Content
- 1 Planting and caring for green beans
- 2 Asparagus beans planting and care in the open field
- 3 Asparagus beans: growing from seeds at home
- 4 Growing asparagus beans in Siberia
- 5 Growing green beans: care after planting
- 6 Video: how to plant green beans
- 7 Video: caring for green beans in the garden
- 8 Dates for planting beans in open ground
- 9 Do I need to soak beans before planting?
- 10 Choosing a place for planting beans
- 11 Preparing a site for planting beans
- 12 Planting scheme for beans in open ground and planting depth
- 13 How to plant beans in rows, look at the video:
- 14 Planting corn and beans together
- 15 Planting curly beans in the video:
- 16 Do I need to water the beans after planting
- 17 How many beans germinate
- 18 How to care for beans outdoors
- 19 Useful video about growing vegetable beans:
- 20 Diseases and pests of beans
- 21 Harvest time of beans
- 22 Bean varieties with photos and descriptions
- 23 The oldest representative of legumes
- 24 Growing
- 25 Sowing seeds
- 26 Seedlings and care
- 27 Important points of harvest
- 28 Description of varieties of green beans
- 29 Green beans: planting, growing. We select the soil
- 30 Green beans: planting seeds correctly
- 31 Features of planting bush and curly beans
- 32 Green beans: growing and care. Watering, feeding
- 33 Harvesting green beans
- 34 Popular varieties of green beans
- 35 Instead of a conclusion
Due to its unpretentiousness and good yield, not only grain, but also green beans are popular among domestic summer residents. Planting and caring for a crop does not require much experience and cost, therefore it is suitable for all gardeners. A large varietal variety allows for the successful cultivation of green beans in any region. The article discusses the advice of gardeners - planting green beans and care, how to prepare seeds and soil for planting in open ground, as well as pest control and other useful tips.
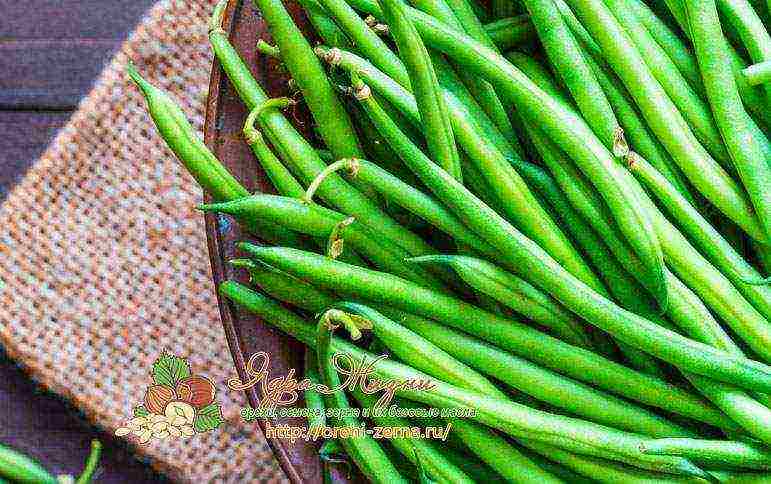 Green beans (asparagus)
Green beans (asparagus)
Many gardeners who cultivate beans on their own in their summer cottage recognize the most delicious variety of plants as green beans - asparagus is distinguished by longer pods, but the principle of planting and caring for them is about the same. Growing and caring for beans is not too difficult, and the juicy and satisfying product is ready to serve in the summer. Fresh green pods are also available to those who do not have personal land - you can successfully grow asparagus beans at home - on a glassed-in balcony or windowsill.
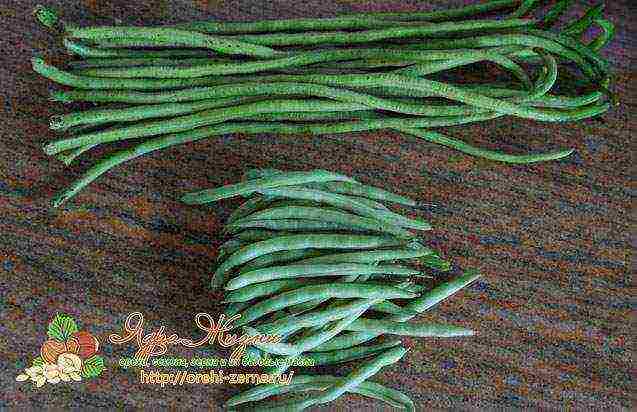 Asparagus beans differ from regular green beans in longer pods.
Asparagus beans differ from regular green beans in longer pods.
Planting and caring for green beans
Asparagus and green beans are one species, more precisely, asparagus is one of the green beans. It is distinguished by the large length of the pods and the absence of clear forming grains inside them. In addition, the flaps themselves are softer, since they do not grow a hard layer of parchment, which gives them good culinary qualities.
Green beans are a low-calorie food packed with many vitamins, amino acids, organic acids, flavonoids and minerals. It is widely used in cooking as a vegetable ingredient in salads, side dishes, first and second courses. The asparagus variety got its name from its characteristic taste, reminiscent of asparagus.
Green Bean Varieties
- The purple queen. An interesting bush variety that combines fruit and decorative functions. Produces dark purple pods up to 15 cm long. The variety is not afraid of many diseases and is suitable for planting in different regions.
- Crane. A compact plant reaching half a meter in height. Non-capricious variety with enviable productivity. The delicate taste of the fiberless pods is excellently preserved in canning and in freezing.
- Sachs 615 (without fiber). A bushy early ripe hybrid with a height of up to 45 cm and green pods up to 12 cm. It is very popular due to its high-vitamin composition.
- The oil king. Shrub variety with a growing season of 55 days. By the end of summer it produces yellow pods with a distinctive flavor.
- A widespread, fast-ripening curly variety, the pods of which grow up to 13 cm in length. Up to 10 pods are harvested from one plant per season.
- Winner. Curly flat-pod variety that decorates the garden with fiery red flowers during flowering. Brings flattened fruit pods up to 30 cm long.
- Caramel. Early ripening fiberless beans, called by many summer residents the best among the species. Produces short pods with large seeds inside. The plant is popular for its high immunity to common viruses.
- Fatima. A variety of curly beans with a medium ripening period. Growth can be 3 meters, but the foliage is always average. The pods are straight in shape - they can be 21 cm each. They have a good taste and a delicate, fibrous structure.
- Panther. Another bushy variety with yellow, fibrous fruits. Differs in high resistance to fungal diseases and a special spicy taste.
- Hell Rem. Curly variety with light pods and rare lilac-pink grains. Differs in characteristic mushroom aroma and high resistance to pests and diseases.
- Neringa. A bush bean variety that ripens in 7-9 weeks. Gives green long (14-16 cm) pods with juicy leaves without parchment layer. The plant bears excellent fruit in different conditions, is versatile in processing.
- Deer king. A bushy variety of green beans with extremely tasty fruits. The bright yellow ripe pods have dense white grains inside. In warm regions, it is possible to harvest twice a season.
- Bona. A plant with a compact bush up to 40 cm in height. It gives rounded pods 13-16 cm long without a parchment layer with 5-6 white seeds. It is appreciated by gardeners for its immunity to diseases, good productivity and versatility. Ripens in 50-75 days after sowing.
- Blue Lake. A tall variety that needs solid support. The green pods grow up to 16 cm in length and reach maturity 50-56 days after the sowing date of the beans. Small white seeds form inside. It is a fruitful hybrid with decent resistance to infection and disease.
- Sweet courage. A shrub plant with fast maturation. Differs in cylindrical yellow pods, growing up to 16 cm in length.
- Gina.A bushy early ripe variety with slightly curved pods up to 17 cm long. It has excellent qualities that are preserved during canning. Highly prized for its productivity and disease resistance.
- Paloma. Dutch beans for early sowing. Bears abundantly in 11-12 cm dark green pods. Versatile in culinary use.
- Bergold. A high-yielding bush variety with soft pods without parchment. Slightly curved fruits grow up to 14 cm in length and keep well in ice cream or canned.
- Nagano. Asparagus beans from a Dutch manufacturer. Suitable for sowing from early to medium terms. High resistance, good yield with 13 cm pods. Good in freezing and preservation.
- Mascott. Western low-growing variety with ripening in 50-55 days after breaking through the seedlings. For dense, fiberless pods with a pleasant crunch, Mascott is very fond of the French. Can be grown at home on a windowsill.
- Pensioned Under Black Wax. Low-rise Italian beans with bushes up to 40 cm in height. Differs in good yield, excellent commercial qualities of fruits, high immunity. The pods grow up to 15 cm and are well preserved in conservation and freezing.
- Kentucky Blue Pole. Favorite by many American farmers, beans have a 65-day growing season. A climbing plant with a total length of up to 2.5 meters. It is very similar in growth and fruit characteristics to the Blue Lake variety.
- Gold Mine. Bush beans, called by some summer residents super-sweet. Strong upright bushes yield up to 800 grams of juicy pods.
- Serengeti asparagus beans. Planting of this early maturing variety is possible in all climatic zones. This variety is distinguished by resistance to many diseases, as well as pleasant taste characteristics and high yields.
On a note!
For middle and northern latitudes, you should choose among early maturing or mid-ripening hybrids that ripen in 50-80 days. Late-ripening varieties of beans are suitable for cultivation in the south, as they reach ripeness no less than 100 days after sowing.
Green Beans: Planting and Caring for the Right Place
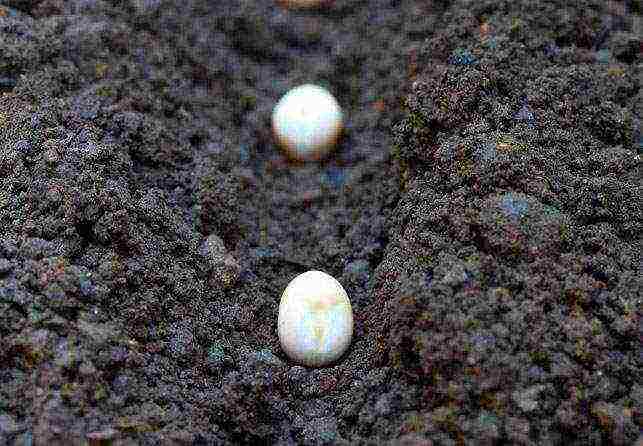 Green beans planting and care
Green beans planting and care
The first thing to think about before planting beans is the ideal garden plot. To allocate a place for this plant at the last moment, where it works out, is incorrect, since it is rather capricious in relation to the illumination and the nature of the soil:
- In the initial stages of development, beans require intense, but not unnecessarily long exposure to sunlight. They should get on plants no longer than 12 hours a day.
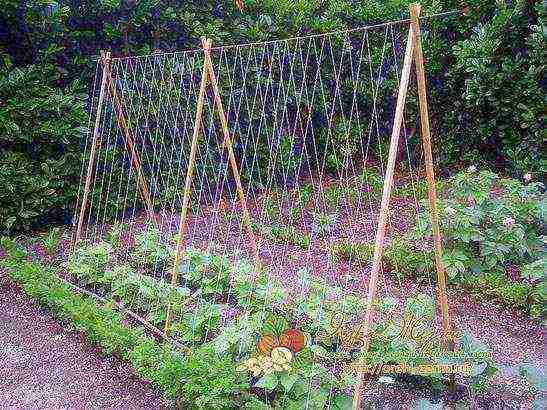
- Curly bean varieties should be planted next to a support for lifting branches, and if there is none, make a trellis yourself. Planting of three plants with a support in the form of a high tripod is practiced.
- Beans grow well and bear fruit when planted after potatoes, onions, cucumbers, carrots, cabbage, and other root plants.
- Poor precursors for green beans are sunflowers, legumes and legumes, and perennial herbs like clover.
- Bush varieties of green beans grow well in the aisles of potatoes and cabbage, they do not need supports for weaving.


When planting green beans in open ground
In most cases, sowing seeds of green beans is carried out in the middle of May - early June. The main indicator is the degree of heating of the earth at the depth to which they are embedded (5-6 cm). The temperature here must be at least + 10˚C. Basically, in the Russian regions, frosts should be over by this time. If, according to the weather forecast, a repeated decrease in temperature is promised, the crops will need to be covered with polyethylene or non-woven garden cloth.
Green beans should be planted to a depth of 60 mm on very loose soils.The harder the soil, the closer to the surface the seeds should be placed so that the soil structure does not interfere with germination. Landing scheme:
- for bush varieties: 15-20 cm between holes and 35-40 cm between rows, the optimal number of rows for cross self-pollination is 4;
- for climbing varieties: 20-30 cm between holes with the obligatory presence of a strong non-plastic support (branches can grow very heavy).
In both cases, it is recommended to throw 2-3 beans into the holes in order to have a guarantee of germination. At least one of them will definitely break through. And if several come up, then you just need to choose the strongest among them, and pull out the rest.
After sowing, you need to water the garden bed and slightly press down the soil with a rake. When punching seedlings, it is necessary to huddle them in a timely manner to impart greater stability and accelerate development.
How to prepare soil and green bean seeds
It is good if the site chosen for planting will consist of nutritious soil and, more importantly, well-drained soil. The lush soil will allow the beans to self-feed on nitrogen from the root nodules. It is not worth risking planting in clay soils or areas with a close passage of groundwater - the seeds may simply not sprout.
To increase the yield, the soil must be enriched with humus or heated compost before deep digging. Ammonium nitrate with the addition of calcium chloride and superphosphate is also a useful additive. Nitrogen is not needed - if you constantly make the soil loose, it will be extracted in excess by the plants themselves.
Presowing treatment of beans:
- Sort out the grains, discarding the damaged ones.
- Soak in thawed water at room temperature for no longer than 12 hours.
- Before sowing for 3-5 minutes, lower the beans in a solution of 2 g of boric acid and 10 liters of water.
Asparagus beans: planting and caring for seedlings
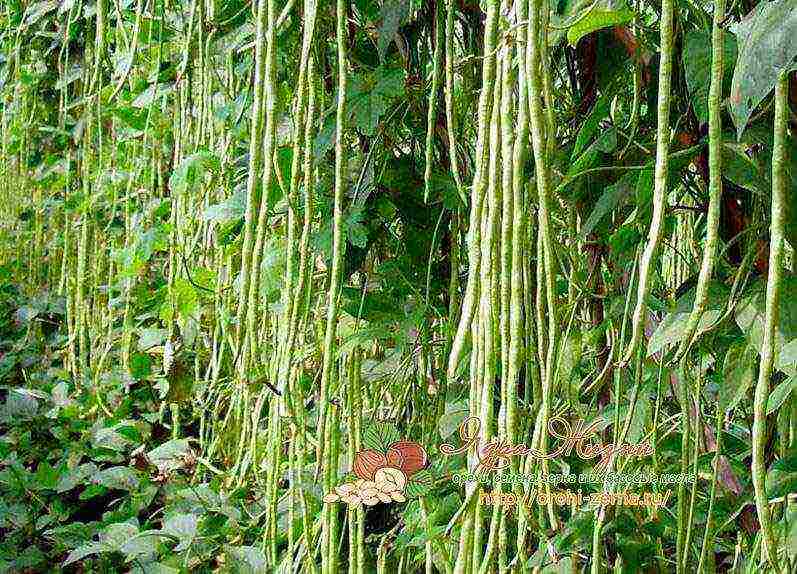 Asparagus beans planting and care
Asparagus beans planting and care
To germinate seeds before sowing, you can use the following method:
- Pour them into a linen bag (or tie them with a cloth) and immerse them in a light solution of potassium permanganate heated to 35-40˚C.
- Rinse the grains with clean running water and wrap them in a damp cloth for 5-6 days. It is necessary to keep its moisture content during this period.
- At temperatures in the range of + 20- + 30˚C and being in a humid environment, the seeds germinate quickly.
It is advisable to sow seedling beans in April. Moreover, it is necessary to place crops in a greenhouse or under a film, since at first they are extremely sensitive to temperature conditions.
It is better to plant according to the 6 × 6 cm scheme - it will be convenient for the plants themselves to grow, but also for the gardener to take care of them. Seeds for seedlings should be laid at a depth of about 2 cm.
Care features:
- for germination and good development of sprouts, you need to constantly water the soil, but at the same time maintain its looseness;
- after the initial weeding, you can start feeding the plantings with a mullein (1: 6 with water) or ammonium nitrate (20 g per 1 m2);
- you should not just flood the seedlings - the soil is needed moist, but without standing water - so the seeds can ferment;
- during the summer, you need to carry out such a make-up several more times, but about 40 g of superphosphate should be added to 10 liters of the mixture;
- to protect against low temperatures in the cold season, it is necessary to cover the seedlings with straw compost or melted manure in autumn.
A significant part of the seedlings will most likely still be unsuitable for further cultivation. Therefore, in the spring, before replanting, it is necessary to select suitable plants. Good candidates should have a solid root system, 5-7 good shoots and a healthy appearance.
Asparagus beans planting and care in the open field
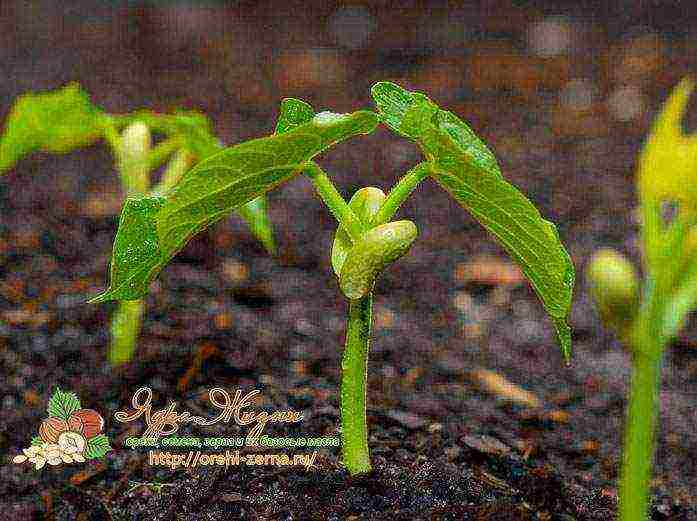 How to plant asparagus beans outdoors
How to plant asparagus beans outdoors
For cultivation from seeds in the open field for asparagus beans, it is necessary to select naturally illuminated areas with light and nutritious soil.A bonus to productivity will be if potatoes, cabbage, onions or carrots were grown in this land last season. Beans take root very reluctantly on clay soils and soils with close underground waters.
In areas with long cold winters, it is better to start growing asparagus beans in a greenhouse, so as not to waste time due to insignificant heating of the soil. This culture is very sensitive to cold weather and usually dies at temperatures below + 5˚C. Because of this, the already sown beans are wrapped in foil when there is an unexpected cold snap.
If asparagus beans have already grown on a specific site, it is recommended to re-organize cultivation from seeds only after 4 years. This is not a problem, given the fact that after this plant, which enriches the soil with nitrogen, any garden crops grow well.
In the autumn months, the land for asparagus beans is enriched before deep digging with organic matter, potassium chloride and superphosphate in a volume of 7 kg / m2, 45 g / m2 and 25 g / m2, respectively. Before planting from seeds in the country, a fertilizer complex with a high proportion of potassium should be applied at the rate of 25 g / m2. After laying the seed, experts advise sprinkling the bed with humus on top and feeding the beans with mineral mixtures up to 3 times during the season. Application scheme: in small grooves, parallel to the rows at a distance of 15-20 cm. One recharge is mandatory in the bud setting phase.
Landing
Seeds of asparagus beans are sown similarly to any other legumes. this should be started when the earth warms up at a depth of 50-60 mm to + 10˚C and the frost stops. The previously selected beans are first soaked for up to 10 hours in melt water for better germination. Many summer residents slightly tint the water with potassium permanganate and add growth accelerators there, but this is not an obligatory practice. It is also believed that it is not necessary to soak the seeds if the soil is moist enough when planting.
A few minutes before laying the beans, they are also kept for 5 minutes in an aqueous solution of boric acid (0.2 g / l), for increased immunity to diseases. Next, the seeds are placed in several pieces in holes 3-5 cm deep. In one furrow for bushy varieties of beans, 10-15 cm should be left between the grooves, and the grooves should be located at a distance of 25-30 cm relative to each other. Curly hybrids should be placed at a distance of 20-30 cm between themselves and 0.5 m between the rows.
Excessive moisture is something that asparagus bush beans do not like very much. Growing should be accompanied by moderate but regular watering once a week, doubling the volume during the flowering period. After watering, it is recommended to loosen the soil around the plants so that air access to the root nodules does not stop. It is also necessary to constantly pull out the weeds, as they deplete the soil. To increase the yield, it is recommended to apply two additional fertilizing from mineral complex fertilizers during the cultivation process.
Asparagus beans: growing from seeds at home
Asparagus beans can be grown quite successfully in indoor conditions, for example, on a glazed loggia or a well-lit windowsill. Better, of course, to choose bush varieties that do not rise above 50 centimeters in height. Curly varieties can be planted on the balcony, not about this you need to be prepared that they will entwine it from the inside, turning it into an indoor jungle.
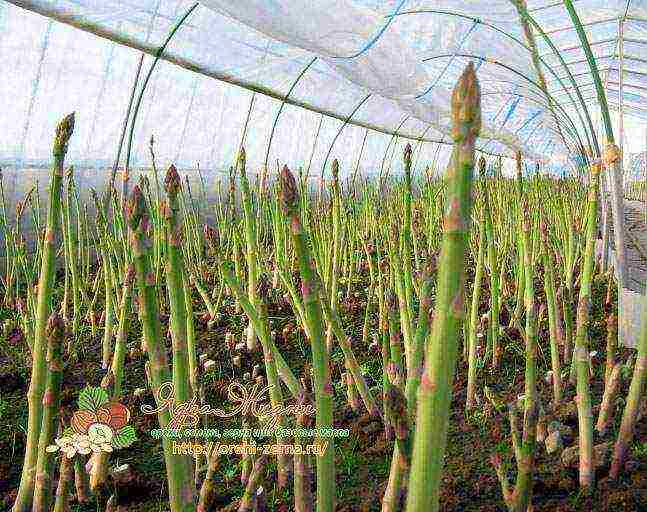 Asparagus beans - greenhouse cultivation
Asparagus beans - greenhouse cultivation
Planting can be carried out either by direct sowing into a growing container or by seedling through peat pots. Planting time depends on individual conditions, you can even organize year-round cultivation. For such a crop cultivation, the varieties Mask, Fatima, Violetta, Zelenopodrukovy 517 and Zolotaya neyka are well suited.
Growing at home often requires additional lighting equipment, but plants do not need a long daylight hours.The soil for planting should consist of two-thirds of garden land and one of humus. You need to constantly keep it loose. Top dressing is desirable - it is enough to use complexes with potassium and phosphorus a couple of times a month. Overexposing the crop on the branches is only when collecting seed.
Growing asparagus beans in Siberia
Siberia is a rather harsh region in terms of weather, with short summers, which does not have the best effect on growing crops. Most varieties of beans grow reluctantly in such conditions, therefore, when planting and caring, the following recommendations should be adhered to:
- Due to the short season, the earliest varieties should be chosen.
- Beans are thermophilic, so you have to wait for favorable weather. Sowing is usually carried out not earlier than the end of May. In cold spring, it is better to think about seedling planting.
- Seeds are best planted dry, without soaking.
- Beans must be sprinkled after the sprouts are higher than 10 cm so that they do not die from the wind or their own weight.
- It is imperative to tie up climbing plants, as there is a lot of precipitation and leaves and pods on the ground can rot.
- During a cold snap, it is better to cover the beans with a film material.
Harvesting should be done when the pods are ripe. When planting early maturing varieties, the collection begins in August. After removing the ripe fruits, they should be left to ripen in the air, hanging or spreading out under a canopy. This allows the remaining pods to mature faster. With the onset of frosts below -1˚C, the plant can be completely pulled out and suspended to ripen.
Growing green beans: care after planting
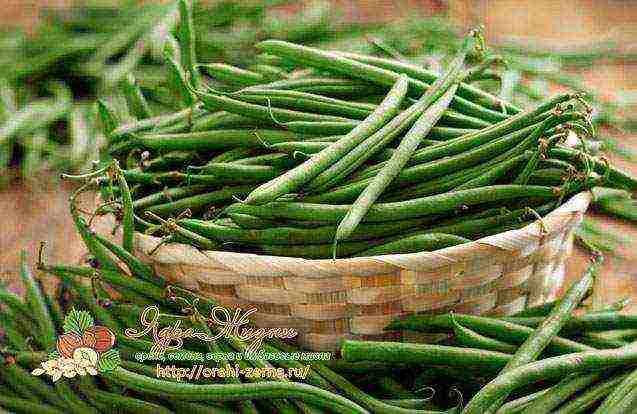

Before the plants enter the flowering phase, the optimal frequency of watering will be 1 time per week. And this is counting on hot weather. If summer does not indulge in heat, then you need to adjust the intensity, looking at the deciduous part of the beans - an excess of moisture provokes its growth. At the beginning of flowering, you need to double watering. Also, after each watering, you need to loosen the soil so that a crust does not form, which prevents the flow of air to the roots.
Superphosphate feeding can be done after the appearance of the ovary with leaves. The second feeding - while tying the buds, using potassium salt.
After the plants reach a height of 2 meters, you need to stop their growth by pinching the top. This, by the way, provokes the formation of ovaries.
Pest control
Common diseases for beans are powdery mildew, white rot, rust, bacteriosis and legume ascochitis. The safest way to avoid them is to choose high-quality seed material, so it is better that it is bought in a good place and meets GOST.
When affected by powdery mildew, white dust or a film appears on the pods and foliage. To prevent the spread of infection, these parts must be torn off and discarded or even incinerated. After that, the bushes should be sprayed with a solution of milk powder and water (1: 9) twice a week. Experienced gardeners also recommend adding 1 part baking soda or apple cider vinegar to the solution.
The harvest time depends on the characteristics of the variety, namely, the growing season. The best time of day to harvest is in the morning, when the dew is still on the pods. It is better not to overexpose the removed fruits, but to collect them while they are green and juicy.
Video: how to plant green beans
Video: caring for green beans in the garden
Many people are familiar with such a culture as beans since childhood. Soups are made from it, added to salads, stewed, and prepared. Beans belong to the Legumes family. Grows in the form of a climbing herb or shrub. The color of the fruit can be varied, with a very interesting pattern.
Beans are among the ten most useful foods. Due to the content of about 20% of protein in terms of energy value, it is equal to meat, the balanced composition of the product supplies almost all body systems with useful substances.
Simple agricultural technology and unpretentious care, the possibility of obtaining a generous harvest of healthy and nutritious fruits - all this prompts you to set aside a piece of land for beans on your site. Even a novice vegetable grower can handle the cultivation of beans. Beans are successfully cultivated in Belarus, Ukraine, the Moscow region, the Urals and even in Siberia.
Dates for planting beans in open ground

Beans planting in spring photo shoots
Beans are a thermophilic crop. They begin to plant it in the second half of May, when the threat of return frosts has completely passed. The lowest temperature that young seedlings can survive is 0 ° C, at -1 ° C the seedlings die. If the frost was short, then the sprouts will survive, but their development will be slowed down, which will negatively affect the yield.
Covering with a film, agrotextile or the construction of a temporary shelter will help protect against a sudden drop in temperature, as an option - make a fire at night so that it smokes until morning, this will help ward off small short-term frosts.
When planting beans, be guided by the weather conditions:
- At a depth of 10 cm, the soil should warm up by 12-15 ° C (according to popular observations, this roughly coincides with the flowering period of chestnuts).
- To start sowing a little earlier (in the future it has a positive effect on the yield), the soil should be "warmed up" by covering it with plastic wrap. After sowing, cover the beds again until the night temperature reaches + 12 ° C.
Erect varieties should be sown first, after a week, start sowing climbing ones. Bush varieties are recommended to be sown in early July (just at this time, the beds will be free after harvesting early-ripening vegetables).
Planting dates for beans in the middle lane and the Moscow region
Experienced gardeners carry out seeding in several stages. From mid-May to early June, you can sow beans every 10 days.
Planting dates for beans in Siberia and the Urals
In open ground, seeds can be planted in early June.
Do I need to soak beans before planting?

How to soak beans before planting and how to process
Seeds are sown directly into open ground without growing seedlings. Whether to soak beans before planting, think carefully: prepared seeds will need to be planted immediately, regardless of weather conditions or sudden cases that have appeared. Therefore, schedule your time so as not to spoil the seed in vain. In addition, soaked seeds should be planted in moist soil, because if there is a lack of moisture, the sprouts will simply die. Therefore, when planting, water the holes and plant the soaked seeds in the mud, or water after planting.
To get earlier shoots and protect young shoots from diseases, it is advisable to pre-treat the seeds before planting.
Start processing in the evening before sowing. The process takes place in several stages:
- For 10 minutes, place in a slightly borosy solution of potassium permanganate, then rinse with water.
- Then soak in wood ash infusion for 2 hours, rinse again.
- Wrap in a damp cloth and leave at room temperature overnight.
- Immediately before sowing, dip in boric acid solution for 5 minutes.
When deciding whether to soak beans before planting, consider the following factors:
- If you plant in dry soil and there is no way to water, do not soak it better.
- If it is raining soon and you are sure that you will have time to plant, you can soak and not water when planting.
- It is advisable to soak if it is already late, and you want to quickly get seedlings.
- When planting large areas in the field, it is better not to soak, you will not have time to water, and the seeds may die from a lack of moisture in sufficiently dry weather.
Choosing a place for planting beans
Illumination
Choose a well-lit place for cultivating beans, avoid drafts and strong winds. Young, immature shoots are very sensitive to this.Beans are often sown along fences, under apple trees.
Soil composition
Clay soils are contraindicated, since they do not allow water and air to pass through well, and the roots of the plant do not tolerate moisture (they will simply rot). Loose soils with a nutritious top layer are best.
Predecessors
Take into account the crops that were previously grown on the site. Excellent predecessors are carrots, potatoes, cucumber, peppers, tomatoes, eggplant.
Preparing a site for planting beans
Site preparation consists in digging to the depth of a shovel bayonet and adding one of the nutrient compositions (per 1 m²):
- Compost or humus (4 kg), 2 tablespoons of superphosphate and dolomite flour, 1 tablespoon of ammonium nitrate.
- About 2 kg of humus or compost, 30 g of superphosphate, 20 g of wood ash.
Planting scheme for beans in open ground and planting depth
Planting bush beans scheme:

Planting bush beans photo
The holes are made at a distance of 20-25 cm, in the aisles they keep a distance of 40 cm, planting depth of beans is 5-6 cm.
Planting curly beans scheme:

How to plant curly beans photo
For climbing varieties, the row spacing should be 45-50 cm. They will need support.
Place a few seeds (5-6 pcs) in each hole, pour warm water. When the shoots appear and give one true leaf each, leave 3 shoots in the hole (the rest can be transplanted or simply removed).
Planting scheme for green beans or asparagus

How to plant asparagus beans photo
It is also convenient to plant green beans, or asparagus, in rows: the depth of the grooves is about 5-6 cm, the row spacing is left 40-60 cm wide, in the row between the beans, 10 cm is enough.
How to plant beans in rows, look at the video:
The method of planting beans described in the video is very convenient for use in a summer cottage and a personal plot.
Planting corn and beans together

Corn with beans planting and care photos
Climbing beans are often grown in conjunction with corn. Landing is done under a hoe: shallow holes are made with a hoe, shoveling the earth in one direction, throw 2 corn seeds and 2-3 beans each, rake the hole with your foot and move on. The distance between the rows is 0.7 m, in the row between the holes - 30-40 cm.
Further care of the plants is simple: timely weeding, if it is in the steppe. If at home, you can water occasionally to get a rich harvest.
Planting curly beans in the video:
Do I need to water the beans after planting
When planting in the steppe, the beans are not watered, if this is a personal plot, it is better to plant the beans in the mud and sprinkle with damp earth (before planting, pour some water into the holes or rows). This does not form an earthen crust on the surface, and it will be easier for young tender sprouts to break through.
How many beans germinate
The acceleration of germination is facilitated by the treatment of seeds with a growth stimulant and soaking.
Untreated beans begin to sprout 7-10 days after planting. If the temperature of the air and soil is below the recommended values, then the seeds germinate for 5-7 days longer.
How to care for beans outdoors
Beans are unpretentious in care, require minimal effort on the part of a person. It is useful to hud up young shoots in order to give them stability.
How to water
The plant is hygrophilous. It is important to ensure regular, balanced watering if you want to get a lot of beans. Pay special attention to this point during the pod formation period. Watering is carried out about 1 time a week, determine the rate of water for the bush "by eye", the main thing is to prevent the soil from drying out. For irrigation, it is better to use softened water with a temperature of at least 18 ° C. For this purpose, you can install a barrel in the garden to collect rainwater or settle tap water.
How to feed
Beans are usually not fed. However, a high level of agricultural technology will allow you to get a much larger harvest.The culture is responsive to feeding, but don't overdo it. Otherwise, the tops will actively develop, which will reduce the ovary of the pods.
If you have taken care of laying the nutrient layer during planting, it is enough to feed three times per season.
- The first feeding is carried out 1-1.5 months after germination. Apply a complex of mineral fertilizers with an emphasis on nitrogen and phosphorus. You can add superphosphate (30-40 g per 1 m²).
- For the formation of fruits, a second feeding should be carried out 3 weeks after the first. Add 10-15 g of potassium salt per 1 m² of area.
- The third time is fed after another 3 weeks.
Remove weeds from the area regularly.
After watering, gently loosen the soil in the tree trunk circle.
Useful video about growing vegetable beans:
Diseases and pests of beans
Sources of disease are infected seeds, so discard poor quality seeds (shriveled, darkened, unevenly colored, with strange dots or spots) and be sure to pre-treat. Choose more resistant varieties (we talked about them earlier). In southern regions, sow later so that plants form at 25 ° C. Also, a measure of control against diseases and pests is the observance of crop rotation (in the same place they are grown with an interval of about 4 years).
Bean diseases:
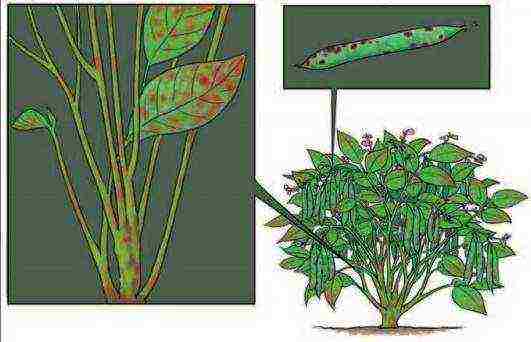
Bean anthracnose
- Anthracnose - the whole plant with leaves and fruits is covered with rusty spots.
- Powdery mildew - recognized by the presence of a whitish bloom.
- Ascochitosis - spots with a black core and a blurry outline appear on the leaf plates. The defeat most often occurs at the fruiting stage - it is too late to heal.
- Rust - the leaves become covered with brown spots, which quickly fill the plant, literally killing it. Most often passes from milkweed weeds. If the disease occurred even before flowering, treat with a 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid.
- Deforming and yellow mosaic - the leaf plates are covered with yellow specks, they become wrinkled, the growth rate slows down. However, the virus may not affect the fetus.
- Bacterial wilting - the edges of the leaves are covered with yellow spots, then they turn completely yellow and fall off. The disease develops in high humidity, so avoid sprinkling.
Bean pests
Pests are not often disturbed. Among them:
- Aphid
- Whitefly
- Bean weevil
- Sprout fly
In addition to the preventive measures described above, timely harvesting (before the pods crack) will help protect the beans from pests. To destroy pests, you should hold the beans in the freezer for 3-4 days.
Before and after flowering, you can carry out treatment with a biological product of a wide spectrum of action.
Bean stems and leaves can attack slugs. It is important to carry out weeding in a timely manner, because gastropods love a cool, moist environment. These pests are collected manually or use special traps.
Harvest time of beans
The timing of harvesting depends on the variety and variety of the crop.
Do not overexpose the asparagus beans in the garden - in the dried state, the quality of the product is lost.
If you plan to use the fruit for conservation, it can be picked slightly unripe. To store the beans dry, you must wait until they are ripe. But don't be late so you don't have to harvest beans from the ground.
Ripening can occur unevenly: in the shade of its own tops, some ovaries remain greenish, and at the tops, the pods are already dry. Remove the last, leave the rest to ripen.
It is not necessary to manually remove the beans from the pods. Take a bag or spread a blanket, lay out well-dried pods, and use a stick or other similar object to walk around with moderate effort. Remove the husks and sort the beans, dry and store. Store in glass jars with a tight-fitting lid (preferably glass or metal).
Bean varieties with photos and descriptions
The common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) is a cultivated species for the purpose of obtaining a crop of beans. Among the varieties (curly or bush), bush beans are most often preferred.
The variety of varieties complicates the choice. Consider the classification depending on the adaptability of the variety to the specific climatic conditions of a particular region.
Bean varieties for Ukraine, Belarus, Moscow region

Green beans Moscow white beans 556 photos
Moscow white green-leafed 556 - forms bushes about 25 cm high. The beans are covered with a very thin parchment layer (it boils rather quickly). The variety is resistant to both drought and high humidity. The period from sowing to technical maturity is 100 days.

Curly beans Nomad photo
Nomad is a climbing variety with medium ripening periods. The beans are ovoid and have a shade of ocher with a pale purple pattern. They do not have fibers and parchment layers, which makes the structure soft and delicate.
Bean varieties for the middle lane and the Urals
Orange - bush plants 35-55 cm high. Ripening early (80-90 days). The fruits are distinguished by their high taste. With 1 m², you can harvest within 200 g.
Pink - the bush curls, the stems reach a length of about 3 m, needs support. The beans have a marbled pink color and are delicate in texture (fibers and interlayer are absent). It is universal in application (the unique taste is preserved in any form). Ripening period is 65-85 days.
Bean varieties for Siberia

Curly beans with red flowering Photo Winner
The winner is the curly variety. The fruits are large, the length of the pods is about 30 cm. Thanks to good immunity, resistance to cold weather, cultivation in Siberia is possible. The variety has fiery red flowers, which is why it is often used for decorative purposes.

Asparagus beans Butter king photo
Butter king - asparagus beans, ripening period is 1.5 months. Tubular fruits will please even gourmets. The length of the pods is about 25 cm. The application is universal: freezing, canning, preparation of beans in dry form.
The cultivation of green beans in summer cottages is becoming widespread. Not so long ago, only large farms grew this useful product. You can buy green pods without any problems - fresh, in the vegetable departments of supermarkets, or frozen, in the refrigerators of all stores, mostly imported products. Meanwhile, it is not difficult to grow this "green miracle" in the country. The most important thing in growing green beans, unlike other legumes, is to harvest on time. Do not overdo the pods in the garden, making them tough and tasteless.
Green beans: growing and care
The oldest representative of legumes
Beans are reasonably considered by biologists to be the oldest cultivated plant on the planet. There are officially three botanical types of beans.
- The shelling, from which the beans are obtained, is characterized by a dense parchment shell.
- Semi-sugar - this type has a parchment shell of medium hardness.
- Sugar, aka asparagus, in which there is no parchment shell at all, but there is a green, juicy and soft one.
In the garden culture, it is customary to call the latter type of green beans, which are eaten together with the pods. In contrast to peeling varieties, the pods of which are not suitable for food.
Useful properties of green beans
Beans can be divided into two more types according to the growth method.
- Curly.
- Shrub.
When growing all types of beans, the basic agrotechnical standards are observed, which include the following points.
- Beans do not tolerate sandy, acidic and too heavy soils.
- Loves light, humidity, warmth, drought with difficulty.If the dry season falls on flowering time, the ovary may fall off and there will be no harvest.
- Beans don't like drafts and winds. The plant must be grown quietly.
- Sowing is carried out not earlier than the soil warms up to + 13 ° C (May - June).
- Sowing is preceded by a procedure for warming up and soaking the seeds.
- The seeds of the plant are buried no more than seven centimeters.
- Seedlings of all varieties must be loosened and preferably mulched.
- When the stem grows back by 15 centimeters, the plants need to be spud.
- For climbing varieties, you need to provide support immediately upon planting.
Varieties of green beans
By the way! Not all varieties have classic green pods. In some, the fruits are whitish, yellowish and even bright yellow, purple. Therefore, it is better to be guided when collecting not by the color of the fruit, but by the period of the expected milk ripeness, which is indicated on the package with the seeds.
Growing
Green beans are thermophilic, but not too warm. This is not an exotic representative of the African flora, which must be carefully grown in seedlings and planted only when the very last of possible frost threats has passed. Beans, along with other garden crops, can be safely sown in the spring directly on the ridges, having subjected the beans to preliminary presowing treatment.
Sowing beans on ridges
How to process beans before sowing
Bean seeds need to be warmed up. And it's best to do it naturally, not on a battery, but in the sun. In industrial agricultural technology, they are heated in special dryers, where the temperature is maintained at + 30 ° C ... 35 ° C. The process takes two days. An acceptable option for summer residents is warming up by the sun. To do this, the seeds must be placed on the southern windowsill and kept there for at least a week. After that, the beans must be soaked. A day spent by seeds in warm clean water (change the water four times) will be enough.
Soaking beans before sowing
How to cook a bed for beans
The soil needs a normal alkaline reaction, in any case, not acidic. Wood ash or dolomite flour will help remove acidity. If you are not sure about the acidity parameters of the soil on the site, add ash to the hole anyway, it will help the plant develop better.
Removing the acidity of the earth with wood ash
Sandstones and heavy clay soils will not work. It is best if the soil is light, fertile, moderately drained.
An important parameter for green beans, especially curly varieties, is the absence of wind. The site should be selected not only warmed up, but also protected from the winds. It is better to place the plants in partial shade than in a draft.
Before sowing the beans, be sure to rid the garden bed and the surrounding paths of weeds. Tomatoes, potatoes and different types of cabbage will be excellent precursors for the crop.
Do I need to remind you that the plot intended for growing beans needs to be dug up and filled with fertilizers in the fall. Be sure to organic - traditional 6 kg per square meter, superphosphate - 35 g, potassium chloride - 20 g.
In the spring, it is also necessary to add a complex that has a high potassium content - this element of green beans is needed more than all other garden plants.
Sowing seeds
The seeds have been prepared, the ridge is waiting for new "tenants". When starting sowing, it is necessary to decide on what scheme to carry out it.
By the way! The sowing depth of beans depends on the density of the soil. If the mechanical composition is light, it can be buried. If heavy, sow as much as possible to the surface. But in all cases, the range of beans sowing depth is 2-7 cm.
Bush varieties are sown in rows (two, three) or staggered. Holes of a given depth are made. Two beans are placed in each hole. Try to maintain a distance of about 25 cm between the holes, and between the rows: two - 45 cm, three - 35 cm.
Curly Bean Supports
Curly varieties are sown differently.By the way, there are still semi-creeping varieties. Sowing them is carried out in the same way as climbing. Before sowing, strong supports are installed on the prepared and treated ridge. They can be of any design and from any available materials. You can bend strong wire into arcs, put U-shaped or X-shaped stakes, pipes, plastic slats. A mesh frame stretched over the frame will also do. The main thing is that the lashes of the plant have something to cling to.
The holes are made in the immediate vicinity of the support pillars. It is along them that the beans will climb up to the light and a good harvest. The distance between the holes can be reduced here - 20 cm is enough.
Video - Support - pyramid for beans
Video - How to make a support for beans
Seedlings and care
Beans sprout, despite the hard shell and the impressive size of the seed, not for long. A strong sprout emerges from the soil already on the sixth day after sowing. The main thing is the right temperature. For successful germination in the daytime, it should be about + 20 ° С.
Bean seed germination
Young sprouts are sensitive to the cold at night. That is why, at the slightest threat of a minus on the ground, it is necessary to cover them with spunbond overnight. And on the eighth - tenth day, all seedlings must be hilled.
Then, after the plants reach the fifteen-centimeter growth mark, they must be huddled again. And repeat the procedure several times throughout the season, as the soil subsides after watering.
Advice! As soon as the lashes of the curly varieties of beans grow to a length of two meters, their ends must be pinched. This will increase fruiting.
Mid-season green beans, with proper care, will begin to bloom massively on the fortieth day after germination. It will take another three weeks for the formation of full-fledged ovaries. And after that - attention! Harvesting of green bean pods begins ten days after ovary formation. If you miss this moment and overexpose the pods on lashes for at least a week, their taste will deteriorate significantly.
Bean Care Tips
Fertilizers
In addition to preliminary autumn and spring soil dressing, green beans will need additional feeding. At least twice more during the growing season, you will have to feed the crop - when it enters the budding phase, and at the beginning of the fruiting phase.
Fertilizer - superphosphate mixed with wood ash (15 /
50 g per square meter). If there is, you can add a complex with a high content of molybdenum, boron and manganese to the feeding. If there is no special fertilizer containing these three trace elements, ordinary potassium permanganate will help to get out of the situation. A medium pink solution is poured over the leaves and into the hole.
Watering
For green beans, moisture is important, especially climbing varieties suffer from a lack of watering. But it is necessary to water intensively and often the beans only during the period of forcing the whips and budding. As soon as the ovary begins to form, watering should be done less often, but more abundantly, and the soil around the bushes should be mulched.
Watering the green beans
Advice! For watering green beans, experienced gardeners use one secret - weeds are placed in a large barrel in the sun (any weeds after weeding the garden, you can slightly grind them beforehand) and fill them up with water. The infusion must stand for seven days. It needs to be stirred from time to time. After a week, a liter of the finished nutritious herbal infusion is diluted in ten liters of water and poured over the beans. It responds to this hydration with fleshy pods and healthy, powerful stems.
Important points of harvest
- In the early variety, the harvest begins on the 50th day after the first sprouts have hatched from the soil.
- In the mid-season - on the 70th day.
- In late maturing - on the 100th.
You need to pick the pods in a state of milk ripeness. It is characterized by the following features:
- pods are not hard, bend rather than break;
- pod length from 10 to 20 cm (depending on the variety);
- inside the pod is a green bean the size of a grain of wheat.
Bean pods in a state of milky ripeness
- Harvesting is carried out in stages, every two days.
- Leave the pods that you did not remove in time for seeds, and henceforth check the lashes more carefully.
- Removing the pods stimulates fruiting. This means that the more beans you harvest, the more they grow.
- Harvesting can continue until frost.
- Harvest per square meter of green beans - two kilograms.
Video - How to grow beans on the site
Description of varieties of green beans
There are many varieties of green beans. Some of them did not take root in their summer cottages, for various reasons. Others, on the contrary, have gained popularity, their amateur gardeners warmly recommend each other. Let's consider the most popular ones.
Green Bean Varieties
|
"Saksa 615" |
One of the earliest, fifty-day variety. Shrub and low - up to forty cm. Compact, does not take up much space on the ridge. Pods of emerald green, there are no fibers in them, length - 12 cm, curved shape. The taste is excellent, fresh sweetish. |
|
"Melody" |
Also precocious. Curly. One lash forms up to nine pods. Their length is 13 cm. The color is bright green. Straight shape, smooth surface. The variety does not differ in increased sugar content, but the pods are fleshy and juicy. |
|
"Deer King" |
It was named so, probably for the arched, strongly curved shape of the pod, which reminded breeders of deer horns. A bushy variety with pods of the color of mature hard cheese. The grains are white inside. Mid-season. Delicious and nutritious fruits. It is said that by growing this variety, two harvest cycles can be harvested per season. |
|
"Zhuravushka" |
Bushy compact mid-season variety. It grows up to half a meter. It is distinguished by its ultra-high yield. The fruits of this variety are herbaceous green. They have no fibers. Especially good for freezing and preservation, but fresh, of course, are also used. |
|
"Panther" |
Also a bush and also a high-yielding variety. Ripening time is average. But the fruits are not green, but bright yellow. Beans are white. The taste is very high. |
|
"Hell Rem" |
A curly variety that has many features, but the main one is the pronounced aroma of forest mushrooms. The pods are pale green, even whitish. And the beans inside are pinkish. Dishes prepared from this variety retain the mushroom aroma and taste unusually good. |
|
"Caramel" |
Early maturing, fibrous, curly variety with delicate fruits of traditional green color. This variety is distinguished for its disease resistance and high yield. |
|
"Winner" |
These green beans are also curly and late maturing. Her pods are simply huge - they can grow up to 30 cm. The color and taste are traditional. The yield is high, due to the doubled mass of long fruits. |
|
"Purple Queen" |
Shrub variety with purple fruits. The pods are about 15 cm, very decorative. Due to the unusual color, they are used very actively in canning. |
|
"Oil King" |
The fruits are formed on the bush. Early - fifty days. The color of the pod is deep yellow. The taste is delicious, soft, slightly oily. No fibers. The yields are high. |
|
"Fatima" |
A mid-ripening climbing variety, distinguished by twenty-centimeter pods, sparse leaves and lashes up to three meters long. The pod shape is straight, the color is dull green. High productivity. |
Something about greenhouse properties
Green beans, like any other legume crop, are the best green manure that nature has come up with to increase the yield of your site in an inexpensive and simple way. Its roots "pull" nitrogen from the soil closer to them. They can be eaten not only by the plant itself, but also by those growing nearby. Therefore, many other crops can be sown in the aisles of beans. Pumpkins, melons, zucchini, cucumbers can be planted in the center between the rows.Along the edges of the ridge, they will feel good: peppers, eggplants, white and red cabbage.
Interesting fact about green beans
And after the harvest is harvested, collect the whips from the supports, or mow the bushes, chop them and bury them in the soil right on the bean bed. Next year you will have a fertile, high-nitrogen field ready for new garden experiments.
Both asparagus and green beans are considered some of the most valuable, tasty, and healthy members of the legume family. Their homeland is the territory of South and Central America. Nowadays, green beans are cultivated almost everywhere, and it is possible to grow a rich harvest even in Siberia. Green beans have gained particular popularity not only due to their pleasant mild taste. It contains vitamins (A, C, B1, E, B2), macro- and microelements, including calcium salts, phosphorus, zinc, iron and folic acid. In addition, green beans contain a sufficient amount of easily digestible protein and fiber. In this article, we would like to talk about growing beans and answer the following questions: "How to plant, how to care for and what kind of beans to choose for your summer cottage?" We hope our recommendations will help you.
Green beans have gained particular popularity not only due to their pleasant mild taste. It contains vitamins (A, C, B1, E, B2), macro- and microelements, including calcium salts, phosphorus, zinc, iron and folic acid. In addition, green beans contain a sufficient amount of easily digestible protein and fiber. In this article, we would like to talk about growing beans and answer the following questions: "How to plant, how to care for and what kind of beans to choose for your summer cottage?" We hope our recommendations will help you.
Green beans: planting, growing. We select the soil
Green beans are a fairly unpretentious plant. It is not difficult to get a rich harvest, observing some agrotechnical rules for cultivation and care. Light, fertile and well-drained soils with moderate moisture are perfect for cultivating beans and green beans and asparagus. Medium or light loams, as well as sandy loam, will allow you to get a really good crop of legumes. Too wet, waterlogged, heavy soils are unlikely to work - the plants will hurt and develop poorly. Beans must be grown in areas protected from the wind, warmed up and normally illuminated. But, in principle, partial shade is also suitable. Of course, the chosen place for planting seeds must be well cleared of all kinds of weeds. It is not bad if potatoes, tomatoes or cabbage were grown before the beans.
Green beans: planting seeds correctly
Since the fall, the site chosen for planting is prepared: they dig up and add organic matter (6 kg per 1 m²), superphosphate (35 g per 1 m²), and potassium chloride (20 g per 1 m²). In spring, a complex mineral fertilizer with a high potassium content (25 g per 1 m²) is added to the soil. On well-prepared soil, green beans will grow better and more actively. How to plant seeds? First, you need to wait until the ground warms up to 15-18 ° C and exclude the possibility of repeated frosts. In southern Russia, sowing beans can be safely carried out already from mid-May, in other regions it is advisable to wait for the onset of June. Remember that green beans are very fond of warmth. How to plant seeds?  Similar to other legumes. Dry seeds are pre-soaked. And then they are placed at a depth of 3 or 4 cm in open ground (or under a film shelter). Many gardeners recommend keeping the seed in a manganese solution for 15-20 minutes before planting, and then rinsing it with water. After planting, the site is sprinkled with humus. For seed germination, a temperature of between 20-25 ° C is required. Usually, the first shoots appear after 10 to 20 days. The distance between individual plants should be about 10 cm, so a little later, excess seedlings are thinned out or planted.
Similar to other legumes. Dry seeds are pre-soaked. And then they are placed at a depth of 3 or 4 cm in open ground (or under a film shelter). Many gardeners recommend keeping the seed in a manganese solution for 15-20 minutes before planting, and then rinsing it with water. After planting, the site is sprinkled with humus. For seed germination, a temperature of between 20-25 ° C is required. Usually, the first shoots appear after 10 to 20 days. The distance between individual plants should be about 10 cm, so a little later, excess seedlings are thinned out or planted.
Features of planting bush and curly beans
As a rule, all varieties of beans are divided into curly and bush. Bushy asparagus beans are sown in rows. A distance of 15 - 20 cm is maintained between the beans, and about 30 cm between the rows. Growing bush beans and harvesting will be more convenient if you leave a free gap of 50 cm every three rows.Before the onset of flowering, the plants must be spud once or twice. Then the bean bushes will become more resilient and will not fall due to strong wind or rain. So, we have determined how best to sow bush green beans. How to plant climbing varieties, we will tell you below. Curly asparagus beans grow beautifully along fences, in this case there is no need to invent supports. If this is not possible, plant the beans in rows, leaving a gap of about 7-8 cm between the beans. After sprouting, sprout the sprouts, and then build supports and tie the seedlings to them. When the curly beans reach a height of 2-2.5 m, they will need to be pinched to stimulate normal fruiting.
Curly asparagus beans grow beautifully along fences, in this case there is no need to invent supports. If this is not possible, plant the beans in rows, leaving a gap of about 7-8 cm between the beans. After sprouting, sprout the sprouts, and then build supports and tie the seedlings to them. When the curly beans reach a height of 2-2.5 m, they will need to be pinched to stimulate normal fruiting.
Green beans: growing and care. Watering, feeding
Green beans and asparagus need good watering. With sufficient and regular moisture, the plants will form fleshy pods and bear fruit abundantly. For watering, you can prepare a nutritious infusion: fill the barrel with more than half with weeds and pour water into it. Leave to sour for seven days. And then dilute 1 liter of the finished infusion in a bucket of water. This solution can be used to moisten beans.  Remember that in case of insufficient soil moisture, bean stalks will develop poorly, and fruiting will deteriorate significantly. In addition to watering, beans need to loosen row spacings and weed weeds. Basically, that's all it takes to get a great crop of asparagus beans. Growing and caring for this plant will not take much time and energy from you. The main thing is to water, sometimes loosen and occasionally feed it. String beans bloom 40 days after germination. The ovaries appear 20 days later, and after another 10 days they reach sufficient maturity. During the growing season, mineral fertilizing should be carried out two or three times, one of them during budding.
Remember that in case of insufficient soil moisture, bean stalks will develop poorly, and fruiting will deteriorate significantly. In addition to watering, beans need to loosen row spacings and weed weeds. Basically, that's all it takes to get a great crop of asparagus beans. Growing and caring for this plant will not take much time and energy from you. The main thing is to water, sometimes loosen and occasionally feed it. String beans bloom 40 days after germination. The ovaries appear 20 days later, and after another 10 days they reach sufficient maturity. During the growing season, mineral fertilizing should be carried out two or three times, one of them during budding.
Harvesting green beans
Asparagus beans are consumed whole, that is, not only seeds are subject to preparation, but also green pods, which have a pleasant taste and aroma.
Harvest the green beans and asparagus selectively, plucking the dairy fruits, preventing their grains from hardening. Remove green "shoulder blades" several times per season, depending on the type of plant. Fruiting of beans will continue in summer and autumn, until the onset of frost. Bushes intended for obtaining seed material are not harvested. They are left until the seeds are fully ripe, and in September-October they are removed from the garden. 
Popular varieties of green beans
One of the most delicious varieties is the Deer King (Holland). This undersized bush bean ripens early and yields a lot. The cultivar is recognized by its lemon yellow pods and white grains. Fana (Poland) is considered another good variety. The pods of this bushy asparagus bean are green in color with white grains inside. The variety is particularly resistant to diseases and high yields. Popular varieties of curly asparagus beans are Golden Nectar and Ad Rem (both US). They are distinguished by high yield and excellent taste characteristics. Blau Hilde (Austria) is another excellent climbing bean variety. You can recognize it by its purple pods and large creamy grains.
Instead of a conclusion
So, in this article we examined the features of growing a valuable plant called green (string) beans. How to plant, how to care for it, feed and harvest - you now know. We hope that in your summer cottage you will definitely be able to grow this wonderful legume, which is a valuable source of protein, fiber, vitamins, macro- and microelements.