Content [show]
 Is it possible to grow forsythia in the Urals? You can, if you plant it correctly and provide proper care for the Forsythia, you will enjoy its beauty in your own garden, and not in the photo.
Is it possible to grow forsythia in the Urals? You can, if you plant it correctly and provide proper care for the Forsythia, you will enjoy its beauty in your own garden, and not in the photo.
Varieties and varieties
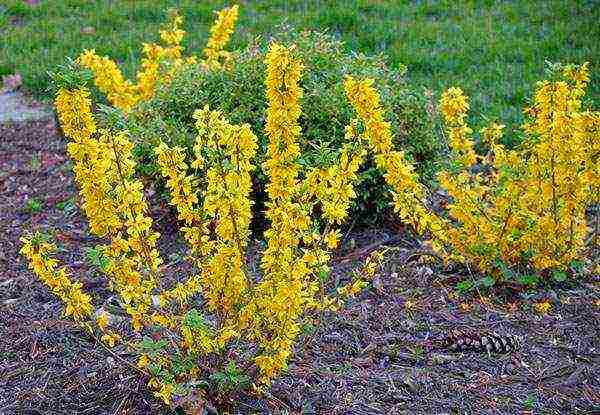
The Asian beauty Forsythia was the conqueror of European gardeners in the 18th century. In the spring, when the garden is just awakening from winter sleep - forsythia is already blooming with a fluffy yellow cloud, young leaves appear later, the unique plant delights.

Forsythia bloom
There are several types of forsythia; in the Urals, only three types feel comfortable, which we will consider:
Forsythia intermediate is a winter-hardy species, effective in hedges and single plantings, as in the photo. On the basis of this species, interesting varieties have been obtained:
- Denziflora - needs a good winter shelter, grows up to 1.5 m;
- Spectabilis is a very beautiful variety, the height of the bush reaches 1 m;
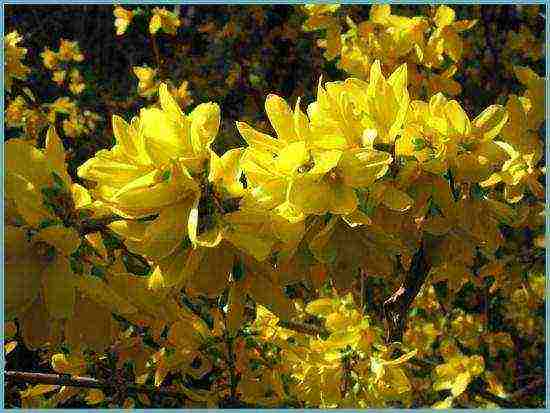

Variety Spectabilis
- Lynwood - blooms for two weeks in May, reaches 2 - 3 m.
Forsythia hanging needs shelter, its varieties are very decorative:
- Siebolda - a short bush, shoots spread;
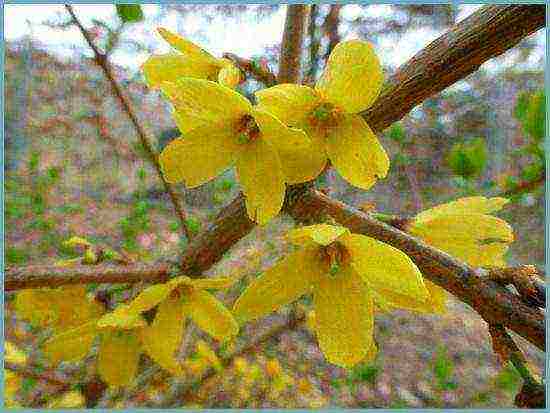

Siebold's variety
- Variegata - distinguished by yellow leaves and flowers;
- Artokaulis - has purple leaves and shoots.
Forsythia ovoid is considered to be the most winter-hardy. It grows well and quickly. Blooms earlier than other types of forsythia, flowering lasts 12 -20 days. Very decorative in autumn. Ovate forsythia varieties:
- Goldsauber - blooms for three weeks, tolerates frost well;
- Spring Glory - blooms for two weeks, the bush reaches 3 m;
- Dresdner Forfrühling - up to 2 m;
- Tetragold - blooms for three weeks, the bush grows up to 1 m tall;

Ovoid forsythia bush
- Melissa is a new variety with a compact crown and large flowers;
- Vic End blooms early, shoots grow upward.
Advice. Forsythia needs formative pruning. But do not get too carried away with this, otherwise the bush will grow, and the flowering will become scarce. It is enough to remove a third of the faded shoot.
Planting and leaving
Forsythia is very fond of sunlit areas, but it can grow in partial shade. The plant does not have any special requirements for the soil, it can grow even on heavy soils, the main thing is that water does not stagnate there. On acidic soils, it slows down in growth. It is not afraid of drought, because at home it grows in the mountains.
It is better to plant the plant in the fall, since in the spring you can not guess the timing of planting, and forsythia begins the growing season early. Pits of a suitable size are prepared, drainage is laid on the bottom with a layer of up to 20 cm. You can use expanded clay, crushed stone or broken brick remaining from the construction site. Pour sand and soil mixture. If you do not have very good land on the site, prepare a mixture of humus and leafy soil, this will help the plant to start growing well. Sour soil is lime or wood ash is added. After planting, the seedling is watered, weeds are removed, and mulched.

Choose a sunny spot for planting forsythia
If the rainfall is regular and in sufficient quantity, then additional watering of the forsythia is not needed.In hot weather without precipitation, water the plant a couple of times a month using a bucket of water on the bush.
In severe frosts, especially in the Urals, flower buds and shoot ends can be severely damaged. For the winter, forsythia should be covered with spruce branches, spunbond, straw. In the spring, before forsythia begins to bloom, it is necessary to inspect the plant and carry out sanitary pruning of damaged shoots.
Advice. Observe the distance between forsythia bushes when planting - at least 1.5-2 m.
Fertilization and feeding
In early spring, the plant needs nitrogen fertilizers, because forsythia grows leaf apparatus and young shoots. You can use an infusion of chicken manure or mullein diluted with water. Or apply any complex fertilizer. Good results are obtained by introducing humus. Any organic matter introduced into the trunk circle will serve as mulch and fertilizer at the same time.
Advice. European and dark green forsythia is thermophilic; the climatic conditions of the Urals are not suitable for it.
Reproduction
Forsythia reproduces well during the season. This can be done with root suckers, seeds, green and lily cuttings, horizontal or arcuate cuttings.
Seeds sown in boxes in early spring. Seedlings appear in a month, they dive in the second year of life, covered with mulch, they winter well. Bloom in 5 years. Seeds germinate very poorly, germination rate is less than 40%.

Forsythia seeds
Cuttings harvested in early summer. The shoots are cut so that the cutting has 2 internodes. The leaves are left only on the crown, shortening them in half. Cuttings are placed for a day in a bucket with root solution or by adding a spoonful of honey to the water.
Cuttings are planted in the school, deepening the lower cut of the cutting by 3 cm. Cover the school with a film. Air when hot, watered regularly. In a month, the shoots will give roots. In the third year, cuttings can be planted in a permanent place, in the same year they will bloom for the first time. This method gives a very high survival rate.
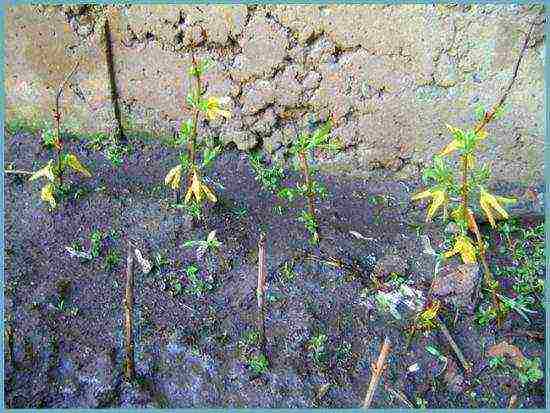

Forsythia sprouts
Layers The easiest way to propagate is, dig in the cuttings to a depth of 15 -20 cm, leave the top above the soil level. The branch will give a root, the next year, separate the young bush from the mother plant and transplant.
Advice. Branches cut in late autumn can be wrapped in foil and stored in a cool place. In winter, placed in water with honey, they will bloom.
Diseases and pests
Despite the fact that forsythia is considered practically invulnerable to diseases and pests, problems can still arise. Forsythia easily tolerates a short drought, but excess moisture can lead to decay of plant roots and the development of chlorosis. If such a disaster has already occurred, urgent action is needed. Dig out the bush, cut off the damaged roots, treat them with a potassium permanganate solution for disinfection. The upper part of the forsythia also needs to be shortened, since the remaining roots will not be able to provide food for the shoots. Now you can plant the bush in a new place.
If you notice that the leaves of forsythia turn yellow prematurely and the bush as a whole begins to fade, cut off the shoot. And if you see dark streaks and darkened vessels on the cut, this is bacteriosis. There is only one treatment - to uproot and remove the bush as soon as possible so that the bacteriosis does not spread to other plants in the garden.

Bacterial lesion
Spots on the leaves indicate the development of moniliosis. Perform sanitary pruning of affected shoots. Spray with an antifungal fungicide. Nematodes on the roots of forsythia are destroyed by carbation. Aphids can be destroyed with folk remedies or chemicals.
With proper agricultural technology, shrub health problems are extremely rare. But in early spring, when all living things are still sleeping and the garden is gray and dull, forsythia will delight you with extraordinary flowering.
How to grow forsythia: video
Forsythia in the garden: photo
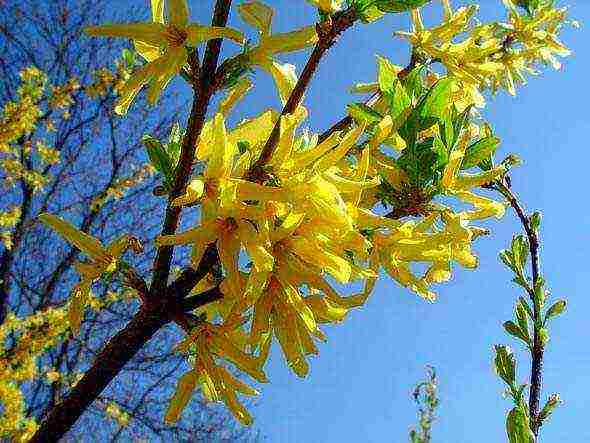





In early spring, forsythia bushes bloom their golden-yellow flowers. Against the background of a still completely dark meadow, the gold of bells with a heady aroma looks like a weightless cloud. The branches of the bush are flexible and long, they are strewn with flowers from the very end to the trunk, which will delight the eye for about 20-25 days. And only after the forsythia in the Urals fades, jagged leaves will appear on the bushes, the foliage will fall off in the fall, the bush will again bring gold flowering in the next early spring.
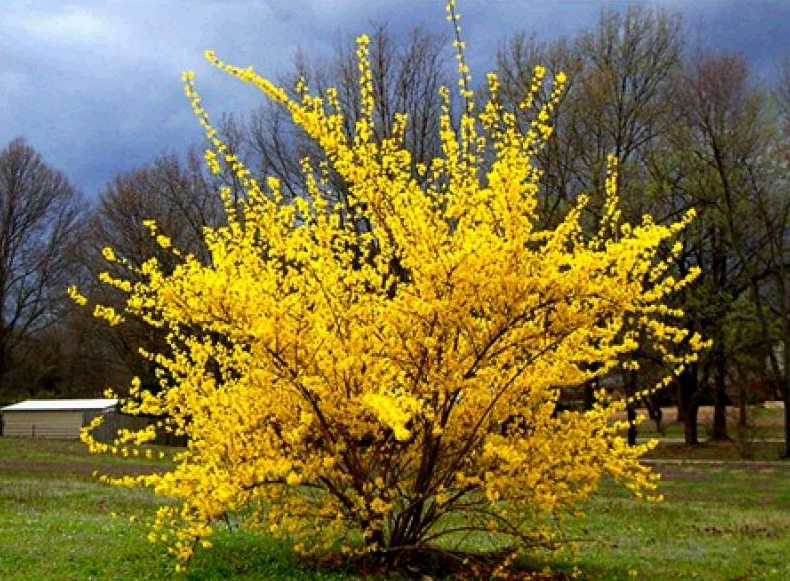

Forsythia varieties for growing in the Urals
On the territory of Russia in the Urals region, varieties are grown: drooping, oval and intermediate. A little further south you can find varieties of dark green and European forsythia, but they require shelter for the winter. In the middle Urals, it is better to grow an intermediate variety. It is a hybrid of drooping forsythia and dark green, characterized by beautiful toothed oblong or oval leaves, flowers are bright yellow bells, collected in inflorescences of several pieces. It tolerates frost and drought well, propagates by layering or dividing the bush.
Seeds for reproduction of forsythia are practically not used, their germination capacity is small. At the age of three, forsythia begins to bloom, flowering lasts a little less than a month, after which bright foliage appears, which does not fall until the first frost.

Among all varieties of shrubs, it is worth highlighting:
- Densely colored forsythia (densiflora), sprawling branches, strongly swirling flowers of light yellow hue;
- Forsythia remarkable (spectabilis), a tall shrub with straight branches, large flowers up to 4 cm in diameter, up to 4 bright yellow flowers in the inflorescence, is considered the most beautiful variety;
- Forsythia primrose (primulina) - resembles dense-flowered, wavy petals, flowers are located at the base of the branches;
- An interesting variety "Beatrix Farrand" is a very tall shrub, reaches 4 m in height, yellow flowers, a dark strip at the base;
- "Lynwood" - grows up to 3 m, flower diameter 3.5 cm, blooms profusely, leaves change color from green to purple;
- "Fiesta" is a low bush (up to 1.5 m), large golden-yellow flowers, green leaves with a tint of yellow, beautiful decorative spots on the entire leaf surface;
- "Veriegata" - with serrated leaves, there is a variety with variegated leaves;
- "Parkdekor" is one of the most winter-hardy varieties. It has flowers up to 5.5 cm in diameter, blooms very early, shrub growth up to 2 m;
- For the Urals, the ovate forsythia variety "Dresden Forfrühling" is perfect - it blooms profusely, winter-hardy, the diameter of light yellow flowers is up to 4 cm;
- Low variety "Tetragold" - shrub about 1 m, shows the earliest flowering;
- Forsythia "Spring Glory" with an interesting color of autumn foliage: pale purple or light yellow. The bell diameter is up to 3 cm.
How young forsythia bushes are grown
It is necessary to plant young forsythia bushes in the Urals in light soil, rich in humus and leafy soil; it is advisable to lighten the soil with expanded clay or river sand. Poorly tolerates acidic soil. Choose a well-lit location that is sheltered from the winds for planting. It will grow well in partial shade.
Prepare a hole for planting a bush up to 0.7 m deep, drainage with a layer thickness of up to 20 cm is required.As drainage, you can use:
- Broken brick;
- Expanded clay;
- River sand.
Plants are planted in a permanent place in the fall, between the bushes they maintain a distance of up to 2 m.
For good growth and abundant flowering, fertilizing in spring with mineral fertilizers is needed. It is not recommended to overdo it with watering. Forsythia tolerates dry soil better than excess moisture. After watering, it is recommended to mulch the ground around the bush. If mineral fertilizers are not applied, then you can once in the spring overlay the bush with burnt manure on all sides, and then water it abundantly. In the spring, before flowering, carefully examine forsythia in the Urals and remove frozen and dried branches.
Plant care in winter, forsythia disease

If a harsh winter is expected, it is advisable to bend the branches to the ground and overlay it with spruce branches. If you wish, you can cut off the branches shortly, they grow back almost instantly, again forming a lush crown. Forsythia is a fairly resistant plant to pests and diseases. Occasionally, for the prevention of diseases, the plant can be sprayed with foundation. Very rarely, it suffers from bacteriosis - such a plant must be completely removed from the site and the soil must be processed. Also, a plant nematode is rarely found - as a treatment, soil treatment with carbation is needed.
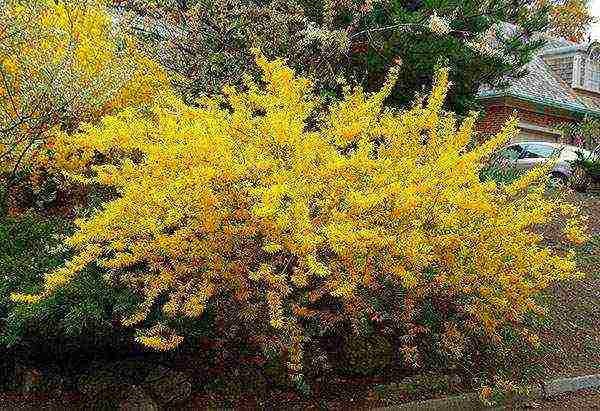
Forsythia is an ornamental shrub plant of exceptional beauty that looks great in single and group plantings.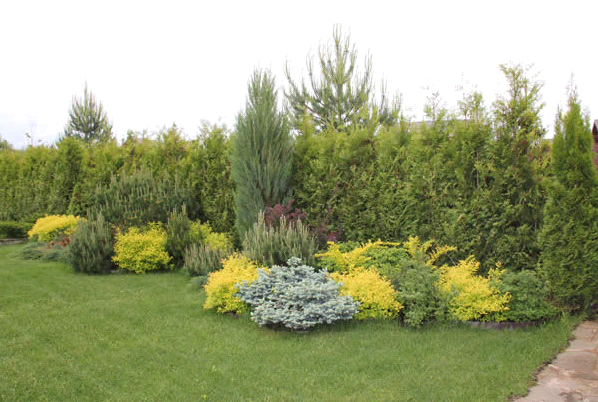
Agrees well with other plants, especially in spring, against the background of coniferous shrubs or trees, amphora.
It is used as a hedge, as it tolerates a haircut well and at the same time retains the ability to bloom profusely.
 Blooming forsythia, strewn with hundreds of bright yellow flowers, is impossible to miss! If the summer resident wants to be decorated with forsythia every spring, planting and care in the open field are key stages on the path to success.
Blooming forsythia, strewn with hundreds of bright yellow flowers, is impossible to miss! If the summer resident wants to be decorated with forsythia every spring, planting and care in the open field are key stages on the path to success.
Perennial shrubs, one of the first to break the monochrome of early spring, came to Europe from Asia and were named after the botanist who brought the first seedlings to the Old World. Today forsythia is the most popular type for landscaping and creating hedges.
How and when to organize planting and caring for forsythia in the open field at their summer cottage? What does a shrub need for friendly growth?
Conditions for planting forsythia in the open field
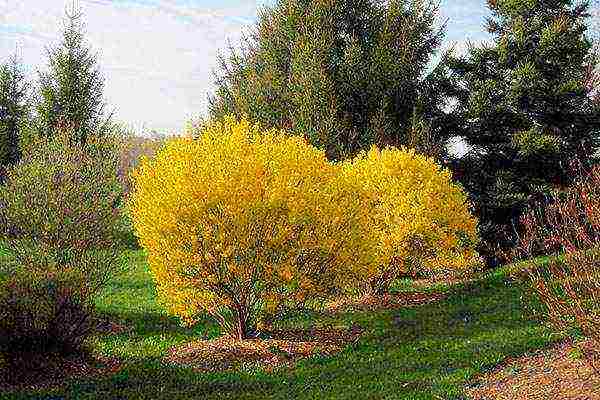 Forsythia is an amazing plant that changes its appearance every season. In the spring, these are branches devoid of leaves, but densely strewn with flowers. In summer, the bush is covered with greenery, which changes color to golden or purple in autumn. When looking for a place for forsythia, you should pay attention to areas where the shrub will be clearly visible and illuminated.
Forsythia is an amazing plant that changes its appearance every season. In the spring, these are branches devoid of leaves, but densely strewn with flowers. In summer, the bush is covered with greenery, which changes color to golden or purple in autumn. When looking for a place for forsythia, you should pay attention to areas where the shrub will be clearly visible and illuminated.
Although forsythia tolerate shade, in the sun the bush forms more dense and even. The plant is undemanding to soil fertility, but it develops better on soil with an alkaline reaction, good drainage. Culture:
- undemanding to care;
- has excellent frost resistance, simplifying the wintering of forsythia in the open field;
- tolerates drought well;
- responds well to haircuts and can be used for growing hedges.
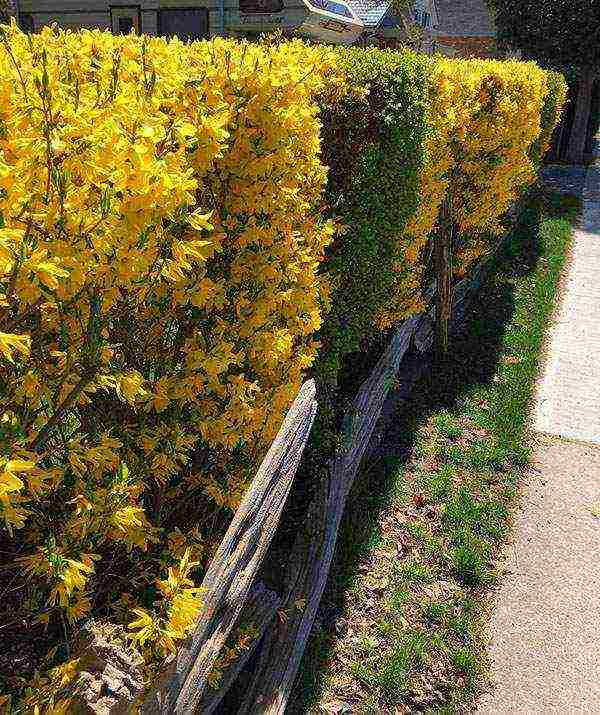 There are two options for planting forsythia in the ground: in spring and autumn. In the first case, young shrubs immediately begin to grow after acclimatization, giving new shoots. Bushes transferred to the garden in autumn only take root, and begin to grow after wintering.
There are two options for planting forsythia in the ground: in spring and autumn. In the first case, young shrubs immediately begin to grow after acclimatization, giving new shoots. Bushes transferred to the garden in autumn only take root, and begin to grow after wintering.
Timing of planting forsythia in the ground
The time for transferring seedlings to the garden is chosen depending on the region and the quality of the planting material. Many nurseries today offer young plants with a closed root system. Seedlings grown in containers are transplanted together with an earthen clod, so the roots do not suffer, the bush easily and quickly adapts to a new place of residence. And the summer resident is guaranteed easy care for forsythia in the open field after planting, whenever it happens: in spring, summer or autumn.
For seedlings with an open root system, it is better to plant in the spring months, when the threat of sudden frosts goes away, or in the fall, about a month before the onset of seasonal cold weather. During this period of time, the shrub will acclimate and be able to prepare for winter.
 Since the climatic conditions in the regions of the country are seriously different, there is a significant difference in the timing of planting and caring for forsythia in the open field, in the Moscow region and, for example, in central and northern Siberia, where the heat comes later, and the summer is much shorter:
Since the climatic conditions in the regions of the country are seriously different, there is a significant difference in the timing of planting and caring for forsythia in the open field, in the Moscow region and, for example, in central and northern Siberia, where the heat comes later, and the summer is much shorter:
- If you delay planting plants in the garden, their adaptation and rooting will be delayed, and the shoots that have dedicated over the summer will not have time to get stronger before the onset of frost.
- Early spring planting threatens with the danger of freezing of the buds, tops of the shoots, and with severe frosts on the soil, damage to the points of growth and roots.
 In autumn, planting forsythia in the ground also depends on weather and climatic conditions and can vary even within the same region, for example, as large as the Urals. If in the south gardeners live according to a calendar similar to that used by summer residents of the middle lane, then in the north the weather is much more severe and changeable.
In autumn, planting forsythia in the ground also depends on weather and climatic conditions and can vary even within the same region, for example, as large as the Urals. If in the south gardeners live according to a calendar similar to that used by summer residents of the middle lane, then in the north the weather is much more severe and changeable.
Planting forsythia in open ground
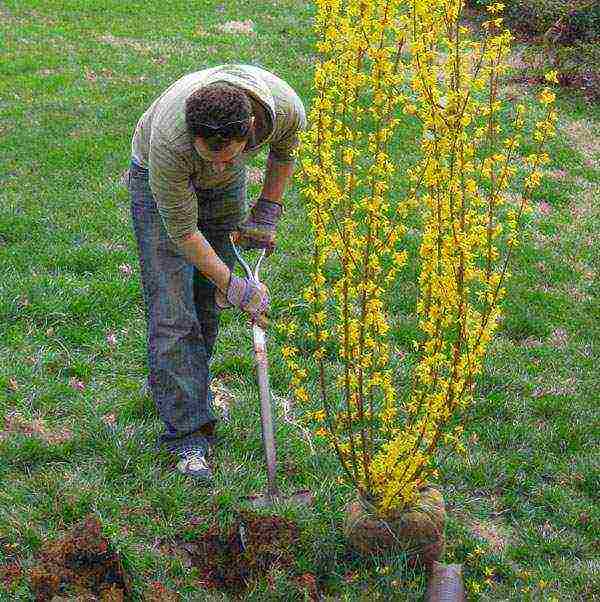 Forsythia prefer dry, drained soil and do not tolerate stagnant moisture in the soil. Therefore, at the bottom of the planting pits 60 cm deep and 50 cm wide, powerful drainage is made from broken brick, expanded clay or gravel. It is especially important not to neglect this measure in areas with dense soil that retains water and where groundwater is too close. An example is planting and caring for forsythia in the Leningrad region.
Forsythia prefer dry, drained soil and do not tolerate stagnant moisture in the soil. Therefore, at the bottom of the planting pits 60 cm deep and 50 cm wide, powerful drainage is made from broken brick, expanded clay or gravel. It is especially important not to neglect this measure in areas with dense soil that retains water and where groundwater is too close. An example is planting and caring for forsythia in the Leningrad region.
A layer of sand and a previously prepared soil mixture are poured over the drainage on the basis of:
- 2 pieces of leafy land;
- 1 part peat;
- 1 part sand.
 For each hole, 200 grams of sifted wood ash is mixed into the ground. The substrate is poured with a mound, on the sides of which the roots of the bush are spread. After filling the hole, the soil is compacted and watered abundantly at the rate of 10-15 liters per plant. In the fall, after planting forsythia, caring for the shrub consists in dense mulching of the trunk circle. This will help conserve water in the soil and protect the roots from hypothermia.
For each hole, 200 grams of sifted wood ash is mixed into the ground. The substrate is poured with a mound, on the sides of which the roots of the bush are spread. After filling the hole, the soil is compacted and watered abundantly at the rate of 10-15 liters per plant. In the fall, after planting forsythia, caring for the shrub consists in dense mulching of the trunk circle. This will help conserve water in the soil and protect the roots from hypothermia.
Mulch will help in spring, especially where summer comes quickly and the soil dries quickly, covered with a dense, impenetrable crust.
Caring for forsythia after planting in the open field
 An important advantage of forsythia is its simplicity and the absence of any special care. In the warm season, shrubs that grow rapidly with minimal care need:
An important advantage of forsythia is its simplicity and the absence of any special care. In the warm season, shrubs that grow rapidly with minimal care need:
- in irrigation, if there is no natural precipitation, and the soil under the plants is completely dry;
- in maintaining the cleanliness and looseness of the trunk circles;
- in a triple feeding;
- in a haircut that helps maintain the health and shape of the crown.
In hot dry times, the plants are watered abundantly once or twice a month, the field of which is loosened, weeded and mulched. Lowland peat mixed with humus and wood ash can be used as mulch. This composition protects the roots from overheating and is an excellent long-acting fertilizer. In addition, shrubs respond well to full fertilization before and after flowering.
In the second half of summer, you should not fertilize shrubs with nitrogen. It will cause active growth of young shoots, which, even with proper planting and caring for forsythia in the Urals, Siberia and in the middle lane, will not have time to ripen and will die with the onset of frost.
An important part of caring for forsythia is pruning the shrub. For sanitary purposes, the removal of dead, old or damaged branches is carried out in the spring, and a haircut to maintain shape - in early summer, when the mass flowering ends. Until recently, shoots yellow from flowers can be shortened by half the length, and old branches are cut above the ground so that several buds remain at the base.
Once every 3-4 years, forsythia is rejuvenated by evenly cutting all shoots by half or two-thirds of the length. Over the summer, the plant will restore the crown, which will be dense, uniform and young, so that next spring it will please with a friendly bright flowering.
In most regions, the plant winters excellently without shelter. If the winters have little snow, before wintering, forsythia in the open field is gently tilted to the ground, fixed and covered with spruce branches or dense non-woven material. At the first opportunity, the bushes are covered with snow.
Reproduction of forsythia in the open field
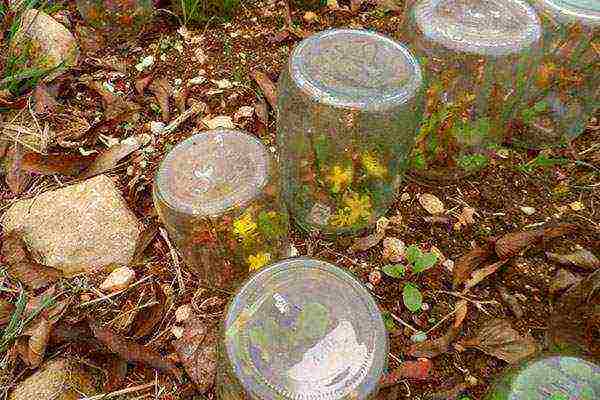
 The remaining parts of the branches after pruning are an excellent material for obtaining cuttings that will serve for the propagation of forsythia. The green shoots are cut into pieces 10-15 cm long so that each one has several healthy buds. The lower leaves are cut off, and the resulting stalk, after treatment with a rooting stimulant, is planted in a greenhouse.
The remaining parts of the branches after pruning are an excellent material for obtaining cuttings that will serve for the propagation of forsythia. The green shoots are cut into pieces 10-15 cm long so that each one has several healthy buds. The lower leaves are cut off, and the resulting stalk, after treatment with a rooting stimulant, is planted in a greenhouse.
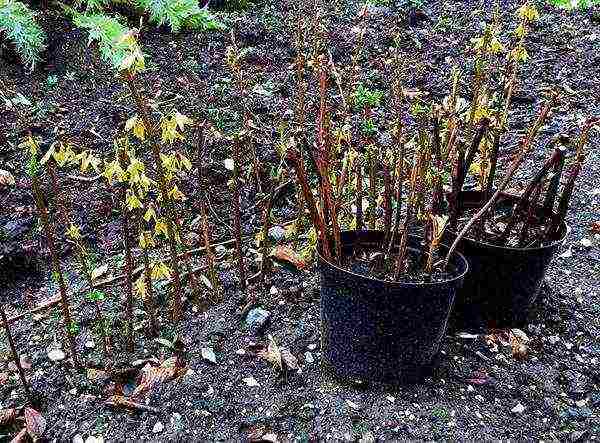
 In the fall, another method for breeding forsythia in the open field is possible. Lignified cuttings are planted in a school organized in a quiet place protected from wind and flooding. For the time remaining before the cold weather, the seedling will give roots, and 2-3 buds left above the surface of the soil will wake up in the spring and form a young crown of a dwarf shrub. In the coming fall, such plants can be planted in a permanent place.
In the fall, another method for breeding forsythia in the open field is possible. Lignified cuttings are planted in a school organized in a quiet place protected from wind and flooding. For the time remaining before the cold weather, the seedling will give roots, and 2-3 buds left above the surface of the soil will wake up in the spring and form a young crown of a dwarf shrub. In the coming fall, such plants can be planted in a permanent place.
Planting forsythia in a permanent place - video
Forsythia is a spreading, rather tall (up to 3 m) shrub of the Olive family.
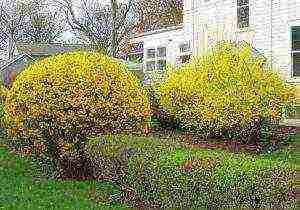 Its homeland is East Asia, but forsythia has long been successfully adapted in the European part of Russia, as well as in Siberia and the Urals. It is prized by landscape designers and loved by gardeners for its spectacular and very early flowering.
Its homeland is East Asia, but forsythia has long been successfully adapted in the European part of Russia, as well as in Siberia and the Urals. It is prized by landscape designers and loved by gardeners for its spectacular and very early flowering.
With the first warm days, bell-shaped flowers of a golden color appear when the leaves have not yet blossomed on the shoots. Against the background of a gray bare orchard, the sun balls densely covered with flowering look fabulous.
But let's leave poetry, because in order for the garden to be beautiful, you need to take care of it, and the work in the garden is very prosaic. For successful cultivation, you need to know what features planting and caring for forsythia in the open field in different regions have.
Requirements for growing conditions
Forsythia, called forsythia in Europe, has become the queen of city squares and alleys due to its unpretentiousness and environmental plasticity. But in order to get an abundant and bright flowering, you need to try to create the best conditions for it.
When choosing a place, it is better to give preference to sunny areas, but even in partial shade, forsythia feels at ease. It is desirable that there is protection from the prevailing winds. Soils should be nutritious, light, breathable, without stagnant water. Heavy and acidic soils need preparation. It grows well in calcareous soils.

Forsythia is quite drought-resistant and does not need frequent watering, as a rule, it gets by with atmospheric precipitation. Waterlogging, stagnation of melt water and poor aeration of the root system have a detrimental effect on the shrub.
Forsythia shows good winter hardiness, but in the conditions of the Urals and Siberia it needs shelter for the winter. In these regions, it is necessary to select southern well-warmed areas for planting.
For the European part of Russia, varieties of 3 types are recommended: hanging (drooping), ovoid and hybrid (intermediate). In the south of Russia, European forsythia and dark green are grown. In Siberia and the Urals, it is better to plant the most winter-hardy species: ovoid and intermediate. In this case, you need to carefully study the characteristics of specific varieties.
Reproduction of a yellow blooming beauty
Forsythia propagation works are carried out mainly in autumn. Let's make a reservation right away that seed reproduction, although possible, is "not worth the candle", leave these experiments to the breeders.
Like all shrubs in private gardening, forsythia propagates vegetatively: by cuttings and layering. Reproduction by layering is the easiest and fastest way to get a new seedling. In the fall, the flexible falling branches are bent to the ground, a shallow incision in the bark is made at the place of the trench, pinned for fixation and added with moist, loose fertile soil.
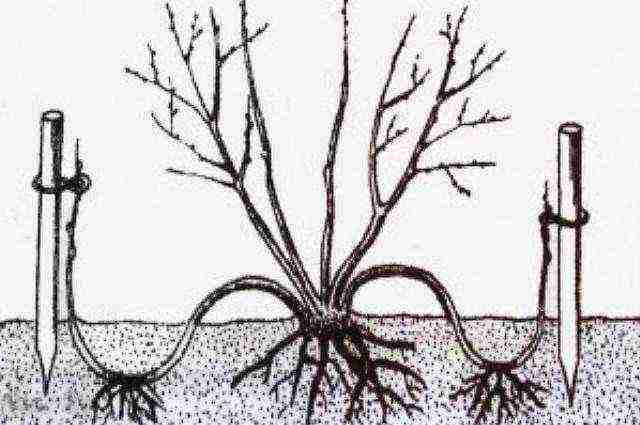
Already next spring you will have a ready-made seedling, which must be separated from the mother plant. Over the summer, the young plant will form a powerful root system, and in the fall it can be transplanted to a permanent place. With this method, the flowering of the shrub will begin as early as 2 - 3 years of age.
Also in the fall (September - October), reproduction is carried out by lignified cuttings. To do this, the ripened shoots of the new year are cut into cuttings 15 cm long and planted in a school in the open ground or a greenhouse, burying 10 cm into the substrate so that 2 - 3 buds remain. For winter, cuttings are covered with dry leaves and covered with snow during winter.
Rooting and growth of planting material will take place for the entire growing season, and only in autumn the grown seedlings can be transplanted to a permanent place. They will bloom a little later than with the first method, but cuttings allow you to get a large yield of planting material. This method is convenient if you want to plant a hedge and arrange an alley.
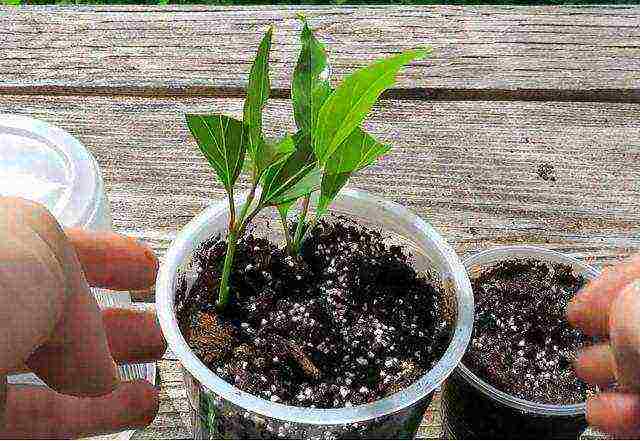

In summer (June), forsythia can be propagated by green cuttings. They are cut from the young growth, the lower leaves are removed, and the upper ones are shortened in two. In this case, it will be necessary to treat the cuttings with growth stimulants and cover the plantings in the school with a film to retain moisture. The amount of maintenance work will also increase: spraying, watering, airing.
Features of planting and subtleties of care
Despite the fact that forsythia can be planted both in autumn and in spring, it is preferable to hold this event in autumn (at the beginning of leaf fall), since in spring you simply may not have time before the start of sap flow.
Forsythia wakes up from winter dormancy early, and in early spring, and without ornamental plants, it is enough trouble. If you still need to plant in spring, then it is better to use seedlings with a closed root system. They do not tolerate transplantation so painfully and adapt faster.

Planting pits are prepared with a length and width of 60 cm, their depth should be about 70 cm for the device at the bottom of a drainage layer of crushed stone or broken brick. The soil mixture for filling the pit consists of humus, rotted leaves, garden soil and sand. Adding lime, wood ash or chalk is encouraged. Autumn plantings in the first year, regardless of the region and variety of forsythia, must be covered for the winter. The trunk circle is mulched with dry leaves, and the aerial part is protected with a covering material.
Forsythia does not require close attention to itself and even feels better when forgotten. In the spring, you can add lower doses of complex fertilizers and organic matter (in the form of mulch from compost or humus). In autumn, on poor soils, it is recommended to apply phosphorus-potassium fertilizers. Reasonable feeding with universal complex fertilizers improves flowering, but an excess of nutrition reduces winter hardiness and negatively affects decorativeness.
In its natural habitat, forsythia conquers the rocky slopes of the mountains, therefore it calmly tolerates drying out of the soil. An excess of moisture affects its condition much worse. In summer, it is watered only during a prolonged drought, but not abundantly and not more often than once a week. In this case, it is necessary to loosen the upper layer to restore the air chambers.
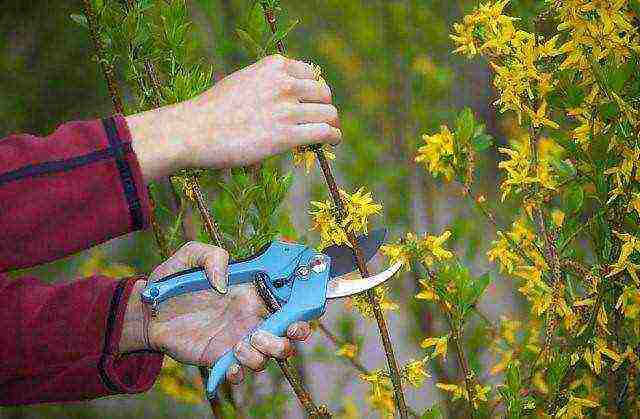

An important spring event is phytosanitary pruning of bushes, during which frozen, dry and broken shoots are removed. Old bushes can be rejuvenated by cutting to half of the entire length of the shoot. Formative pruning is carried out after flowering, giving the bush the shape of a ball or making out a flat hedge.
When pruning, do not touch the young growth, since flower buds are laid on it for the new season. Old lignified shoots are removed, and young ones are only slightly shortened to stimulate branching. Forsythia grows quickly and tolerates pruning well, but you should not overdo it with it, so as not to get unrestrained growth of shoots with poor flowering.

Forsythia in the Moscow region, with the correct selection of varieties, survives winters well with minimal shelter (mulching of near-trunk circles with dry leaves and spruce branches). Even in the case of a severe winter with little snow, only the young growth will die, but the bush itself will quickly recover.But for the Urals and Siberia, complete shelter is recommended. In young plants, shoots are pressed to the ground and covered with spruce branches or agrofibre. Winding with a suitable covering material will also help protect the crown.
Forsythia in the garden: where and with whom to plant
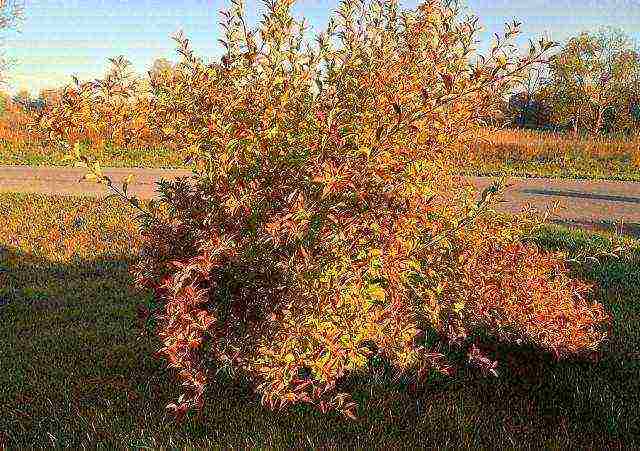
Forsythia blooms in April (for the Moscow region and the middle zone) or May (for the Urals and Siberia). The flowering period is up to 3 weeks, and then the yellow bells are replaced by light or dark green leaves. The shrub does not lose its decorative effect even in autumn, when the leaves turn purple or golden.

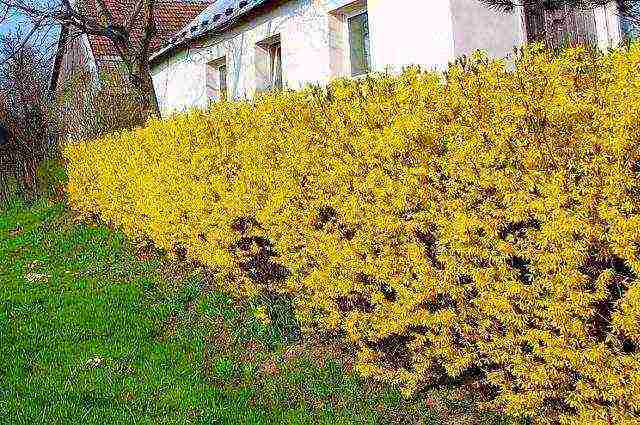
In European gardens, forsythia is very popular in landscape design and in Russia it is found more and more often. It is great for creating hedges as it grows quickly and tolerates pruning well.

It also goes well with evergreen conifers, especially during the flowering period.
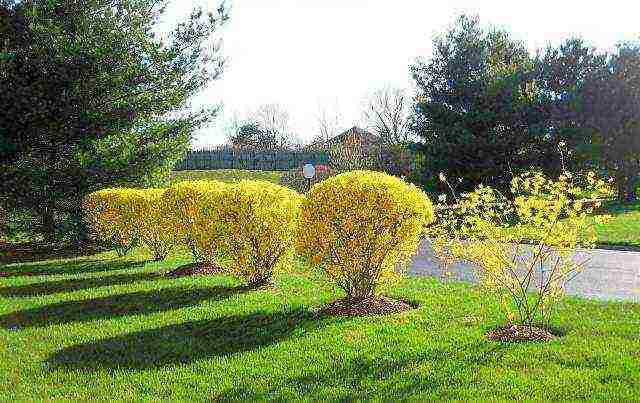


Single plantings, with a spherical formation of the crown against the background of a well-groomed green lawn, will give the garden a special grace.
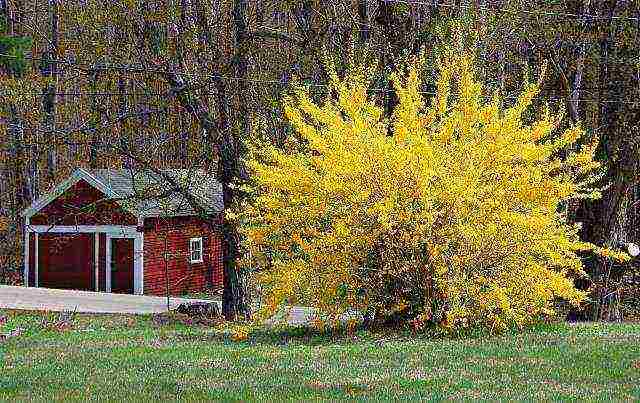


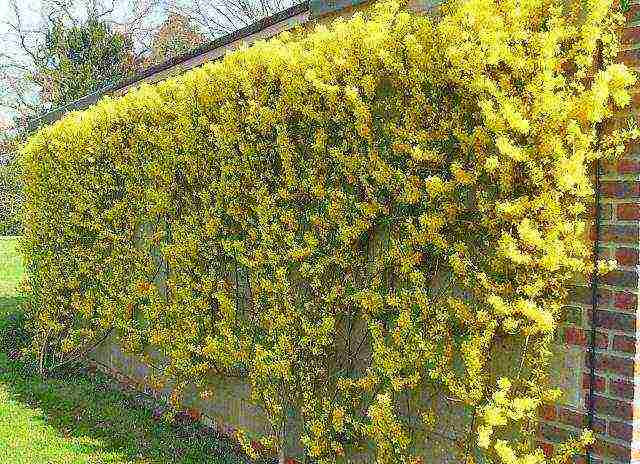
Forsythia goes well with spirea and euonymus. Hanging (drooping) forsythia varieties are used for trellis growing along the walls of houses or for decorating a gazebo.
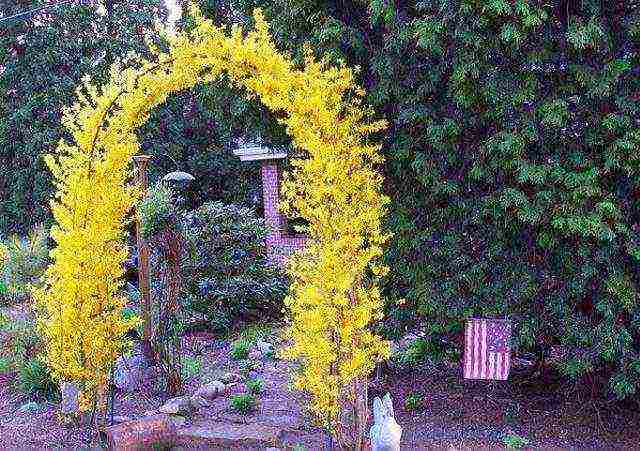


In late autumn, ending the season in the garden, cut off a few young shoots of forsythia, wrap them in plastic and put them in a cool place (cellar, loggia or refrigerator). In winter, it is enough to dip the shoots into the water with diluted honey and the room will fill in a few days with the bright yellow color of the blossoming forsythia.
Description of species and popular varieties
The most versatile and common type is intermediate forsythia. It has good winter hardiness and is very decorative. However, other varieties deserve attention.
- Forsythia ovoid - the most winter-hardy and drought-resistant species with the earliest flowering of average duration. The shrub reaches a height of no more than 2 meters, the flowers are small, the crown is spreading. The varieties of this species are very decorative in autumn, when the leaves take on a purple hue.
Tetragold is a meter high shrub with dark yellow flowers.
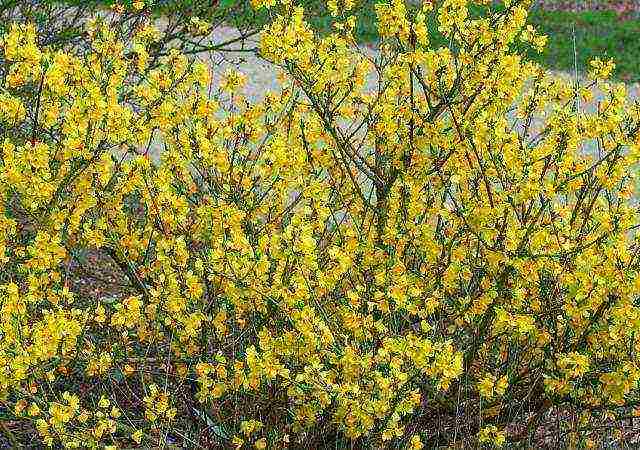

Spring Glory is a real giant in its group (up to 3 meters high) with large flowers and powerful shoots. In autumn, the bush is dazzled with pale yellow and purple leaves.
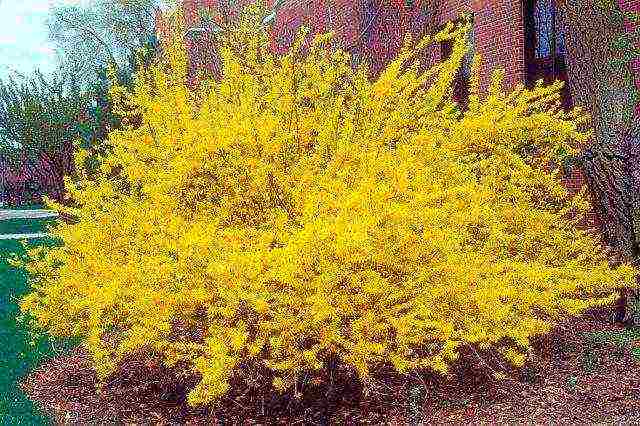

- Forsythia hybrid (intermediate), or the middle one is distinguished by a powerful tall shrub up to 3 meters and a dark green color of large leaves. Bright yellow flowers are collected in simple inflorescences of several pieces.
Spectabilis is one of the most decorative varieties. Reaches a height of more than two meters and forms a wide crown with cascading shoots. Flowering later, flowers are large (more than 4 cm in diameter). In autumn, the bush turns yellow and purple.

Lynwood is a medium-sized shrub (2-3 meters) with golden flowers. In autumn, the leaves acquire a bright decorative color.
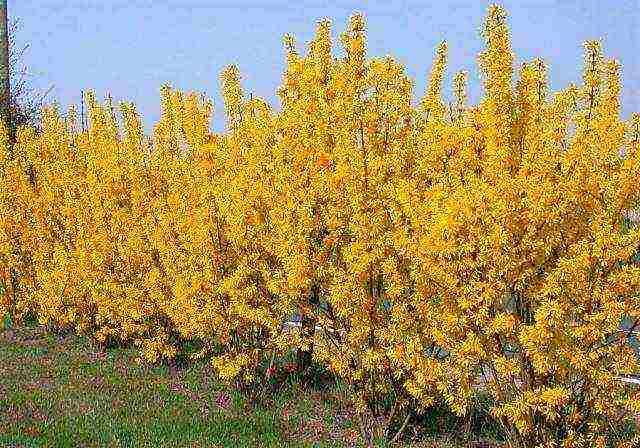

Minigold is a slow-growing dwarf variety with a compact crown and small flowers.
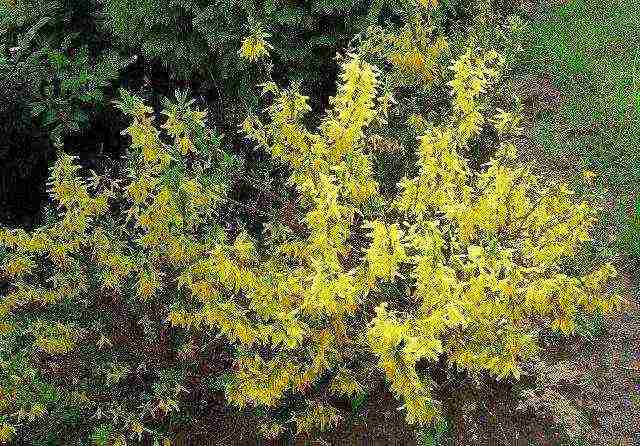

Goldsauber is a popular variety with golden flowers, often grown in Siberia and the Urals.
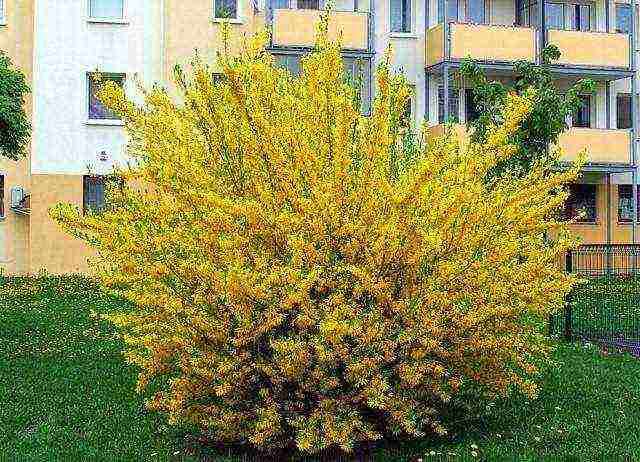

- Hanging forsythia (drooping) characterized by a spreading crown and drooping branches covered with olive bark, which in combination with yellow looks very impressive.
Forsythia Fortune forms flowers with an orange tint. In the first years of life, the bush forms erect shoots, and after 2-3 years long drooping branches appear. It blooms profusely.

Forsythia motley is distinguished by the unusual color of the xiphoid leaves: a dark green middle and a lighter yellowish border.
Forsythia Siebold is a winter-hardy undersized variety for Central Russia, which still requires shelter (shoots are removed from the trellis and covered with leaves or spruce branches).
- European forsythia - a more thermophilic species, which, with careful shelter, can winter in the Moscow region. The bush is 2 meters high and is covered with large lemon flowers.The leaves are oblong, light green.
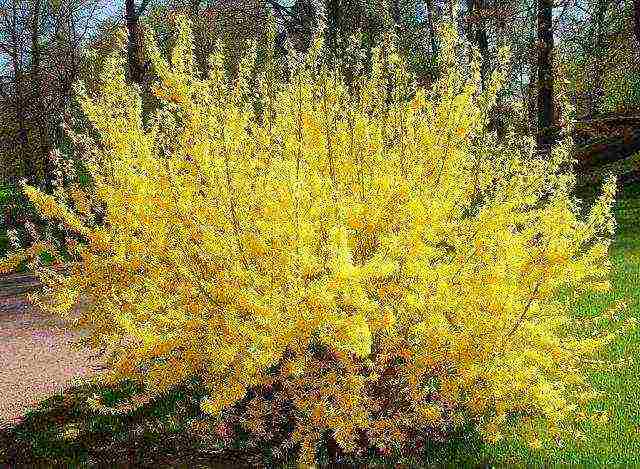

- Forsythia dark green (greenest) - a tall, highly leafy shrub. The flowers are greenish, the bark of the shoots is dark green. The species is drought-resistant, but has a low winter hardiness, therefore it is grown only in regions with a mild climate.

Separately, I would like to note the low-growing hybrid variety Kumson with drooping branches. It is distinguished by its leaves with a milky mesh of veins. Its flowers are pale yellow. When grown in the suburbs, flower buds can freeze, so shelter is required.

Forsythia will decorate any garden and will not cause trouble if you choose the right variety. It is rapidly gaining strength and pleases with consistently abundant early flowering in a season that is poor in colors.


