well as in Korea.
In the conditions of home gardening, it is used in landscaping even in the northern regions. Winter-hardy and very hardy shrub plant with a height of the aboveground part from 30 cm to one and a half meters, it has a varied coloration of not only flowers, but also leaves, which can vary depending on varietal characteristics. Flowering is abundant and long-lasting.

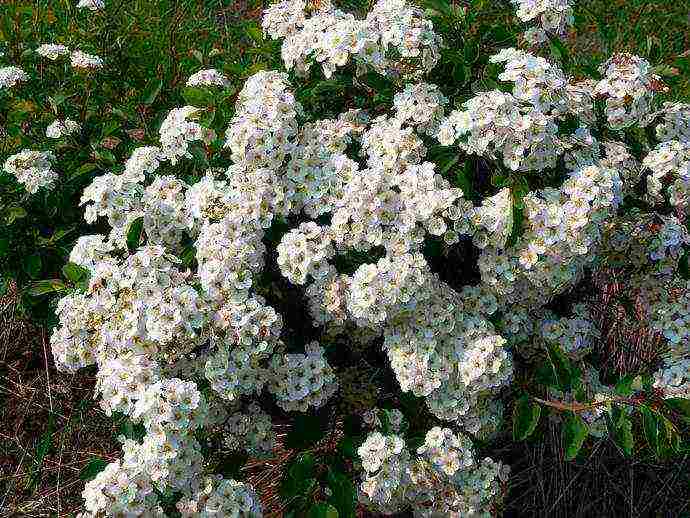
Spirea nippon
A shrub plant no more than two meters high, with a very dense, spherical crown, as well as horizontally directed branches. It is characterized by a compact type of aerial part and a very abundant, rather long flowering.
The foliage is round, crenate or whole-edged in the upper part, green in color. The species is very light-loving, with high winter hardiness. Particularly popular are such decorative forms as Snowmound or Snowmound and Halvare Silver or Halward's Silver.

Features of planting and transplanting spirea in the open field
It is advisable to plant shrubby perennials in previously prepared areas in the spring, after the snow melts and the soil warms up. In order to properly plant an ornamental plant, it is necessary to select a sufficiently sunny and well-heated area, represented by sod land, peat and sand mixed in a ratio of 2: 1: 1 with soil acidity at 6-7 pH.
If the groundwater is too high it is important to provide high-quality drainage, consisting of gravel in a layer of 10-20 cm. The planting pit should have dimensions of 50 x 50 x 50 cm. The standard distance between the planting pits should not be less than half a meter. When planting a shrub as a hedge, it is possible to reduce the gap between the planted plants to 40 cm, with the distance between rows within 30-40 cm. After planting, it is recommended to mulch with peat, the layer of which is 70 mm.
Types and varieties of spirea (video)
Haircut and other types of spirea care
It is necessary to take care of the spireas not only in the spring-summer period, but also in the fall, at the stage of preparation for wintering. In early spring, 100-120 g of highly effective fertilizer "Kemira-universal" must be applied. Irrigation should be moderate, but in a too dry and hot season, as well as after pruning, the plant should be watered at the rate of one and a half buckets of water for each bush.
Young and newly planted plants need more frequent and abundant watering. After watering, it is required to perform surface active loosening of the soil, as well as organic mulching. The shrub plant tolerates a haircut well enough, therefore it is very actively used to create hedges or borders. After pruning, the perennial is able to quickly restore the crown, so it is recommended to cut off all faded shoots by about half of the length.

Reproduction of spirea by dividing the bush, cuttings, seeds and layering
Reproduction of a decorative perennial can be carried out in several ways:
- seed material;
- bush division;
- layering;
- cuttings.
Best of all, seeds reproduce varieties of Japanese spirea and oak-leaved, and the germination rate of seed of such varieties, as a rule, exceeds 80%. For sowing seeds, seedling containers with a height of 20-30 cm are used, which are filled with a mixture of leaf and sod land in a 1: 1 ratio with the addition of a small amount of humus and medium-grained sand to loosen the soil. When diving, the central root is pinched by about a third of the length, after which the seedlings are seated at a distance of 5-7 cm.
Vegetative propagation is very widely usedif there is a need to keep well all the characteristics of the parent plant. This method of reproduction allows you to get full-fledged adult plants much faster. By bush division, spireas are propagated at the age of three or four years, when the shrub is already fully formed, and the size of the root system allows division into separate divisions.
For execution reproduction by layering lower, only completely healthy shoots of an ornamental culture are used, which in the spring are dug into pre-prepared grooves of 8-10 cm.If there is a need to obtain the maximum number of plants with fully preserved varietal characteristics, then the most convenient and easy way is propagation by cuttings. Cutting is one of the main methods used by amateur gardeners.
How to plant a spirea (video)
Some features of planting and caring for spirea in the Urals
When grown in insufficiently favorable and comfortable conditions for the growth and development of culture, the plant's immunity weakens, so you need to regularly check the planting for the absence of damage by haplits, aphids and sawflies.
In a winter that is too harsh or with little snow, the ends of the shoots are sometimes frozen in the varieties of the Nippon and sharp-toothed varieties, therefore in Siberia or the Urals it is recommended in the autumn to use dry leaves or peat chips with a layer of up to 10-12 cm to cover the root system.
When choosing a variety need to rememberthat spring-flowering species are distinguished by inflorescences of white or cream coloration, collected in inflorescences on the shoots of the previous year and blooming in May. Summer-flowering species are characterized by high decorativeness and bright inflorescences formed on the shoots of this year, therefore, they must be pruned only in early spring.
Attention, only TODAY!
Reviews and comments
Spirea, numbering more than 100 varieties, is known as a versatile shrub for landscape design. Among them there are giants over 2 meters high and dwarf species less than 20 cm high. It is successfully grown as a hedge in gardens and parks, serves as an element of rockeries and flower beds.
Lush color, a variety of colors, a long flowering period and unpretentious care are good reasons to settle this beauty in the garden.
You will learn how to grow spirea, how to create ideal conditions for it and all the nuances of care by reading this article.
Description of the plant and species

Spirea or, as it is often called, meadowsweet is an ornamental shrub of the Rosaceae family. The natural conditions for its growth are steppe, forest-steppe, semi-desert areas of most of the northern hemisphere.
Her flowers are small, but due to their large number and large inflorescences in which they are collected, the blooming spirea looks luxurious. Flowers of various colors can be collected in inflorescences in the form of a panicle, an ear. Leaves, depending on the variety, are of various shapes: round, lanceolate, colors vary from yellowish green to bright green, small-leaved and large-leaved varieties are found. Therefore, it is not surprising that different varieties of spirea differ significantly from each other.
The meadowsweet varieties are conventionally divided into two main groups: spring-flowering and summer-flowering.
Spring blooming
Plants of this group are characterized by flowering in late spring and early summer. At the same time, the buds are formed in the fall, so in the spring it is absolutely impossible to cut the bushes. From this group, the following varieties are especially attractive, shown in the photo:
Spirea is gray.A characteristic difference of this variety is gray foliage. Snow-white flowers form a shield-like inflorescence. A bush growing up to 2 meters in height with soft branches looks great both growing alone and in group plantings.

Thunberg.The height of the bush is up to 2 meters, in natural conditions it grows in the mountainous regions of China, Japan, Korea. Long bloom - from May to late June. White flowers on drooping branches are collected in umbellate inflorescences.

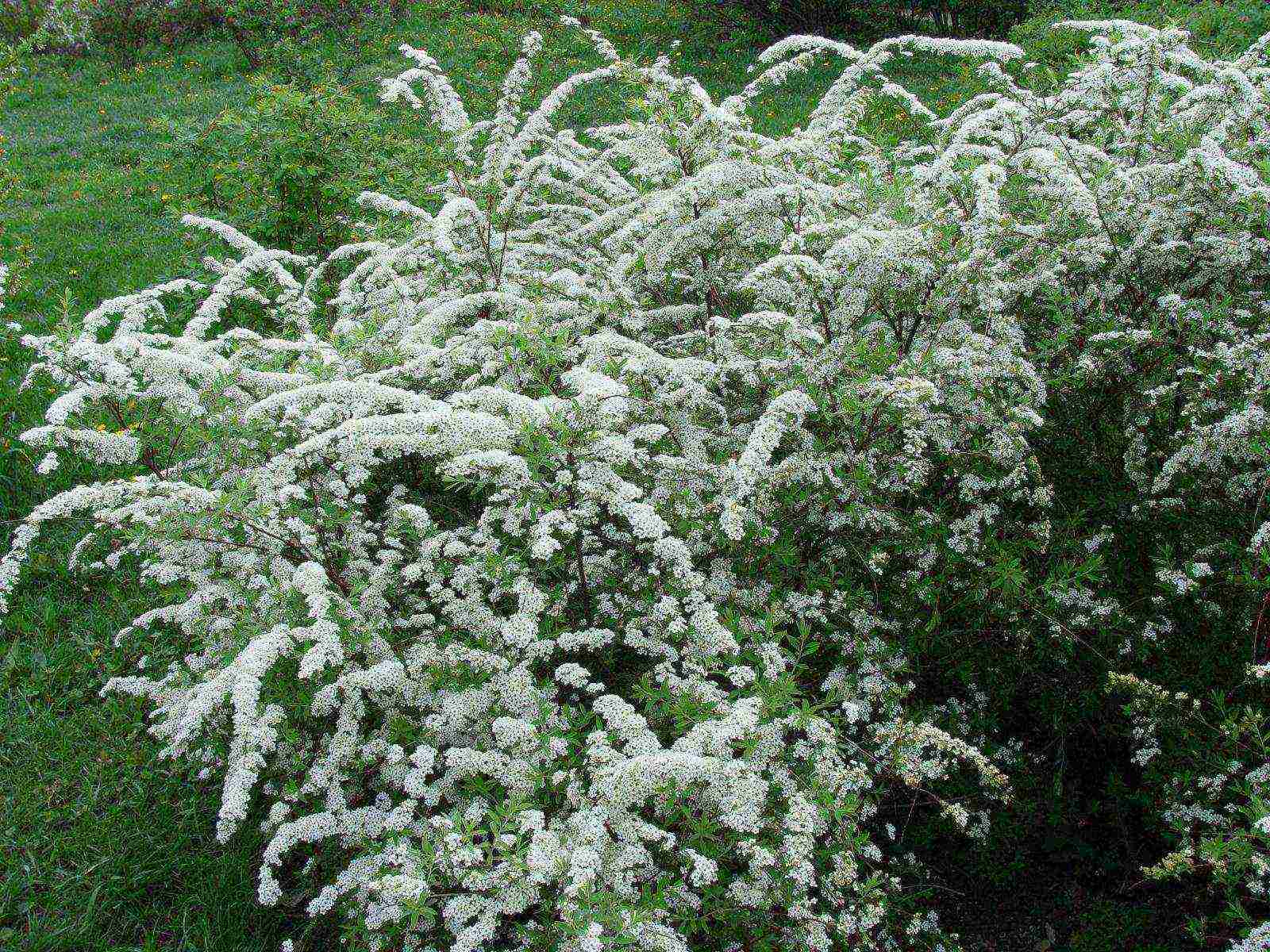
Arguta.This variety is so lush that the foliage is not visible due to the white lace of the flowers. Due to the spreading structure of the plant, shoots do not need pruning, they grow up to 2m in an arched shape. A short flowering period from the end of April, lasts about 20 days.

Summer blooming
Varieties of this group form buds in the spring only on young shoots, which is why the plant needs pruning of last year's already faded branches. Flowering begins later in the summer.
This group includes:
Japanese spirea.The height of the shrub is no more than 1.5 meters. The peculiarity of Japanese spirea is in oblong bright green leaves, on the underside of a bluish tint, which later become reddish.Long flowering period (all summer), pink flowers are collected in shield-like inflorescences.

White spirea. Sprawling shrub about 1.5 m high with long pointed leaves. Flowering begins in July.

Billard. With pink flowers and wide leaves, it blooms from mid-summer until frost. It grows in height up to 2 meters. Due to its cold resistance, it is successfully grown in the northern regions.

Planting spirea
The condition for obtaining a beautifully blooming spirea is compliance with the basic rules of cultivation, including planting.
The optimal planting time is September.
In spring, only summer-flowering species are planted, it is recommended to plant before bud break. Before buying a seedling, you need to make sure of the suitability of the planting material: the root system should not be overdried, and the shoots should be flexible, have formed buds.
It is necessary to prepare the seedling. Overgrown roots should be shortened, and, conversely, with dried roots or if they have damage, the shoots are shortened. It is useful to soak overdried roots in water for a while before planting.
For spirea, leafy or soddy soil is optimal. To prepare the soil, sand and peat are added to the sod land in a ratio of 2: 1: 1. The planting hole must be provided with good drainage, since the spirea does not tolerate stagnant water well.
It is advisable to plant in rainy or cloudy weather. Planting depth - 0.5 meters, not less. The planting hole is filled with soil, and the seedling is planted in such a way that its root collar is at surface level. After planting, water should be abundantly at the rate of 15-20 liters per bush.
Care rules
Like all other plants, the relatively unpretentious spirea needs certain growing conditions.
Watering
Watering required abundant and frequent, especially for young plantings and flowering in summer. Well protects against moisture evaporation and the formation of a crust on the surface of mulching. Watering rate: 25-30 liters of water per plant up to 3 times a month.
Top dressing
Top dressing with fertilizers stimulates the growth of spirea and the formation of new shoots. Mineral complexes are introduced into the root circle immediately after pruning. In the middle of summer, organic mullein feeding is beneficial.
To provide the root system with oxygen, it is important to loosen the soil.
Pest control
The most common pests are aphids and spider mites. The fight against them should be started immediately after detection, since due to the spreading of the spirea, delayed processing can be difficult. Treatment with complex insecticides is recommended.
Diseases
One of the advantages of spirea is resistance to many diseases. However, if the rules of care are violated, it can be struck by root rot, the main reasons for which are waterlogging of the soil, lack of drainage and the formation of stagnant moisture, heavy soil. For prevention, such phenomena should be avoided; in the event of a fungal infection, treatment with fungicides can save the plantings.
Pruning shoots
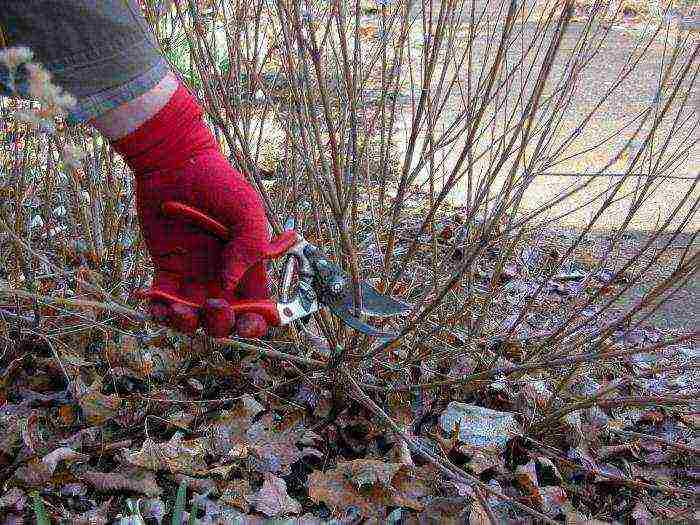

Pruning is done to prevent overgrowth and shape the plant.
Depending on the type of flowering, it is carried out in different ways.
In spring-flowering varieties of spirea, only the frozen tips are cut off. To update the spirea after 7-14 years, you can remove all old branches, leaving the stumps. A new bush is formed from the young growth. In the first year, 5-6 shoots are left on it, which grow rapidly. After a year, weak and old branches are cut again.
Summer flowering species need annual pruning in the spring. In this case, the branch is cut to large buds, and it is advisable to remove the weakened branches completely. After 4 years of growing season, it is recommended to prune the branches annually, leaving them up to 30 cm from the ground.
Reproduction
Layers
The most effective way is propagation by layering, which is also the simplest. During the blooming of the leaves, the shoot is bent to the ground and sprinkled. With regular watering in the fall, a young seedling with a sufficiently strong root system will form from it to separate from the main bush and plant in another place.
If you want to get more than one layer from one branch, you should pinch its top, bend the entire shoot to the ground and sprinkle it. With this method, by the spring of next year, several young plants suitable for transplantation will be formed from the grown lateral shoots.
Cuttings

Cutting is a rather laborious process. Cuttings are cut at the end of flowering and planted in a peat-sand mixture and placed in a greenhouse. For planting in open ground, the cuttings will be ready for the next one only in a year.
Seeds

Seed propagation is rarely used. Sowing is carried out in the spring under the film. After their germination, the film is removed, and then grown as a normal seedling until the end of summer. Then the seedlings are transplanted into open ground. In the winter cold, young seedlings must be covered with foliage, spruce branches.
Seed propagation is rarely used due to low seed germination and a long waiting period for flowers (after 3-4 years).
Good day to all readers!
Today we'll talk about planting a spirea, further care, reproduction and many different varieties.
You rarely find such a variety of species and varieties as in spirea! Among them there are giants up to 2.5 m in height, there are also dwarfs less than 20 cm in height. Branches are creeping, they can be recumbent or spread out, there are also erect branches.
The bark on them can be from light to dark brown. On woody shoots, the bark begins to flake off.
The leaves are incredibly diverse, the shape depends on the species or variety - they are all petioled, but they can be lanceolate, they are round, and in some varieties they have three or five lobes.
The flowers are small, from snowy white to crimson, in large numbers collected in inflorescences. All spireas bloom in spring or summer. In some varieties, these are panicles, in others, scutes or pyramids, but spike-shaped inflorescences are also found. In different spirales, the inflorescences are located in different ways: they can be located only at the ends of the shoots, they can be along the entire length of the branch. And now more about
Planting and caring for spireas
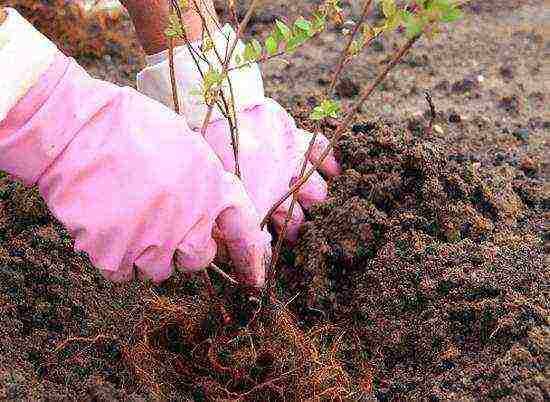
Selection and preparation of a seedling
Planting spirea, both spring and summer blooming, can be done in spring and autumn. In a garden center or nursery of ornamental crops, it is better to choose a seedling with a closed root system or with a lump of earth.
The seedling should be young, compact and free of leaves. Spireas, on which leaves have appeared, do not tolerate transplantation well.
You should not buy overgrown bushes with very branched shoots. Not the best choice - plants in which roots have sprouted from the drainage hole. On the one hand, this is a confirmation that the seedling has been growing in this pot for a long time, and not planted in it an hour before the sale, on the other hand, the earthen lump is all entwined with roots and is already cramped in a closed volume.
In plants with an open root system, it is necessary to check the quality of the root lobes. The roots should be moist, elastic, free of broken off and blackened on the cut. There should be no dry and brittle roots. Useful when the open root system is covered with a mixture of clay, manure, and a root stimulant.
The branches should be lively, flexible, with green bark, healthy buds. Small numbers of second-order branches are welcome.
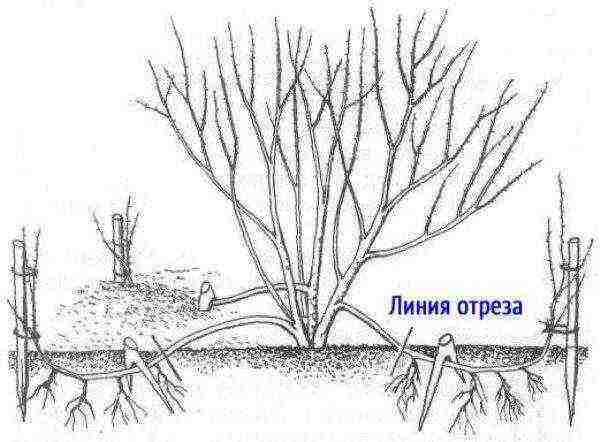
 Reproduction of spirea by dividing the bush. Landing of the parcels.
Reproduction of spirea by dividing the bush. Landing of the parcels.
Selecting and preparing a landing site
Like every plant, the spirea has its own characteristics of choosing a place and method of planting.
- All spireas can grow both in a sunny place and with some shading. In partial shade, the bushes grow better, but form fewer flowers.At the same time, on spireas, in a slight shade, flower baskets are brighter in color and retain their decorative effect for a longer time.
- The soil is preferable permeable, moderately moist. To improve the composition of the garden soil, leafy or sod soil can be added to its composition. Heavy clayey soils are loosened with peat and sand. Spirea Billard and its hybrids do not tolerate calcareous soils.
- When planting spireas, they must create a drainage layer of expanded clay or broken brick.
- A pit for planting is prepared one third larger than the earthen clod of the seedling, at least 0.5 m deep, while the root collar should be at the same level as in the nursery.
- It is better to plant in cloudy weather, during the rain, the survival rate of plants is higher.
- Suitable neighbors for spirea bushes are conifers.

Planting spirea in spring
Spireas are planted in spring, blooming in summer. You need to hurry up with planting and have time to plant the bushes before bud break.
At any time of planting, the pit is prepared in the same way: the walls must be vertical and dig it 2-4 days before planting. The drainage layer should be at least 15, and preferably 20 cm.
- When planting, you need to shorten the aerial part and cut off the very long and dried roots.
- The soil removed from the planting pit is mixed with fertilizer, if necessary with peat or sand.
- At the bottom of the pit, a mound of earth is arranged, a seedling is placed on it.
- With an open root system, all the roots are straightened, directed in different directions and sprinkled with earth.
- Having covered the roots by half, a bucket of water is poured into the pit.
- The pit is completely filled up.
- The soil around the bush is compacted and the seedling is slightly pulled up so that the roots are straightened.
- An earthen rampart is formed around the bush, watered and sprinkled with mulching material to retain moisture.

Planting spirea in the fall
In the fall, spireas of any flowering period are planted and transplanted. It is important to complete this process before the end of the leaf fall. At this time, you can propagate the bushes by dividing the bush. The age of the spirea should not exceed 3-4 years. In older shrubs, the root system is very large, it is difficult to remove it from the ground and divide it.
The bush to be divided is dug out, leaving a clod of earth slightly larger than the projection of the crown. Chopped off some of the roots will not harm the bush. The bush extracted from the ground is lowered into a container of water. The damp earth will remain at the bottom, the root system will be fully visible. It is allowed to remove old soil from the roots with running water.
It is better to divide the bush with a sharp pruner. On each plot we leave a branched lobe of roots and two or three one or two summer shoots. Then they are planted as in spring: a drainage layer is created, an earthen mound is poured, roots are spread on it, covered with soil and watered as the roots are buried, an irrigation hole is created and the surface is mulched.
 Japanese spirea
Japanese spirea
Care: watering, fertilizing, pruning, sheltering
All spireas belong to plants from the "Self-grows" series. Caring for it is minimal: moderate watering, loosening, weeding, top dressing, pruning.
The root system of spirits is shallow, hence the need to mulch the soil, watering at least twice a month. 1.5 buckets of water are poured into each watering under the bush.
It is imperative to loosen the soil and remove weeds. As a top dressing, a complex fertilizer or mullein infusion with the addition of superphosphate (10 g per bucket of infusion) is used. The most important top dressing is after pruning and before flowering.
Spireas are almost not damaged by pests and diseases. Aphids and spider mites are found on them. Pests often settle on young shoots. Aphids not only suck out the juices, weakening the plants, but a sooty fungus settles on the secretions of aphids, which impairs the appearance. You can fight them with any chemical means or herbal decoctions. With a small number of pests, they can be washed off with a stream of water. But damage from pests is often insignificant and does not affect the decorative effect of the bushes. 
Spirea pruning
Sooner or later, spirea bushes grow to such a size that they need to be trimmed. How to do it correctly without losing decorativeness?
Flowers on spring-flowering varieties are located along the entire length of the shoot, which means that only the tips frozen in winter are removed from them. Old shoots are removed once every 7-14 years. Such branches are cut at ground level, and 5-6 of the young shoots that have grown are left for future flowering. After another year or two, the next obsolete shoots are removed. Thus, the entire bush is rejuvenated. Sanitary pruning can be done throughout the season.
Spireas blooming in summer are trimmed in early spring. The pruned shoot is shortened to large buds, small and inconveniently located shoots are removed completely. After strong pruning, new, strong branches grow. Aging shoots must be removed regularly, otherwise the bush will not have the strength to form renewal shoots. Bushes aged 4 and older can be pruned up to 30 cm from the ground annually. If such pruning does not rejuvenate the bush and strong shoots do not appear on it, then the bush must be divided or replaced. The average life span of a spirea bush is 15-20 years.
 Spirea gray Grefsheim
Spirea gray Grefsheim
Reproduction of spirea
Spire breeding methods - seeds, cuttings, dividing the bush and layering. Let's consider each of them.
Seeds
The most inconvenient breeding method. In this way, non-hybrid species are propagated. The varietal qualities of seedlings are not transmitted through seeds. In addition, laborious seed stratification is required to increase germination.
Cuttings
Produces good results. Correctly and timely harvested cuttings in 70% of cases are rooted without the use of root formers. Cuttings from bushes that bloom in spring are harvested in early June, summer-flowering spireas are cut in late June-July. Lignified cuttings of all spirits take root in early - mid-autumn.
For rooting, a strong one-year shoot is taken, it is divided into cuttings with 5-6 buds. The lower 2-3 leaves are removed along with the cuttings, half of the leaf is cut off on the rest. A good result is obtained by soaking the cuttings for several hours in a solution of epin (1 ml of epin is dissolved in 2 liters of water). The lower cut of the cutting can be treated with a root. 
Prepared cuttings at an angle of 30-45 degrees are planted in a moist substrate. It can be sand, perlite, vermiculite, nutrient soil. It is very convenient to cover the planted cuttings with plastic bottles, which have cut off the bottom. In such an improvised greenhouse, a more uniform temperature is maintained (laminated plastic, transparent) and the humidity can be flexibly regulated.
First, the plugs can be screwed on and a complete tightness can be arranged, then, after removing the plug, we arrange airing. Having arranged a shade over the plantings, it is not necessary to spray the cuttings under plastic caps several times a day; it is enough to periodically water the soil around the cuttings.
Before the onset of stable frosts, the cuttings, together with the bottles, are covered with insulation - leaves, tops, branches. In winter, they are insulated with snow. In the spring, the shelter is removed, and when shoots appear, young bushes can be transferred to a permanent place.
Dividing the bush
It is better to divide the spirea bush in the fall. Carefully dig out the bush to be divided. It is better to shake the earth from the roots so that you can better see where the bush can be divided. Each divided bush should have 2-3 strong shoots and sufficient root lobe. The divided bush is planted in a new place, taking into account the planting depth in the old place. Drainage device, creation of an irrigation hole and watering are required.
Reproduction by layering
In the spring, a strong one-year-old shoot is bent to the ground (you can cut the bark at the point of contact with the ground), placed in a prepared hole, pinned to the ground and covered with a nutrient mixture. Long shoots can be dug in several places - you get several layers.By autumn, roots are formed on the damaged area and the seedling can be separated. 
Shelter spirea for the winter
Although the fibrous root system is located close to the surface, low and high temperatures, most of the spirales are easily tolerated. Some types of spiraea, such as gray, medium, low, three-lobed, oak-leaved, are not damaged even up to -50C, on spiraea Bumald, birch-leaved, Emilia, densely flowered, white, sharp-toothed in such frosts, it is possible freezing of annual shoots.
It is possible to secure the planted spireas in Central Russia if the shoots are tied into one bunch and, bending to the ground, covered with fallen leaves with a layer of about 15 cm, and covered with cut branches on top, protecting from leaf blowing and better snow retention. Bushes planted in autumn in any region are better covered for the winter. To do this, you can use fallen leaves, tops of vegetable plants, cut branches.
Types and varieties
The whole variety of spirits is divided into two large groups blooming in spring and summer. Spring blooming spireas create fountains of white flowers and fill the garden with a cloud of white flowers. The leaves of some types of spirits in the fall paint shrubs in various colors from yellow to purple-red.
The spiraea flowering season opens with gray spirea. It is a voluminous shrub with arched drooping branches, densely covered with small white flowers. The most famous and popular variety of sulfur spirea is "Grefsheim".
 Spirea gray Grefsheim
Spirea gray Grefsheim
Behind her, Thunberg's spirea blooms. Its bush grows no higher than 1m. A distinctive feature of the species is that the leaves remain on it for almost a whole year.
 Spirea Thunberg
Spirea Thunberg
The flowering of the Thunberg spirea is supported by the sharp-toothed spirea. Its white flowers are collected in medium-sized inflorescences that bloom on gracefully curved branches.
 Spirea sharp-toothed or spirea Argut
Spirea sharp-toothed or spirea Argut
Spirea Wangutta blooms next. Shrubs up to 2m in height bloom profusely in May-June.
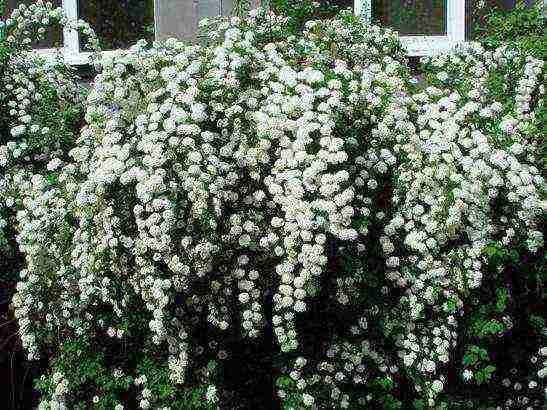 Spirea Wangutta
Spirea Wangutta
In May-July, the Nippon spirea blooms. Its bushes have erect shoots slightly drooping in the upper part.
 Spirea nippon
Spirea nippon
The most abundant flowering spirea is Plena. Blooms in May-June, in autumn the bush turns purple-red.
 Spiraea lily
Spiraea lily
A few more photos of the beauties of spirea!
 Spirea Japanese "Little Princess"
Spirea Japanese "Little Princess"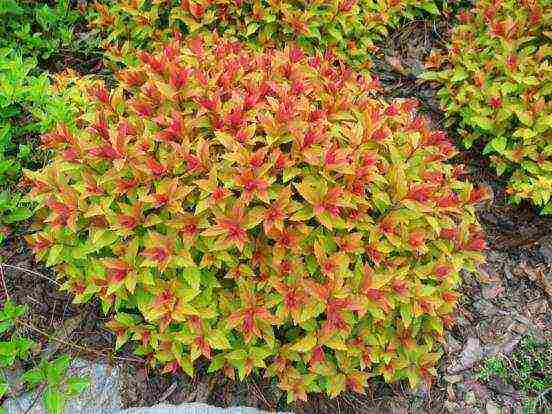 Spirey Bumald "Gold Flame"
Spirey Bumald "Gold Flame" Spirea Billard
Spirea Billard
Garden use and partners
The use of all spirits is very diverse. These shrubs quickly form living flowering hedges that easily fill large areas. It is successful to combine spireas in individual plantings, and in combinations with other trees or shrubs, and to create mixed hedges. The eye-catching shape of the spirea bushes and slender shoots create an attractive contrast to the dark-colored neighbors.
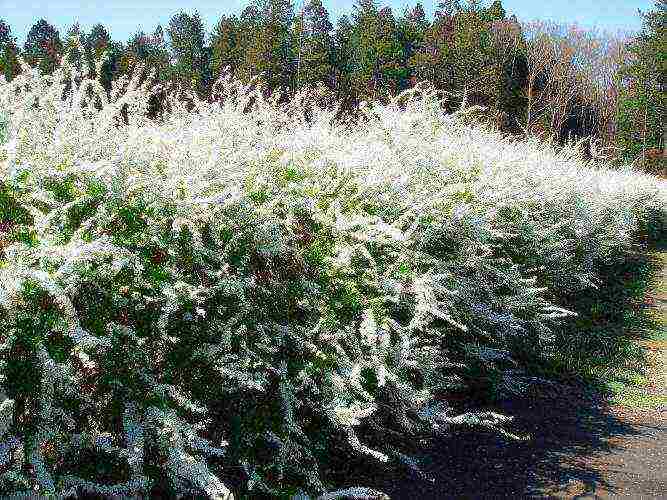
Spire bushes successfully create bright, flowering, hedges. They cut their hair easily. Especially beautiful are uncut shrubs of weeping shape, strewn with boiling white flowers.
 Spirea hedge
Spirea hedge
Solitary spireas are good as a backdrop for perennial herbaceous or bulbous plants.
Summer blooming spireas will fill the voids between the conifers well, where they will create bright accents throughout the season.
Low-growing, dwarf spirea varieties form a unique colored carpet when planted on a sunlit slope. Such low bushes will adorn rockeries, rocky gardens, alpine slides.
Taller hybrids are suitable for framing, on the edge of the lawn, in the foreground of living partitions, in a flower bed with herbaceous perennials.
The shining white flowers of the spirea make it a good partner for bulbs, bushes and perennials that bloom in early spring.
A good solution for a bright spring flower bed is yellow daffodils and red tulips against the backdrop of undersized spirea.
White jets of "fountains" of Wangutta spirea will add elegance and add energy to plantings of herbaceous perennials blooming in late spring - bearded irises or peonies.
Spring-flowering spireas are organically combined in bright hedges, they are successfully combined with lovely and red weigels planted nearby, Golden rain bean or purple-leaved hazel will create a suitable background.
If you plant a spirea, an ordinary viburnum and a chubushnik next to it, you get a "white dream"
In July, when most of the shrubs have already faded, summer-flowering spireas begin to bloom. They are planted in the foreground of mixed hedges, against the background of conifers, or as separate shrubs.
The bright red flowers of Bumald's spirea will become even brighter if planted against a background of white or yellow cinquefoil shrub. Spiraea and St. John's wort are successfully combined with each other, if they are picked up at the same height. It is better to combine large groups of these colors.
David's Buddley is good to use as a background.
Having correctly selected the varieties and varieties of spirea, its flowering can be enjoyed from spring to mid-summer.
Video about the reproduction of spirea
I wish everyone to enjoy the flowering of spirea in the garden, planting and care is now no secret for you.
Best regards, Sophia Guseva.
Other interesting articles:
- Dogwood - planting and care
- Heather - planting, reproduction, care
- Tulips - planting and care
- Irises - planting and care
- Lilies - planting and care

Yulia Krivenko
The spirea bush is attractive not only during flowering. Its beautifully curved shoots adorn the garden throughout the season.
Planting and growing spirea is easy, which attracts gardeners.
Features of planting spirea
Like any plant, spirea has its own growing characteristics. For full flowering, they must be taken into account:
• The shrub prefers a soil consisting of deciduous humus and sod land. Part of the sand is added to two parts of the resulting soil to loosen the soil;
• Spiraea is grown only in well-drained soil, since the shrub does not tolerate stagnant moisture, often suffers from root rot or soaks in winter;
• The root collar of the bush is not buried so that it does not rot. Ideally, the root collar should be at ground level;
• Planting shrubs is carried out only in cloudy weather, and preferably in the rain. The optimal planting time is the second half of autumn, somewhere in the middle of September. Some varieties of spirea are planted in early spring.
Planting spirea in the spring is carried out early, until the buds have blossomed. At this time, only summer-flowering hybrids can be planted. When buying seedlings, pay attention to the condition of the root system and the appearance of the plant. In well-developed healthy seedlings, the roots should be lively, not overdried, and the branches should be flexible with good buds. If the seedlings look suspicious, then it is better to refuse to purchase. What to do if the planting material has been stored for a long time in unsuitable conditions? It needs to be brought into “human9raquo; view.
Long and overgrown roots are shortened, which facilitates planting and increases the survival rate of seedlings. If the root system is dry or damaged, then the shoots should be shortened, and the roots should be soaked in water before planting. To do this, the seedling is soaked in a bucket of water for 24 hours.
Planting spirea: site selection and planting pit depth
Spirea is an unpretentious shrub, but it will not bloom fully everywhere. The main condition for growing spirea is full lighting during the day. Choose a sunny area protected from cold winds. Please note that the shrub grows quickly, gives a lot of root growth, so it needs enough space. If there is no way to allocate a lot of space, then the root growth is removed.
The planting hole on the site is prepared in advance. Its depth should be at least 60-70 cm, which is one third larger than the size of the root system. At the bottom of the pit, drainage from scrap materials is laid with a layer of 15-20 cm.Some of the onions are covered with fertile soil mixed with sand, peat and leaf humus. During planting of seedlings, a mound is formed, a plant is placed on it, the roots are straightened on the sides. The hole is filled to the top with fertile soil, slightly compacting the earth, and watered abundantly. The root zone is well mulched with peat or humus.
Important! The root collar must be placed at soil level.
The autumn planting of spirea is carried out during the division of the bush. It is best to complete the procedure before the end of the leaf fall. For reproduction, still young bushes are used, the age of which is no more than 5 years. Adult specimens do not tolerate division well.
Since the shrub grows rather quickly, the distance between the plants must be taken into account. To create a hedge between seedlings, leave up to 70 cm.When planting spireas in compositions with thuja and other junipers, up to 1 m is left around the plant, which will greatly facilitate the care of the shrub.
Spirea care secrets
Shrub maintenance is a pleasure for lazy gardeners, but some of the features will be useful to learn.
Spirea belongs to drought-resistant plants, therefore it is extremely rarely watered. In rainy weather, the shrub can get by with natural precipitation. In the dry season, it is enough to water abundantly with spirea and mulch the soil several times a season.
Around young seedlings, the soil must be loosened regularly. In order for the spirea to please with flowering, it needs to be fed with a full-fledged mineral fertilizer. Top dressing is done twice a season: immediately after pruning and in the second half of summer.
How to trim spirea
The shrub needs a haircut, thereby forming a beautiful crown. A haircut is carried out taking into account all the features of the bush.
• In early flowering varieties, only the tops of the shoots that are frozen in winter are cut off. It is not necessary to shorten them strongly, since the spirea blooms on last year's shoots. After 7-8 years of cultivation, all shoots are pruned at ground level to renew the bush.
• Summer-flowering spireas are pruned in early spring to their strongest bud. The more pruning, the more powerfully the bush forms. Every 5 years, shoots are cut to a height of 25-30 cm. If, after such pruning, the shrub starts up weak growth, then it must be completely replaced. Duration of cultivation in one place is 15 years.
In addition, in the spring and summer, as necessary, they carry out a sanitary cleaning of the bush, cutting out all twisted, weak and dry branches.
Photo of the correct trimming of the spirea
Pest control
When caring for spirea, one must not forget about diseases and pests that can annoy the shrub. In most cases, spiraea is resistant to diseases and pests, but sometimes it is attacked by aphids and spider mites. To quickly get rid of pests, insecticide spraying is used.
Horse rot is more common among diseases. Follow the rules for growing shrubs, choose a suitable planting site and be sure to drain the soil.
How to propagate spirea
If you decide to get a spirea, then it is not at all necessary to buy seedlings. You can grow planting material yourself by taking a stalk from a neighbor in the country. In addition, spirea multiplies easily and quickly by dividing the bush and layering. Let's dwell on each method in more detail.
The division of the bush is carried out in autumn or early spring, depending on the perennial variety. Planting is carried out in the usual way, preparing the soil and planting hole.
Spirea cuttings are carried out throughout the season. Early-flowering species are cut in the first half of summer, a little later, planting material is cut from late-flowering varieties. The survival rate of cuttings is very high, even without the use of special preparations, which cannot but please gardeners.
For cuttings, one-year straight shoots are chosen, from which the lower leaves are removed. The upper leaves are cut by half. The lower cut of the cutting is processed in the root or simply dipped in crushed ash.Prepared cuttings are planted at an angle of 45 degrees in a greenhouse. Caring for the cuttings of spirea is simple, it is enough to water the plants at least 1 time in 3 days. With the onset of frost, the plants are covered with dry foliage, an old wooden box is additionally installed on top. In this form, the cuttings overwinter. In the spring, the shoots are transplanted to a permanent place.
Photo of ready-made spirea cuttings for planting
It is easy to propagate the spirea by layering. In the fall, a semi-lignified shoot is instilled, and in the spring the seedling is transferred to a permanent place. By that time, it should have formed its own root system.
Important! Spirea seeds are propagated extremely rarely, since this is a rather complicated method. In addition, plants rarely retain their parental qualities.
As you can see, spirea is a perennial flowering shrub for busy gardeners. Planting does not take much time, and plant care is not difficult.
However, despite the winter hardiness of the shrub, with the arrival of autumn it is better to cover it with dry leaves. This will save the perennial from freezing in snowless winters.
Portal editor-in-chief: Ekaterina DanilovaEmail: Editorial office phone: +7 (926) 927 28 54Editorial office address: st. Suschevskaya, 21Information about advertising placement

Spiraea is by far the most popular shrub. Many varieties of this plant can bloom from spring to late autumn. This plant is very often used in the decorative sphere, because they have abundant flowering and even a small area can be turned into real works of art. But you need to know how to plant and care for a spirea bush in order to grow a truly beautiful and healthy plant.
Types and varieties
Spirea or in another way meadowsweet refers to the genus of ornamental deciduous shrubs of the Rosaceae family. From the Greek name for the shrub, it translates as bend. And he really confirms this by the name by the fact that he has a special flexibility of shoots. Its main quality is considered unpretentiousness, so many summer residents plant it on their site with pleasure. There are about 100 species of spirea bushes in the world. All of them grow in steppe, semi-desert and forest-steppe.
Spireas can be planted and cared for in the Urals, although many species can freeze there. Plants of this kind can be dwarf and be no more than 15 centimeters, as well as very large and grow up to 2.5 meters. As for the root system, it is shallow and fibrous. Depending on the type, the branches can be completely different: creeping or erect, recumbent or outstretched, light or dark. The bark has its own peculiarity, it can peel off longitudinally.
The leaves are most often petiolate, lanceolate or rounded. The flowers of the bush are small, but there are always a lot of them. And thus they form different inflorescences, for example, spike-shaped, pyramidal, paniculate or corymbose shield. And these flowers can have different shades, ranging from snow-white to crimson. In each type of spirea, the inflorescences can be located in different ways: along the entire shoot, on the upper part, at the ends of the branches.
Today, the spirea shrub is used as a decoration in order to build a hedge. If the summer resident chooses dwarf varieties, then his goal is to create a living carpet. The spirea shrub also looks perfect as a solitary plant. Some varieties are used more often, others less often, but they are all divided into:
Spring-flowering spirea blooms very early and only white shades are characteristic of this species. The following types are popular in the world:
- Spirea gray... She is a hybrid of St. John's wort and whitish-gray spirea. Truly, the flowers of this plant are white, and it got its name from the gray-green leaves. The shrub can be 180 centimeters high. Its branches are drooping, flowering is thyroid and flowers are located along the entire length of the shoot.
It begins to bloom from mid-May to the second half of June.The most popular variety of this type is "Grefsheim" spirea. In height from 1.5 to 2 meters. The branches are as they should be in this species. Snow-white, double flowers, which are collected in umbrellas. It blooms for about 45 days, but only in the second year of life.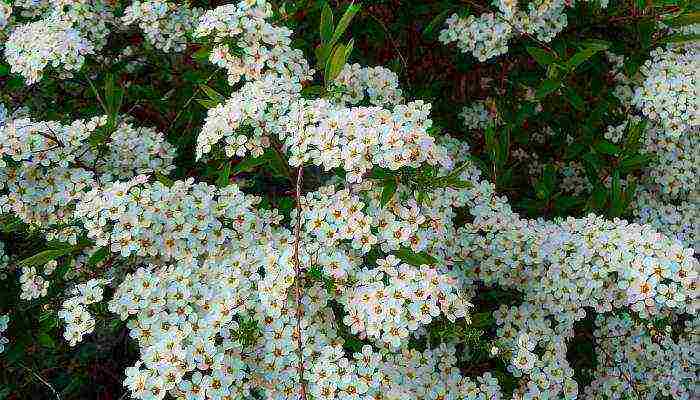
Spirea Wangutta... It turned out as a result of crossing the Cantonese and three-bladed spirea. This is a huge two-meter bush that has drooping branches, jagged dark green leaves that turn red-orange in autumn. The flowers have a diameter of 0.6 centimeters, they are white and are located along the entire shoot. Blooms in the second half of June, sometimes it can bloom again in August.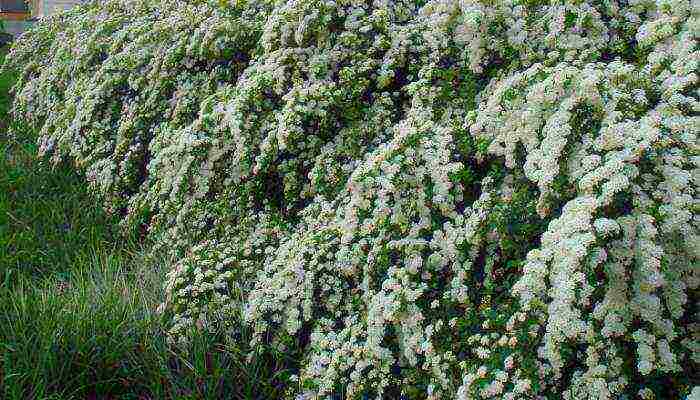 Spirea of Nillon... This type can often be found on the island of Honshu. The growth of the shrub is 2 meters, the crown is spherical, dense, and the branches are horizontal. Leaves can be up to 4.5 centimeters long. Flowering lasts only three weeks. This usually lasts from the beginning of June. Yellow-green flowers up to 1 centimeter in diameter. In the bud itself, the flowers are purple.
Spirea of Nillon... This type can often be found on the island of Honshu. The growth of the shrub is 2 meters, the crown is spherical, dense, and the branches are horizontal. Leaves can be up to 4.5 centimeters long. Flowering lasts only three weeks. This usually lasts from the beginning of June. Yellow-green flowers up to 1 centimeter in diameter. In the bud itself, the flowers are purple.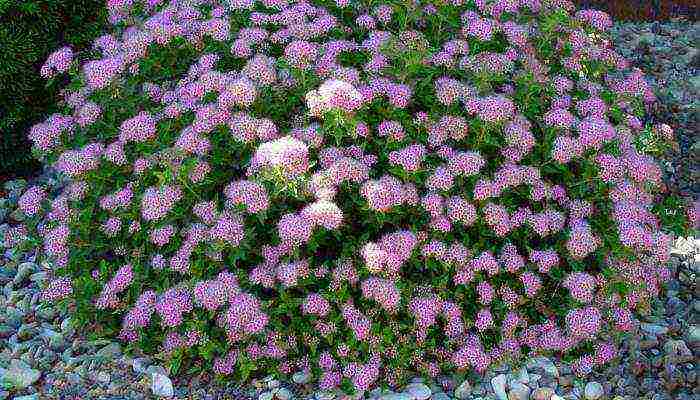 Spirea Argut... It blooms in the same way as the Nillon spirea for three weeks, but only it all starts from the end of May. This species is the earliest. The bush reaches 1.5-2 meters in height. It has a very beautiful shape, as it resembles a foamy waterfall, which consists of numerous small fragrant flowers, which are also distributed along the entire length of the branches.
Spirea Argut... It blooms in the same way as the Nillon spirea for three weeks, but only it all starts from the end of May. This species is the earliest. The bush reaches 1.5-2 meters in height. It has a very beautiful shape, as it resembles a foamy waterfall, which consists of numerous small fragrant flowers, which are also distributed along the entire length of the branches.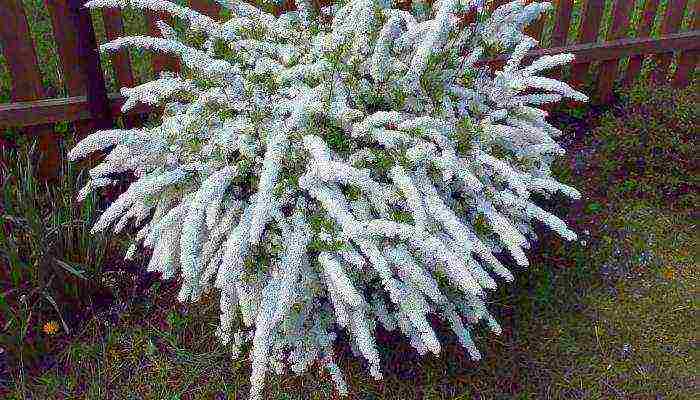
Summer-flowering species include those in which inflorescences are at the tips of young branches, and the old, last year's shoots gradually dry out. Usually these are varieties of Japanese spirea. The flowers are pink in most varieties, but can also be red or reddish pink. Here are all the popular types:
- Japanese spirea... A very beautiful shrub, which has tomentose-pubescent shoots as long as they are young, and then become naked. The height of the bush ranges from 1 meter to 1.5. The leaves are slightly oblong, glaucous below, and green above. When autumn comes, they turn yellow, red and even purple. This species blooms for no more than 45 days with red-pink flowers. All of them are collected in a small thyroid inflorescence and are located at the ends of the shoots. Here is a list of the most popular varieties: Little Princesses, Golden Princesses, Shirobana, Goldflame, Crisp.
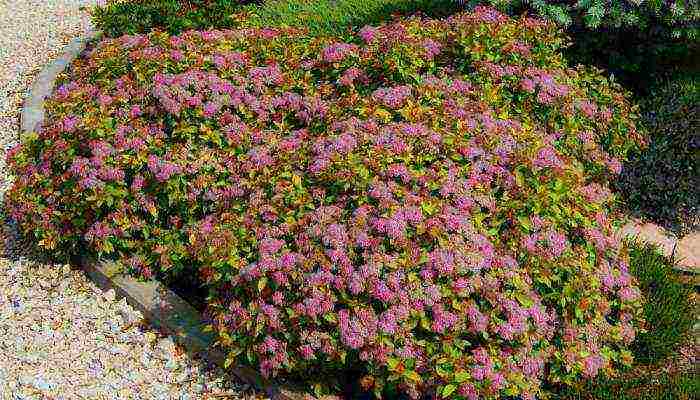

- Spirea Bumald... It appeared as a result of crossing the Japanese and white-flowered spirea. This is a low-growing shrub, as its height is from 50 to 80 centimeters. The branches are erect, the leaves are green in summer and red and yellow in autumn. Flowering lasts approximately two months starting in July. As for the tones, it can be either pale pink or dark pink. One of the leading varieties is Bumald's Spirea "Goldflame". Initially, while the flower is young, the leaves on it are bronze-orange, then they gradually become yellow-golden, in the fall - copper-red. Such changes can only occur if the bush grows in the sun, in the shade the leaves remain green.
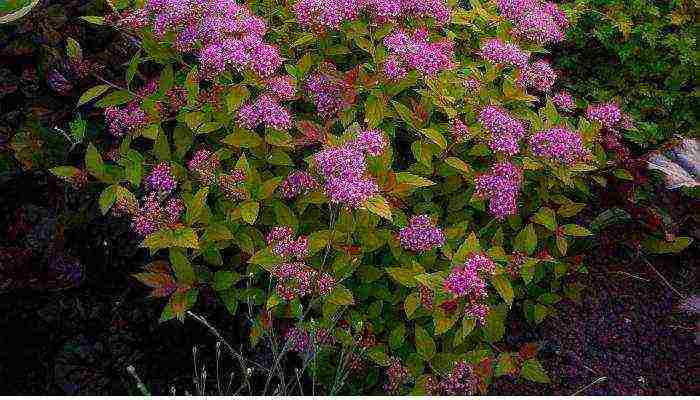

Planting in spring and autumn
When spring comes, a summer flowering plant is planted at such a time. The main requirement for planting is to be in time before the leaves bloom. You need to buy seedlings carefully. Remember that the roots should not be overdried.
The flexibility of the shoots of the plant should be checked. If they are flexible and have good kidneys, then you should definitely buy. It is also worth tidying up the planting material:
- If the roots are dry or damaged, then it is worth cutting off the branches;
- The roots have grown greatly, respectively, they need to be shortened;
- During storage, the root system has dried out, then you need to pour it with water or lower it for a while in a bucket of water and only then plant it.
The spirea shrub is an unpretentious plant, but it is worth knowing a few secrets that will help if you want to have abundant and long flowering. First you need to choose a place. The site should be sunny and fertile soil.Then you need to pay attention to the layout, since the spirea gives abundant root growth, which means it takes up more space and this should be taken into account.
On the site, it is necessary to make a pit with strictly vertical walls. It should be one third larger than the root system. After that, the pit should stand for 2-4 days. It is desirable that on the day of the appointed landing be cloudy, rainy weather. A small layer of drainage is poured into the bottom of the pit, which can be created using broken bricks.
If the soil is clay, then you can add a little leaf and sod land, as well as peat, sand and mix it all thoroughly. Pour the mixture into a hole and lower the roots there, spread them and cover them with earth to the root collar. After that, it is necessary to pour the spirea with a large bucket of water and mulch with peat.
Planting spirea in the fall usually takes place when the plant should be transplanted. Such a spirea transplant in the fall is carried out by dividing the bush, which is already 3-4 years old. If this is done at an older age, then it will be much more difficult, since the plant already has a huge amount of land around it. You will need to work hard before removing it and washing it.
The spirea should be dug out along with half of the crown. You may need to chop off some of the roots, but this will not affect the plant as a whole. After the procedure done, the extracted bush must be washed well. If the plant is young, then it is enough to lower the roots in a bucket of water and give time to the soil to turn off, and only then calmly rinse the roots under running water.
After that, it is worth cutting the bush with pruners into several parts, so that each part has a good root lobe and a couple of strong shoots. Remember to trim the cord roots. We dig a hole, make a mound in the middle and set the seedling on it, straighten the roots. Cover with earth on top and tamp. Sprinkle water over the seedling in a few steps.
How to care for a bush
Like all plants, the spirea also has basic care requirements. Here are the main ones that should never be forgotten:
- Sunny side, although many grow remarkably well in partial shade;
- Fertile, loose earth;
- Drainage;
- Mulching with peat immediately after the planting procedure.
But in addition to the above, there are a few more rules that need to be taken into account. For example, the spirea does not have a very deep root system, so it does not tolerate dry soil well. Therefore, it needs moderate watering. Usually, during the dry season, she needs 15 liters of water for each bush, and only twice a month. Otherwise, it will simply dry out.
Constant loosening and weeding of the soil is a must for spirea. Top dressing, as for many plants, should be mineral and carried out after pruning.
In the middle of summer, you can also fertilize with spirea, but already with a mullein solution. It is worth adding superphosphate to it about 10 grams per 10 liters of solution.
You cannot do without diseases and pests. Most often, spireas annoy aphids and spider mites. But they can be destroyed with karbofos and pyrimor. Spirea has no diseases, and pests cannot harm the beauty of the bush.
Those species that bloom early and bloom throughout the shoot only cut off the tips of the shoot. That is, those that froze over the winter. But after 7-14 years, all the old shoots will be cut off, so that later the 5 strongest ones will germinate and form a new young bush. After a few years old and weak shoots are removed again. The tips are removed only in the spring before the leaves begin to bloom. Sanitary pruning should be done either in the spring or summer.
Summer flowering shrubs are pruned in early spring. It is necessary to shorten to large buds, and remove small and weak ones. It is believed that the more you cut, the more powerful the shoots will grow. Do not forget to remove aging shoots in time.Once the shrub is four years old, it can be trimmed every year to a height of 30 centimeters. If even after such a procedure you grow weak shoots, then it is best to replace the bush with a new one. In the fall, pruning of spirea can also be carried out, but only if you decide to transplant the plant.
Reproduction
Reproduction of spirea can be by dividing the bush, seeds, cuttings and layering. If you decide to propagate the plant by seeds, then you will only need those species that are not hybrids, since spirea seeds do not retain varietal qualities. But the propagation of spirea by cuttings brings very good results. More than 70% of cuttings can take root without the use of a growth promoter. Early flowering species are propagated by cuttings in early June, and late flowering species - in the second half of June or already in early July.
For such reproduction, it is necessary to cut off the one-year straight shoot and cut it into pieces, so that each has 5 leaves. The lower leaves should be removed along with the petioles. The rest should be cut in half and left in the epin solution for half a day. The lower node is sprinkled with a stimulant and placed in a pot of wet sand at an angle of 30-45 degrees.
After that, the cuttings are covered with film or glass, put in the shade and sprayed with water several times a day. As soon as frost sets in, the cuttings should be planted in open ground and covered with leaves, and a box should be placed on top. This structure must be left until spring. The next year, the cuttings will sprout, which means that they can be planted in their permanent habitat.
Good day to all readers!
Today we'll talk about planting a spirea, further care, reproduction and many different varieties.
You rarely find such a variety of species and varieties as in spirea! Among them there are giants up to 2.5 m in height, there are also dwarfs less than 20 cm in height. Branches are creeping, they can be recumbent or spread out, there are also erect branches.
The bark on them can be from light to dark brown. On woody shoots, the bark begins to flake off.
The leaves are incredibly diverse, the shape depends on the species or variety - they are all petioled, but they can be lanceolate, they are round, and in some varieties they have three or five lobes.
The flowers are small, from snowy white to crimson, in large numbers collected in inflorescences. All spireas bloom in spring or summer. In some varieties, these are panicles, in others, scutes or pyramids, but spike-shaped inflorescences are also found. In different spirales, the inflorescences are located in different ways: they can be located only at the ends of the shoots, they can be along the entire length of the branch. And now more about
Planting and caring for spireas
Selection and preparation of a seedling
Planting spirea, both spring and summer blooming, can be done in spring and autumn. In a garden center or nursery of ornamental crops, it is better to choose a seedling with a closed root system or with a lump of earth.
The seedling should be young, compact and free of leaves. Spireas, on which leaves have appeared, do not tolerate transplantation well.
You should not buy overgrown bushes with very branched shoots. Not the best choice - plants in which roots have sprouted from the drainage hole. On the one hand, this is a confirmation that the seedling has been growing in this pot for a long time, and not planted in it an hour before the sale, on the other hand, the earthen lump is all entwined with roots and is already cramped in a closed volume.
In plants with an open root system, it is necessary to check the quality of the root lobes. The roots should be moist, elastic, free of broken off and blackened on the cut. There should be no dry and brittle roots. Useful when the open root system is covered with a mixture of clay, manure, and a root stimulant.
The branches should be lively, flexible, with green bark, healthy buds. Small numbers of second-order branches are welcome.

Reproduction of spirea by dividing the bush. Landing of the parcels.
Selecting and preparing a landing site
Like every plant, the spirea has its own characteristics of choosing a place and method of planting.
- All spireas can grow both in a sunny place and with some shading. In partial shade, the bushes grow better, but form fewer flowers. At the same time, on spireas, in a slight shade, flower baskets are brighter in color and retain their decorative effect for a longer time.
- The soil is preferable permeable, moderately moist. To improve the composition of the garden soil, leafy or sod soil can be added to its composition. Heavy clayey soils are loosened with peat and sand. Spirea Billard and its hybrids do not tolerate calcareous soils.
- When planting spireas, they must create a drainage layer of expanded clay or broken brick.
- A pit for planting is prepared one third larger than the earthen clod of the seedling, at least 0.5 m deep, while the root collar should be at the same level as in the nursery.
- It is better to plant in cloudy weather, during the rain, the survival rate of plants is higher.
- Suitable neighbors for spirea bushes are conifers.

Planting spirea in spring
Spireas are planted in spring, blooming in summer. You need to hurry up with planting and have time to plant the bushes before bud break.
At any time of planting, the pit is prepared in the same way: the walls must be vertical and dig it 2-4 days before planting. The drainage layer should be at least 15, and preferably 20 cm.
- When planting, you need to shorten the aerial part and cut off the very long and dried roots.
- The soil removed from the planting pit is mixed with fertilizer, if necessary with peat or sand.
- At the bottom of the pit, a mound of earth is arranged, a seedling is placed on it.
- With an open root system, all the roots are straightened, directed in different directions and sprinkled with earth.
- Having covered the roots by half, a bucket of water is poured into the pit.
- The pit is completely filled up.
- The soil around the bush is compacted and the seedling is slightly pulled up so that the roots are straightened.
- An earthen rampart is formed around the bush, watered and sprinkled with mulching material to retain moisture.

Planting spirea in the fall
In the fall, spireas of any flowering period are planted and transplanted. It is important to complete this process before the end of the leaf fall. At this time, you can propagate the bushes by dividing the bush. The age of the spirea should not exceed 3-4 years. In older shrubs, the root system is very large, it is difficult to remove it from the ground and divide it.
The bush to be divided is dug out, leaving a clod of earth slightly larger than the projection of the crown. Chopped off some of the roots will not harm the bush. The bush extracted from the ground is lowered into a container of water. The damp earth will remain at the bottom, the root system will be fully visible. It is allowed to remove old soil from the roots with running water.
It is better to divide the bush with a sharp pruner. On each plot we leave a branched lobe of roots and two or three one or two summer shoots. Then they are planted as in spring: a drainage layer is created, an earthen mound is poured, roots are spread on it, covered with soil and watered as the roots are buried, an irrigation hole is created and the surface is mulched.

Care: watering, fertilizing, pruning, sheltering
All spireas belong to plants from the "Self-grows" series. Caring for it is minimal: moderate watering, loosening, weeding, top dressing, pruning.
The root system of spirits is shallow, hence the need to mulch the soil, watering at least twice a month. 1.5 buckets of water are poured into each watering under the bush.
It is imperative to loosen the soil and remove weeds. As a top dressing, a complex fertilizer or mullein infusion with the addition of superphosphate (10 g per bucket of infusion) is used. The most important top dressing is after pruning and before flowering.
Spireas are almost not damaged by pests and diseases. Aphids and spider mites are found on them. Pests often settle on young shoots. Aphids not only suck out the juices, weakening the plants, but a sooty fungus settles on the secretions of aphids, which impairs the appearance.You can fight them with any chemical means or herbal decoctions. With a small number of pests, they can be washed off with a stream of water. But damage from pests is often insignificant and does not affect the decorative effect of the bushes. 
Spirea pruning
Sooner or later, spirea bushes grow to such a size that they need to be trimmed. How to do it correctly without losing decorativeness?
Flowers on spring-flowering varieties are located along the entire length of the shoot, which means that only the tips frozen in winter are removed from them. Old shoots are removed once every 7-14 years. Such branches are cut at ground level, and 5-6 of the young shoots that have grown are left for future flowering. After another year or two, the next obsolete shoots are removed. Thus, the entire bush is rejuvenated. Sanitary pruning can be done throughout the season.
Spireas blooming in summer are trimmed in early spring. The pruned shoot is shortened to large buds, small and inconveniently located shoots are removed completely. After strong pruning, new, strong branches grow. Aging shoots must be removed regularly, otherwise the bush will not have the strength to form renewal shoots. Bushes aged 4 and older can be pruned up to 30 cm from the ground annually. If such pruning does not rejuvenate the bush and strong shoots do not appear on it, then the bush must be divided or replaced. The average life span of a spirea bush is 15-20 years.

Spirea gray Grefsheim
Reproduction of spirea
Spire breeding methods - seeds, cuttings, dividing the bush and layering. Let's consider each of them.
The most inconvenient breeding method. In this way, non-hybrid species are propagated. Varietal qualities of seedlings are not transmitted through seeds. In addition, laborious seed stratification is required to increase germination.
Cuttings
Produces good results. Correctly and timely harvested cuttings in 70% of cases are rooted without the use of root formers. Cuttings from bushes that bloom in spring are harvested in early June, summer-flowering spireas are cut in late June-July. Lignified cuttings of all spirits take root in early - mid-autumn.
For rooting, a strong annual shoot is taken, it is divided into cuttings with 5-6 buds. The lower 2-3 leaves are removed along with the cuttings, half of the leaf is cut off on the rest. A good result is obtained by soaking the cuttings for several hours in a solution of epin (1 ml of epin is dissolved in 2 liters of water). The lower cut of the cutting can be treated with a root. 
Prepared cuttings at an angle of 30-45 degrees are planted in a moist substrate. It can be sand, perlite, vermiculite, nutrient soil. It is very convenient to cover the planted cuttings with plastic bottles, which have cut off the bottom. In such an improvised greenhouse, a more uniform temperature is maintained (laminated plastic, transparent) and the humidity can be flexibly regulated.
First, the plugs can be screwed on and a complete tightness can be arranged, then, after removing the plug, we arrange airing. Having arranged a shade over the plantings, it is not necessary to spray the cuttings under plastic caps several times a day; it is enough to periodically water the soil around the cuttings.
Before the onset of stable frosts, the cuttings, together with the bottles, are covered with insulation - leaves, tops, branches. In winter, they are insulated with snow. In the spring, the shelter is removed, and when shoots appear, young bushes can be transferred to a permanent place.
Dividing the bush
It is better to divide the spirea bush in the fall. Carefully dig out the bush to be divided. It is better to shake the earth from the roots so that you can better see where the bush can be divided. Each divided bush should have 2-3 strong shoots and a sufficient root lobe. The divided bush is planted in a new place, taking into account the planting depth in the old place. Drainage device, creation of an irrigation hole and watering are required.
Reproduction by layering
In the spring, a strong one-year shoot is bent to the ground (you can cut the bark at the point of contact with the ground), placed in a prepared hole, pinned to the ground and covered with a nutrient mixture. Long shoots can be dug in several places - you get several layers. By autumn, roots are formed on the damaged area and the seedling can be separated. 
Shelter spirea for the winter
Although the fibrous root system is located close to the surface, low and high temperatures, most of the spirales are easily tolerated. Some types of spiraea, such as gray, medium, low, three-lobed, oak-leaved, are not damaged even up to -50C, on spiraea of Bumald, birch-leaved, Emilia, densely flowered, white, sharp-toothed in such frosts, it is possible that annual shoots freeze.
It is possible to secure the planted spireas in Central Russia if the shoots are tied into one bunch and, bending to the ground, covered with fallen leaves with a layer of about 15 cm, and covered with cut branches on top, protecting from leaf blowing and better snow retention. Bushes planted in autumn in any region are better covered for the winter. To do this, you can use fallen leaves, tops of vegetable plants, cut branches.
Types and varieties
The whole variety of spirits is divided into two large groups blooming in spring and summer. Spring blooming spireas create fountains of white flowers and fill the garden with a cloud of white flowers. The leaves of some species of spirits in the fall paint shrubs in various colors from yellow to purple-red.
The spiraea flowering season opens with gray spirea. This is a voluminous shrub with arched drooping branches, densely covered with small white flowers. The most famous and popular variety of sulfur spirea is "Grefsheim".

Spirea gray Grefsheim
Behind her, Thunberg's spirea blooms. Its bush grows no higher than 1m. A distinctive feature of the species is that the leaves remain on it for almost a whole year.

The flowering of the Thunberg spirea is supported by the sharp-toothed spirea. Its white flowers are collected in medium-sized inflorescences that bloom on gracefully curved branches.

Spirea sharp-toothed or spirea of Argut
Spirea Wangutta blooms next. Shrubs up to 2m in height bloom profusely in May-June.

In May-July, the Nippon spirea blooms. Its bushes have erect shoots slightly drooping in the upper part.
The most abundant flowering spirea is Plena. Blooms in May-June, in autumn the bush turns purple-red.

A few more photos of beauties of spirea!

Spirea Japanese "Little Princess"

Spirey Bumald "Gold Flame"

Garden use and partners
The use of all spirits is very diverse. These shrubs quickly form living flowering hedges that easily fill large areas. It is successful to combine spireas in individual plantings, and in combinations with other trees or shrubs, and to create mixed hedges. The eye-catching shape of the spirea bushes and slender shoots create an attractive contrast to the dark-colored neighbors.
Spire bushes successfully create bright, flowering hedges. They cut their hair easily. Especially beautiful are uncut shrubs of weeping shape, strewn with boiling white flowers.

Spirea hedge
Solitary spireas are good as a backdrop for perennial herbaceous or bulbous plants.
Summer flowering spireas will fill the voids between the conifers well, where they will create bright accents throughout the season.
Low-growing, dwarf spirea varieties form a unique colored carpet when planted on a sunlit slope. Such low bushes will adorn rockeries, rocky gardens, alpine slides.
Taller hybrids are suitable for framing, on the edge of the lawn, in the foreground of living partitions, in a flower bed with herbaceous perennials.
The shining white flowers of the spirea make it a good partner for bulbs, bushes and perennials blooming in early spring.
A good solution for a bright spring flower bed is yellow daffodils and red tulips against the backdrop of undersized spirea.
White jets of "fountains" of Wangutta spirea will add elegance and add energy to plantings of herbaceous perennials blooming in late spring - bearded irises or peonies.
Spring-flowering spireas are organically combined in bright hedges, they are successfully combined with lovely and red weigels planted nearby, Golden rain bean or purple-leaved hazel will create a suitable background.
If you plant a spirea, an ordinary viburnum and a chubushnik next to it, you get a "white dream"
In July, when most of the shrubs have already faded, summer-flowering spireas begin to bloom. They are planted in the foreground of mixed hedges, against the background of conifers, or as separate shrubs.
The bright red flowers of Bumald's spirea will become even brighter if planted against a background of white or yellow cinquefoil shrub. Spiraea and St. John's wort are successfully combined with each other, if they are picked up at the same height. It is better to combine large groups of these colors.
David's Buddley is good to use as a background.
Having correctly selected the varieties and varieties of spirea, its flowering can be enjoyed from spring to mid-summer.
Video about the reproduction of spirea
> I wish everyone to enjoy the flowering of spirea in the garden, planting and care is now no secret for you.
Best regards, Sophia Guseva.
Other interesting articles:
Published: 29 May 2014
Updated: 12 February 2017
 Spirea (Latin Spiraea)... or spiraea... is a genus of ornamental deciduous shrubs of the Rosaceae family. Translated from the ancient Greek "speira" means "bend", and the validity of this name is confirmed by the special flexibility of its shoots. The main advantage of the spirea is its unpretentiousness. There are about a hundred species of spirea growing in the steppe, forest-steppe and semi-deserts. There are references to spirea, or rather, meadowsweet, in the epic "Sadko" (about 1478), then in the 19th century information about this plant falls into the dictionary of V. I. Dal: he writes that the strong and thin branches of meadowsweet used for ramrods and whips. Today, different types and varieties of spirea are grown in culture, and they all differ not only in high decorativeness, but also in frost resistance, and the duration of flowering.
Spirea (Latin Spiraea)... or spiraea... is a genus of ornamental deciduous shrubs of the Rosaceae family. Translated from the ancient Greek "speira" means "bend", and the validity of this name is confirmed by the special flexibility of its shoots. The main advantage of the spirea is its unpretentiousness. There are about a hundred species of spirea growing in the steppe, forest-steppe and semi-deserts. There are references to spirea, or rather, meadowsweet, in the epic "Sadko" (about 1478), then in the 19th century information about this plant falls into the dictionary of V. I. Dal: he writes that the strong and thin branches of meadowsweet used for ramrods and whips. Today, different types and varieties of spirea are grown in culture, and they all differ not only in high decorativeness, but also in frost resistance, and the duration of flowering.
Content
Listen to the article
Spirea shrub - description
 Plants of the genus Spirea are both dwarf (15 cm) and very tall (up to two and a half meters). The root system is shallow, fibrous. Branches are creeping or erect, spread or recumbent, from light brown to dark, the bark tends to exfoliate longitudinally. The leaves are petiolate, alternate, three to five-lobed, lanceolate or rounded. The flowers of the spirae are small, but numerous, forming a variety of inflorescences - paniculate, spike-shaped, pyramidal, corymbose. The color of the flowers is varied, from boiling white to crimson. In different types of spirea, the inflorescences are located in different ways: in some, along the entire shoot, in others - only on the upper part of the shoot, in some - only at the ends of the branches. Spireas reproduce by dividing the bush, seeds, layering and cuttings.
Plants of the genus Spirea are both dwarf (15 cm) and very tall (up to two and a half meters). The root system is shallow, fibrous. Branches are creeping or erect, spread or recumbent, from light brown to dark, the bark tends to exfoliate longitudinally. The leaves are petiolate, alternate, three to five-lobed, lanceolate or rounded. The flowers of the spirae are small, but numerous, forming a variety of inflorescences - paniculate, spike-shaped, pyramidal, corymbose. The color of the flowers is varied, from boiling white to crimson. In different types of spirea, the inflorescences are located in different ways: in some, along the entire shoot, in others - only on the upper part of the shoot, in some - only at the ends of the branches. Spireas reproduce by dividing the bush, seeds, layering and cuttings.
Spirea flower is used for group plantings, for hedges. Dwarf varieties of spire are great for rockeries, rocky gardens and for creating living "carpets". The spirea bush also looks great as a single plant.
Types and varieties of spirea
Some types and varieties of spirea are often used in culture, others rarely. By the time of flowering, spireas are divided into spring-flowering and summer-flowering.
Spring flowering spireas.
They differ not only in early flowering, but also in that they are characterized by flowers of different shades of exclusively white color, which bloom on last year's shoots. Flowering begins only in the second year of the shoot's life. These spirits are characterized by strong tillering. The following types are popular in culture:
Spirea is gray.
It is a hybrid of St. John's wort and whitish-gray spiraea - in fact, it is white spirea, and it is called gray because of the color of the leaves. The bush reaches a height of 180 cm, drooping branches, lanceolate gray-green leaves on the lower side are gray, corymbose inflorescences of white flowers are located along the entire length of the branch. Blooms from mid-May to mid-June. Most popular variety:
Spirea gray "Grefsheim"... the diameter and height of the bush of this variety is 1.5-2 m, drooping branches, a spreading crown, red-brown branches, flowers up to 1 cm in diameter, snow-white, terry, collected in umbrellas. The plant is a honey plant, blooms up to 45 days, starting from the second year;


Spirea Wangutta.
A hybrid of Cantonese and three-lobed spirea - a huge bush with a diameter and growth of up to 2 m, drooping branches, toothed leaves, glabrous, three-lobed, dark green above, gray below, turning red-orange in autumn. Numerous hemispherical inflorescences consist of white flowers up to 0.6 cm in diameter and are located along the entire length of the branch. Blooms in mid-June, sometimes blooms again in August;


Spirea nippon.
In nature, it grows on the island of Honshu, reaches a height of 2 m, the crown is spherical, dense, the branches are horizontal, green leaves up to 4.5 cm in length until late autumn, blooms for up to three weeks from the beginning of June with corymbose inflorescences consisting of yellow-green flowers up to 1 cm in diameter, with purple flowers in the bud;


Spirea of the argument.
The earliest of the spring-flowering spirits. A spreading bush of 1.5-2 m in height, very beautifully shaped, drooping flowering branches, like a foamy waterfall, consisting of numerous snow-white fragrant flowers, streaming along the entire length of the branches. Argta blooms for three weeks from the end of May.


Summer blooming.
These are species in which inflorescences are formed at the ends of young shoots and in which old, last year's shoots gradually dry out, represented primarily by varieties of Japanese spirea. It is pink spirea in most of its varieties, but sometimes it is red or red-pink spirea. So:
Japanese spirea.
A very beautiful shrub with tomentose-pubescent shoots when they are young and bare when they age. The bush is 1-1.5 m high, the leaves are oblong, ovate, gray-gray below, green above, in autumn - yellow, red, purple. Japanese spirea blooms for up to 45 days with red-pink flowers, collected in paniculate-corymbose inflorescences located at the ends of the shoots. The most popular varieties:
Spirea japanese little princesses - shrub only 0.6 m high, crown diameter 1.2 m, rounded crown, oval leaves, dark green, corymbose inflorescences consist of red-pink flowers 3-4 cm in diameter, blooms in June-July, grows very slowly ;


Spirea Japanese Golden Princess - a variety of the previous variety, it differs from it in that it grows up to 1 m in height and the color of its leaves is yellow;


Spirea Japanese Shirobana - low shrub (0.6-0.8 m), but the diameter of the crown is 1.2 m, the leaves are narrow-lanceolate, dark green, small (2 cm). White or pink flowers bloom in July or August;


Spirea Japanese Goldflame - height 0.8 m, yellow-orange leaves eventually turn bright yellow, then green-yellow, and in the fall - copper-orange. The flowers are red-pink, small;


Spirea Japanese Crisp - openwork undersized shrub up to half a meter high and slightly wider, spherical crown, numerous erect shoots, inflorescences - flat umbrellas 5.5 cm in diameter from small pale pink flowers with a lilac tint, blooms from July 1.5-2 months.


In addition to Japanese spirea, there are such types of summer-flowering spiraea:
Spirey Bumald.
A hybrid of Japanese and white-flowered spirea is a low-growing shrub with a height of 50 cm to 80 cm. Shoots are erect. Leaves, green in summer, in autumn are especially picturesque - red, purple, yellow. It blooms for about two months, starting in July with flowers from pale pink to dark pink. Popular variety:
Spirea Bumalda Goldflame - spiraea 0.8 cm high, the leaves are bronze-orange when young, then they become yellow-golden, then yellow-green, and in the fall - copper-red. But these changes occur if the bush is in the sun, in the shade the leaves are green;


Spirea willow.
Two-meter shrub with upright shoots of red-yellow-brown color, pointed leaves up to 10 cm long, white or pink flowers are collected in pyramidal-paniculate inflorescences about 20 cm long;


Spirea Douglas.
One and a half meter bush with straight, pubescent red-brown shoots. Leaves 3-10 cm long, oblong-lanceolate, dark pink flowers are collected in apical, narrow paniculate-pyramidal inflorescences, blooms for a month and a half from July to September;


Spirea Billard.
Douglas spirea hybrid and willow - bush height up to 2 m, broadly lanceolate leaves up to 10 cm long, bright pink flowers, collected in narrow twenty-centimeter pyramidal-paniculate inflorescences. Blooms from mid-July.


Growing spirea - features
Each plant has its own requirements for both planting and care. Growing spirea also has its own characteristics:
- - Spirea prefers leaf or sod soil. Optimal composition: one part of sand and peat and two parts of land;
- - a drainage layer is required, you can use broken brick;
- - planting spirea is carried out in a hole, which is one third of the volume more than the butt of the plant;
- - planting depth - at least half a meter, and the root collar of the plant should be at the surface level;
- - Spirea should be planted in cloudy weather, and even better - in the rain. The best time is September;
- - the best neighbors for spirea are juniper, spruce, thuja.
Planting spirea
Planting spirea in the spring.
In the spring, only summer flowering spireas are planted. The main condition for a spring planting is to be in time before the leaves bloom. If you buy spirea seedlings, carefully consider the roots - they should not be overdried. Check the shoots of the seedling and only buy if they are flexible and have good buds. Adjust the planting material: if the roots of the seedling have grown too much, carefully shorten them, if, on the contrary, the roots are too dry or damaged, cut the branches. If the root system is dry during storage, spill it with water or soak it briefly in a bucket of water, and only then plant it.
Spirea is an unpretentious plant, but for a long and abundant flowering, it is nevertheless necessary to observe certain conditions: the site for the spirea must be sunny, the soil fertile. In addition, spirea bushes give abundant root growth, which increases the area occupied by the plant, and this must be taken into account when planning spirea planting.
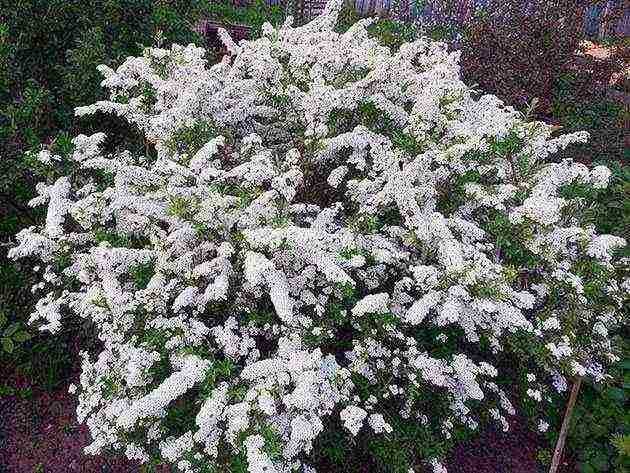

So, in the area where the spirea will grow, you need to make a pit with strictly vertical walls, at least a third larger than the volume of the root system of the seedling. Then you need to let the pit stand for 2-4 days. On the day of planting (preferably rainy or cloudy weather), you need to make a drainage layer of 15-20 cm from broken bricks, especially if the soil is clay, add 2 parts of leafy or turf soil and one part of peat and sand to the pit, mix this mixture, lower the roots of the spirea into the pit, spread them, cover them with earth to the root collar and then compact. Immediately after planting, the spirea is watered with one or two buckets of water and mulched with peat.
Planting spirea in the fall.
In autumn, both spring-flowering spireas and late-flowering ones are planted. Usually, the autumn planting is combined with the spirea planting by dividing the bush. This must be done until the leaf fall is over. Spireas, which are 3-4 years old, are divided and transplanted, older plants can also be planted, but this is already quite difficult to do because of the large earthen coma, which is difficult to remove and wash from the ground.
The spirea bush must be dug out, capturing slightly more than half of the crown projection around the circumference.You will probably have to chop off a few roots, but this will not do much harm to the plant. Then the roots of the extracted bush must be washed well. If the plant is young and not very overgrown, just place it in a container of water and let the soil turn off and settle in the water, then rinse the roots under running water while spreading them out. Cut the bush with pruning shears into two or three parts so that each delenka has a good root lobe and 2-3 strong shoots. Trim the cordlike roots.

Dig a hole, put a mound in the middle, set the seedling on a mound and smooth out the roots. Fill the hole with soil and apply it over the surface. In several steps, pour the planted cuttings with water.
Spirea care
How to care for spirea.
We have already talked about the basic requirements of the spirea: bright lighting (although many species grow well in partial shade), loose fertile soil, good drainage and mulching with a seven-centimeter layer of peat immediately after planting. What else is needed in order for the spirea to delight you with beautiful and long flowering?
Since the spirea has a shallow root system, it does not tolerate dry soil and begins to dry out, therefore it needs moderate watering during the dry season: 15 liters of water per bush twice a month. Loosening the soil is imperative, as is regular weeding. Top dressing of spirea is carried out with complex mineral fertilizer after pruning the bush, and in the middle of summer it would be good to fertilize the spirea with a mullein solution with the addition of superphosphate at the rate of 10 g per 10 liters of solution.
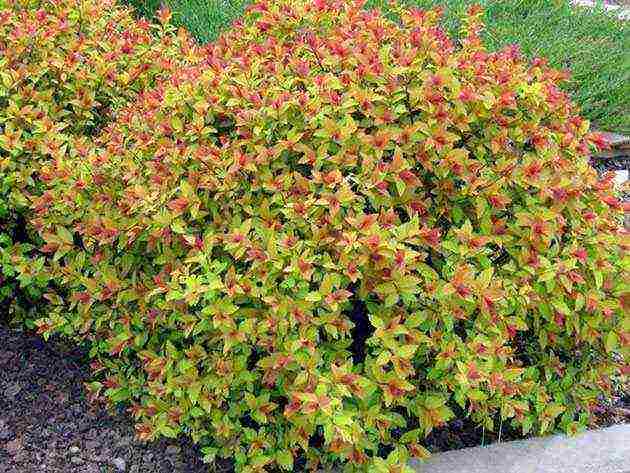

Of the pests, aphids and spider mites are the most annoying spire. The mite is destroyed by karbofos, and the aphid by the drug pyrimor. But for the most part, spireas are not susceptible to diseases, and pests cannot do much harm to their beauty and reduce the decorative qualities of the spirea.
Trimming the spirea.
Bushes tend to grow, so you have to cut them from time to time. In early flowering, since flowering takes place along the entire length of the shoot, only the tips are cut off annually, which froze over the winter, but after 7-14 years all old shoots are removed from the bushes, that is, the plant is cut almost to the stump, so that later from the very 5-6 strong shoots of young growth to form a new bush, removing the remaining shoots during the growing season. After a year or two, weak or old shoots are again removed from the bush. At the ends of the shoots, pruning should be carried out in the spring, before the leaves bloom, sanitary pruning of old shoots can also be carried out in the spring, or in summer.

Summer-flowering spireas are cut annually in early spring. It is necessary to shorten the shoot to large buds, it is better to remove weak and small shoots altogether. The stronger the pruning, the more powerful the shoots will grow. It is necessary to remove aging shoots in time, otherwise they begin to dry out on their own. When the bush is four years old, you can annually cut the bush to a height of 30 cm from the ground, but if the spireas still give weak growth, you should think about replacing the bush, although on average late-flowering spirea species live 15-20 years.
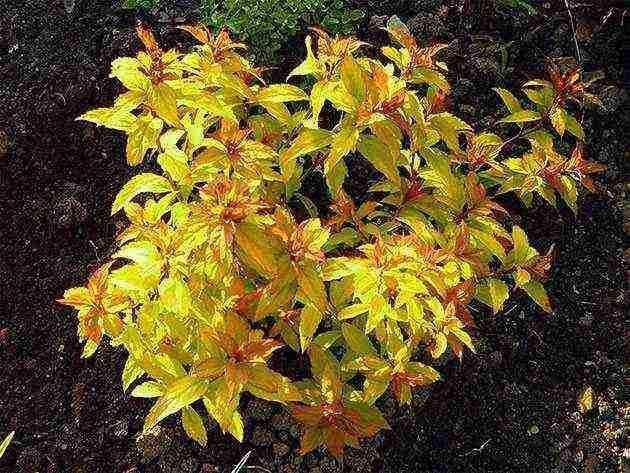

Reproduction of spirea.
Spireas reproduce, except for dividing the bush, by seeds, cuttings and layering. Only those spireas that are not hybrids can be propagated by seeds, since spirea seeds still do not retain varietal qualities. But the method of cuttings brings very good results - over 70% of cuttings are rooted even without the use of growth stimulants. Early flowering spireas are cut in the first half of June, late flowering - in the second half of June or July. Lignified cuttings are rooted in autumn, in September-October.
Cut a straight annual shoot, cut it into pieces so that each has 5-6 leaves. Remove the lower leaves on each cuttings along with the petioles, cut the rest of the leaves into half a leaf and put the cuttings in an epin solution for half a day (1 ml per 2 l of water).Then dust the lower knot of the cutting with root stimulant and plant in a pot in wet sand at an angle of 30-45º. Cover the cuttings with glass or plastic. Place the container of cuttings in the shade and spray them with water two to three times a day. When the frost sets in, dig in the cuttings in the garden bed, cover with leaves, place an inverted box on top and leave until spring. When the cuttings give new shoots next year, they can be planted in a permanent place.

When propagating by layering, the shoot is laid in a groove dug in the ground, pinned and sprinkled with earth. If you want to get several new shoots, then the top of the cut must be pinned, then each lateral bud can give a shoot. In autumn, the layers are carefully removed and divided into regrown shoots, which are planted.
Spirea after flowering
As already mentioned more than once, caring for the spirea is not difficult, including in terms of preparing the plant for the dormant period. Almost all types and varieties of spirea tolerate the cold well, but if the winter is very frosty, and most importantly, snowless, you can take care of the plant by covering the roots of the bush for the winter with a layer of foliage of 10-15 cm. In any case, spirea is not worse from this. will be.
Clematis - planting, care, pruning, growing
Irises - planting and care, varieties, cultivation
Please rate our website. We tried so hard 😉
Peach (Latin Prunus persica) is a plant of the Almond subgenus of the Pink family. Where the plant came from, there is no reliable data. In any case, it is known.
Modern florists will not be frightened by difficulties, because lovers of garden bulbous flowers undertake to grow not only traditional tulips, lilies or.
Cherry plum (Latin Prunus cerasifera), or spreading plum, or cherry-bearing plum - a species of the genus Plum of the Pink family, woody fruit plant, cat.
 Spirea is a deciduous type of ornamental shrub belonging to the pink family Spiraea (Spiraea) is a deciduous type of ornamental shrub belonging to the rose family (Rosaceae). This plant is represented by nine dozen species common in forest-steppe and semi-desert zones, as well as in the subalpine mountainous zone in the Northern Hemisphere.
Spirea is a deciduous type of ornamental shrub belonging to the pink family Spiraea (Spiraea) is a deciduous type of ornamental shrub belonging to the rose family (Rosaceae). This plant is represented by nine dozen species common in forest-steppe and semi-desert zones, as well as in the subalpine mountainous zone in the Northern Hemisphere.
Botanical features of spirea
The height of the aboveground part, depending on the species characteristics, can vary within 15-250 cm. The root system of the decorative perennial is of the fibrous type, located not deeply. Erect and spread, recumbent type, ascending or creeping branches, have a light brown or dark brown bark, which can flake off. Young branches are characterized by light green, yellowish-reddish or brownish coloration, as well as the presence or absence of pubescence.
Small buds. The foliage is alternate, petiolar, without stipules, narrow lanceolate-linear or rounded. The racemose inflorescences of early flowering species are sessile or practically sessile, umbellate or corymbose type, with a leaf rosette at the base. Flowers are bisexual, less often dioecious, white, pink-red or purple in color. The fruits are multi-seeded leaflets, with flat, lanceolate winged brown seeds.
How to grow spirea (video)
Variants of using spirea in landscape design
The variety of types of spirea makes it easy to choose a shrub that will be ideal for decorating a backyard area. Undersized and miniature species are widely used.... which are optimal when creating rockeries.
Varieties with different flowering periods can be combined to zone the area. Spireas are widely used in the creation of mixborders, as well as green hedges. They harmonize very well with scumpia, dahlias, turf and actions, and also look attractive and original with conifers, including spruces, thuja, pines and junipers.
Description of shrub varieties
On the territory of our country, several varieties of a shrub plant are quite successfully grown. All of them differ not only in appearance, but also in terms of flowering. Paniculata spirea, as well as varieties Junia Bright and Little Princesses.
Uncomfortable carrying heavy hoses through your garden beds?
Garden hoses are often too heavy, kinked and dirty. At the same time, water consumption is often not controlled in any way, and watering the entire site can take a whole day. Fortunately, autonomous irrigation is no longer a gimmick and is available to any gardener. But the main thing is that when watering with an ordinary hose, sunburn appears on the leaves of plants, which means.
Spirea hybrid Billard Triumfans
Billard's spirea is a hybrid form obtained by crossing the willow and Douglas spirea. The two-meter shrub has spreading branches and foliage of a wide lanceolate shape with a grayish-tomentose lower part.
Variety "Triumfans9raquo; has purple-pink spike-shaped inflorescences a quarter meter high, as well as green or reddish-brown young shoots with pubescence and ribbed bare old shoots, which gradually dry out. By the sixth year of life, there is a loss of shape by a shrub, so it is necessary to properly prune.
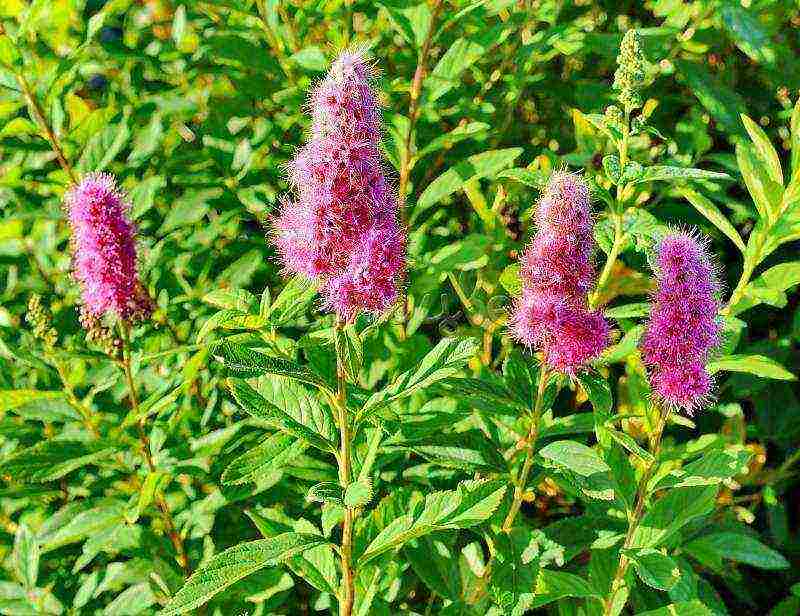 Spirea hybrid Billard Triumfans
Spirea hybrid Billard Triumfans
Spirea willow
Under natural conditions, the species grows in Siberia and Europe, as well as in the northern part of America, in Japan and China, where it forms thickets near lakes, along river floodplains. This is an upright shrub plant no more than two meters high, with very characteristic red-yellowish shoots and pointed foliage of an elongated lanceolate shape.
The base of the leaves is sharp, serrate. The surface of the plate is dark green in color, and the bottom has a lighter color. The flowers are white or pink in color, located on short pubescent peduncles, which are collected in inflorescences of the pyramidal or cylindrical paniculate type. The variety is frost-resistant, blooms in the fourth or fifth year.
White-flowered spirea argut
One of the most spectacular spring blooming varieties. A tall culture with a two-meter aboveground part, a spreading crown, and also narrow lanceolate foliage with strong serrated.
Snow-white flowers gather in numerous, umbrella-shaped inflorescences that densely cover the shoots. Flowering is observed on the shoots of the last year. The species is slow growing and needs to be pruned after flowering. The branches are quite thin and spreading, with small and relatively narrow leaves of a characteristic green color.
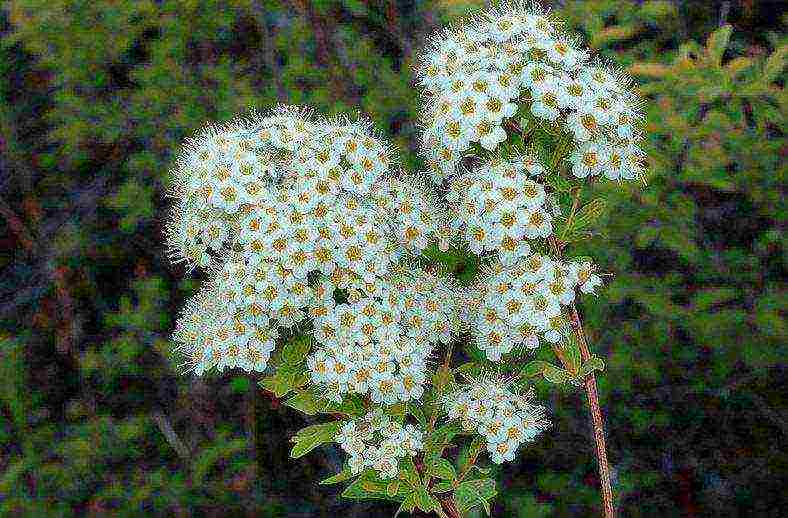 White-flowered spirea argut
White-flowered spirea argut
Spirea gray
A large and fairly frost-resistant plant with a height of the aerial part of up to two meters and numerous shoots, which are covered with pointed leaves of a grayish-green color. Flowers are formed in May, white, collected in corymbose inflorescences. The most popular variety in home gardening is "Grafsheim9raquo; with very characteristic drooping arcuate branches.
Japanese spirea
One of the most famous and very common species in our country, represented by a variety of varieties, excellent for use in modern backyard landscape design. Under natural conditions, the Japanese variety grows in China and Japan, as well as in Korea.
In the conditions of home gardening, it is used in landscaping even in the northern regions. Winter-hardy and very hardy shrub plant with a height of the aboveground part from 30 cm to one and a half meters, it has a varied coloration of not only flowers, but also leaves, which can vary depending on varietal characteristics. Flowering is abundant and long-lasting.
Spirea nippon
A shrub plant no more than two meters high, with a very dense, spherical crown, as well as horizontally directed branches. It is characterized by a compact type of aerial part and a very abundant, rather long flowering.
The foliage is round, crenate or whole-edged in the upper part, green in color. The species is very light-loving, with high winter hardiness. Particularly popular are such decorative forms as Snowmound9raquo; or Snowmound and Halvare Silver or Halward's Silver.
Features of planting and transplanting spirea in the open field
It is advisable to plant shrubby perennials in previously prepared areas in the spring, after the snow melts and the soil warms up. In order to properly plant an ornamental plant, it is necessary to select a sufficiently sunny and well-heated area, represented by sod land, peat and sand mixed in a ratio of 2: 1: 1 with soil acidity at 6-7 pH.
If the groundwater is too high it is important to provide high-quality drainage, consisting of gravel in a layer of 10-20 cm. The planting pit should have dimensions of 50 x 50 x 50 cm. The standard distance between the planting pits should not be less than half a meter. When planting a shrub as a hedge, it is possible to reduce the gap between the planted plants to 40 cm, with the distance between rows within 30-40 cm. After planting, it is recommended to mulch with peat, the layer of which is 70 mm.
Types and varieties of spirea (video)
Haircut and other types of spirea care
It is necessary to take care of the spireas not only in the spring-summer period, but also in the fall, at the stage of preparation for wintering. In early spring, 100-120 g of highly effective fertilizer "Kemira-universal 9raquo;" must be applied. Irrigation should be moderate, but in a too dry and hot season, as well as after pruning, the plant should be watered at the rate of one and a half buckets of water for each bush.
Young and newly planted plants need more frequent and abundant watering. After watering, it is required to perform surface active loosening of the soil... as well as organic mulching. The shrub plant tolerates a haircut well enough, therefore it is very actively used to create hedges or borders. After pruning, the perennial is able to quickly restore the crown, so it is recommended to cut off all faded shoots by about half of the length.
 Spirea tolerates a haircut well enough
Spirea tolerates a haircut well enough
Reproduction of spirea by dividing the bush, cuttings, seeds and layering
Reproduction of a decorative perennial can be carried out in several ways:
- seed material;
- bush division;
- layering;
- cuttings.
Best of all, seeds reproduce varieties of Japanese spirea and oak-leaved, and the germination rate of seed of such varieties, as a rule, exceeds 80%. For sowing seeds, seedling containers with a height of 20-30 cm are used, which are filled with a mixture of leaf and sod land in a 1: 1 ratio with the addition of a small amount of humus and medium-grained sand to loosen the soil. When diving, the central root is pinched by about a third of the length, after which the seedlings are seated at a distance of 5-7 cm.
Vegetative propagation is very widely used... if there is a need to keep well all the characteristics of the parent plant. This method of reproduction allows you to get full-fledged adult plants much faster. By bush division, spireas are propagated at the age of three or four years, when the shrub is already fully formed, and the size of the root system allows division into separate divisions.
For execution reproduction by layering the lower, only completely healthy shoots of the ornamental culture are used, which in the spring are dug into the pre-prepared grooves of 8-10 cm.If there is a need to obtain the maximum number of plants with fully preserved varietal characteristics, then the most convenient and easy way is propagation by cuttings. Cutting is one of the main methods used by amateur gardeners.
How to plant a spirea (video)
Some features of planting and caring for spirea in the Urals
When grown in insufficiently favorable and comfortable conditions for the growth and development of culture, the plant's immunity weakens, so you need to regularly check the planting for the absence of damage by haplits, aphids and sawflies.
In a winter that is too harsh or with little snow, the ends of the shoots are sometimes frozen in the varieties of the Nippon and sharp-toothed varieties, therefore in Siberia or the Urals it is recommended in the autumn to use dry leaves or peat chips with a layer of up to 10-12 cm to cover the root system.
When choosing a variety need to remember... that spring-flowering species are distinguished by inflorescences of white or cream coloration, collected in inflorescences on the shoots of the previous year and blooming in May. Summer-flowering species are characterized by high decorativeness and bright inflorescences formed on the shoots of this year, therefore, they must be pruned only in early spring.
And a little about secrets.
Have you ever experienced unbearable joint pain? And you know firsthand what it is:
- inability to move easily and comfortably;
- discomfort when going up and down stairs;
- unpleasant crunching, clicking not on their own;
- pain during or after exercise;
- joint inflammation and swelling;
- unreasonable and sometimes unbearable aching pain in the joints.
Now answer the question: does this suit you? How can you endure such pain? And how much money have you already "poured" on ineffective treatment? That's right - it's time to end it! Do you agree? That is why we decided to publish an exclusive interview with Professor Dikul. in which he revealed the secrets of getting rid of joint pain, arthritis and arthrosis.


