Content
- 1 Lavender care
- 2 Propagation of lavender by cuttings or layering
- 3 Growing lavender from seeds at home
- 4 Autumn lavender pruning
- 5 Spring pruning lavender
- 6 Landing place
- 7 Features of planting lavender
- 8 Sowing lavender seeds
- 9 Soil processing near bushes
- 10 Pruning lavender bushes
- 11 Fertilization
- 12 Preparing for winter
- 13 Types of lavender
- 14 Features of growing lavender
- 15 Role in landscaping
- 16 Popular varieties
- 17 Planting methods
- 18 Care in the garden from the moment of planting in the open ground
- 19 Features of cultivation in different regions
- 20 Useful Growing Reviews
 It is impossible to walk past the area where lavender grows. And the point is not even in the luxurious lilac bushes, but in the enchanting aroma that they spray around the neighborhood. And for a minute, frozen near this magic, you are already rushing home at full speed, elated. You need to find out as soon as possible: how capricious lavender plant is, are planting and care difficult, what is it sick of? After all, the fact that from now on it will be in your garden is a question that has already been resolved.
It is impossible to walk past the area where lavender grows. And the point is not even in the luxurious lilac bushes, but in the enchanting aroma that they spray around the neighborhood. And for a minute, frozen near this magic, you are already rushing home at full speed, elated. You need to find out as soon as possible: how capricious lavender plant is, are planting and care difficult, what is it sick of? After all, the fact that from now on it will be in your garden is a question that has already been resolved.
Description: varieties and varieties of lavender
Lavender is an evergreen, rather unpretentious plant widely used in cosmetology and medicine. The scent of lavender has a calming effect and helps relieve headaches. But not only medicinal properties are appreciated in lavender. It is widely used in perfumery and cosmetology. Lavender and cooking did not pass by, because this plant has a specific spicy taste. And in everyday life, dried lavender sprigs are used as a reliable remedy for moths.

There are many varieties of lavender. Which one to plant in your garden - choose according to your taste
More than 25 types of lavender are known, but several varieties are most popular in the garden culture.
Narrow-leaved lavender (English). It is a bush no more than a meter in diameter. The leaves of this variety are medium-sized, narrow, gray-green. Blooms in June and July. The variety is unpretentious and tolerates low temperatures well.
Lavender broadleaf (French). This lavender variety is considered the ancestor of the decorative varieties. It differs from other varieties in a wide color range of inflorescences, as well as a very strong and not always pleasant aroma.
Hybrid lavender (Dutch). This variety is considered the largest. Its bushes can grow up to two meters. It is a natural hybrid of narrow-leaved and broad-leaved varieties. Blooms in July. Its frost resistance is lower than that of narrow-leaved. Refers to industrial grades.

Dutch lavender has the most beautiful flowers
Lavender toothed. One of the most thermophilic varieties. Prefers to grow indoors rather than outdoors. It is the owner of soft silvery leaves and inflorescences of large flowers in all shades of purple.
Planting a plant
Lavender can be propagated in different ways: cuttings, dividing the bush, layering, seeds. Lavender seeds can survive for many years if you follow the rule: store them in sealed containers.
Attention! Lavender seeds need to undergo preliminary processing - stratification. For this, the seeds must be kept at a temperature of +5 ° C for at least two months.Most often, for this purpose, the seeds are mixed into wet sand and placed in a refrigerator.
Lavender seeds can be sown directly outdoors, but certain requirements must be followed.

Lavender seeds
The best time to plant lavender outdoors is October. It is sown to a depth of no more than 4 mm, the soil must be slightly compacted. If the weather is dry, then the seeds can be watered. In winter, the area sown with lavender should be covered with snow as much as possible.
In open ground, you can sow seeds in the spring. To do this, first, in March, you need to remove the seeds in the refrigerator for stratification, and in May sow in open ground in a previously prepared place.
Advice. Choose a place for lavender in a dry and sunny area. This flower does not like waterlogging.
Lavender care
Water the lavender only when the soil is dry. Excessive moisture leads to root decay, but it is not recommended to dry out lavender either.
In autumn and spring, shrubs need to be hilled, and cutting lavender significantly extends the life of the plant. A small pruning can be done immediately after the lavender has faded, but a more significant shortening should be done only at the end of autumn, leaving up to 4-5 new green shoots.

Prune the bushes - this will not only give them a more decorative look, but also benefit the plant.
If your lavender will be hibernating outdoors where temperatures drop below -25 degrees, provide a warm shelter. To do this, it will be enough to cut the bushes before wintering and cover them with branches of coniferous trees.
Attention! Covering lavender with foliage, as is usually done to protect plants from freezing, should not be, this may result in plant decay.
Fertilizing and feeding lavender
In spring, it is recommended to feed lavender with nitrogen fertilizers. To do this, you need to dilute 1 tbsp. l. urea or 2 tbsp. l. "Sodium humate" for 10 liters of water. The consumption of such a solution for 1 bush should be no more than 5 - 6 liters.
At the beginning of flowering, lavender can be fed with a fertilizer solution "Agricola-Fantasy" (it is diluted in a proportion of 2 tablespoons per 10 liters of water). The consumption of this solution is 3-4 liters per one bush.

To make lavender bloom better - feed the plant with mineral fertilizers
Instead of Agricola, a solution of organic fertilizer Rossa Universal is also used, dissolving 2 tbsp. spoons in 10 liters of water. And the third option for feeding: 2 tbsp. l. dilute nitrophosphate and half a liter of liquid mullein in 10 liters of water. The consumption of the last two solutions is 10 liters per bush.
Plant propagation
Lavender is propagated by division, cuttings or layering.
Reproduction by division perhaps when there are already lavender bushes on the site. In summer, lavender produces a lot of young growth. It is something that can be rooted. To do this, you need to cut the plant and huddle in such a way that all the free space between the stems is densely filled with earth. And by the fall, the bush can be divided.

Dividing the lavender bush
The most suitable way to propagate home-grown lavender is propagation by cuttings... To do this, lignified annual shoots should be divided into cuttings no more than 10 cm and rooted.

Propagation of lavender by layering
The easiest breeding method, which is suitable even for novice gardeners, is reproduction by layering... With this method, in the spring, 2-3 shoots are carefully folded back and placed in a groove 3-5 cm deep, fixed, sprinkled with earth and watered. These shoots need to be watered a little more abundantly in order for the formation of lateral roots to occur successfully. After a year, the shoots are already completely independent, and you can plant them from the mother bush.
Diseases and pests
Lavender is not very susceptible to diseases, and parasites attack it infrequently, but this does not mean that nothing like this can happen. Of the diseases, gray rot is most common. Caring for a diseased plant consists in cutting off the damaged parts.The cut off parts must be burned.

Monitor plant health and remove insects
Of the garden pests on lavender, you can find the rainbow beetle eating leaves. You need to collect it from plants by hand. But more often lavender is prone to the dominance of pennies, which do not cause any damage to the plant, but spoil the appearance pretty much, because they cover their larvae with a layer of white foam, which looks very much like saliva. Caring for lavender that has been attacked by pennies is very simple. It is enough to rinse off the foam with a stream of water.
Lavender: Combination with other plants
It is known that smells have a great influence on a person's subconsciousness. Therefore, when growing flowers, it is important that the flowerbed is not only pleasing to the eye, but also enchants with its aroma. When planting plants, it is important to take care not only that the appearance of the flowers complements each other, but also that the floral aromas do not mix. This means that you will have to carefully consider the selection of flowers that you want to plant, otherwise you will hardly be able to rest or recharge in your garden.

Lavender looks very good next to plants with contrasting colors.
Lavender goes very well with sage and catnip. She also looks amazing next to yarrow and garden hydrangea, liatrix, or surrounded by grown herbs and perennials.
Lavender in landscape design
Lavender, planting and caring for which is so easy that any budding gardener can handle it, is ideal for decorating the area. A significant advantage of lavender among other landscaping plants gives a bright and intense color in different shades, from pale pink to bright lilac. This makes it possible to accentuate the grace of any corner of your garden.

Lavender in landscape design
Advice. Use decorative designs to highlight the originality of your flower garden.
There are several options for decorating your garden with these flowering shrubs.
- Perhaps the most well-known and common way is to plant lavender along paths and sidewalks. This design of your site makes it possible to visually limit, as well as create a clear division of the garden into zones.
- The second option is to plant the bushes in such a way that the lavender will grow in accordance with the order of the cells on the chessboard. But this type of landing will only work on a completely horizontal surface.
- Another unusual way to emphasize the originality of a garden plot or flower garden is to form a "carpet" of these shrubs. If you decide to choose this option, you need to immediately determine the height of the lavender and regularly cut it at this level in the same plane. Such a carpet will not become a semblance of a soft grassy one on which you can comfortably sit, but planting shrubs in this way will allow lavender to brilliantly show its color.

Lavender is often planted along paths and fences.
Of course, lavender in landscape design is not as common as planting roses or all kinds of loaches, but this is what will emphasize the uniqueness and originality of the decorative design of your garden.
Growing lavender is the perfect way to highlight your garden or flower garden with color, shape, and an elegant scent that will impress everyone who walks by.
How to plant lavender correctly: video
Lavender in the garden: photo
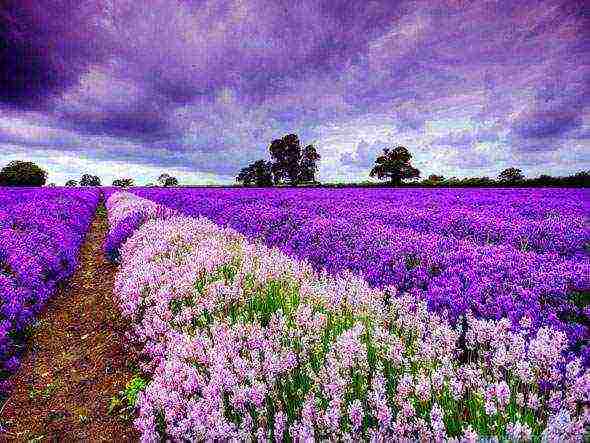





Lavender is a vibrant plant of an unusual shape, which is most often associated with the endless fields of Provence. It is planted as a decoration for borders and in the form of beautiful partitions, combined with other flower cultures and left as the basis for creating rockeries. Photo of lavender adorns many albums of travelers in France.
In addition to aesthetic pleasure, the owner of the "lavender color" will also benefit enormously.The fact is that flowers contain substances that can calm the nervous system and normalize sleep. In fact, by planting lavender next to the gazebo where you like to spend the evening or near the tea table on the terrace, you will be provided with a nightly exercise against depression and despondency). This flower is very popular not only with healers, but also with perfumers. Even the ancients used lavender essential oil for hair, to make it silky and shiny.
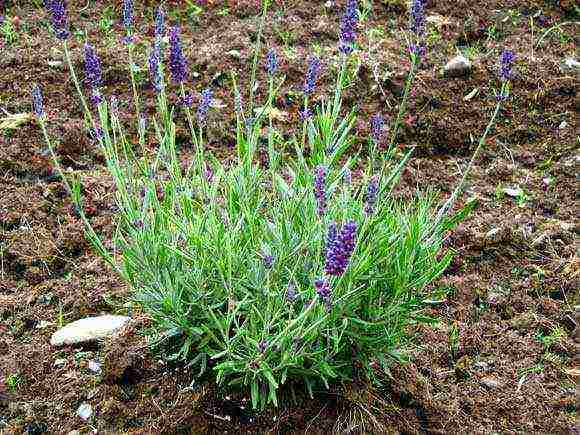

This flower has long been popular with gardeners, however, you need to know all the intricacies of caring for it in order to achieve maximum and long flowering.
Lavender care
The list of activities that must be taken to ensure the growth of lavender is voluminous on the one hand, and simple on the other. It includes:
- loosening the soil. This is a prerequisite for the growth of lavender. It is ideal to mulch this land,
- elimination of weed crops,
- pruning the plant. Lavender is very fond of pruning! It should be carried out regularly as well, and to give the lavender plantings a neat and decorative look, it is necessary to regularly prune the flower bushes. Lavender pruning is done in both fall and spring. How to make spring and autumn pruning - see I saw at the end of the article.
- proper watering of the flower. Lavender is a rather capricious plant, so it should be watered very carefully. It does not tolerate drying out of the soil, but excessive moisture of the surface will also adversely affect the development of the plant. More precisely: for lavender, it is better to dry out a little than to be waterlogged)
- fertilization. During the period of abundant flowering, lavender must be fed with various mineral fertilizers. First of all, this is the introduction of potash-phosphorus fertilizers. Fresh manure is completely unsuitable for fertilizing flowering ones.
- mandatory preparation of lavender for the winter period.
This is about leaving. But how much more important is the correct planting of lavender! Please note that mature plants do not tolerate transplanting well enough (lavender has a large root system and is always damaged during transfer), so it is better to choose a place for planting in advance.
How to choose a landing site
The key to a successful lavender color is the right planting site.
Temperature regime
Lavender feels great in regions with a southern climate, where it is provided with optimal conditions for development and long flowering. In those regions where climatic conditions are less favorable, it is more convenient to plant lavender in small outdoor boxes or flowerpots, which can be easily brought into the room with a sharp change in temperature. In winter, lavender is not going through well, and for the safety of the bushes, you need to provide for a shelter in advance (with dried flowers or coniferous branches or agrofibre). Foliage for sheltering lavender is not suitable, as it can rot under them in winter. At very low temperatures (more than -20 degrees), the plant also needs to be insulated.
Soil type
Lavender does not tolerate acidic soil. Therefore, to reduce acidity, add ash or eggshells to the soil. Lavender also dislikes dense soils. Therefore, stock up on mulch in advance, you can use rotten leaves.
Sunny open place
For him, areas with open terrain are suitable, which are well exposed to the sun's rays. In the shade, already small bushes will grow dwarf, and may not bloom. It would be more correct to say this: if there is little sun, lavender simply will not bloom.
Not very wet earth
Do not plant sprouts in a marshy area - the roots will immediately respond to the amount of moisture. Even high water tables can be detrimental to lavender. Lavender is very, very sensitive to moisture and suffers from fungal diseases. Although lavender also does not tolerate overdrying the earth.
Spreading distance
The distance between the seedlings should be equal to the estimated height of the bush.It is in this case that each bush will become lush and rounded. However, if it is necessary to achieve just a green fence around, then it is enough to halve the distance and the lavender will no longer bloom.


For those who are going to grow and care for lavender in the country, you should pay attention to 3 points:
- the soil in which you will plant (not acidic and not wet);
- sunny open place, no shade;
- fertilizer during flowering.
When you grow this beauty in your country house, you can still make real lavender oil, which will make you younger and more beautiful and happier.
Most often, lavender is bred in two ways - cuttings and seeds.
Propagation of lavender by cuttings or layering
Of course, it is better to buy lavender seeds and seedlings in specialized outlets, additionally consulting with experienced specialists in the selection of a suitable plant variety and the rules for caring for it. But, if there are already plantations of lavender at the summer cottage and there is still a little experience in growing this plant, then it is quite possible to try to carry out the procedure for obtaining young lavender seedlings on your own.
The first way is quite simple to execute - stalk you need to plant it in the ground two to three centimeters, and then cover it with a film (or a cut plastic bottle). The soil should be constantly moistened, and after the emergence of roots, planted in a permanent place of growth. Rule for cutting:
- cut off the stiff process;
- cut off the top with flowers so that it does not draw life-giving forces.
Can be bred layering (by dividing the bush). It is necessary to choose the lavender bush you like, pin one of the branches to the ground (a small shoot) and dig it in lightly with earth, which must be covered with a film until the roots appear. Then, when the root system is more developed (this will be the next year), the young plant is separated from the mother bush and transplanted into a new territory.
Rule for layering:
- choose a lignified branch, but at the same time a soft one, so that the root system develops faster;
- cut off the top with flowers so that it does not draw life-giving forces.
Can be bred through growthwhich lavender gives abundantly in summer. To do this, the bush is pruned, separating the shoots and earthing up with earth. By the fall, you already have a new young bush ready, which needs to be dug up and transplanted to a permanent place.
What the lavender shoots look like can be clearly seen in the video from 1:35 minutes.
Propagation of lavender by seeds
Lavender planting by seeds, cultivation and care. Reproduction of lavender seeds is a troublesome process. Although in relaxed conditions, the seeds germinate in part and give good growth.
Growing lavender from seeds at home
Seeds need to be cooled (stratified):
- according to the first option, having planted in the soil in late autumn, when the air temperature has already dropped steadily to a maximum of +5 degrees;
- on the second, the mass of seeds mixed with sand must be refrigerated for at least 1-1.5 months. The optimum temperature is +5 degrees. This method is much safer and more productive.
Stratification the seeds are exposed due to the fact that lavender contains a large amount of ethers, and during a period of sufficiently long cooling, the "dense shell" is destroyed. Therefore, when the seeds are taken out and placed in the heat, an intense production of growth hormone begins. The process is so intense that the seeds germinate. Without stratification (cooling), the seeds will simply rot.
After the seeds are stratified, we sow them into the ground. Sowing can be carried out when the air temperature in the place where lavender will germinate was at least 15 degrees, and preferably +20. It is better to do this in a separate flowerpot and plant in a greenhouse or on a glazed loggia (this is ideal).
The soil you need is light, and you need to sow lavender seeds very superficially, since they germinate in the sun.After sowing, cover the soil with foil. It is imperative to conduct airing to remove condensation that forms on the film.
It is possible to plant the shoots grown from seeds when 1-2 leaves have formed. After the sprout has hardened and the temperature is right outside, it can be planted in open ground in a pre-selected place.
So once again the stages and nuances (lavender planting by seeds, cultivation and care):
- seeds are stratified;
- we sow the seeds in a separate flowerpot with a light loosened soil;
- seeds are sown superficially;
- the flowerpot should stand in the sun and in a room with a temperature of at least +15 degrees;
- after the appearance of 1-2 leaves, we plant the sprouts;
- after rooting, we transplant it into open ground in a selected place.
Please note that when lavender is propagated by seeds, the bushes will not begin to bloom during the first 1-2 seasons - the root system will actively develop and it will be this plant that will start up its forces.
Autumn lavender pruning
Spring pruning lavender
Lavender
- a beautiful plant that conquers with its graceful, delicate aroma. She has gained wide popularity among gardeners for a very long time. Fluffy bushes of lavender, dazzling with bright inflorescences-spikelets - a great plant for borders,
alpine slides
and
rockeries
.

And you can learn about the beneficial properties of lavender from the article.
"Lavender: beauty and benefit!"
.
Of course, to get a luxurious flower bed, you have to try. Lavender care is required on a regular basis. The complex of measures must include:
- loosening the soil;
- elimination of weeds;
- watering;
- pruning;
- fertilization;
- preparation for winter.
Lavender is a thermophilic plant. Therefore, to grow this
perennial
in the open field it is not possible in any climatic zone. In cold climates, the bushes should be planted in
flowerpots
and at the first hint of a cold snap, quickly transfer them to a warm place. Any variety of lavender can be grown as a pot plant.
Landing place
The key to successful
growing lavender - the right choice of landing site. Most of all, the plant will like open areas, well-lit by the sun's rays. The bushes will take root in the shade, but it will not be possible to achieve abundant and long flowering.
Plant roots are sensitive to high soil moisture levels. Therefore, you should refrain from planting lavender in wetlands and areas where they lie too high
groundwater
... If there is no other option, you can try to build a hill and plant bushes on it. Excess moisture near the roots can be easily removed with a drainage layer.
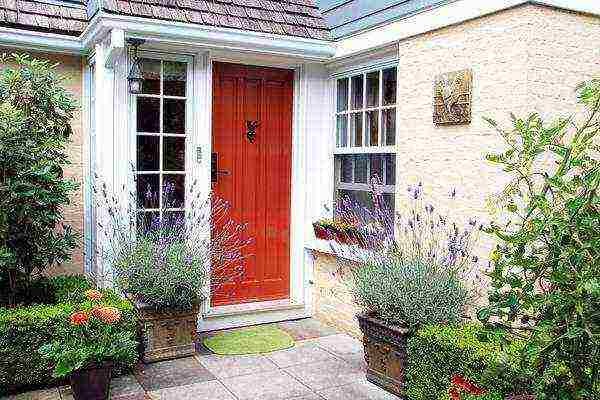

Any variety of lavender can be grown as a pot plant.
Lavender is also demanding about the level of acidity and soil structure. Therefore, if in doubt, it is better to play it safe - before boarding, deposit in
soil
a little woody
ash
or lime. These are effective soil deoxidizers. And to ensure the porous structure of the soil, it is enough to regularly apply to the garden
compost
... It will not only loosen the soil, but also supplement it with nutrients.
Features of planting lavender
Planting lavender - a responsible process. Adult bushes do not tolerate transplanting well, if you have to do it, then carefully and only with a voluminous lump of earth. It is better to immediately determine where the bushes grown from seeds, cuttings or cuttings will be located.
The distance between adjacent specimens should be approximately equal to their maximum height. Then the bushes will be lush. And to get slender green
hedges
we reduce this parameter by half. This way you can achieve the maximum solidity of the plantation block.
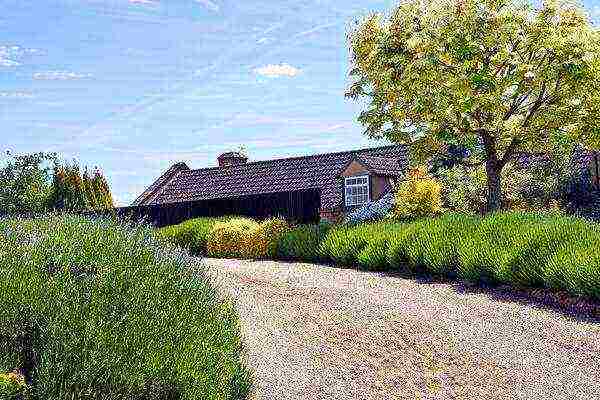

Lavender curbs are great Lavender cuttings take root quite quickly.The planting algorithm is simple: deepen a couple of centimeters into a loose soil mixture, cover with a film and regularly moisten the soil. Gently dig out the rooted cuttings and transplant to the chosen place.
Layers are rooted branches of a plant. To obtain planting material, bend one of the lower shoots to the side in the spring. Fix the place of contact with the ground level and cover with soil. When a lump of roots forms, carefully cut off the cut with a sharp knife. Sprinkle the place of the cut with crushed coal to protect it from decay processes. That's it - the layering is ready for planting.
You can choose lavender seedlings of various varieties in our catalog, where various online stores present their products. Choose lavender seedlings
Sowing lavender seeds
Lavender is difficult to propagate by seed. But if it is not possible to purchase an adult plant or twigs, you can also try sowing seeds.

Lavender can be propagated by seed. A very important step is stratification. Lavender seeds need to be kept at low temperatures for some time. Here you can go in two ways: plant them at the end of autumn immediately in the ground or carry out artificial stratification. The first method is only suitable for warm climates. With significant frosts, seeds may die. Therefore, it is better to opt for the second option.
For artificial stratification, the seeds must be mixed with a small amount of sand, poured into a container, wrapped in polyethylene and refrigerated. Keep them there for at least a month and a half. Better - longer. In this case, seedlings will appear faster. Then you can sow seeds in boxes (at the end of winter) or in
greenhouses
outside (late spring).
When sowing with seeds, it will take a whole year to expect flowering. In the first seasons, seedlings will only develop, increasing the root system. And only after a year, and maybe even after two, they will delight the gardener with cute spikelets-inflorescences.
You can choose lavender seeds in our catalog, where products from various online stores are presented. Select lavender seeds
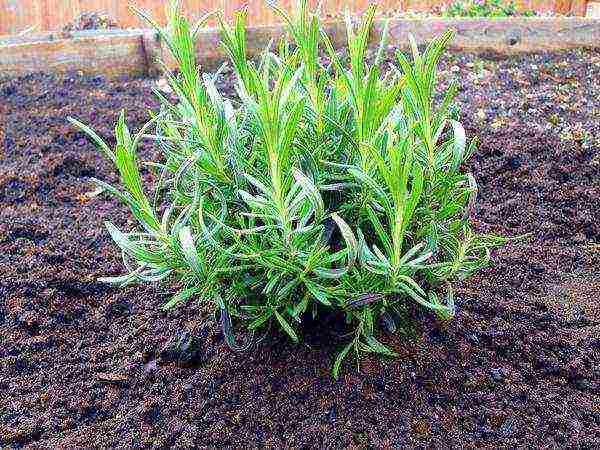

Lavender grown from seed will only flower for 2-3 years.
Soil processing near bushes
Lavender does not like dense soils. Its roots really need good air circulation. In addition, of course, you need to get rid of pest weeds next to lavender. Therefore, loosening and weeding should become a regular procedure.
You can do it easier - organize a good mulching layer on the lavender garden. As
mulch
you can use the decayed
foliage
or decorative multi-colored substrates. But in any case, near the base of the trunk, the soil should remain uncovered. This will keep the plant from rotting.
Water the lavender very carefully. Excessive irrigation can lead to root rot and yellowing of the aerial part of the plant. Drought is also bad for the plant - the lavender will not die, but the flowering will not be as luxurious as we would like. The ideal watering regime is as the soil dries up.
Pruning lavender bushes
This stage of lavender care cannot be called mandatory. But only by pruning can you achieve the formation of beautiful lush bushes. Therefore, you should not give up a useful procedure.

Pruning lavender The first pruning should be done immediately after the inflorescence spikelets wilt. You need to shorten the shoots literally by a couple of centimeters. At the end of the warm season, more drastic pruning is carried out. But here, too, you should not show excessive enthusiasm. If you shorten all the branches to the level of the lignified part, the bush may die.
Fertilization
Great as a fertilizer for lavender
mineral
complexes that are sold in all garden and flower shops. They should be applied during the beginning of flowering. Concentration - 2 tbsp. spoons in a bucket of water.With the resulting solution, you need to shed soil around the perimeter of the bushes.
Responsible for the development of green mass
nitrogen fertilizers
(2 tablespoons per bucket). Therefore, they are indispensable at the beginning of the growing season (growth). But in the second half of the summer, it is forbidden to use them. Under the influence of nitrogen, the growing season is significantly extended. As a result, the plant does not have time to prepare for wintering.
The use of fertilizers can be completely abandoned if there is a thick layer of compost mulch under the bushes. Decomposing under the influence of external factors, it will supply the plant with nutrients throughout the season.
Preparing for winter
For lavender bushes that have to spend the winter outdoors, you can organize a reliable
shelter
... True, in warm climatic zones, you can do without this - according to experts, lavender will survive the winter well, even if the temperature drops to -25 ° C. If frosts are expected to be stronger than this mark, insulation is necessary. In addition, it will not be superfluous to play it safe in cases where the winter may turn out to be little snow.
At the end of the season, lavender bushes are pruned. Branches are laid on top of the garden bed (best of all from conifers). But the usual insulation in the form of a layer of foliage is not suitable. Lavender can rot under it.

In general, caring for lavender is not as difficult as it might seem at first glance. Using compost mulch will eliminate weeding, loosening and top dressing. Therefore, the gardener will only have to cut the bushes in a timely manner so that they grow strong and bloom profusely.
The topical question "How to preserve lavender in winter" was asked by a reader of our site. You can read the tips and take part in the discussion.
Types of lavender
Many people associate lavender bushes with a constant purple color. In fact, shades of different varieties conquer with variety. There are specimens with blue, white, pink and even greenish colors. And this is just the basic palette. And the shades of inflorescences-spikelets are even more. But color is not the only difference between different lavender varieties.
According to the generally accepted classification, there are two broad groups:
english and
french .
English lavender - the owner of narrow leaves and elongated spikelets-inflorescences. It is worth noting that it is this type that has received the most widespread use. Such varieties quietly winter in the middle lane, not needing to be dug up in late autumn.

French lavender - a more capricious plant. Outwardly, it is similar to the previous species, but its leaves are wider, and the inflorescences are shorter. Traditionally used as a pot culture. After all, even minor frosts down to -15 ° C can instantly destroy the plant.

French lavenderAll articles about lavender on our website
Foreword
Lavender is a perennial evergreen shrub from the Yaroslavl family. This thermophilic plant is widespread throughout the world. In its natural state, it grows in the Canary Islands, India, Africa and southern Europe. In the middle lane, planting and caring for lavender outdoors is a laborious task, but this plant is popular with many gardeners.
Features of growing lavender
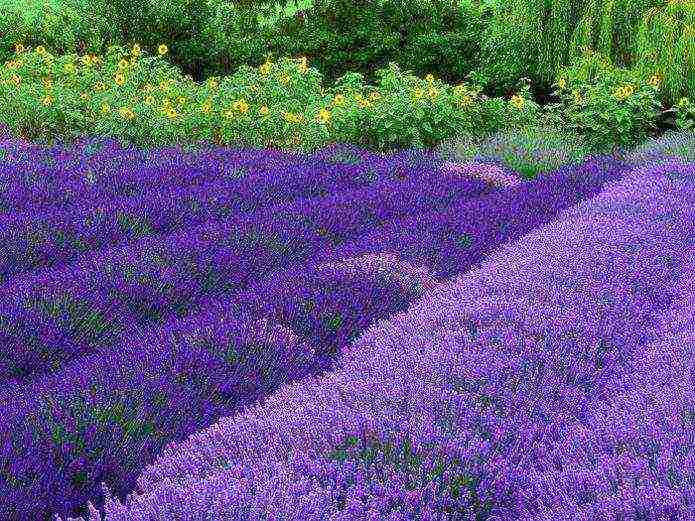

Lavender fields can be seen not only in France
This plant prefers the southern regions, although many varieties have been bred for open ground in the middle zone and the Urals. In climates with harsh winters, lavender is often grown in flowerpots and containers. Some varieties are used as annuals.
Lavender blooms in lilac or blue flowers with an exquisite scent. Its flowering time depends on the species. In the middle lane, the plant blooms for two months - from July to August. In the south, some species can have two phases of flowering: first in spring, then, after a break, at the end of summer.
What climate is suitable for
The cultivated species are divided into two groups: English and French lavender. They have different winter hardiness.
French lavender is a gentle, thermophilic plant that cannot stand the cold. It originated from the southern regions of Europe and is considered a symbol of Provence.
It is grown in soil in the Crimea and in the south of the Krasnodar Territory, and in colder climates it is cultivated as a pot culture. At frosts below –15 ° C, the plant dies.
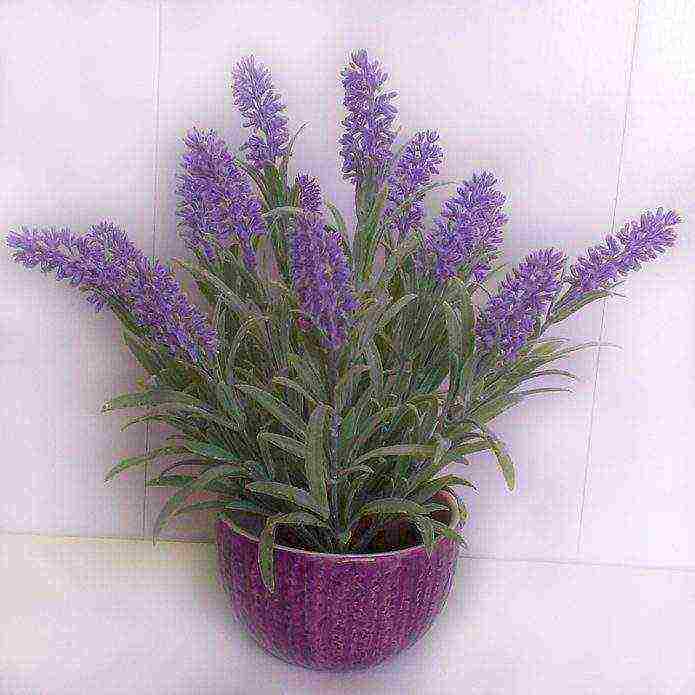

The diameter of the pot should be at least 30 cm, as the lavender roots need space
English lavender is quite unpretentious and has good winter hardiness. It is grown in the open field of the middle lane. It tolerates temperatures down to –25 ° C, but where winters are harsh or with little snow, shrubs need shelter.
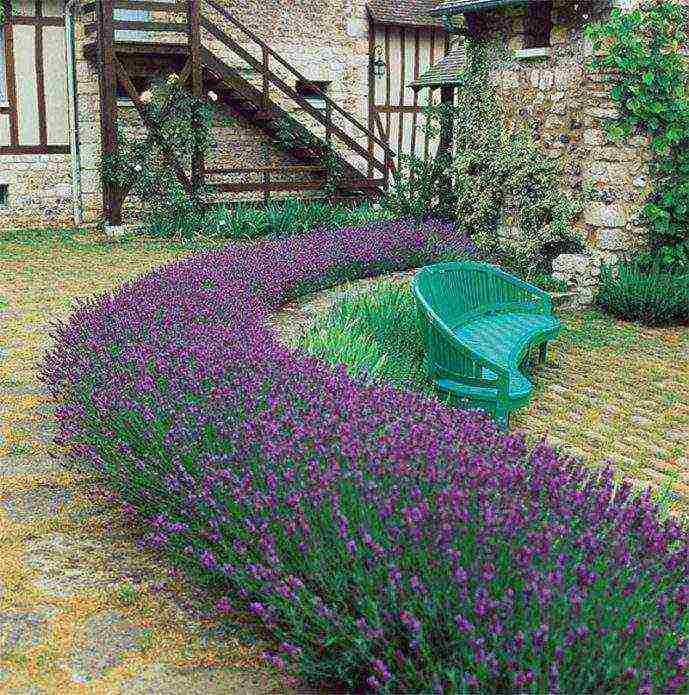

This type of lavender is widespread in the Kuban. Domestic breeders based on it have developed varieties intended for cultivation in many regions of Russia.
Role in landscaping
Graceful lavender bushes can decorate any area. The plant is versatile and great for any composition. Some of the options:
- Lavender is a mountain plant that blends seamlessly into rocky landscapes. It is often used to decorate alpine slides and rockeries.
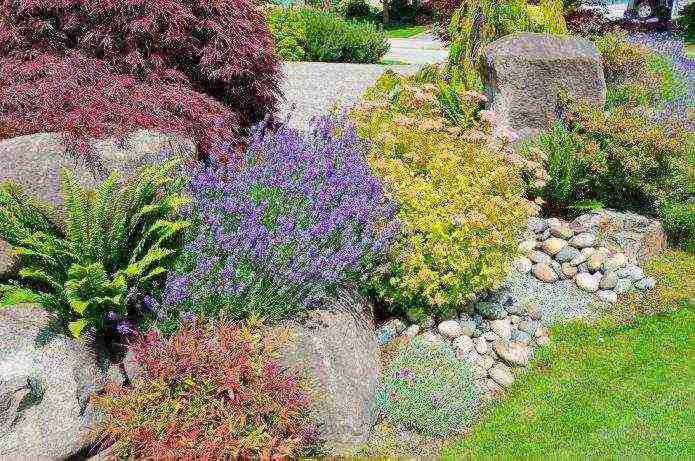

When planting lavender in a rock garden, take into account the height of nearby plants
- Low-growing species are often grown in containers and flowerpots. They decorate balconies, terraces, gazebos. Bushes in hanging pots not only decorate the exterior of the house, but also repel insects.
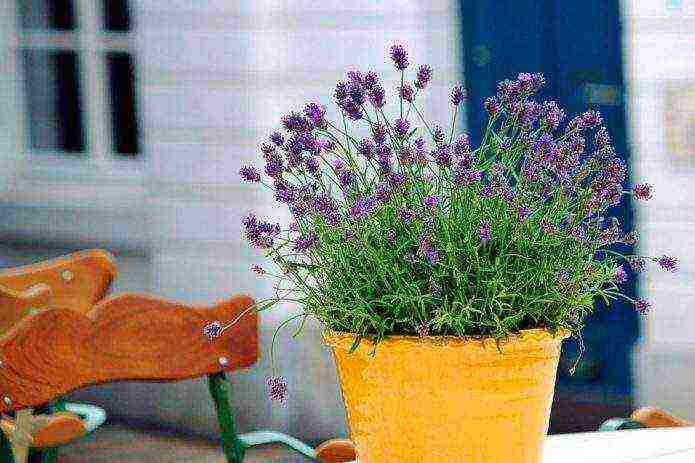

You need to put pots with lavender in lighted areas, the plant needs long-term sunlight
- Lavender is great for single lawn plantings. In mixborders, it forms spectacular combinations with bright orange, yellow, white and dark purple flowers and herbs. It is often planted together with sage, poppy, sedum.

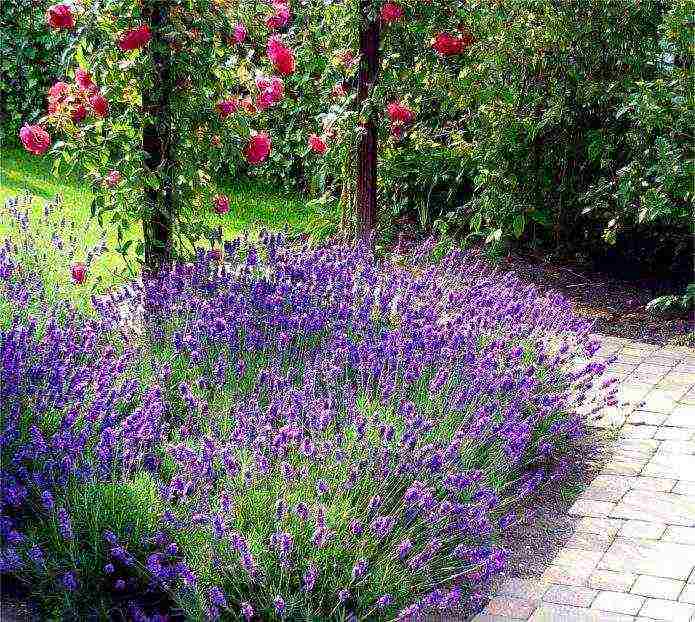
Lavender paths are a typical feature of the English garden
- Overgrown lavender is a good border for the site and flower garden. It will decorate even the most unsightly metal mesh. In the south, lavender forms fragrant hedges that not only confine the site, but also ward off insects. In the middle lane, there are varieties up to 60 cm in height, which are also planted along fences and near the walls of buildings.

Care should be taken not to overgrow lavender curbs
- Lavender is often used as a planting material to strengthen the slopes. It is planted along with juniper, rhododendron, lilac and many other plants.

You can also use different types of ivy to strengthen the slopes.
- Fragrant lavender bushes will be a wonderful decoration for a garden path. It is necessary to ensure that they are of the same height, and trim on time.
- The plant is often planted with roses, especially with varieties that have large and bright buds. They form ideal combinations not only in color, but also in smell.
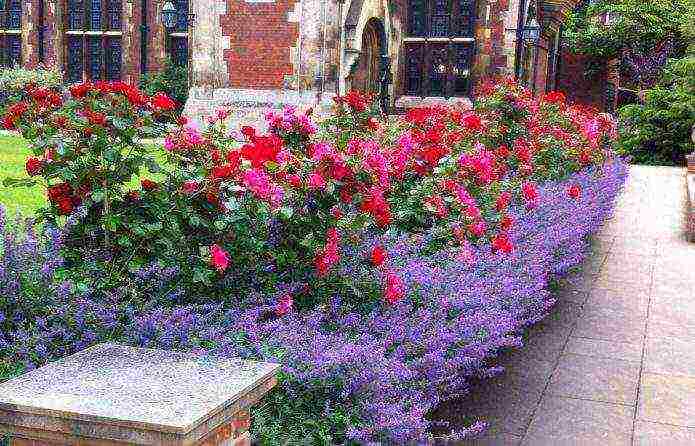

Lavender and roses - traditionally bright and fragrant tandem
- Lavender can be used to decorate flower beds with herbs. It is planted with mint, thyme, sage, oregano and other aromatic herbs.
- Fragrant bushes are used not only in flower beds, but also in the garden. Their scent is an excellent repellent that many pests cannot tolerate.
Popular varieties
In total, there are about 37 types of lavender in the world. Only two of them are used as cultural ones: French and English.
French
French lavender has wide leaves and lush buds with a distinct aroma. Flowers have a wide range of shades: white, pink, lilac, burgundy. French lavender blooms twice: in April or early May and mid-August.
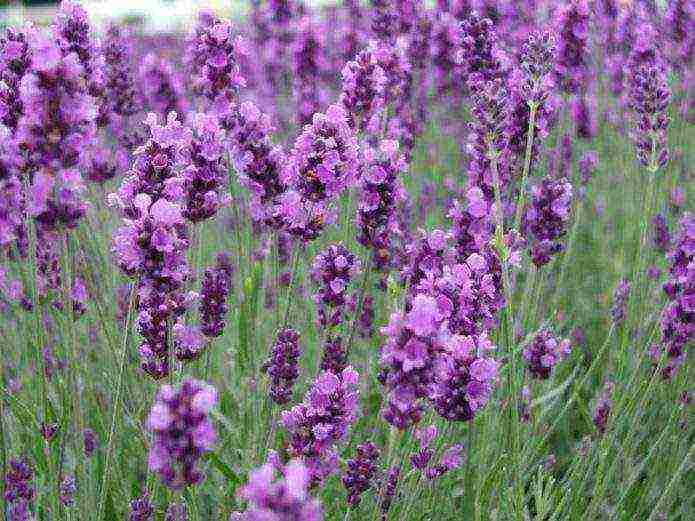

French lavender is a wonderful honey plant - its nectar attracts bees
English
English Lavender (Narrow-leaved, or Medicinal, or Angustifolia) is a plant with silvery-green leaves and small bluish-lilac flowers. It gives many shoots with a whitish edge, which is why it acquires a bluish tint. The bushes bloom in July and bloom for about two months.
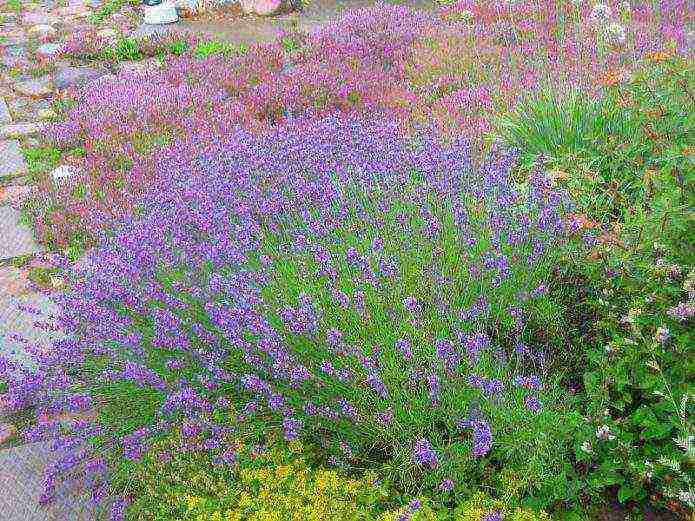

The plant is of great industrial value - it is used to obtain essential oils and medicines
Dutch
Hybrid Dutch lavender, derived from English, is very popular with gardeners. This is a plant with large peduncles, reaching two meters in height. It blooms in July. Dutch lavender is less hardy than English lavender.
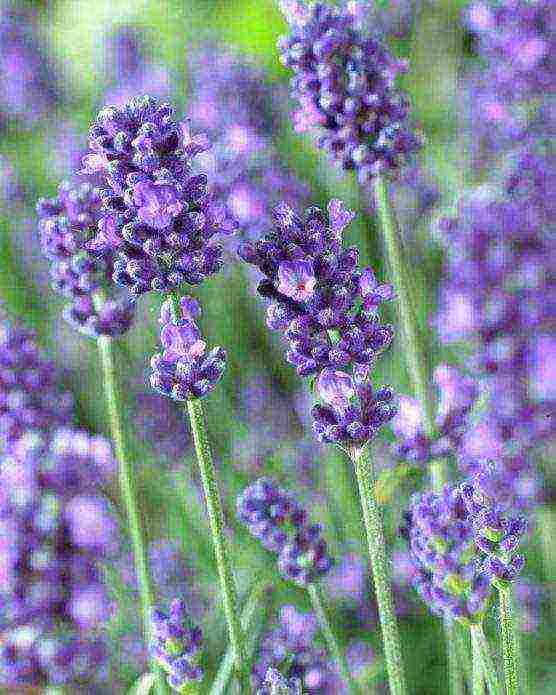

Most popular hybrid lavender varieties: Alba, Arabian Knight, Sawyers, Grosso, Richard Gray
Jagged lavender with carved leaves and large fragrant flowers is widely known. It is used as a houseplant.
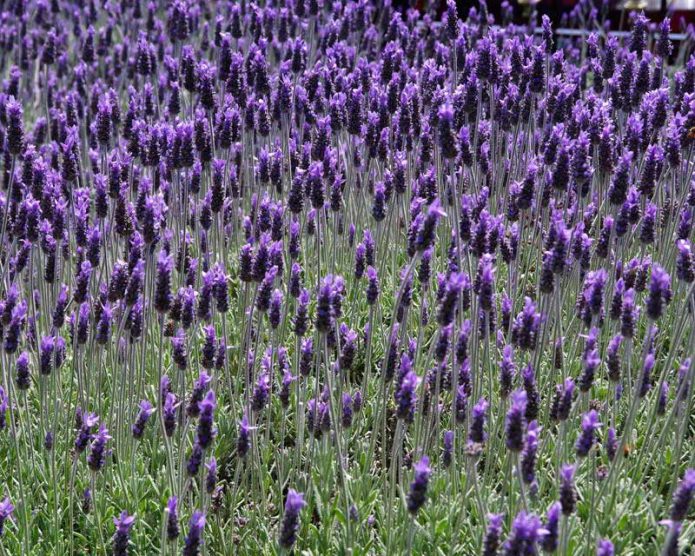

Outdoors, this thermophilic shrub grows only in the Crimea and the Mediterranean.
Planting methods
Lavender on the site is grown in three ways: seeds, cuttings and layering. It reproduces easily vegetatively and gives a lot of young growth for reproduction. But if you want to plant a new variety, then you can try growing a plant from seeds - it's not that difficult.
Sowing seeds
Growing lavender from seeds has its advantages: their price is low - much lower than that of seedlings or cuttings. With proper seed treatment, plants grown from them acquire good immunity.

Lavender seeds retain the ability to germinate for a long time
Seeds must be stratified before planting. This procedure improves their germination and increases the resistance of future seedlings to diseases and cold weather. Stratification is done in two ways:
- Natural. Seeds are planted in the fall in the ground. During the winter, they will be exposed to low temperatures, their germination and adaptability will increase. This method is not suitable for the middle zone - the seeds may die from frost. If the climate is quite warm, then sowing is done in October. The seeds are planted at a depth of 4 mm and compacted. If the land is dry, then irrigate. In winter, the planting site is covered with snow.
- Artificial. The seeds are placed in a container with wet sand and mixed, put it in the lower drawer of the refrigerator for one and a half to two months. Seeds are planted on seedlings in the second half of February - early March, so stratification is carried out from late December - early January.
Light soil must be prepared for seedlings. Three parts of garden or forest soil are mixed with one part of sand. If the soil is not fertile enough, humus is added to it. You can also buy ready-made seedling soil from a flower shop. Landing is done as follows:
- Seeds are rarely planted in a container, since the roots of lavender immediately begin to grow;
- They are not buried - they are only sprinkled on top with a thin layer of sifted earth;
- Moisten the soil;
- The container with seeds is covered with glass or tightened with plastic wrap, then placed in a warm, bright place.
Seeds germinate for a long time. In two weeks, single shoots will appear, and mass shoots will appear in a month. After their appearance, the shelter is removed from the seedlings. When two true leaves appear at the seedlings, they are dived into separate pots or cups. In order for the seedlings to grow strong and healthy, they need proper care:
- The containers must be drained to prevent water stagnation. For this, there must be holes in the bottoms. Additionally, a small layer of pebbles is placed there.
- You need to water the seedlings at the root, for which you can use a medical syringe.
- If the soil is compacted, then it is loosened with a toothpick.
- For proper development, plants need ten hours of daylight. If there is not enough light, they make a backlight.
- If it is warm enough in April, then the seedling boxes can be placed in the greenhouse.
Seedlings are transplanted into open ground 60 days after germination. In the middle lane, planting is carried out at the end of June, when the soil warms up enough.
Lavender seeds can also be planted directly into the soil. Planting is carried out in May, when the threat of frost has passed.
Plant propagation
This is the fastest and most effective way to propagate lavender. Cuttings are carried out in the same way as in other plant species:

Cuttings from last year's shoots must be pre-soaked before planting in a root formation stimulator
- An annual shoot is cut with a sharp knife.
- Cut into cuttings 8-10 cm long.
- They are planted in light soil, rooting 2-3 cm.
- Cover with a small greenhouse on top.
The soil must be constantly moist. After three to six weeks, the cuttings will develop roots, after which they can be transplanted to a permanent place.
Reproduction by layering
It happens quickly and easily. To obtain layering at the beginning of summer, the lower shoot is bent to the ground and placed in a previously prepared groove. To keep it in place, it is fixed with wire and sprinkled with earth. The shoot is regularly watered with water. After two months, he will develop roots, after which he is separated from the bush and transplanted to a permanent place.
Landing in the ground
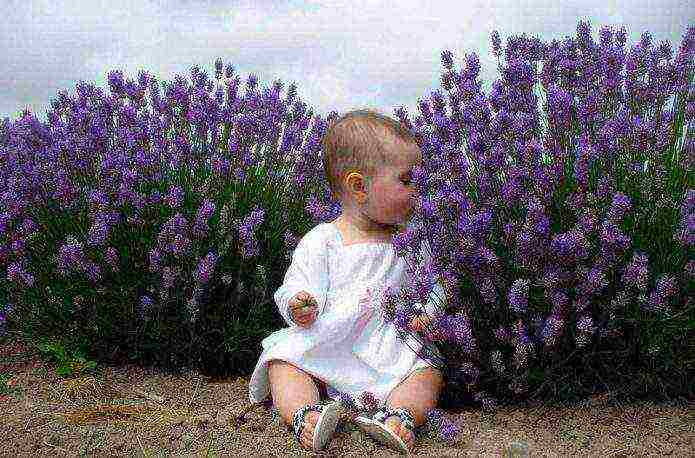

For children, the smell of lavender helps with increased excitability and sleep problems
In order for the bushes to grow lush, they need to be planted rarely. 50-60 cm are left between ordinary seedlings, about 100 cm between tall ones. Lavender prefers light, air-permeable soils. The earth must have a slight alkaline reaction, for which you can add some ash or lime to it.
Before planting, the earth is dug up and the roots of the plants are removed. The seedling is placed in a prepared hole, the roots are straightened and covered with earth so that the root collar is deepened by 4–6 cm. The plant is watered abundantly. Lavender blooms in its second year after planting.
The plant has some features to consider when choosing a planting site:
- This is a light-loving shrub that is planted in sunny places. Young plants are shaded so that they are not burnt by the sun.
- Lavender loves moisture. In dry summers, it needs to be watered frequently. It is better not to plant the plant where it is difficult to organize watering.
- Lavender is a good honey plant that attracts bees. It should not be planted near places where children play. Also, don't plant lavender under your bedroom windows. The strong odor and essential oils it releases can cause headaches, allergies, and disrupt sleep.
- The plant does not like stagnant moisture, so there must be good drainage at the planting site. It can be organized from broken bricks.
Care in the garden from the moment of planting in the open ground
Post-planting lavender care takes place from early spring to late fall. She will thank you for the care with abundant flowering.
Care during growth and flowering
After the end of winter (before the start of sap flow), the plants are pruned. They are given a rounded shape and frozen twigs are removed. The bushes are pruned as follows:
- remove old dried shoots that can cause plant diseases;
- the height of the bush is reduced by 1/3. You can't cut it anymore, otherwise it may die.

Pruning needs to be done every year
Lavender loves fertilizers. She quickly assimilates them, which has a beneficial effect on growth and flowering. In the spring, the intensive growth of the shrub begins - nitrogen fertilizer is applied under it. In the summer, when the buds develop and flowering begins, the plants are fed with potassium-phosphorus fertilizers. Top dressing is carried out several times during the summer with an interval of half a month.
During the entire warm period, the bushes are regularly loosened and weeded. This is especially important for young plants, since otherwise their roots will lack oxygen, and weeds will drown them out.To facilitate maintenance, the soil around the plants is mulched, for which tree bark or special mixtures are used.
Lavender is a moisture-loving plant, but it should be watered in moderation. Watering is done only when the soil dries up. In hot dry seasons, the bushes are watered 1-2 times a week. In the off-season, watering can be reduced to once every 14 days. Moisture is especially needed for young seedlings, they need to be watered more often.
Preparing for winter

Usually the plant is cut off before wintering, but this has its opponents.
How lavender will cope with the winter depends on its placement on the site. Plants should be protected from the wind by other plantings. The landing site should not be close to groundwater.
Pruning plants for the winter is a controversial issue. Sprawling bushes trap snow and form a good shelter. On the other hand, long shoots can freeze and break when the wind blows. Therefore, it is up to the owner of the site to decide whether autumn pruning is needed.
English lavender tolerates winter well. In regions with a warm climate, it should not be covered. If in winter the temperature drops below -25 ° C or there is little snow, then the bushes freeze. The hardest of all the plant tolerates not winter frosts, but spring thaw with subsequent frosts, when ice forms on the soil. Air does not get to the roots, and the plant can rot. To prevent this, the bushes are covered as follows:
- branches are tied to prevent snow from getting inside;
- the soil around the bush is mulched abundantly;
- the bushes are covered with pine or spruce branches.
A layer of fallen leaves is not suitable for shelter - the bushes under it begin to rot.
French lavender does not endure the winter well. She needs to be covered especially carefully. Each plant is spud and wrapped in straw. A shelter is erected above the bushes from a thick layer of spruce branches and brushwood. In winter, lavender needs to be visited occasionally to check if the shelter has been swept away by the wind.
Plants in pots are never allowed to winter outdoors. It is also undesirable to bring them into a warm apartment. The pots can be put for the winter in a glassed-in veranda, in a greenhouse or in an insulated loggia. If you still carry lavender into your apartment for the winter, then in the spring you need to cut off all winter shoots.
Video: preparing lavender for winter
Growing problems
Lavender can be susceptible to fungal infections. The cause of their occurrence may be improper care, an abundance of weeds, and adverse weather conditions. Possible problems and solutions:
- In a cold, humid summer with sharp changes in temperature, the inflorescences and stems of the plant sometimes begin to turn brown and become covered with a grayish coating. This gray mold is a known fungal disease. To eliminate it, preventive measures are taken: diseased shoots are cut and destroyed. Row spacing should be thoroughly weeded.
- Sometimes lavender cuttings, as well as mature plants, begin to wilt. A white or pink coating forms on their root collar. These are signs of defeat by fusarium wilt. To prevent disease, plants and soil are treated with chemicals. Old bushes need to be rejuvenated regularly.
- On young shoots of plants, yellowish spots sometimes appear, which later become gray. Shoots dry quickly and curl, covered with black dots. These are signs of stem phomaosis. In order to prevent its spread, the affected shoots are destroyed. Plants are treated with Bordeaux liquid and other preparations.

Provide the plant with light, otherwise it will definitely wither and look bad.
Lavender is also attacked by pests. Sometimes, in hot weather, the leaves and stems of the plant begin to wither, whitish cobwebs appear on them. These are signs of spider mite damage. The pest drinks the juices of the plant, which is why the young shoots die. To combat it, lavender is sprayed with soapy water, and special agents are used - acaricides and insectoacaricides.
Often, the bushes are attacked by pennies, which lay eggs on stems and leaves. They cover their masonry with foam. To destroy them, the bushes are washed with a strong stream of water.
A rainbow beetle sometimes appears on French lavender bushes. This pest eats leaves and young shoots. It is collected by hand and destroyed.
Features of cultivation in different regions

In the Moscow region, lavender is unlikely to take root in areas with clay soil
Planting and caring for lavender in the Moscow region, the Leningrad region and in the Urals are successful, mainly English varieties are grown in the open field.
In the Moscow region and the Moscow region, it is better to use seedlings for breeding. Plants grown from it are more resistant to temperature extremes and diseases. Seedlings are planted in the ground in early June. On clay soils, lavender develops poorly - it prefers loams with an alkaline or neutral reaction. In the fall, the bushes are cut to a lignified part and covered with spruce branches for the winter. You cannot close them tightly - due to mild winters and frequent thaws, plants often rot. Shelters should be made breathable.
In the Leningrad Region, you cannot plant seeds before winter - they will freeze out. The soils in this region are acidic and poor in humus, so they have to be improved. Plants are best planted in higher elevations, as it can be very humid in the lower areas.
The climate of the Urals is very different in different regions. In the mild natural conditions of the Southern Urals, it is much easier to grow lavender than in the north. Cold-resistant varieties are used for the northern regions. Lavender seeds must be stratified before planting. Adaptation of seedlings is necessary in the northern regions. It is planted in open ground in June, and seeds in May. During the growing season, it is necessary to make additional feeding of the plants: in the spring - with organic fertilizers, in the summer - with potash or universal fertilizers. Spring pruning is necessary to form bushes and remove dead branches. Faded peduncles are cut off in autumn. For the winter, the soil is abundantly mulched and the bushes are covered with spruce branches.
It is also possible to grow frost-resistant lavender varieties in Siberia. Seeds must be stratified before planting, the seedlings are hardened. For the winter, the plants are covered with brushwood and spruce branches.
Useful Growing Reviews
Lavender is a southern plant, and cultivating it in cold climates requires work and patience. But if you properly care for it, cut and cover it for the winter, you will get healthy and strong bushes. They will delight you with abundant flowering.
Rate the article:
(3 votes, average: 5 out of 5)