Content [show]
Thanks to the incomparable flowers of the most beautiful color and variety of forms, the genus of dahlia deserves a noticeable place in any garden. Few of the florists do not admire the splendor of this plant. The history of the appearance of the dahlia is connected with the legend that the dahlia appeared on the site of the last fire that died out with the onset of the ice age. And the first to sprout after the arrival of warmth, marking the victory of life over death, and warmth over cold.
Intensive selection work has led to the creation of a huge number of varieties - now their number is in the tens of thousands. This flower has two official names - Dahlia (most common in England) and Dahlia.
The Aztecs worshiped this plant, considering it the embodiment of the sun, the warriors depicted it on their shields and clothes, worn it as an amulet, believing that it gives them strength and courage. The natives used the tubers for food, and the hollow stems were used in the construction of the aqueduct. Dahlia is considered a symbol of all-conquering life, fortitude, freedom, inaccessibility, pride. The Japanese consider it a symbol of greatness. Dahlia is the national flower of Mexico.
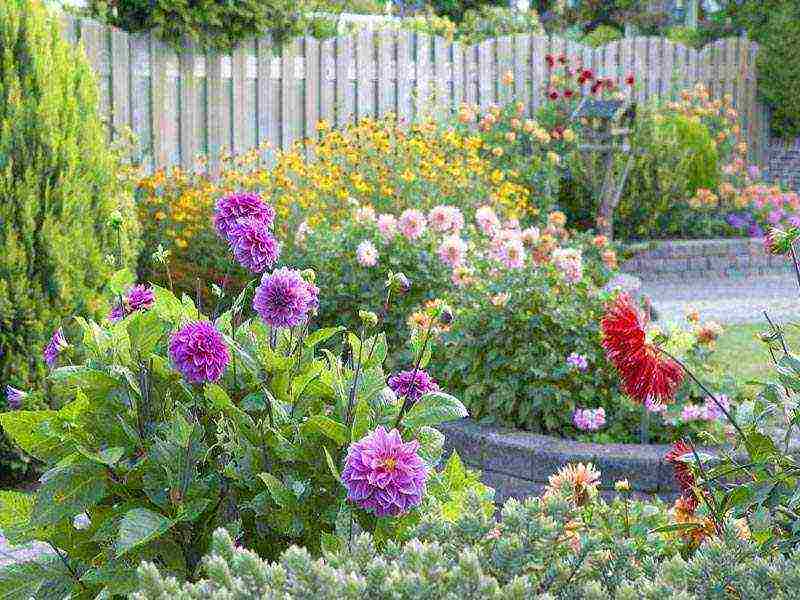

Dahlias in the garden photo Application in landscape design
The dahlias we admire today were obtained by crossing the Mexican species Dahlia coccinnta and Dahlia variabilis. These are herbaceous perennial plants, the roots of which have powerful tuberous thickenings with a supply of nutrients. Stems are hollow, branching with pinnately separated, opposite, green-blue leaves on elongated petioles. Flowers are collected in inflorescences-baskets, blooming from summer to the first small frosts. Reed flowers are flat, spatulate, ribbon-shaped, rolled into a tube, different in color; tubular - yellow or orange.
Depending on the size of the inflorescence, dahlias are subdivided into giant (more than 25 cm in diameter), large (up to 25), medium (20-25), small (10-15) and miniature - up to 10 cm.
Growing dahlias from seeds

How to plant dahlias Dahlia seeds photo
Sowing directly into the ground
Considering that these plants are very thermophilic and do not tolerate even short-term light frosts, they can be sown into the ground only after the 20th of May, in order to be sure that the night frost will not destroy the seedlings.
However, there is a significant drawback: flowering in this case can be seen not earlier than August.
Therefore, many gardeners still arrange a mini-greenhouse or greenhouse for these flowers and sow already in the twenties of March. You can use old window frames or stretch the film over the arcs.
- The prepared bed should stand for a couple of days after digging for the earth to settle.
- The furrows are filled shallow, a distance of 60 cm.
- We sow less often in a row, the plants need space, dense shoots are then broken through or transplanted, leaving a distance between the bushes of at least 60 cm.
- After sowing, the soil is leveled with a rake, filling the furrows.
- We water well, you can sprinkle the bed with rotted humus in a thin layer to prevent the formation of an earthen crust.
Watering is often unnecessary, natural moisture should be enough for several days. But if the weather is hot, make sure that the ground does not dry out.
Growing dahlias for seedlings at home
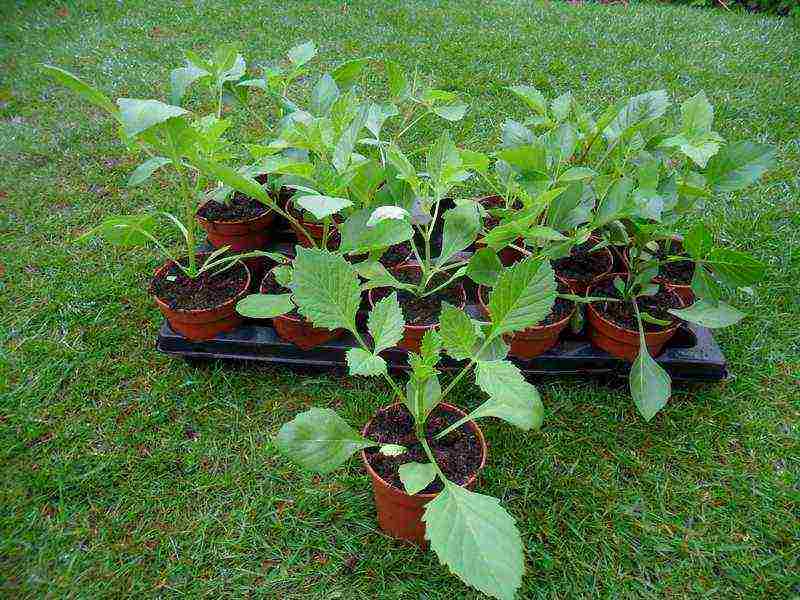

Dahlias from seeds How to plant dahlias for seedlings photo
When planting dahlia seeds, flowering immediately on the garden bed will not occur until mid-August. When planting seeds at home for seedlings, an earlier start of flowering is achieved. Growing in this way usually does not cause any trouble for flower growers. The only point that should be taken into account is that dahlia seedlings cannot stand even weak frosts.
Seeds are convenient for growing undersized dahlias for decorating borders, rabatok. Plants grown from seeds form a small tuber by autumn. Therefore, you can save your favorite specimen and plant it next season to admire it next summer. Dahlia seeds ripen well - they can be harvested and saved for planting next year.
Annual dahlias are sown for seedlings in April, but if you want to get perennial nodules, you need to sow in early March.
- Prepare containers for drainage. If using food packaging, be sure to make holes in the bottom.
- Fill containers with nutritious, organic-rich, loose soil. Remember, simple garden soil will have a bad effect on the health of the seedlings: during the care it tends to become very compacted. Therefore, it is better to buy a special mixture for flowers. Well, or not be lazy, adding rotted organic matter, peat and sand in equal proportions to the garden soil.
- Sowing is done shallow, 1-1.5 cm. It is advisable to sow less often, leaving a distance of 2-3 cm between seeds.
- When little dahlias release 2-3 true leaves, they are carefully dived into separate cups. You can use a fork, teaspoon, or any other convenient tool. The main thing is not to damage the delicate roots and transfer them with a lump of earth.
- Then just water and provide sufficient lighting.
- When the weather is warm, we arrange for the seedlings to walk outside: we teach them to the wind and the sun.We gradually increase the time and by the end of the second week of hardening, our seedlings should be outside for a full day. These hardened seedlings will not hurt after planting and will quickly take over.
When to plant dahlias outdoors
At the end of May, when there is no longer a threat of night frosts, seedlings and tubers are planted in a flower bed... In some regions even earlier, it all depends on the weather. Dahlias bloom 60-90 days after they ascend, depending on the variety.
Planting seedlings of dahlias in the spring in the ground
Planting dahlia seedlings in the ground - a joyful stage for the gardener. Finally, the flowers will go to the flower bed. Here I would like to give some advice:
- Try to avoid strict rows, the landing will look unnatural, too prim. It is better to combine dahlias with garden balsam, rudbeckia bushes, buzulnik or asteriscus, imitating the natural chaos.
- Give more space for each bush, the distance to other plants is at least 60 cm.
- The wells are prepared in advance, they are made wider and deeper than the seedling cups, it is advisable to pour a little humus on the bottom.
- Seedlings are planted, carefully removing a clod of earth so that the earth does not crumble from the roots.
- Placed vertically in the hole, trying to maintain the existing level of the root collar.
- Sprinkle with earth, moisturize abundantly.
- It is advisable to mulch the root space with any available material: fresh grass, sawdust, pine needles.
Planting dahlias tubers in spring
Before planting, dahlia tubers should be prepared: wash from the ground and soak in a slightly pink solution of potassium permanganate for about half an hour. Then the tubers are laid out in boxes with sawdust treated with boiling water and germinated at room temperature until sprouts appear.
For more information on the preparation of tubers, see the video:
After the tubers have sprouted, they should be divided before planting to allow the bushes to develop fully in the new season.
How to divide tubers before planting, look at the video:
After the tubers are ready for planting, we begin the process itself. Prepare deep holes, approximately 30 cm deep and 40 cm in diameter. Pour humus on the bottom, mix with garden soil. Lay out one cut of tubers in each hole, cover with earth, the distance from the tuber to the surface of the earth is about 5-8 cm.
For details on planting dahlias with tubers in spring, we look at the video:
Reproduction of dahlias by dividing tubers
- Tubers are prepared for planting in advance. First, they are placed in wet sawdust or peat.
- After the sprouts appear, they are carefully divided with a sharp knife into several parts, so that each one has sprouts.
- Sections are dried and sprinkled with ash or activated carbon. After that, they are again placed in sawdust for rooting.
- As soon as the weather is warm without frost, they are planted in pre-prepared holes.
- Add 1/3 of a bucket of humus or compost to each hole.
- The rag is placed in the hole so that the sprouts are at the surface of the soil.
- They are well spilled and covered with compost.
- The root collar should be at ground level.
Propagation of dahlias by cuttings
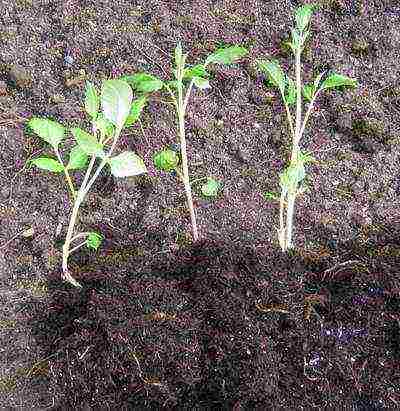

Reproduction of dahlias by cuttings photo how to plant
- At the end of February, the roots of the dahlia are treated with a weak solution of potassium permanganate and placed in boxes, half covered with a light nutritious substrate, moderately watered.
- Cuttings are taken in 3-4 weeks.
- They are treated with root roots and planted in individual cups.
- To speed up rooting, you can cover the plantings with plastic.
- Rooting takes place within two weeks.
- In early June, they are planted in groups or rows at a distance of 60 cm.
Growing conditions
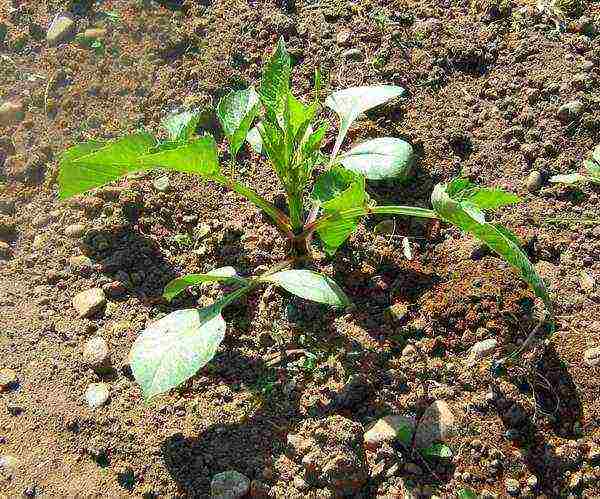

How to plant dahlias tubers Planting dahlias in spring How to plant dahlias photos and videos
- Dahlias prefer sunny areas. In partial shade, they grow excellently, but are much higher than plants planted in the sun.
- Deep shade is detrimental to development and flowering.
- They love rather moist soil - for this, the land under the plantings should be mulched with half-rotted sawdust or mowed grass. This will prevent moisture from evaporating and eliminate weeding.
- Top dressing is done in cases where organic components were not introduced into the soil during planting.
- Use a liquid compound fertilizer every two weeks.
- A support must be placed under tall varieties - this will protect against stem breakage during bad weather and strong winds.
No more than 3 shoots should be left on each bush.... To get larger flowers on the central peduncles, all lateral shoots should be cut off. It is imperative to remove faded buds to enable the young to develop. The fewer the buds, the larger the flowers.
After the first frost has damaged the bushes, they should be dug up... Cut the stem at a height of 15-20 cm from the ground and carefully dig out the root, trying not to damage it at the same time. Very often, liquid accumulates inside the hollow stem and this causes the plant to rot during storage. Therefore, the tuber is turned over with the stem down, allowing the liquid to flow out. After that, you can dry the tubers outdoors during the day, weather permitting. They are then transferred to a dry cellar for storage.
Diseases and pests
Dahlias are quite stable, but waterlogging of the soil should be avoided, which contributes to the development of diseases and the attack of slugs. Against aphids and mites, irrigate your plants periodically with tar water. When infected with a viral mosaic, light spots appear on the leaf plates, yellowing along the veins. Such plants should be discarded. If uncharacteristic growths are found on the tubers, which indicates bacterial cancer, the infected tubers are destroyed.
Types of dahlias with photos and descriptions
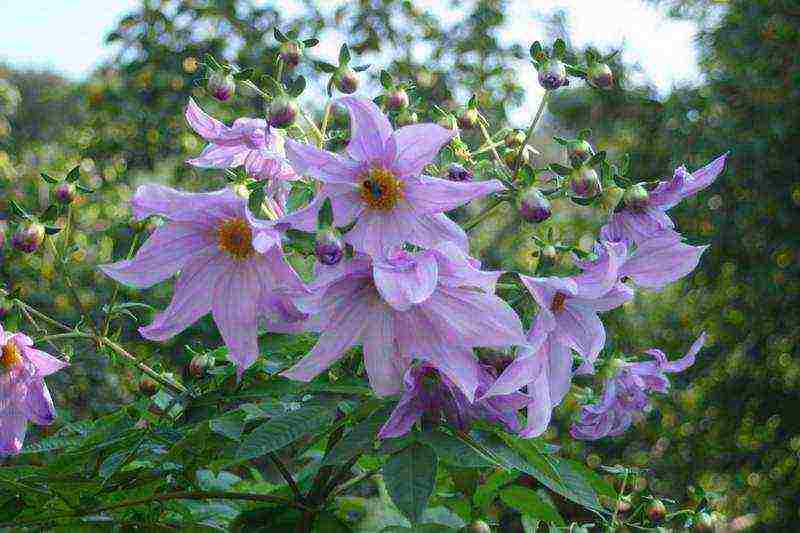

How to plant dahlias in spring Dahlia tree Dahlia arborea photo
Dahlia tree Dahlia arborea - a species with a powerful woody stem reaching a height of 2 m. It has simple lilac baskets.
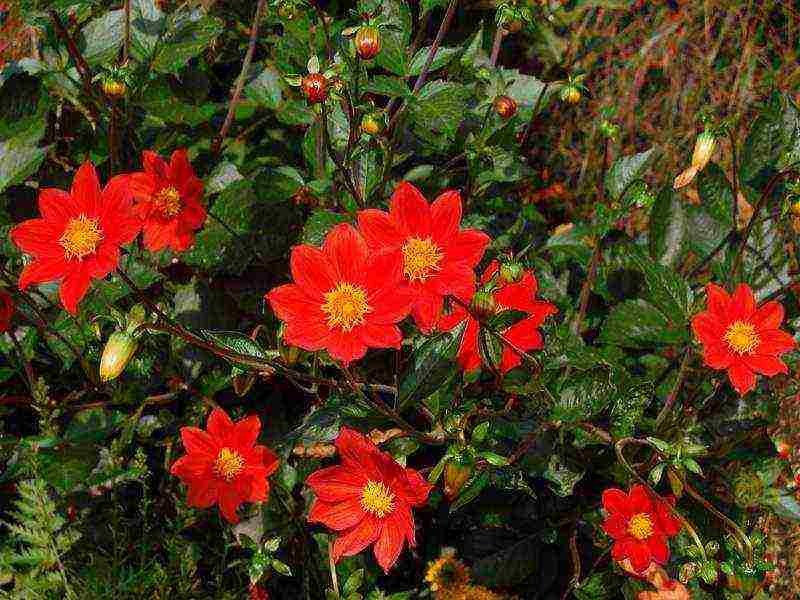

Dahlias perennial planting and care of Dahlia Dahlia coccinea photo
Dahlia coccinea - the leaves of this species are pinnate with pointed lobes. The baskets are simple and small.
The species Dahlia juarezii has a stem about 1 m high with deeply indented dark malachite leaves and multi-colored inflorescences. from it cactus dahlias originated.
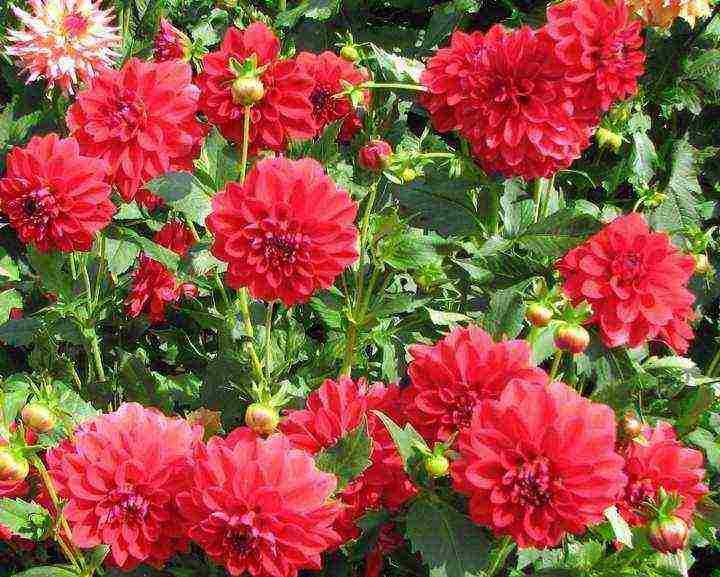

Dahlias annual planting and care Dahlia changeable Dahlia variabilis photo
Dahlia changeable Dahlia variabilis - has simple baskets with red ligulate and yellow tubular flowers.
All of these species, originally from Mexico, laid the foundation for a variety of varieties, so beloved by our flower growers. They absolutely do not tolerate even the lightest frost and are grown in our strip as annual plants. But dahlia tubers overwinter well in dry, cool rooms like potato tubers. To do this, they are dug up and re-planted in the spring.
There is a division of dahlias according to the shape of the inflorescence.
Anemone... Medium-sized group with semi-double inflorescences that look like anemones.
Collar... The tubular petals of this plant are shorter than those of other species. The middle of the inflorescence is made up of small tubular petals with a collar of one row of large flat petals of a contrasting color.
Peony... Outwardly they are similar to peonies. The most extensive and colorful species.
Lotus-shaped or nymphaean... All varieties of this species are terry and the largest.
Decorative... The most common variety, including the largest number of varieties.
Spherical and pompous... They are similar to each other and differ in the size of the inflorescence. Both have double flowers that resemble a ball, consisting of many petals. Pompous diameter of which does not exceed 5 cm. Spherical - 8-15 cm. Both species are tall.
Cactus... The most original variety, their inflorescences consist of long narrow, folded petals, sometimes dissected at the ends.
Application

Planting dahlias with tubers When to plant dahlias Dahlias after winter photo and video
The medicinal properties of dahlias make it possible to classify them as medicinal plants. Decoctions of these flowers normalize metabolic processes, are useful for the cardiovascular system. Tincture of rhizomes is used as a prophylactic agent against diabetes mellitus. Fresh leaves are applied to the skin to treat acne. Rhizomes are used in crushed form as a mask for aging facial skin. Powder from the tubers is rubbed into the base of the hair follicles to strengthen the hair.
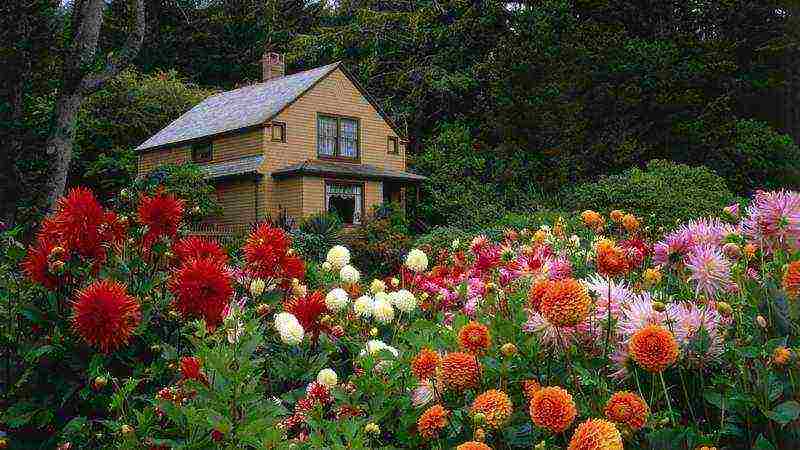

When to plant dahlias in the ground in spring Dahlias photo of flowers in the garden
Low-growing varieties are used for borders, flowerpots, balcony boxes. Most varieties are used in free compositions or group plantings. And especially spectacular, profusely flowering - in single plantings. Varieties with long, strong peduncles are used for cutting and stand well in water for more than a week.
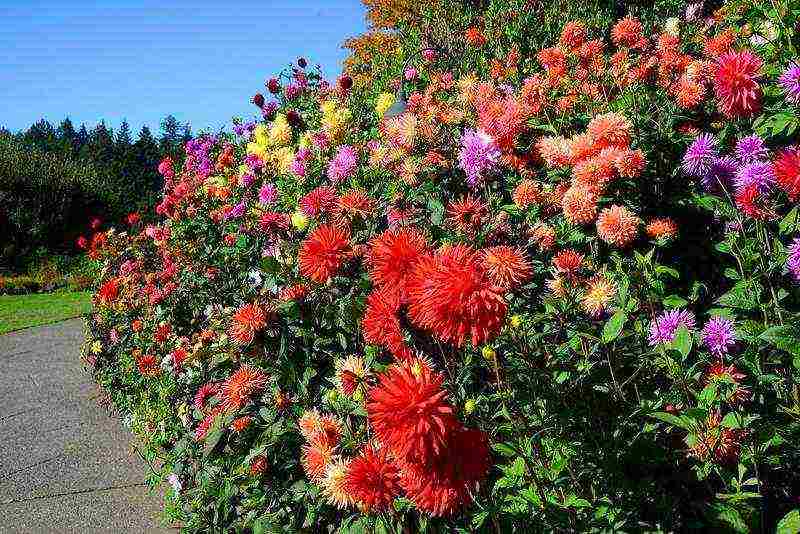

Growing dahlia planting and care in the open field Photo in the garden
Dahlias have always been loved by our flower growers. Some of them collect whole collections - their flower beds attract attention with an abundance of blooming dahlias. The abundance of planting material on store shelves, sufficient unpretentiousness, lush blooming put dahlia among the most popular plants in our plots.

Dahlias tubers in spring When to plant dahlias Planting and care photo and video
Dahlias are a luxurious decoration for any flower bed. Bright, large flowers attract a variety of shapes and colors, while planting dahlias and caring for them in the open field is not very difficult.
 Bright and elegant dahlias are a wonderful and demanding decoration of the garden.
Bright and elegant dahlias are a wonderful and demanding decoration of the garden.
When choosing a place where dahlias will settle in the future, you need to take into account the purpose of their cultivation - decorative or reproduction for sale. If the plans include the implementation of dahlia tubers, then the planting scheme will differ from that when growing these flowers to decorate the site.
The recommendations below for planting dahlias and caring for them in the open field are relevant for central Russia and the CIS countries (Primorsky, Altai Territories, the southern part of the Khabarovsk Territory and Western Siberia, the Southern and Middle Urals, the Baltic States, Belarus, the northwestern part of Ukraine) ... When growing in more southerly regions and countries, you will have to make adjustments for the climate, shifting the timing of planting and harvesting, as well as changing agricultural technology.
When choosing a place to grow dahlias, you need to take into account their features, including:
- high water demand (the higher the air temperature, the more water is needed);
- short growing season;
- the need for support and a garter due to the fragility of the stems.
It is important to create an optimal microclimate that will allow you to get the maximum decorative effect of dahlias in a relatively short period. The landing site should be protected from cold north, north-east and north-west winds and drafts, warm up well. In combination with a low air temperature (from +1 to -4 degrees), strong winds can cause dahlias to freeze, especially if they were recently planted from greenhouses or greenhouses and did not have time to get the necessary hardening.
In the southern regions, the danger is posed by dry winds - northeastern, eastern and southeastern winds carrying heated dry air. They dry out the soil and the aboveground part of the dahlia, causing the young foliage and plant tops to be burned.
To protect the flower beds with dahlias from the winds, the site is planted with trees, ordinary or fruit, using fences or protective strips. Often the site is given a slope - south or south-east for the middle zone and north or north-west for the southern regions.
Important! Lowlands, hollows, valleys should be avoided, where cold air usually accumulates and late spring frosts often occur.
In the shade of trees or fences, dahlias grow beautifully and retain a high decorative effect if the sun illuminates them for at least half a day. At the same time, planting these flowers in the area of \ u200b \ u200bthe root system of large tall trees should be avoided, since they will not be able to bloom normally and form viable root tubers.
When choosing a site for planting dahlias, great attention should be paid to the issue of the occurrence of groundwater. They should not rise above 60-70 cm from the ground surface. If the water rises higher in the area, a flower bed with dahlias should be artificially raised to protect their root system from decay.
In hot southern regions, on the contrary, they often arrange flower beds with dahlias in a depression surrounded by ramparts of earth. At night, this depression is filled with water to ensure sufficient moisture supply to the roots.
Soil preparation
Dahlias prefer moisture-absorbing, structural soil, which is also highly permeable to water. The wrong choice of soil is very often the cause of the death of dahlias. You can improve the structure of the soil with organic additives:
- humus;
- fresh or rotted manure;
- peat;
- straw cutting;
- compost;
- turf and other materials that are readily degradable in the soil.
In heavy, clayey soils, to improve water permeability, add:
- coarse river sand;
- gravel;
- ash (peat or coal);
- peat;
- coal slag (fine, sieved and washed).
If the site is dominated by sandy soil that does not hold water well and is easily eroded, you can add to it:
- vermiculite or perlite;
- peat;
- clay and other materials to help retain moisture.
Advice: it is not required to clear the soil of gravel or small stones; such additives in any type of soil will not interfere with the normal development of dahlias.
Dahlias are not too demanding on the acidity of the soil and can put up with its excess or lack, but they show the best results on slightly acidic or neutral soils. But strongly alkaline soils inhibit their development and growth. Before planting dahlias, you can analyze the acidity in order to then bring it to the desired indicators:
- at a Ph value of 4-5, slaked lime is introduced into the soil (30-100 kg per 100 square meters);
- at Ph 8 and above, the soil is acidified by introducing peat into it.
The place where the dahlias will grow is plowed deeply in the fall - by 30-35 cm. Then, 2-3 weeks before planting the flowers, the soil is dug up or plowed again, paying special attention to harrowing and loosening.
Planting dahlias
Exactly when to plant dahlias outdoors in spring depends primarily on the region. As a rule, in the middle lane this is done after June 1-10, when the last night frosts leave. At this time, already grown tubers are planted. You can plant them earlier - around May 15-20, as soon as the soil warms up enough. Unsprouted tubers are planted, which have pronounced eyes. Shoots appear after 2 weeks. With such a planting, it is necessary to constantly monitor the air temperature and, if there is a threat of frost, cover a flower bed with dahlias.
It is interesting. To obtain even earlier flowering in May, already grown tubers can be planted, but in this case, they will need constant shelter from frost and cold air.
Before planting dahlias, you need to prepare seats for them. Next to the stakes driven into the ground, holes are dug in the soil. The distance between plants should be equal to half the height of an adult plant - approximately 60-100 cm, between rows - at least 1 meter.
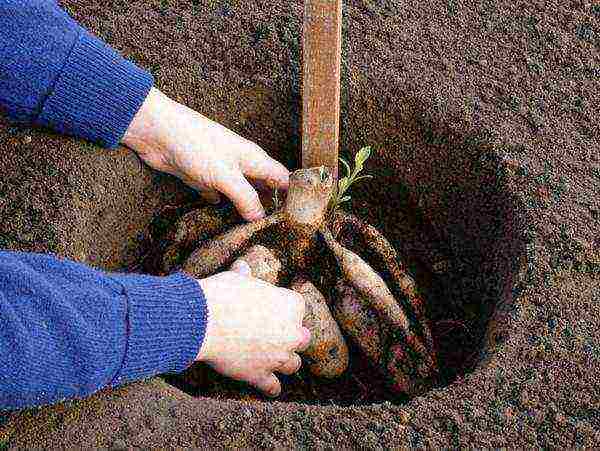 It is very important to immediately establish a support for the flower, since if you do this later, there is a very high probability of damage to the root tubers.
It is very important to immediately establish a support for the flower, since if you do this later, there is a very high probability of damage to the root tubers.
Stakes for supporting dahlias must be strong and high - at least 160-180 cm.It is better to make them from coniferous wood, they will last longer. To increase their service life, they are treated with a 7% solution of ferrous sulfate and painted. Even more durable will be metal stakes - from old pipes or fittings with a diameter of 12-20 mm.
Stakes are driven to a depth of 40 cm, then sprouted tubers are planted in the hole, placing them closer to the support. At the same time, the root collar of the tuber should be 4-5 cm below the soil level. If the seedling was obtained from a cuttings or is a hybrid seedling, it is planted deeper, 8-10 cm.
Recommendation: it is better to plant cuttings seedlings two in each hole.
It is better to plant dahlias with tubers in spring in cloudy weather or in the late afternoon, so that the plants do not suffer from the sun and have time to settle in a new place. Seedlings obtained from cuttings or divided tubers are poured abundantly with water before planting, and then placed in a hole, trying not to break the lump and not damage the plant itself. For the convenience of watering, ring-shaped holes are made around the planting pit, or they simply do not completely fill the hole. Over time, it will become equal to the soil level, and furrows are made for irrigation.
Immediately after planting, dahlias are tied to stakes in 2-3 places - depending on the height of the plant. Labels with the name of the variety are attached to the top of the support. The first few weeks after planting, dahlias need regular, abundant watering. The frequency depends on the temperature and humidity of the air - in dry and hot weather, plantings are watered daily.
Dahlia care
Dahlias are quite demanding in terms of planting conditions and further care. To achieve high decorativeness of the flower bed, it will be necessary to provide the plants with the most suitable conditions.
Watering, loosening, mulching the soil
After the seedlings settle in a new place, watering is reduced, but at the same time the soil under the dahlias must constantly remain moist. With a lack of water, the stems quickly become woody, growth slows down and flowering worsens. It is quite difficult to restore the decorativeness of dahlias after this - it returns slowly, after the onset of cool rainy weather.
To provide dahlias with optimal air humidity, moisturizing irrigation is carried out using sprinklers (with small holes). 10-15 minutes of such watering allows you to increase the humidity for a while in hot weather.
It is very important to keep the soil under the dahlias loosened and to regularly remove weeds. They loosen it, as a rule, after each watering or fertilization. After buds appear on the dahlias, and the green mass of plants closes, loosening stops, and the soil is mulched with peat or humus. This is done to slow weed growth, prevent soil crusting and reduce the amount of watering, as the mulch keeps the soil moist for longer.
Recommendation: in case of excessive development of the vegetative mass, the lower leaves of the bushes are cut off to a height of 30-40 cm in order to improve air ventilation. This avoids the formation of a thick stem at the root collar, which impairs the safety of the tubers.
After the onset of stable cold weather, dahlias huddle. This will protect the roots from the first frost, while the hilling height should be 15-20 cm. If the plants were planted deeply, then hilling can be omitted.
Top dressing
The need to apply mineral or organic fertilizers for dahlias depends on the type of soil in which they are planted. Fertile soils, which were regularly fertilized with organic matter, humus, need it less. To determine which fertilizers dahlias need on a particular soil, you can hand over samples to an agricultural laboratory for chemical analysis. It allows you to plan fertilization for the next 2-3 years.
Fertilization occurs in three ways:
- when plowing the soil before planting;
- when landing in each hole;
- foliar or root dressing.
With the wrong choice of fertilizers, they can be ineffective or even harmful to plants. That is why it is recommended to regularly, once every 2-3 years, carry out a chemical analysis of the soil.
In the fall, for digging, as a rule, organic fertilizing is introduced - manure, composts, especially if they have not had time to decompose enough. In spring, wood ash, superphosphate and aged peat are plowed into the ground.
It is not recommended to introduce readily soluble chemicals into the soil, since they are easily washed out of the soil and are not used by dahlias for their intended purpose. Among such substances:
- ammonium and other nitrate;
- potassium salt;
- urea (synthetic urea);
- potassium chloride.
The latter is advised to be introduced into heavy clay soils. Fertile lands before planting dahlias are not additionally fertilized, but top dressing is applied only to the planting pits. To do this, use humus (leaf or dung) mixed with wood ash or stove soot. 3-4 tablespoons of ash are added to a bucket of compost, a quarter of a bucket of the mixture is added to each hole.
During the period of growth and flowering, dahlias are regularly fed with organo-mineral fertilizers - once every 12-14 days. To do this, use diluted cow manure or chicken manure (for 10 liters of water, 1 liter of manure solution or 0.5 liters of chicken manure solution) with the addition of potash (15 g) or ammonium (10 g) nitrate, superphosphate (15-20 g) and potassium sulfate (10-15 g). A bucket of fertilizing mixture (10 L) is divided between 4-5 plants.
Such dressings continue until mid-July, then they are replaced by phosphorus-potassium fertilizers. And after the second half of August, preference is given to phosphorus fertilizing. After each fertilization, the bushes must be watered from a sprinkler.
Important! Lack of water, phosphorus and potassium can slow down the transfer of nutrients from the stem and leaves to the root tubers in autumn.
Preparation for wintering
Dahlias do not hibernate outdoors. In the fall, after the ground part dies off (as a rule, after the first frost), the root tubers are dug up and stored.
It is necessary to dig out the tubers on the first day with a positive air temperature, because with a delay, the buds can wake up and cause the tuber to rot. Before digging, the stems are cut with a garden pruner at a distance of 3-4 cm from the root collar, and then using a pitchfork or a shovel, remove the nests from the soil. The tubers are laid out in boxes and placed in a cool, damp room for several weeks (+8 degrees with a humidity of 80%).
After 2-3 weeks, the nests are cleaned of small roots and old tubers, the cuts are processed, and stored in boxes. The bottom of the boxes is covered with earth with a layer of 3 cm, then the tubers are laid out and covered with earth. The boxes are stored at a temperature of 1-7 degrees Celsius and high humidity (80-100%).
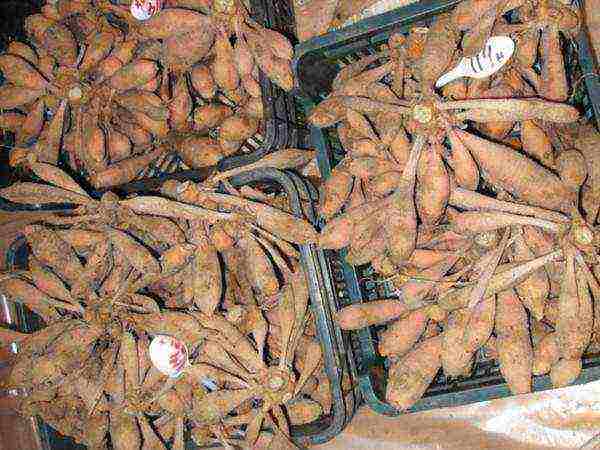 There are several ways to store tubers in winter. Each gardener chooses the most convenient for himself. The main thing is to ensure the safety of the planting material.
There are several ways to store tubers in winter. Each gardener chooses the most convenient for himself. The main thing is to ensure the safety of the planting material.
You can also store the tubers by treating them with a clay mash. The peeled root tubers are washed under running water, dried in the sun, dipped in a chatterbox and dried again. The resulting "dragees" are sent for storage until spring.
Bush formation
In the case when the reproduction of dahlias took place in tubers, it is recommended to leave the two strongest shoots for each seedling, removing all the rest as early as possible. Cuttings are grown, as a rule, in one stem, sometimes pinching the top above the third internode to add splendor to the bush.
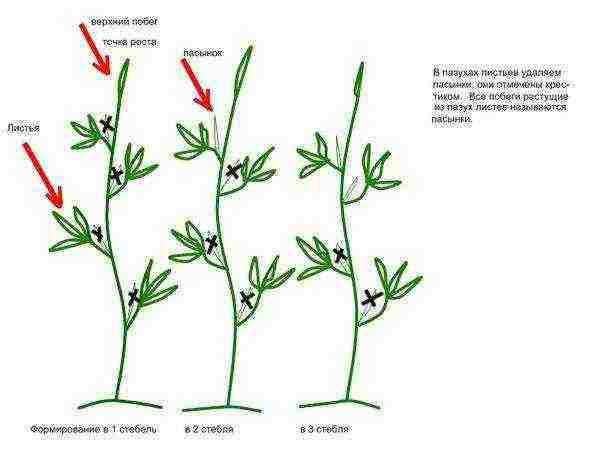 As a rule, dahlias are grown in 1 or 2, less often 3, stems, so as not to thicken the bush too much
As a rule, dahlias are grown in 1 or 2, less often 3, stems, so as not to thicken the bush too much
For large-flowered varieties, a mandatory measure is the regular and complete removal of all stepchildren formed on the stem - lateral shoots in the leaf axils. This is done as early as possible and as close to the stem as possible.If the stepchildren are not removed, especially on the lower part of the stem, then the growth of dahlias slows down, the flowering decreases, and the size of the flowers decreases. In addition, stepchildren close to the ground often break off, and fungal infections can easily occur at the site of the break, which will cause the death of the entire plant.
The removal of stepchildren is carried out regularly, from the moment of planting and until the buds are formed. Lateral shoots are removed to the internode preceding the one where the bud was formed.
Important! Dwarf, pompom, collar and small-flowered types of dahlias are not stepchild.
Quite a few species and varieties of dahlias need to be removed not only stepchildren, but also buds. This is especially true for those plants that are grown for further cutting or participation in exhibitions.
As a rule, on the stems of dahlias, buds are formed in groups of three. The middle bud usually develops faster than the others, but at the same time it has a short peduncle, which is not very convenient for cutting. Therefore, the central bud is removed, after which the remaining two develop faster, have a longer peduncle and are distinguished by lush flowering.
During the flowering period, in order to preserve the decorativeness of the plant, faded inflorescences should be removed daily, which spoil the appearance of the bush.
Formation of undersized bushes
Almost all varieties of dahlias are tall - from 160 cm and above. If you need to get a stunted plant, you need to follow the following algorithm:
- At the end of February, parts of the tubers are planted in nutrient soil and placed in a well-lit place at a temperature not lower than + 15-20 degrees.
- After the emergence of shoots, 1-2 are left, the most powerful. The rest can be used as cuttings.
- Above the fourth pair of leaves at the bush, pinch the top.
- As a result, two stems develop from one, each of which is pinched again after the second pair of leaves.
With such a pinching system, the bush does not grow more than 1 meter in height. The grazing of such dahlias is carried out according to the general scheme.
Reproduction and preparation of tubers for planting
Dahlias are propagated by seeds, cuttings or parts of tubers. Since it is quite simple to grow dahlias from tubers, while getting 3-5 new ones from one tuber, this method is the most common. Root tubers dug up in autumn in early April begin to prepare for planting. To do this, they are kept for 10 minutes in a solution of potassium permanganate and left in a warm, well-lit room for about a week.
As soon as sprouts 7-9 mm long appear on the tubers, you can start dividing. One medium tuber can usually be divided into 3-5 parts. It is important to ensure that at least 2 kidneys remain on each division. A sharp knife is used for dividing, acting very carefully so as not to damage the root collar.
Recommendation: if dry or rotten parts are found during the division, they are removed, and the cut site is treated with crushed coal or foundation.
The prepared parts of the tubers are planted for germination in boxes with a mixture of sawdust, peat, river sand and humus. They sit in these boxes until the onset of stable heat without recurrent frosts, when they are transplanted into open ground.
Propagation by cuttings
It is recommended every two years to replace old tubers with new ones obtained from sprouted cuttings. Cutting dahlias allows you to update the planting material, preserving the varietal characteristics of the mother plant.
For renewal, the healthiest and most consistent with the characteristics of the variety, the tuber is selected, planted in the nutrient soil at a third of its height. After a while, sprouts begin to appear. When they reach a height of 2 cm, they are cut off and put to rooting.
 After the sprouts appear, watering is reduced, and the temperature is lowered to + 15-17 degrees so that the cuttings do not stretch
After the sprouts appear, watering is reduced, and the temperature is lowered to + 15-17 degrees so that the cuttings do not stretch
You can root cuttings in water or in a substrate.To accelerate root formation, it is recommended to treat them with stimulants. Cover pots or containers with cuttings with plastic wrap and place in a warm, bright place.
Important! The mother tuber will release new shoots after a while. In total, up to 30 cuttings can be removed from it.
Seed propagation
Typically, seed dahlias are grown as an annual crop. They can be planted in seedlings or sown directly into open ground.
To obtain seedlings, seeds are sown in early April in loose soil, the containers are covered with foil or glass. Seedlings appear already on the 4th-7th day. Two weeks after the emergence of seedlings, they are dived into separate pots. In open ground, matured and pre-hardened seedlings are planted after the end of night frosts, observing a distance of 20-25 cm between the plants.
When sowing in the ground, the seedlings will need to be thinned out in order to provide the plants with room for growth. Dahlias are sown in May, after the threat of night frosts has passed. Crops will bloom only towards the end of August.
The brightest representatives of annuals are pompon dahlias, varieties "Gelleri", "Sylvia", "Merry Guys"; they are grown from seeds using the same technology.
Despite the fact that dahlias require quite a lot of attention and participation from the gardener, their bright and lush bloom will adorn any flower bed. With some effort, you can admire the luxurious inflorescences until the first frost.
Moscow, Russia, on the site since 11.01.2017
varieties ❀ planting ❀ care
Dahlias (lat.Dahlia) are from the aster family. These are some of the most beautiful and long-flowering garden flowers, represented by the widest palette of colors and variety of shapes. They bloom from July until frost. In addition to the variety of forms, dahlias are also distinguished by a variety of colors, and there is even a black dahlia, or rather, red-black, which appeared due to the accumulation of a large amount of anthocyanin pigments in the plant.
| ARTICLE IN THE TOPIC: Forcing bulb flowers at home |
The shapes, colors and varieties of dahlia are so diverse that they can be used to decorate not only flower beds, but also border lines, as well as as salt, even potted, plants. Dahlias are dazzlingly beautiful, but at the same time they are completely unpretentious. The main thing that is required for their successful growth and lush flowering is to choose the right planting site, provide the necessary soil composition, timely watering and feeding. You need to buy seedlings not earlier than mid-spring, and the tubers should be fleshy and strong, with already noticeable, but not tall sprouts. It is better not to take soft or dry tuber.
Dahlias growing from seeds
Growing dahlias involves laborious digging and responsible storage of tubers, but if you are afraid of these chores, you can grow annual dahlias from seeds. Annual dahlias are as beautiful and unassuming in culture as perennials, and their choice is wide enough: Coltness hybrids up to 50 cm high with abundant non-double flowers of various colors; bronze-leaved Redskin; terry small Rigoletto; early Figaro .. You can, having bought seeds, sow them in open ground in mid-May, but then they will bloom only by mid-August. If you want to achieve an earlier flowering, you will have to germinate the seeds.
To do this, in early April, you will need to sow dahlia seeds in greenhouses or plastic containers, using calcined sand as soil: seeds are poured onto a layer of sand, sprinkled with sand on top, moistened well and covered with transparent polyethylene. You need to germinate the seeds for about ten days at a temperature of 25-27 ° C, then the sprouts need to be dived into separate pots. The soil mixture should be moisture-absorbing and loose, you can buy it, or you can prepare it: one part of peat and sand and two parts of leafy soil.Three days before picking, the soil must be treated with a hot solution of potassium permanganate (70 °) of a dark pink color. After picking, the seedlings are watered as the soil dries up. In mid-May, it can be planted in the ground.
Dahlias planting in open ground
You need to start preparing by choosing a landing site. The dahlia flower hates drafts, but requires a well-ventilated and well-lit place, so dahlias should be planted in a sunny area, protected from the wind. The soil on the site must be well-drained, permeable and nutritious. Dahlias can grow in soil with a lack or excess of acidity, but a slightly acidic or neutral environment will be optimal for them. If the soil on the site is too acidic (pH 5-4), add slaked lime to it, but if the pH is more than 8.5, you can "acidify" the soil with peat.
In autumn, when digging, enrich the area allocated for dahlias with humus and compost (3-5 kg per 1 m3). In the spring, before planting, sprinkle mature compost (not deciduous) and some wood ash on the site again and rake it. To save dahlias from diseases and prevent them from degenerating, it is advisable to change the planting site every year, giving the soil a rest from dahlias for at least three years. Do not plant dahlias where asters or plants that are susceptible to fungal diseases grew before them.
In April, the roots of dahlia (tubers) should be prepared for planting: clean them of dry roots, remove damaged areas by treating all sections with brilliant green. Then the tubers are planted in a container with nutritious soil or peat so that the dahlia tubers protrude 2-3 cm above the surface, and they are kept for two weeks at a temperature of at least 18 ° C with good lighting. As soon as the buds appear, the tubers are cut into pieces so that each has a bud with a root collar.
Sometimes one tuber gives five such parts. The tubers, divided into parts, need to be germinated for some time in the box, and then, after removing the side shoots that have reached a height of 10 cm, they should be planted in the soil. Cut shoots can be used as cuttings: plant in soil, place in a dark place and water well. The established cuttings are planted in a permanent place. Tubers are divided and cuttings are made to increase the amount of planting material and prevent plant degeneration. If you do not have such a need, you can not divide the tubers.
Dahlias can be planted in the ground when the ground warms up, usually in late May or early July. The holes for the dahlias should be three times larger than the lump of roots (40x40x40), so that the roots of the dahlia sink into them completely and there is still 5-7 cm left.At the bottom of the hole, lay a layer of rotted compost or manure, then sprinkle the manure with earth so as not to burn the roots of the dahlia , lay the sprouted tuber and dig in so that a few centimeters of the stem are under the ground.
If you have chosen a variety of tall dahlias, install and secure immediately a support for the future stem. After planting, water the seedlings abundantly with cold water, and mulch the soil around them with a five-centimeter layer of fine tree bark or sawdust, having previously mixed them with peat or compost.
Dahlias outdoor care
Mulching a plot with dahlias, in addition to protecting plants from slugs, will give you the opportunity to abandon such tedious work as weeding and loosening the soil, and also prevent the soil from drying out quickly on hot days. Dahlias should be watered abundantly 1-2 times a week (unless it rains), but do not let moisture stagnate in the roots: dahlia tubers are prone to decay. In extreme heat, hilling after watering helps to retain moisture. Before the next watering, the soil should be shaken off from the stems, the plants should be watered, and then the soil should be piled up again.
Fertilizing dahlias. In the process of growth, dahlias need to be fed every two weeks, alternating mineral fertilizers with organic ones: ammonium nitrate (15 g per 1 m3), tincture of mullein 1:10 or bird droppings 1:20.With the appearance of the first buds, they begin to apply superphosphate and potash fertilizers at the rate of 30 g per bucket of water (enough for 8 bushes).
Supports for dahlias. Since dahlias have a hollow stem and strong wind or rain can break them, you need to tie the dahlia to a peg. If the stem does break, try putting a tire on it: attach a sturdy branch to the stem, secure it and support the stem so that it does not bent. Timely and careful caring for dahlias can save even a broken shoot, which will reward you with a beautiful bloom for your care.
Pruning dahlias. If you are not interested in the quantity, but in the quality of the inflorescences, do not leave more than three shoots in the bush, otherwise the inflorescences will be smaller in size and not so decorative. On each peduncle, you need to leave 1-2 buds. Remove faded buds so that they do not delay the formation and growth of new ones. Throughout the season, try to remove the lower side shoots from tall varieties of dahlias, these shoots can then be used as cuttings. In undersized (pompom, cactus) and single dahlia bushes, side shoots can not be removed
Cleaning and storage of dahlia tubers
After the first frost, the dahlia tubers need to be dug up, the remaining foliage and pagons should be cut off, leaving only five to ten centimeters of the stem. Some gardeners cut the stems and leaves a few days before digging up the tubers, but if moisture gets on the cut part, the base of the stem may rot, so after cutting off the stems, immediately cover the dahlias with aluminum foil. The tuber neck is particularly fragile, so start digging up the tubers in the morning, in dry weather, so that they have time to air dry and become less "brittle". In addition, soil residues are easier to remove from dried tubers.
Dig in the plant on four sides at a distance of about 30 cm from the stem to cut the long, conductive roots, move the pitchfork under the earthen ball and push it out of the ground. Thoroughly scrape dirt off the tubers and turn them over to dry. When you have dug up all the tubers, rinse them out of the garden hose from the soil, which contains microorganisms that carry diseases. Do not be late in harvesting tubers, because after the first frost, warming may occur, and the buds sleeping in the tubers may wake up and begin to sprout, which is detrimental to plants at such a time.
How to store dahlias in winter
Proper storage of dahlias in winter is 90% of the success in growing them. Tubers left for winter storage should not dry out too much, because in spring they give rise to weak shoots. Insufficient drying leads to the fact that the roots rot during storage. If any mechanical damage is found on the tubers, they need to be pruned, and then sprinkled with charcoal. Root collars, so that they do not rot during storage, are powdered with ash or chalk.
It is best to store dahlia tubers at a temperature of 3-5 ° C with an air humidity of 60-70% in a well-ventilated area. A dry basement is suitable for this, but vegetables stored nearby can create high humidity, increasing the risk of rot and fungal diseases in tubers. You can put the tubers in a box on a layer of dry peat and sprinkle it with peat, you can use coniferous sawdust or sand instead of peat. If the tubers suddenly begin to dry out or wither, the insulating material is slightly moistened. If there is no ventilation in the basement, you will have to turn on the fan for half an hour three times a week.
If you don't have a basement or cellar and have to store dahlia tubers in your apartment, place the tubers in the coolest place (next to the balcony). You can fold the tubers into plastic bags with insulating material (sawdust, sand, dry peat) and tie tightly. Some growers, wrapping each tuber in newspaper, put them in a plastic bag, which they put in a cardboard box and put in a cool place, for example, on a glazed loggia.Only in this case, you will have to monitor the temperature outside all the time so that a sharp cold snap or frost does not destroy your planting material.
Warm and humid rooms are least suitable for storing dahlia tubers, but you can store them even in such unsuitable conditions if you cover the tubers with paraffin. Melt the paraffin in a water bath, immerse the tuber in it for a second, let the film harden for a few seconds, and again lower the tuber in liquid paraffin. After the waxing procedure, place the tubers together with dry peat, sand or sawdust in a plastic bag and tie it tightly. Before planting, these tubers will need to be rubbed lightly to crack the film.
During the winter, do not forget to inspect the tubers in order to be able to eliminate the possible appearance of rot in time. The affected areas should be cleaned to healthy tissue and treated with hardwood charcoal powder or brilliant green.
Dahlias diseases and pests
Young juicy dahlia stems attract slugs, and the buds attract earwigs, so when the first signs of pest aggression appear, treat the bushes in the evening with broths of wormwood or celandine about once a week. In hot weather, spray dahlias with systemic insecticides against thrips, aphids, ticks and caterpillars. Most of all pests of dahlias are fond of aphids. Try the old-fashioned old-fashioned way of dealing with it: spraying plants with soapy water.
Dahlias species and varieties
Dahlias are classified according to the shape and structure of inflorescences, in modern culture there are 12 main classes of dahlias, but as new varieties appear, new classes appear. We present you the most popular varieties of dahlia:
Simple dahlias
Simple dahlias, which have one row of flowers, reaching a diameter of 10 cm, a height of 45 cm to 60 cm. Varieties of simple dahlias are Yellow hammer yellow, pink Princess marie jose, reddish orange Orangeade.
Dahlias anemone
They have from one or more rows of marginal flowers, in the middle are elongated tubular flowers. The inflorescences reach a diameter of 10 cm, a height of 60 cm to 90 cm.The most popular varieties are Vera Higgins bronze color, yellow-purple Lucy, red Comet.
Collar dahlias
Collar dahlias of the same size, but higher - from 75 cm to 120 cm. They have one outer edge row of flowers, on top of it there is a row of shorter and twisted flowers of a different color, looking like a collar: Chimborazo (red with cream), La Gioconda (scarlet with gold), Claire de luna (yellow with cream).
Peony dahlias
Peony dahlias are slightly larger - from 12 cm to 15 cm, flat marginal flowers from two or more, in the center - tubular flowers. In height, they reach the same dimensions as collar. Popular Fascination lilac and crimson red dahlia Symphonia.
Decorative dahlias
These include the purple giant Jocondo, large yellow Thames valley, miniature orange David Howard... All varieties have terry inflorescences from 8 to 25 cm in diameter, height - up to 60 cm.
Dahlias are spherical
Spherical dahlias are terry inflorescences of a round, sometimes slightly flattened shape, 8 to 15 cm wide and 90 to 120 cm high: red Doreen Hayes, yellow Esmonde and red-peach Crichton honey.
Pompon dahlias
Ball-shaped terry inflorescences from 5 centimeters or more in diameter. The marginal flowers are curled up, with a blunt or rounded end. Reach in height from 90 to 120 cm: pink Noreen, Hallmark lavender and lavender Willo's Violet.
Dahlias cactus
Cactus dahlias have double inflorescences with a diameter of 8 to 25 cm and more, reach a height of 90-150 cm.The marginal flowers are rolled, narrow and sharp: giant pink Danny, miniature yellow Pirouette, large red Visit, fine red Doris Day.
Semi-cactus dahlias
: Terry inflorescences 8-25 cm in diameter, 90-150 cm high, marginal flowers are curled from the middle of the length to the ends: large yellow Nantenan, miniature yellow Yellow Moodmedium orange Autumn fire and white small White swallow.
Nymphaean dahlias
Similar to water lilies, terry, beautiful regular shape, 7-20 cm in diameter, 70-130 cm in height: purple Brushstrokes, pale pink Gerry Hawk, snow-white Genette.
Mixed dahlias
Mixed species include dahlia species that are not similar to any of the other varieties listed.
Where to buy dahlia tubers
The Scientific and Production Association "Sady Rossii" has been introducing the latest achievements in the selection of vegetable, fruit, berry and ornamental crops into the wide practice of amateur gardening for 30 years. In the work of the association, the most modern technologies are used, a unique laboratory for microclonal reproduction of plants has been created.
The main task of NPO Sady Rossii is to provide gardeners with high-quality planting material for popular varieties of various garden plants and novelties of world selection. Delivery of planting material (seeds, bulbs, seedlings) is carried out by Russian post.
We are waiting for you to shop at the Sady Rossii NPO.
Did you like the article? Share with your friends on social networks:
Aster from the Asteraceae family came to Europe from China in the 17th century. Since that time, flowers have become an integral attribute of the autumn landscape of garden and park compositions. A simple planting and caring for asters in the open field contributed to the rapidly growing popularity and universal love.
Varieties and varieties
In the wild, mainly in North and Central America, from 200 to 500 species of the genus Aster grow (according to different sources, the numbers vary significantly).

All varieties are divided into two large groups:
- Annual asters - the group is represented by single-stemmed herbaceous plants with large inflorescences, which are often grown for cutting.
- Perennial - bushy plants with highly branching shoots.
Perennial asters
The classifications of perennial varieties are based on such a parameter as the flowering period, which unites asters into two subgroups: early flowering and autumn flowering.
Early flowering

A large subgroup, including such prominent representatives as:
- Alpine aster is a perennial aster with a height of 15 to 30 cm, which blooms in late spring. Popular varieties: Wargrave, Glory.
- Italian aster - chamomile aster with large corymbose inflorescences, which are observed in the first half of summer. Plant height can reach 70 cm. Rosea, Rudolf Goeth stand out from the varieties.
- Aster Bessarabskaya is a branchy, medium-sized bush up to 75 cm in height, the shoots of which are crowned with inflorescences painted in lilac tones.
Autumn blooming

A subgroup characterized by a variety of species composition:
- Shrub aster is the earliest flower of the subgroup, the height of leafy stems of which does not exceed 60 cm. The most famous varieties: "Niobe", "Blue Bird".
- New Belgian aster is a widespread variety in gardens. It is represented by both tall and dwarf varieties, among which dwarf Snowsprite, Jenny, medium-sized Royal Velvet, Winston S. Churchill, tall Dusty Rose, Desert Blue deserve special attention.
- New England aster - another popular variety is represented by tall plants, up to 160 cm high with a large number of small inflorescences. Common varieties: Browmann, Constance.
Annual asters
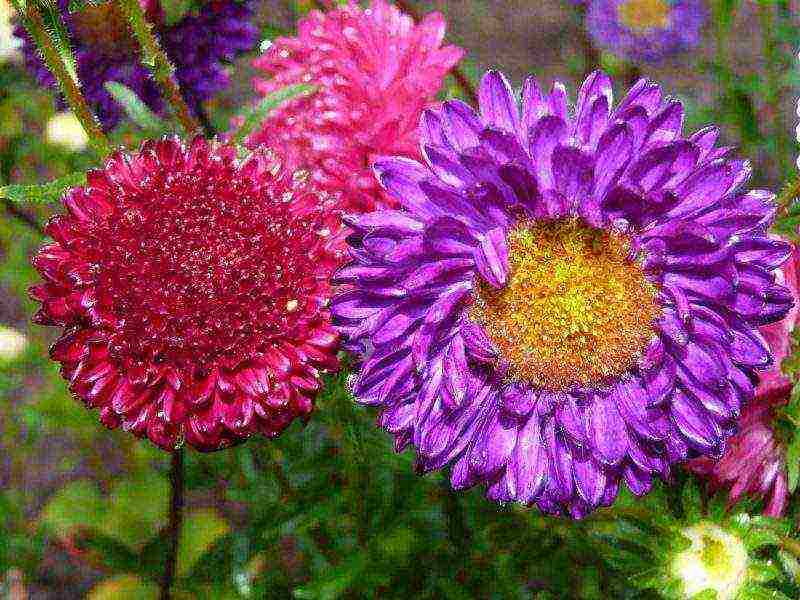
Garden aster, or also known as callistephus (Chinese monotypic genus), has over 4,000 different varieties that are often mistaken for dahlias, chrysanthemums and even peonies.

There are several classifications based on different parameters:
- by the timing of flowering (early, middle, late);
- in height (dwarf, undersized, medium-sized, tall, giant);
- for the purpose of cultivation (shearing, casing, universal);
- by the structure of inflorescences (tubular, transitional, reed).
Among the huge variety of varieties, the spherical large-flowered aster "American Beauty", the needle "Record" with medium inflorescences, the curly variety "Ostrich feather" and the semi-double "Rosette" stand out.
Growing asters from seeds
Aster is grown from seeds in two ways: seedling and non-seedling.
Seedless planting of asters
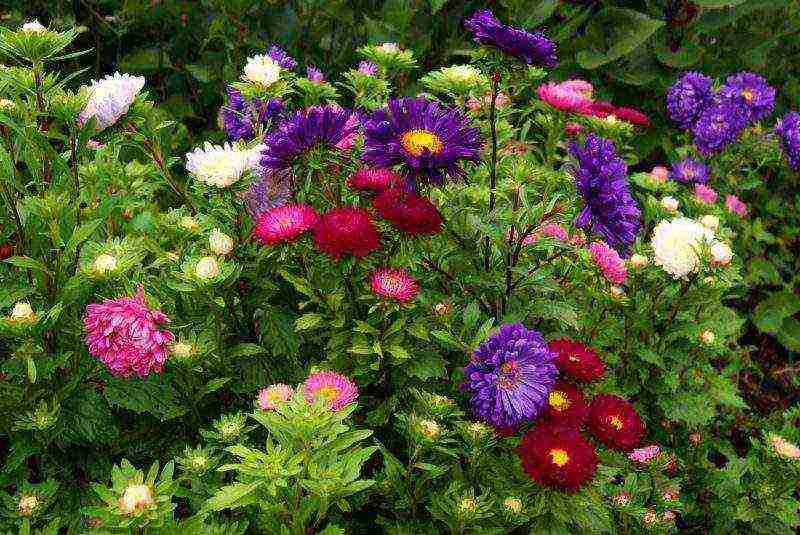

Sowing of early varieties is carried out in early or mid-March, and later ones - in the second half of spring, when the weather is stable above 10 ° C.
Wherein:
- Grooves are prepared with a depth of 4 cm.
- Seeds are placed in the grooves and filled with water.
- With the arrival of dry weather, crops are mulched.
- After the formation of two pairs of true leaves in the seedlings, the rows are thinned out so that an interval of 15 cm remains between the seedlings.
In addition to spring time, asters are planted in the fall before winter:
- On the frozen soil, grooves are made into which the seed is placed, which is practically not damaged by fusarium.
- After the snow melts in the spring and the emergence of seedlings, thinning is carried out.
Sowing asters for seedlings
The seedling method is more reliable, while asters grown through seedlings, the florist will be able to admire much earlier.
Sowing is carried out in the first half of spring as follows:
- 7 days before sowing, the seed, wrapped in cloth, is soaked in a manganese solution for 10 hours.
- After the allotted time, the fabric is wrung out and, together with the seeds, is placed in cellophane for germination.
- The seedling boxes are filled with a light substrate, which is watered with a fungicidal solution for disinfection.
- The seeds are planted to a depth of 5 mm.
- The container is covered with glass, after which it is moved to a warm place.
- When shoots appear, the seedlings are taken out to a room with a temperature of 16 ° C.
- After the seedlings have two pairs of true leaves, they are picked with shortening of the roots.
Planting seedlings in open ground
Before planting, the seedlings are hardened. The optimal time is the second half of spring, when the seedlings reach a height of 10 cm and have 4 pairs of true leaves.
Site selection and soil preparation

Asters thrive in sunny areas with well-drained, light neutral soil.
The soil for flowers is prepared in advance:
- In the fall, humus is introduced under deep digging with an application rate of 2-4 kg per 1 m2.
- In the spring, the site is loosened again with the simultaneous introduction of complex mineral fertilizers at the rate of 50 g of nitroammofoska per 1 m2.
Landing technology
The disembarkation procedure is carried out as follows:
- Shallow holes are dug with a distance of 20 cm from each other and a row spacing of 50 cm.
- The landing pits are filled with water.
- After drying, seedlings are lowered into the grooves, which are sprinkled with soil.
Garden aster care
Asters are unpretentious, so leaving will not take a lot of time and effort from the grower.
Watering and loosening
Water the plants abundantly, but not too often. In a dry summer, water consumption per 1 m2 is 3 buckets. After each moistening, the soil will lie down loosening to a depth of 4-6 cm.
Weeding and hilling
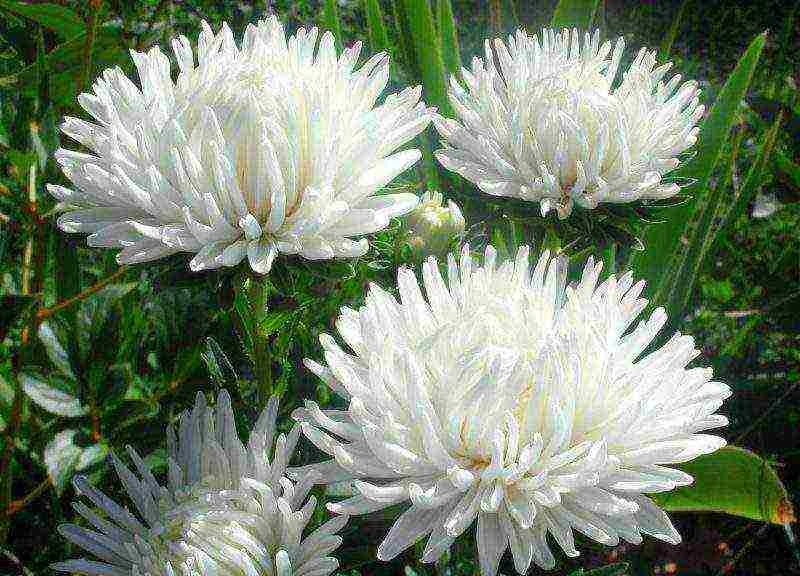

To accelerate the growth of the root mass before the start of branching of the aster stems, it is recommended to spud to a height of 8 cm. An important care measure is the cleaning of the soil from weeds.
Top dressing

For lush flowering, plants need additional nutrition, which is carried out at least three times per season:
- 10 days after planting seedlings in open ground, fertilizing is carried out using complex mineral fertilizers, which include nitrogen.
- In the budding phase, phosphorus-potassium fertilizers are applied under the plants.
- At the beginning of flowering, asters are fed for the third time also with fertilizers with a high content of potassium and phosphorus.
Asters have faded - what to do?
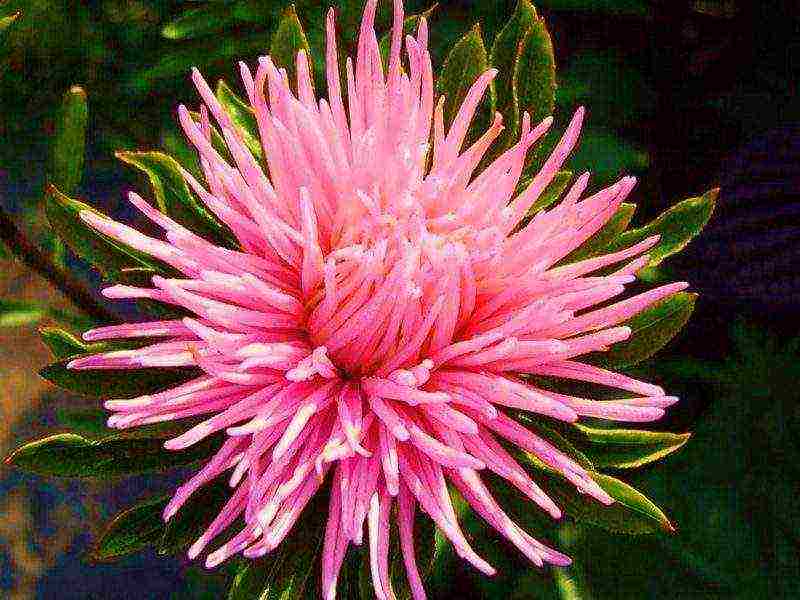

If annual varieties grew on the site, then all plant residues should be removed and burned, having previously collected the seeds from the varieties you like. Sowing material can be sown before winter, but in a different area that is not infected with specialized harmful organisms.Perennial representatives of the culture are winter-hardy and can grow in one place for up to 5 years. When the age limit after flowering is reached, it is worth digging up the bushes and dividing them. Place the delenki in other areas.
Diseases, pests and care during this period
A delicate and graceful flower, in violation of cultivation techniques, can be affected by both diseases and pests. Among the diseases, the greatest danger is fusarium, which does not respond to treatment, as well as rust, powdery mildew and black leg, which develops in the seedling phase. Of the pests on asters, there are meadow bugs, slobbering pennits, plowed slugs, common earwigs, spider mites, kidney aphids and scoops, which should be fought with systemic insecticides.
Use in landscape design

The choice of an art object for the design of which asters will be used depends on the size of the variety. For example, aster heather ground cover is perfect for decorating an alpine slide, and medium-sized varieties of Italian asters will be harmoniously combined with decorative yarrows in a mixborder. Flowers will fit into any floral arrangement, if you choose the right shape of the plant.
Thus, aster is a beautiful flower with high decorative qualities, which, with all its grace, remains undemanding to care for.


