Content
- 1 Basic rules for growing garlic outdoors
- 2 When to plant garlic outdoors?
- 3 Garlic precursors in the beds
- 4 Soil preparation
- 5 Preparation of planting material
- 6 Landing in open ground
- 7 Outdoor garlic care
- 8 Harvest
- 9 Conclusion
- 10 Garlic: a description of the culture
- 11 Winter garlic varieties
- 12 Growing winter garlic
- 13 Planting winter garlic
- 14 Garlic care
- 15 Harvesting and storage
- 16 What is the difference between spring garlic and winter garlic
- 17 Garlic varieties with photos and descriptions
- 18 What soil is needed for garlic
- 19 What to soak garlic before planting
- 20 Growing garlic outdoors
- 21 Outdoor garlic care
- 22 Tips on how to grow large heads of garlic
- 23 Harvesting and storing the harvest of garlic
- 24 How to store garlic in the winter at home to keep it dry
- 25 What can be planted after garlic next year
- 26 Basic rules for growing
- 27 Outdoor planting of spring garlic
- 28 Winter garlic: the nuances of growing
- 29 Outdoor care
- 30 Breeding features
- 31 Sowing winter garlic bulbs
- 32 Diseases and pests: control methods
- 33 Types and varieties of garlic
Garlic is a hot spice that is actively used in cooking and traditional medicine. Growing and caring for garlic in the open field on their own gives gardeners the opportunity to get the maximum benefit from it without harm to health, which the purchased one can bring. Meanwhile, it is quite easy to grow a culture at home if you know and follow the basic rules of planting and caring for a plant.
Basic rules for growing garlic outdoors
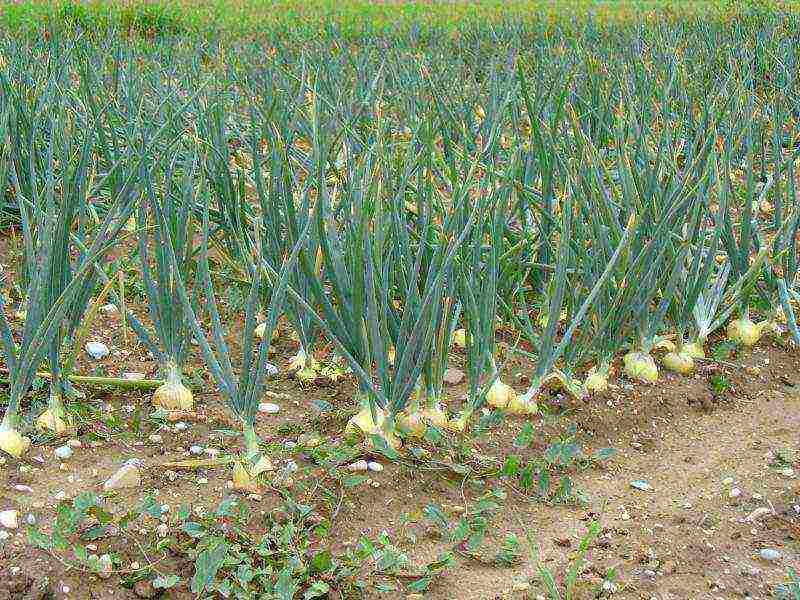

Before starting the growing procedure, it is recommended that you familiarize yourself with the basic rules and recommendations:
- Garlic beds are best chosen in places well-lit by the sun.
- Avoid planting a crop in a low-lying area. In such conditions, the accumulation of liquid is possible, which will have a detrimental effect on the condition of the plants.
- It is important to add natural or synthetic fertilizer to the soil before planting.
- It is recommended to mulch over the winter bed and cover it with brushwood to retain the snow masses.
- The sowing depth directly depends on the size of the seed. The largest varieties should be deepened by eight to nine centimeters, the smaller ones by six to seven.
- Only large seeds should be chosen for planting. Separate them from each other carefully. You do not need to peel the cloves.
- Do not sow into freshly dug soil, otherwise the tines will be deeper than necessary. Prepare the soil no earlier than a week.
- The sowing site should be changed regularly (at least once every two years). You can use the same ridge only with an interval of four years.
The correct approach to growing crops will allow you to grow a high-quality and rich harvest, and also significantly reduce the likelihood of disease and plant death during the nursing period.
When to plant garlic outdoors?
 There are two options for planting garlic in open ground: autumn (for winter) and spring (for spring).
There are two options for planting garlic in open ground: autumn (for winter) and spring (for spring).
It is recommended to plant a crop in autumn from the second half of September to mid-October. You can also calculate the timing of the expected frost period, depending on the region. The most suitable time for sowing is 35-45 days before the start.
Spring garlic should be planted when the soil temperature warms up to 5-10 degrees Celsius. As a rule, this time falls on the end of March or the beginning of April.
All sowing dates in spring are relative. In this case, a lot depends on the region. So, in the warmest it is best to plant the crop earlier, in the colder ones - later. The final landing date is the end of April.
Garlic precursors in the beds
Potatoes are considered the best precursor to garlic. You can also sow a crop in those places where zucchini, cucumbers and peas grew. The worst predecessor is onion of all varieties and varieties. If you grow garlic the next year after the onion is harvested, you can expect a small and poor quality harvest. The same goes for tomatoes and carrots.
The culture can also coexist with raspberry bushes, roses, strawberries, currants. In this case, the plant will help repel pests.
Soil preparation

The soil for sowing in open ground must be sufficiently fertile and drained, moisture-consuming. Loam is perfect. It is important that the soil is not dry. The ridge should be prepared for spring sowing in the fall.
To do this, you need to dig up the soil and apply fertilizer to it. Each square meter will require twenty grams of potassium salt and superphosphate, as well as a bucket of humus. This procedure can be performed in the spring, no later than two weeks before sowing.
The distance between the finished rows should be d2 decimeters, between other ridges - at least 1. It is best to plant the teeth in the grooves, but at the same time they should not be pressed into the ground. Too dense soil mixture will contribute to the freezing of the plant from the roots.
Important: You can neutralize the increased acidity of the soil with the help of dolomite flour, chalk or hydrated lime.
Preparation of planting material
 First of all, all potential seed must be sorted out and sorted. Choose for growing only whole, healthy, large seeds. It is them that should be further subjected to pre-planting processing.
First of all, all potential seed must be sorted out and sorted. Choose for growing only whole, healthy, large seeds. It is them that should be further subjected to pre-planting processing.
Important: the presence of at least one tooth damaged by the disease in the head automatically rejects the entire bulb.
The selected seed must be treated with the antifungal agent Fitosporin. To do this, it is enough to soak the cloves in the drug solution for five minutes. In the absence of this remedy, you can use a pink solution of potassium permanganate or 1% iodine solution.
Before direct planting, it is useful to carry out a second processing of the material. To do this, pour half a kilogram of wood ash with a liter of water and boil the composition for half an hour. Each clove will need to be dipped in the cooled solution, and then dried thoroughly.
Sowing is also possible with the so-called bulbs - the organs of vegetative propagation of garlic. These are small bulbs that form in the seed case on the arrow of the plant itself during ripening.The system of material selection, planting and cultivation practically does not differ from the system of using cloves.
Landing in open ground
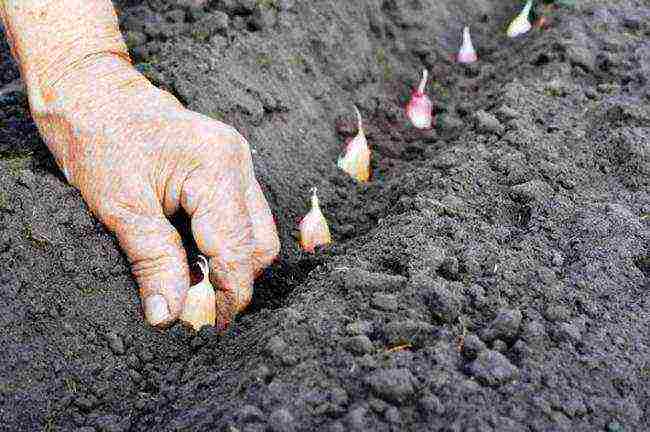

Having prepared the soil and planting material, you can proceed to planting directly.
The procedure will take several steps:
- Loosen the prepared soil with a spatula, hoe or other most convenient tool.
- Make grooves with a depth corresponding to the dimensions of the prepared teeth from five to 10 cm. The distance between them should be twenty to thirty centimeters.
- Place the garlic sprouts down into the grooves, about five centimeters apart. The teeth should be deepened by about half.
- Fill the grooves with soil, trying not to unnecessarily tamp the ridge. Otherwise, the garlic may not sprout.
- Smooth the surface of the ridges with a rake, avoiding deep penetration of the tool into the soil.
The soil for sowing in open ground should be moist, but not wet. Therefore, it is recommended to shed it in advance.
Outdoor garlic care
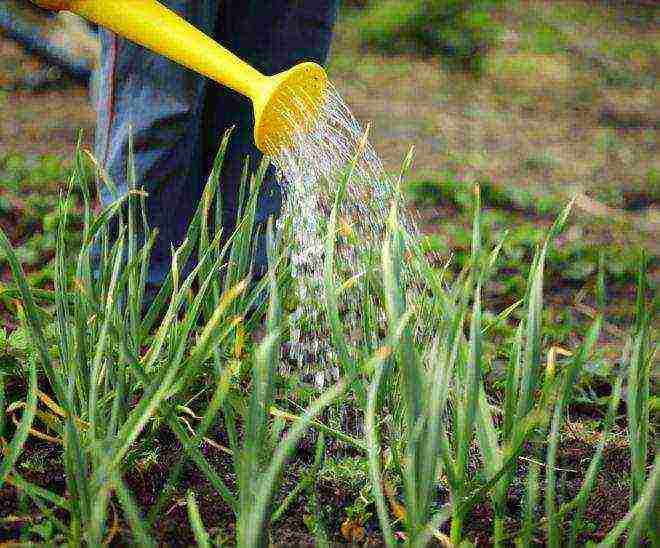

Basic crop care includes four aspects: timely watering, weeding, fertilizing and loosening the soil.
Watering
It is recommended to bring water into open ground regularly, but infrequently (once every one to two weeks). It is enough to use 10 liters of water per square meter. During the rainy season, the number of waterings should be reduced to a minimum. At the same time, it is important to periodically loosen the soil so that it absorbs moisture better.
As the ridges mature, they are watered with less and less moisture. Watering is completely stopped 2 weeks before harvesting.
Fertilization and pest control
1 time in 10 days, it is necessary to add potash and phosphorus additional fertilizing to the soil. It is important to strictly follow the instructions for use indicated on the package.
In addition, at the very beginning of the growing season and after the seed box is formed, it is recommended to fertilize the soil with natural fertilizers, which you will need to make yourself.
A kilogram of mullein or chicken droppings requires about 10 liters of water. It is important to keep such a solution for 3-5 days for fermentation. After that, each liter should be diluted with a bucket of water and irrigated.
With high-quality processing of planting material, the risk of disease and fungus is reduced. Additionally, it is useful to disinfect the soil by spilling it with a weak solution of potassium permanganate immediately before planting. It is also recommended to carry out treatment with insecticides and fungicides in the spring. It is important to weed as needed. Removing weeds once a week is usually sufficient.
Important: as soon as the formed seed pod bursts, it must be removed from the plant by breaking or cutting the arrow.
Harvest
Harvesting garlic should be carried out at a time when the greens turn yellow by about 2/3. As a rule, it takes about 100 days for a crop to mature, and the end of the period falls in mid-September. The ripeness of the crop is indicated by a loose connection of teeth in the head and dry husk.
In order to carry out cleaning, it is necessary to dig up the onion and pull it out by the tops. In this state, the plants should be laid out to dry. After that, it is important to remove the soil, and move the heads for storage in a cool place. You can trim the roots and tops as early as a week after harvesting.
Conclusion
Growing garlic in the country or in a garden plot in the open field is a useful and interesting activity. If you use all the rules of sowing and care, you can get a tasty and healthy crop that can be stored for a long time. Such garlic can be used both in cooking and traditional medicine without fear for the health and quality of the finished product.
Garlic is a herbaceous perennial. It is a popular vegetable crop. The homeland of garlic is considered to be Central Asia, but now it is cultivated all over the world.Garlic is prized for its ability to strengthen the immune system, improve digestion, and stimulate appetite. This vegetable can be planted in spring and fall. It all depends on the species. Let's talk today about winter garlic, about planting and care in the open field. Let's talk about the most popular varieties of winter garlic.

Garlic: a description of the culture
Garlic has a fibrous root system, the bulb is rounded, complex, which forms many children in the sinuses, which are called cloves or cloves. They are covered with dark purple, white or yellowish scales. The leaves of garlic are lanceolate, narrow, erect, more than 30 cm long. The peduncle reaches a height of 150 cm, arrows with inflorescences are formed at its end. There are spring and winter garlic depending on the planting time. Distinguish between winter shooters and winter non-shooters types of garlic. This type of garlic is planted in crops before winter.
Winter garlic varieties
Winter garlic is poorly stored, so it is more often used for cooking. But it is distinguished by early ripening, rich harvest with large bulbs and cloves. The most popular varieties:
- Petrovsky. High-yielding shooting variety of winter garlic. It has a pungent taste and firm flesh. The variety is resistant to disease.
- Jubilee Gribovsky. Medium late shooter grade. It is disease resistant. The taste of this garlic is pungent. The heads are large, with a lilac husk, each bulb has 10-12 cloves.
- Boguslavsky. Cold-resistant variety. Ripening heads are small, they have only 6 cloves, lilac-gray scales.
- Losevsky. Shooting winter-hardy variety with high yields. The bulbs are round-flat, weighing up to 80 grams. It can be stored for six months.
- Komsomolets. Arrow variety, mid-season, cold-resistant. The dense head is covered with a pinkish husk, it contains from 6 to 13 teeth of winter garlic.
- Gulliver. Shooting variety, medium late. Heads with dark gray scales, pungent taste, white flesh. Head weight up to 120 grams. Refers to varieties with a long shelf life (up to 8 months).
- Gribovsky 60. The variety is early ripening, with a sharp taste. It is weather resistant. Each head has up to 11 teeth.
- Jubilee 07. Mid-season high-yielding variety. Harvest - round-flat white heads. Head weight up to 80 grams.
- Flight. Cold-resistant variety. Small heads, cloves in bulbs from 6 to 8.

The following varieties of garlic are often used: Sakskiy, Donetskiy violet, Parus, Lyubasha, Kharkovskiy violet and others.
Growing winter garlic
Planting of winter garlic is carried out in the fall. It is necessary to comply with the terms and scheme of planting. The timing depends on the climate and geography of the place where the garlic will be grown. You can be guided by the lunar calendar, you can use your own experience, but the planting of winter garlic should be done before the first frost. And not in one day, but at least three to four weeks. This is essential for the garlic to take root well. A hardened root system will prevent garlic from dying. It is too early to plant garlic, because then before the cold snap it will have time to sprout, which will freeze, this will destroy the culture.
You can't just plant garlic anywhere in your backyard. You need to choose the right place, prepare the soil, take into account the predecessors of garlic. Only if the growing conditions are observed, a number of activities are performed, can a good result be achieved.
Where to make a garden
The garlic area should be very sunny. It is worth giving preference to a hill over a lowland, since moisture will accumulate there, and although garlic loves watering, it is unlikely to tolerate stagnation of water. It is necessary to take into account the cultures that grew up before. The most suitable crops are squash, cabbage, peas or pumpkin. Garlic grows well after green manure crops (clover, alfalfa). But tomatoes, carrots and cucumbers are best avoided. Onions and garlic can also be attributed to the worst predecessors.
Garlic grows well next to berry crops: raspberries, gooseberries, raspberries. If you plant garlic next to strawberry bushes or in the same bed with them, it will grow well, will not hurt, and will delight you with the harvest. Good neighborhood of garlic with flower crops. These are tulips, gladioli, roses. Garlic will scare away caterpillars and slugs from these flowers.
How to prepare the soil
The soil in the garden must be prepared in August. It is carefully dug up, the plants that grew in the garden along with the roots, weeds are removed. When planting, fertilizers are applied to the soil. Potassium salt mixed with superphosphate and humus feeds well any soil. The soil is leveled with a rake, the bed is covered with a film, in this form it will wait for the day of planting.
How to process planting material
Winter garlic can be planted in bulbs and cloves. The yield of the variety depends on how high-quality the planting material is. It all starts with the preparation of the seed. The teeth are sorted out, the damaged ones are immediately removed. The cloves should lie in the refrigerator for a couple of weeks before planting. Then they are sorted by size. Selected specimens must be disinfected by flooding with potassium permanganate solution for a couple of hours. Ash solution can be used. Pour 200 grams of ash with a liter of water and boil for half an hour. Cool and place the cloves in it for two hours.
Planting winter garlic
Prepared large cloves are embedded in holes to a depth of 12-15 cm. If planting is carried out with bulbs, grounding is carried out to a shallower depth. The planted seeds are sprinkled with earth, on top with a layer of peat. Sawdust mulching is carried out. This will help protect the garlic from frost. As soon as frost hits and snow falls, it is necessary to make sure that it lies flat on the beds, creating a snow cover. It will help withstand any frost.
Garlic care
In the spring, when the snow melts, the first shoots will appear. It is necessary to care for garlic in the open field: weeding, watering, feeding, fertilizing the garlic. Watering should correspond to weather conditions, it should be regular, but without stagnant moisture. Three times a season, you need to fertilize the planting with fertilizers of different composition. Top dressing should be nitrogen fertilizers, urea or mullein.
Diseases and pests can overtake winter garlic. This is powdery mildew, stem nematode, gray rot. To prevent infection from occurring, you need to be careful about the planting material and the landing site.
Harvesting and storage
Harvesting begins in early August. Signs of harvest time are:
- yellowed old leaves;
- formed heads with a characteristic color;
- cessation of the formation of new leaves.
Cleaning of garlic from the beds takes place on a dry day. They dig in the garlic, pull it out of the ground, freeing it from the ground. You can spread the garlic right in the garden. The garlic is kept for about 10 days, then the leaves and roots are cut off. Winter garlic should be stored at 2-4 ° C. It is prone to rot, so it cannot be stored for too long.
You can braid the garlic into braids. For this, the stem is not cut, but only the leaves are removed. These braids can be hung under the roof of an attic or shed. You can store garlic in wooden boxes, sprinkle with salt. From time to time you need to sort out, some heads may deteriorate.
All about the correct cultivation of spring and winter garlic in the open field, about what to do if it turns yellow in spring, what to water and how to feed, you will learn from this guide. The information will be especially useful for beginners, as well as for experienced gardeners. Growing garlic usually does not cause big problems, but for a good harvest, you must follow the rules of planting, care and feeding.
What is the difference between spring garlic and winter garlic
Gardeners know that there is winter and spring garlic, and what are the differences between them you can see from the table and photo:
| There are more teeth - from 12 to 30 pieces, but they are smaller | An arrow sticks out in the middle of the bottom, which is surrounded by 4-12 large cloves |
| The bulbs are smaller and have more scales | Bulbs and cloves are larger and more productive |
| The teeth on the bottom of the bulb are located in a spiral from the periphery to the center, with the outer ones being larger | In the middle there is a thick and hard rod, around which the teeth |
| Planted in early spring | Planted in autumn |
| It ripens in September, it is laid for winter storage and consumed until the new harvest | Can only be stored until February |
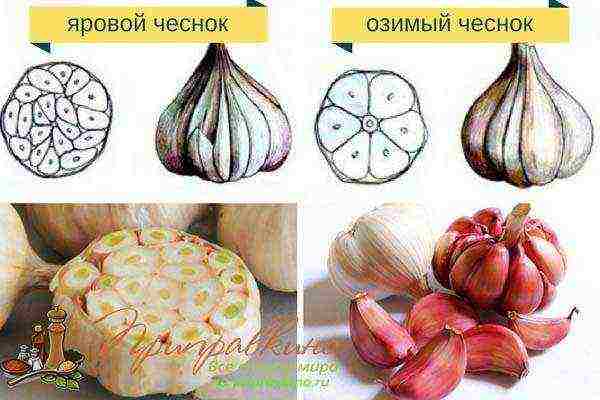

Winter garlic is more common, but in the northern regions they prefer to grow spring garlic, since the plants under winter planting can freeze out.
Garlic varieties with photos and descriptions
Most often, garlic is propagated by chives, of which there are from 4 to 12 in each bulb, and sometimes more.
Do not use grocery store garlic as a planting material. It may not be suitable for growing in your area, and in most cases it has been treated with special substances that inhibit growth. It's best to buy garlic for planting from a trusted online seed store or local nursery.
Garlic varieties are divided into two groups:
- Shooters - they have a flowering shoot coming out of the center of the bulb - an arrow ending in an inflorescence. It consists of bulbs (air bulbs) and flower buds, which subsequently dry out without forming seeds. A sign of ripening in them is the yellowing of the leaves and arrows. All arrowed garlic varieties are considered winter garlic.
- Non-shooting - in such plants only leaves develop during the growing season. These varieties can be both winter and spring.
The best varieties of garlic for planting before winter
For podzimny planting, varieties with high winter hardiness are recommended.
Shooters
Dubkovsky is a medium-ripening variety - 98-114 days pass from germination to harvest. Productivity 5.6 kg per 10 m2. Bulbs weighing 30 g, round-flat, dense. There are 10-12 cloves in an onion. The taste is spicy. Recommended for growing in the Krasnodar Territory, Kurgan, Rostov and Pskov regions.

Jubilee Gribovskiy is the most common variety of the middle term - from germination to drying of leaves 83-122 days pass. The yield is high - an average of 12.5 kg per 10 m2. Bulbs of 20-30 g, round-flat, with large cloves. The taste is very spicy. The variety is relatively winter hardy, resistant to drought, major pests and diseases, and adapts well to different weather conditions. For cultivation in the northern and central regions of Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Ukraine.

Otradnensky is a mid-late variety - it takes 95-135 days from germination to drying of leaves, universal use. The yield is very high - 12-13.5 kg per 10 m2. Bulbs over 30 g, round-flat, each with up to eight cloves. The variety is very winter hardy. Good for growing in the Primorsky Territory and Mordovia.

Sail - a variety of medium ripening - time from germination to harvest: 96-108 days. Yields a yield of 6 to 10 kg from 10 m2. Bulbs weighing 30–47 g, round-flat, dense, well stored, they contain 7–10 cloves. The taste is spicy. The variety is winter-hardy. Recommended for growing in Voronezh and Nizhny Novgorod regions, Ukraine, Stavropol Territory and Kazakhstan.

Siberian - medium term - from germination to harvesting 81-113 days, universal. Yields on average 5.8 kg per 10 m2. Bulbs weighing 20-30 g, round-flat, with medium-sized cloves (4-5 pcs.). The taste is spicy and semi-sharp. Suitable for growing in Novosibirsk, Kemerovo, Omsk and Tomsk regions.

Non-Shotgun
Novosibirskiy is a variety of medium early ripening period - 68–82 days pass from germination to harvesting, universal purpose. Productivity 5-6 kg per 10 m2. Bulbs weighing up to 30 g, round, well stored. There are 9-13 cloves in the onion. The taste is semi-sharp, delicate. Recommended for Novosibirsk and Kemerovo regions.

Saki - an early variety - from germination to yellowing of leaves takes 100-115 days, universal purpose. Yield 4,2 kg per 10 m2 Bulbs weighing 20 g, flat and round-flat, with wide cone-shaped cloves. There are 11-13 of them in the onion. The taste is spicy. Well suited for growing in Crimea.

Garlic varieties for planting in spring
Among the spring varieties, a particularly large role belongs to the numerous local forms, which are usually very well preserved. Among them:
- Danilovsky (variety of the Yaroslavl region).
- Bryansk, Ufimsky (varieties of Bashkortostan).
- Cheboksary (grade of Chuvashia), etc.
Garlic varieties quickly degenerate, so they need to be changed periodically.
What soil is needed for garlic
Garlic grows well on fertile loose light sandy loam or loamy soil, in non-flooded areas, with sufficient sunlight; tree-shaded areas are not suitable for this crop. It does not tolerate either excessive moisture or prolonged drying out of the soil.
It is good if the bed is located on a sunny hillock and is protected from the wind by a fence, trees or shrubs. In the spring, water should not stagnate there.
Before planting, the soil is dug up, loosened, the roots of perennial weeds are selected and carefully leveled.
When digging, humus (1-2 buckets) and wood ash (2-4 kg) are added per 1 m2. Instead of ash, you can take superphosphate and potassium salt (15-20 g each).
The acidic soil is limed. The garden bed is prepared two weeks before planting, as it should settle a little so that the garlic cloves do not go deep into the ground.
What to soak garlic before planting
Before planting, the garlic is treated with a weak solution of trace elements (one tablet is dissolved in 1 liter of water) or infusion of birch wood ash: 1 tablespoon of ash is thoroughly stirred in 1 liter of hot water and the garlic is soaked for one night.
To avoid the most common disease of garlic - downy mildew, the cloves are heated for 12 hours at 40 C before planting and treated with a 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid.
Growing garlic outdoors
The bulbs and chives of winter garlic are larger and more productive than that of spring garlic, but the latter, thanks to the many scales, is stored longer. Better to grow both forms outdoors.
When and how to properly plant winter garlic
Chives of winter garlic are planted before winter after harvesting vegetables
cultures. The largest and healthiest bulbs are chosen for planting - without a single spot. Small teeth are discarded, only large ones are planted. It is very important to do it on time.
- In central Russia, planting dates are usually recommended from September 15-20 to October 5, a few weeks before the onset of stable November cold weather.
- Winter garlic is planted in the central regions of the Non-Black Earth Zone in the third decade of September.
- In the Moscow region, the best planting time is from September 25 to October 5.
- In the northern regions, the dates are moved to earlier ones, in the southern regions - to later ones.
Such planting dates are due to the fact that the cloves must take root well before the onset of stable winter cold weather.
Following such advice, amateur vegetable growers are often mistaken if in late September - early October, after cold weather, a relatively warm weather suddenly sets in. And then not only the roots, but also the sprouts begin to grow actively, and the subsequent November frosts destroy them.
With a delay in planting, the teeth do not have time to take root until the end of October and hibernate poorly. In the spring, such seedlings are sparse and frail at best. To avoid mistakes, it is advisable to know a long-term and reliable weather forecast.
Planting scheme for winter garlic
Teeth of the same size are planted in two lines. The landing pattern is as follows:
- the distance between the rows is at least 20 cm;
- between cloves in a row - 8–10 cm;
Planting depth depends on the type of soil: on light soils, it is 8-10 cm from the top of the clove to the soil surface, on heavy soils - 5-6 cm.A shallow planting of garlic can lead to the fact that when the temperature drops to minus 15 C, a significant part of the plants can die.
For each square meter, you need 50 cloves, or 300 g of garlic (6-7 heads).

Although garlic is a cold-resistant crop, in November-December, the snow "coat" is still too unreliable and thin, so it is better to insulate the garden bed by sprinkling it with peat, well-rotted manure or loose compost soil with a layer of 2 cm.
Such mulching will do a good job in early spring, as the soil will warm up faster. In addition, mulch will keep the soil surface from crusting and help to retain the moisture that garlic needs so much. As a result, this technique alone noticeably stimulates the development of young plants, increasing the yield by 10-15%.
How to grow winter garlic from bulbs (air bulbs)
Usually, air bulbs are used to obtain planting material - sevka. One or two days before harvesting the garlic, the arrows are cut off, leaving 2–3 cm above the bulb, tied into sheaves and left under a canopy for 25–30 days.
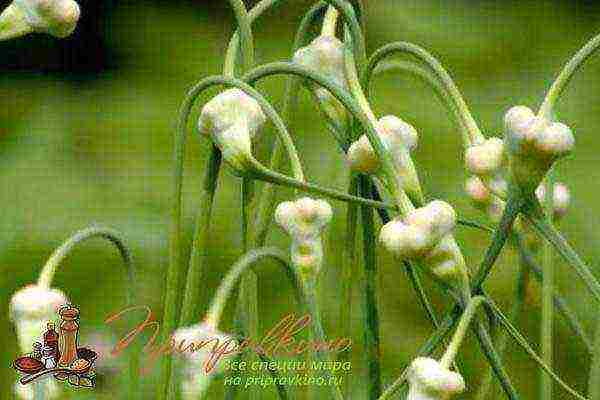


If you plant bulbs before winter, next year they will give single-tooth bulbs (sets), which will be the planting material.
Before sowing the bulbs - air bulbs are separated from the arrows by shaking, then calibrated. The smallest ones (less than 2 mm in diameter) are not suitable for sowing, as they produce very small single-toothed bulbs. It will take three years to grow them into bulbs that can be divided into cloves.
Bulbs are sown in the third decade of September, like chives, on the ridges with lines, between which a distance of 10-15 cm is left. On one square meter of the ridge, 8-10 g of bulbs are sown to a depth of 3-4 cm. Crops are mulched with peat or humus layer 2 cm.
The next year after the emergence of seedlings, the plants are fed with nitrogen and potassium fertilizers: 10-15 g of ammonium nitrate and 5 g of potassium salt per 1 m2. The crops are watered, the aisles are shallowly loosened, the weeds must be removed.
When the leaves turn yellow and dry, the plants are dug in, the one-toothed bulbs are selected from the soil, dried and prepared for autumn planting.
One-toothed onion sets are planted in the same way as chives. In the second year, normal arrowhead plants and bulbs are obtained, dividing into cloves.
Growing garlic from bulbs (how to rejuvenate garlic) - video
Aerial bulbs can also be sown in spring. To do this, they are stored in a cold (2–5 ° C) or warm (18–20 ° C) room in unmilled sheaves. This way they are better preserved. Early spring sowing of aerial bulbs after cold storage is almost the same as for winter sowing.
After storage in warm (18–20 ° C) and early spring sowing, well-developed plants grow: their growing season is longer than that of plants under winter sowing and cold storage. They give large sets, but later ripening.
If you didn't have time to sow garlic in early spring, you can do it in June. In this case, the plants do not form a bulb and continue to grow until the onset of winter. After overwintering in the soil, the next year they grow and develop in the same way as the arrowhead garlic plants grown from the cloves, but produce a smaller bulb.
How to plant spring garlic in spring
Two to three weeks before planting spring garlic in the open ground in the spring, the storage temperature of the planting material is reduced from 18-20 to 2 C. Immediately before planting, the heads are divided into cloves and the largest of them are selected.
After preparing the soil, it is carefully leveled with a rake, longitudinal grooves are made, the distance between their centers is 20 cm, between the cloves is 5-6 cm.
Planting depth is 2-3 cm. The teeth should be planted in the center of the groove, bottom down. Seedlings begin to appear in 13-15 days.

Outdoor garlic care
Caring for garlic plants consists in systematic loosening to a shallow depth (4-5 cm), so as not to damage the root system, in killing weeds, watering and feeding.
How to water garlic
During the period of active growth of garlic plants, the soil should always be moist. The lack of a sufficient amount of moisture reduces the yield, reduces the number of cloves in the bulbs.
Spring garlic is more moisture-loving than winter garlic and needs watering. Watering is necessary until mid-June. But garlic also does not tolerate waterlogging of the soil.
How and what to feed garlic after winter so that it does not turn yellow
The leaves of winter garlic begin to grow very early, when the snow has not yet melted everywhere. However, gardeners often see pale yellow and frail ones instead of bright green young shoots. The reason lies in insufficient plant nutrition. So that the garlic planted before winter does not turn yellow, in the spring water your plantings with a solution of ammonium nitrate (dissolve the fertilizer matchbox in a bucket of water).
Do the second feeding around mid-May. At this time, it is customary to feed the plants with a mixture of mineral fertilizers: ammonium nitrate, superphosphate and potassium salt (10, 20 and 10 g per 1 m2, respectively).
How to water the garlic in spring so that it does not turn so yellow if you want to do without the "chemistry"? In this case, it is better to use organic fertilizers for feeding, for example, a weekly infusion of fresh chicken manure (compared to mullein, it contains more nitrogen).
If the plantings dry up, water the soil abundantly, starting from the third decade of May and throughout June. The earth is periodically loosened with a hoe, I weed the weeds, preventing their regrowth.
The last, third, time they feed the garlic at the end of June, when the bulbs are finally formed. Summer nutrition is an infusion of mullein (1 liter of fertilizer is diluted in a bucket of water) or an infusion of weeded weeds growing on a compost heap, in the same concentration. You can limit yourself to feeding with superphosphate (5 tablespoons per 10 liters of water). Since this fertilizer is poorly soluble in water, it is preliminarily boiled for 30 minutes in a mug of water, stirring often.
How and what to feed spring garlic
Spring garlic shoots begin to appear 13-15 days after planting. With mass seedlings, the soil surface must be loosened and fertilized with nitrogen fertilizer. To do this, 15 g of ammonium nitrate is dissolved in 10 liters of water and evenly poured into the grooves at the rate of 10 liters per 1 m2. When the liquid is absorbed, the grooves are closed with dry soil.
The second feeding with nitrogen and potassium (potassium chloride) fertilizers should be given in the phase of formation of four leaves at the rate of 20 g per 10 l of water.
The third top dressing - potassium and phosphorus (superphosphate) fertilizers - in the phase of the seventh leaf - at the rate of 20 g per 10 L of water, solution consumption 10 L per 1 m2. After each feeding, the garlic is watered.
Tips on how to grow large heads of garlic
At about the twentieth of June, garlic throws out flower arrows, at the end of which airy bulbs (bulbs) develop. A few of the most powerful arrows that appear first can be left for seeds. The rest are gradually removed at the stage of formation, when they are good as vitamin greens for salads and canning.

Timely breaking of the arrows at the very base, from the leaf axils, increases yield and allows you to grow large garlic.

Do I need to tie the garlic after breaking the arrows? Tying the garlic arrows in a knot, practiced by some growers, does nothing, since the development of the arrows does not stop, and a good half of the nutrients do not enter the bulb.
Harvesting and storing the harvest of garlic
Stop watering the garlic a few weeks before harvest. To determine if the garlic is ready to harvest, inspect several bulbs by thoroughly cleaning the dirt.
When to dig out garlic planted in the winter
A sign of the ripening of garlic is the cessation of the formation of new leaves.In non-streaked varieties, the leaves turn yellow, in those with shooters, the caps on the bulbs crack, dense wrappers form on the bulbs, the head becomes ribbed.
As soon as the leaves begin to turn yellow and dry, it means that the garlic is ripe. Now it is impossible to hesitate with cleaning - if there is a delay, the teeth break the wrapper and crumble, such heads will be unsuitable for long-term storage.
Garlic is harvested in dry weather. Ripe bulbs are dug out with a pitchfork, carefully picked out of the soil and laid out in rows for several days to dry in the sun.
Then the roots and stem are cut with pruning shears, leaving about 1.5 cm. If the stem is shorter, you can damage the hard scales of the cloves, and then the garlic will be poorly stored.

When to harvest spring garlic
Depending on the variety and weather conditions, spring garlic ripens at the end of August or September. The main signs of ripeness:
- lodging of tops;
- drying of the lower leaves;
- yellowing of the upper leaves;
- dying off of roots (they become thin, dark).
Choose dry weather for cleaning. It is impossible to delay harvesting, as in rainy weather the garlic forms new roots and germinates. The bulbs are dug in with a shovel or pitchfork and picked from the soil. Dry them in the air or indoors until the leaves are completely dry.
Then the bulbs are cleaned of the remnants of adhered earth, the roots and the false stem are cut off 4–5 cm above the shoulders. After that, the garlic is finally dried (it should rustle during tedding) and put into storage.
How to store garlic in the winter at home to keep it dry
It is better to process the main part of the crop immediately and make preparations for the winter. The rest is stored until spring in a room where in winter it keeps a rather low, but positive temperature with low air humidity. The prepared heads are placed in boxes, baskets or mesh bags, they can be woven into braids.

At a temperature of 1-3 C, they will remain juicy and fresh for a long time, and until spring they will not germinate or dry out.
Experienced growers know how to properly store garlic at home at room temperature. There are two reliable methods suitable for a city apartment:
- Well-dried heads of garlic are folded into a canvas bag, tied and put into a plastic bag, leaving it open.
- Another method - you need to take a jar or a saucepan, pour a 2-3 cm layer of salt on the bottom, then put the heads of garlic and fill it with salt again, etc. The top row must be covered with salt, but it must not be wet.
What can be planted after garlic next year
Garlic can be returned to its original place only after four to five years. As an exception, this is possible, but only if an infection has not accumulated in the soil during the first year of cultivation, which is easy to check if you carefully examine the heads of garlic that have grown there. If he is completely healthy, without the slightest signs of any lesions, you can take a chance and plant garlic in the same place for the next year, but not more.
It is undesirable to plant onions after garlic, since these crops are affected by the same diseases.
Here's what you can plant after garlic:
- cucumbers;
- zucchini;
- pumpkin;
- early harvested root vegetables and early cabbage;
- all legumes and greens.
No vegetable garden is complete without a bed of garlic. It is not only a necessary seasoning, but also an invaluable aid in the fight against flu and colds. Growing garlic and caring for it on the shoulder of any gardener, you just need to know his preferences well and follow all agricultural techniques.
Basic rules for growing

It doesn't take so much to get a good harvest of this crop:
- high-quality and healthy planting material;
- loose fertile soil;
- timely landing;
- proper watering and feeding;
- adherence to cleaning deadlines.
The choice of planting material
If teeth are planted from their own harvest last year, then only the largest heads need to be selected for seeds. They should not have double teeth, as well as double tops - these are signs of degeneration. Teeth with external damage and traces of diseases are not suitable for planting. Before planting spring garlic cloves, you need to prepare them: vernalize and germinate.

- vernalization - kept in the refrigerator (not in the freezer!) for a month;
- germination - placed in a damp cloth, wrapped in a bag and kept in the vegetable section of the refrigerator until root rudiments appear.
The yield from the prepared planting material will be higher. To disinfect it, the heads disassembled into teeth with root rudiments are soaked in an ash solution or in a solution of potassium permanganate. To prepare an ash solution, 400 g of ash are boiled in 2 liters of water for half an hour. The teeth are laid out for 2 hours in a cooled solution.
To prepare a solution of potassium permanganate, a spoonful of the drug is diluted in a ten-liter bucket of warm water. The exposure time is 10 hours. Prepared teeth are planted in the beds.
Outdoor planting of spring garlic
The prepared and germinated seed of spring garlic is planted in the ground in early spring.
Soil preparation and site
Growing garlic starts with preparing the soil. This procedure is carried out in the fall. The place for the plants needs a sunny one, the leaves will also grow in the shade, but you cannot get a good head. Spring garlic prefers loose fertile light or medium loamy soils with a sufficient humus content. The reaction of the soil should be neutral or slightly acidic.

Since autumn, when digging, they bring in for each square. m:
- 0.5 buckets of humus or well-ripened compost;
- 2-3 glasses of ash;
- 15 g of complex mineral fertilizer.
Immediately before planting, the bed is loosened, but not dug up. It should have a flat surface so that all planted teeth are on the same level.
Then plant the garlic
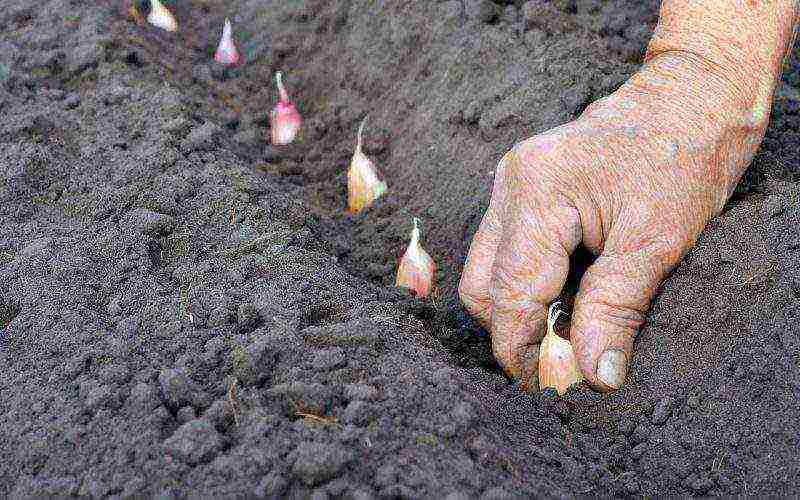

The correct precursors for spring garlic are very important. The health of plants largely depends on them. It is best to plant spring chives after any pumpkin crops. They do not have common pests and diseases, and after harvesting the beds remain well manured, the soil is loose and fertile. Cereals, greens, or legumes are good predecessors. But you can return the garlic to its original place or plant after the onion only after 4 years. The neighborhood of beds with garlic and peas and beans is undesirable. Their allocations do not like each other, and the yield of all crops will be low.
How and when to plant
Spring garlic is planted only in spring. With a podzimney landing, it can easily freeze out. Nevertheless, this representative of onions is not afraid of frost, so it is planted as soon as the ground warms up to 5 degrees, but still fully retained moisture after the snow melts. Spring garlic grows better at low temperatures, so you can't be late with planting dates. They depend not only on the region of cultivation, but also on the weather.
Planting method: grooves with a depth of about 4 cm are formed on the garden bed, into which the teeth are neatly laid out with the roots down. They cannot be pressed into the ground - the fragile rudiments of the roots are easily damaged, and then the seedlings will have to wait for a very long time. Ideally, the orientation of the rows will be from west to east - this way they will receive the most light.
Landing scheme
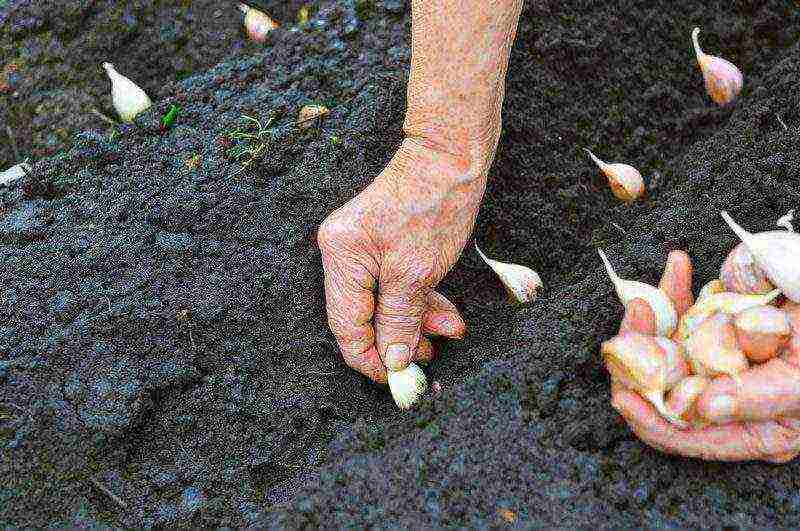

The cloves are planted shallowly, sprinkling with a layer of earth 2 cm thick.The distance between small cloves is about 8 cm, and between large cloves - up to 12 cm.The row from the row should be at a distance of 25 cm.Mulch well with a layer of humus 3-4 cm thick It will serve as additional food for plants and protect the soil from drying out.
Winter garlic: the nuances of growing
This type of garlic boasts large heads. In some varieties, the cloves weigh 12 g or more. Even from the name it is clear that they plant it before winter. After planting, the teeth should have time to take root before frost, but not sprout.Usually they need 1-1.5 months for this. Therefore, the landing dates are calculated based on the onset of a frosty period in this region.
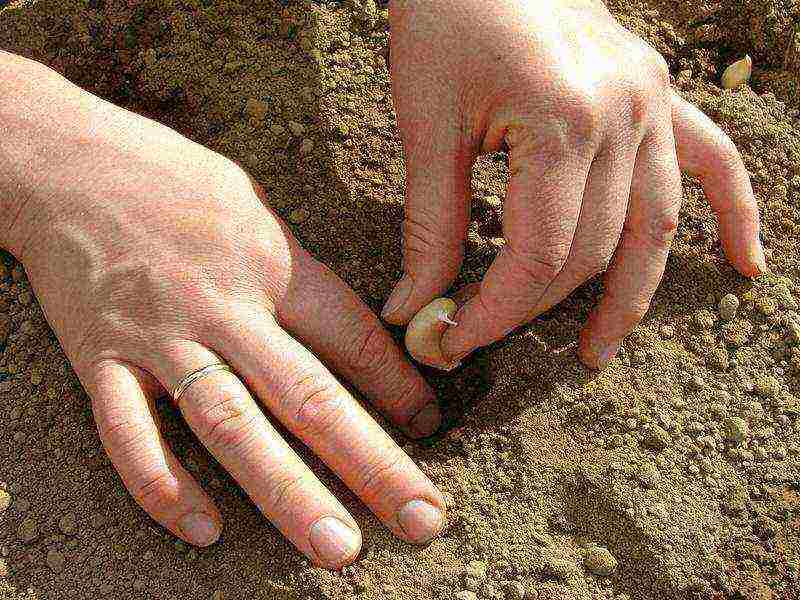

What winter garlic prefers:
- light sandy loam soil, rich in humus and good moisture retention;
- location with all-day lighting;
- a garden bed prepared in advance, for each sq. m which add a bucket of humus, 25 g each of nitrophosphate and superphosphate.
Planting winter garlic is carried out 2-3 cm deeper than spring garlic, the technology and planting scheme do not differ significantly. But there are differences in the preparation of planting material. Like spring garlic, the largest cloves are selected for planting, but they do not need vernalization. It is also not necessary to germinate it, but it is necessary to treat it with a solution of potassium permanganate or an ash extract. This is done in the same way as with chives of spring garlic. Plantings are best mulched with peat or humus in case of severe frosts without snow.
In the spring, the first thing to do is loosen the beds with sprouted shoots. So that the tips of the leaves do not turn yellow, loosening can be combined with foliar feeding with a solution of nitrogen fertilizer at the rate of Art. spoon for 10 liters of water. In cold soil, the roots do not work well and do not absorb nitrogen. It is lacking in fast growing foliage, so the tips of the leaves turn yellow.
Winter varieties are divided into arrow and non-arrow. The first ones release a flower arrow, but they form not seeds, but air bulbs. If they are not needed for subsequent reproduction, the arrows are broken out as soon as they begin to twist, leaving a stump of 1 cm. 1-2 arrows should be left as beacons. Cracking the cover on the formed bulbs will serve as a signal for harvesting.
Outdoor care

Like onions, garlic has not lost the habits that it got growing in its natural habitat: spring and early summer, rich in moisture from the melting of mountain snows, contribute to the formation of green mass. The dry period that comes in summer is a signal for the formation of a bulb or head. The mode of watering garlic in the beds should take this feature into account.
Watering
In the absence of rain, watering should be regular. It is done as the top layer of the soil dries up to a depth of 2-3 cm. The root layer should be completely wet. Watering is stopped 3-4 weeks before harvesting, allowing the head to gain weight corresponding to the variety.
Fertilization and feeding
If the garlic grows on fertile soil, and the bed was well filled with nutrients before sowing, then a good harvest can be obtained without additional nutrition. Otherwise, you cannot do without dressing. At different stages of development, the nutrient requirements of garlic are different.
- When growing green mass, plants need nitrogen most of all. It can be given in the form of root dressings with solutions of ammonium nitrate or urea. Fertilizer is diluted in accordance with the instructions, usually - Art. spoon on the bucket. Most often, two dressings are practiced: the first at the stage of germination, the second at the formation of 3-4 leaves. Per sq. m of the garden, 2-3 liters of solution is enough. If the land is fertile, one top dressing is enough.
- The third feeding is carried out 2 weeks after the second with full complex fertilization - Art. spoon on a bucket of water. Per sq. m beds are poured 3-4 liters of solution.
- The last feeding is carried out at the stage of bulb formation. At this time, plants are most in need of phosphorus and potassium. It is good to pour ash under them and loosen them. To enrich the soil with phosphorus, dissolve 2 tbsp. tablespoons of superphosphate in hot water. When it cools down, it is poured onto the square. m 3-4 liters of solution.
Each liquid top dressing is combined with watering with clean water. The next day, the beds are loosened.
The following agrotechnical technique will help to get larger heads: 3-4 weeks before harvesting, the soil from the bulbs is carefully raked into the aisles, exposing them completely. Thus, there is freedom to grow, which increases the yield.
Harvesting garlic
It is better not to tighten the garlic when harvesting, otherwise the heads will crack and will be worse stored. The signal for harvesting is the lodging of the shoots and the yellowing of the lower leaves. The cracked cover pouch on the beacons left behind will also tell you that it's time to harvest. You cannot dig up garlic ahead of time. Unripe bulbs will not only be smaller in size than they could, but will also be worse stored. After harvesting, the garlic is dried in the garden for several hours, and then dried in the shade in a well-ventilated place.
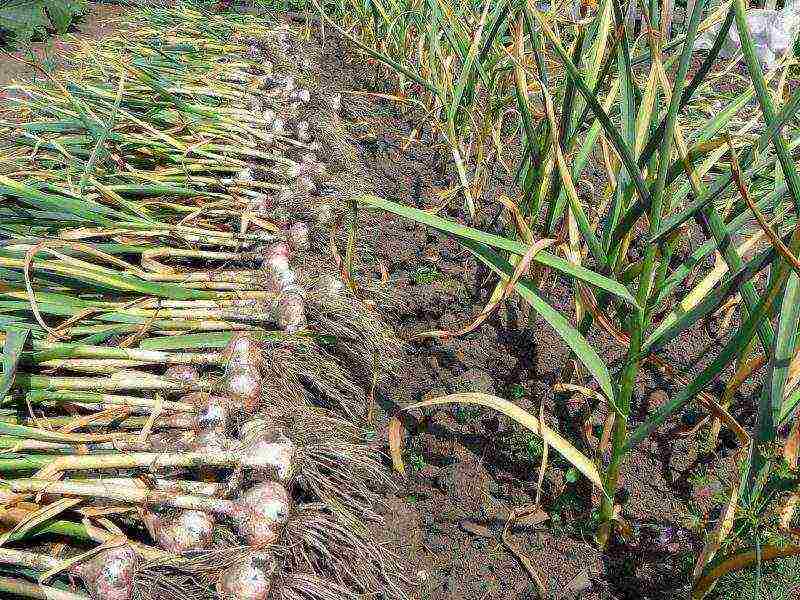

The harvesting period for winter garlic is July, and that for spring garlic is September. It is removed after the leaves turn completely yellow.
Breeding features
Spring garlic reproduces only vegetatively - with chives. Winter garlic can also be propagated. But the shooting varieties have another option: sowing air bulbs, the so-called bulbs. They are formed at the end of each arrow. When growing garlic from bulbs, the seed material is healed. In the first year, one-tooth bulbs, consisting of one tooth, grow from them. They are used for autumn planting along with traditional cloves and give a good harvest of large and healthy bulbs.
Sowing winter garlic bulbs
They can be sown in autumn or spring. Sowing time depends on the size of the bulbs. Large air bulbs can be stored in the room until spring, small ones will simply dry out, and in the soil they will survive the winter perfectly. Collect the bulbs when they acquire the color corresponding to the variety, and the seed sac bursts. For planting, it is better to select the largest specimens. Prepare a bed for sowing in the same way as for winter garlic. Sowing dates are all September and early October. Sowing pattern: 10 cm between rows and 2-3 between bulbs. They are laid out to a depth of about 3 cm. To prevent the crops from freezing, it is better to mulch them. The easiest way is to sprinkle the beds with a layer of humus of 2-3 cm. Care for crops in spring and summer does not differ from that for winter garlic.
Diseases and pests: control methods
Despite the large number of phytoncides, this plant is also susceptible to diseases, and pests can also attack it.
Table: diseases and pests of garlic.
| Root and four-legged mites | Lagging of the bottom of the bulb and its decay, ulcers on the teeth | Compliance with crop rotation, warming up the garlic at 40 degrees after harvest, careful selection of seed |
| Onion fly | The larvae eat away part of the cloves, the tips of the garlic feathers turn yellow | Joint planting with carrots, dusting the beds with ash and tobacco dust or ground hot pepper, watering with a solution of salt from 1 glass to 10 liters of water, watering with mullein infusion or urea solution |
| Nematodes | The green shaft is bent, the heads are loose, the integumentary scales are lagging behind | Compliance with crop rotation, disinfection of planting material |
| Fusarium | Caused by a fungus, the stems lose leaves that dry out. Pale pink or white traces of mycelium on bulb and stem | Treatment of seed and soil with fungicides: Hom, Fitosporin, Maxim |
| Rust | Rusty spots on the leaves, developmental delay, scanty harvest | Seed and bed treatment with fungicides |
| Peronosporosis | The upper part of the stem turns yellow and dries up, growth slows down | Warming up the harvested crop and sowing material in the bright sun at a temperature of about 40 degrees, treatment with fungicides: Thiram, Polycarbacin |
| Bacteriosis | Yellowish brown wounds on the teeth | Do not harvest until fully ripe, treat the beds with Hom. |
Types and varieties of garlic
Garlic is divided into two groups, which differ not only in terms of storage, bulb structure and growing season, but also in terms of planting. For spring garlic, a lower yield is characteristic, but it is stored almost until the new harvest. Its teeth are smaller and arranged in a spiral. Winter garlic has a central core around which the cloves are grouped; spring garlic does not.
Winter varieties
Gribovsky jubilee.
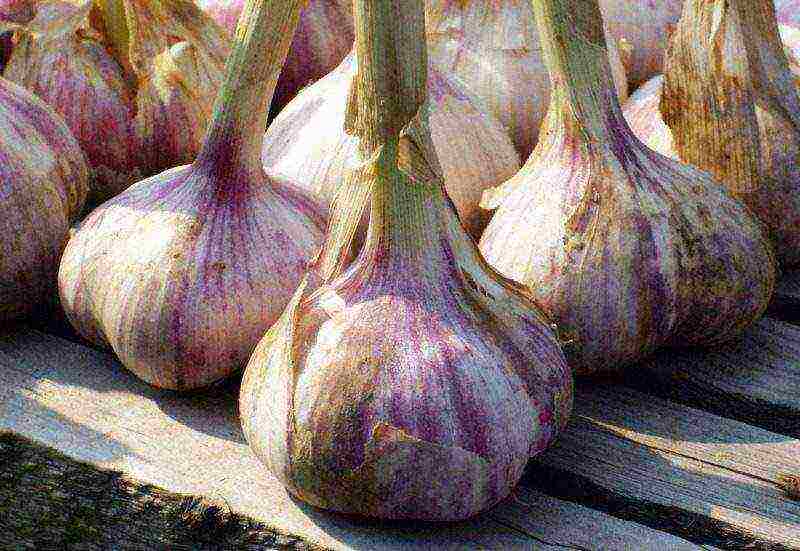

There are 11 cloves in the onion. Its average weight is about 40 g. The taste is spicy. Ripening time - late. Arrowhead variety. The color of the covering scales is purple.
Gribovsky - 60.
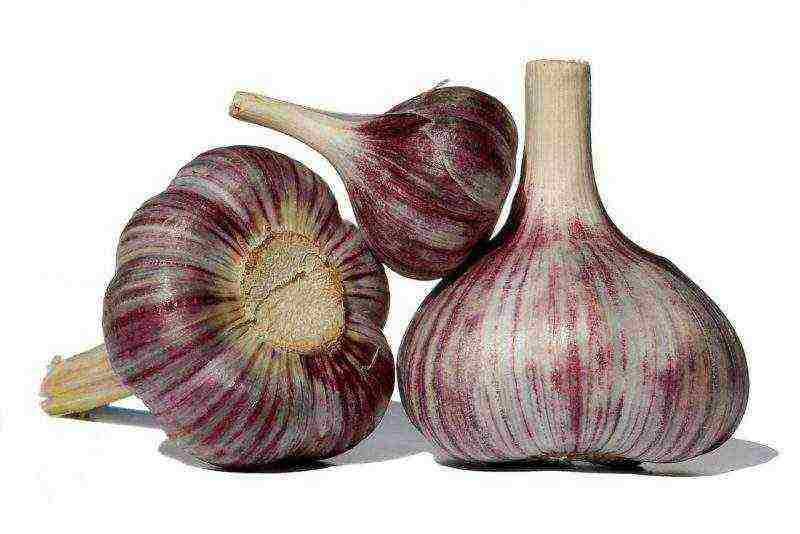

Early ripening variety that gives an arrow. The pungent-tasting bulb consists of 11 cloves and weighs 40-60 g. Covering scales are reddish with a lilac tint.
Komsomolets.
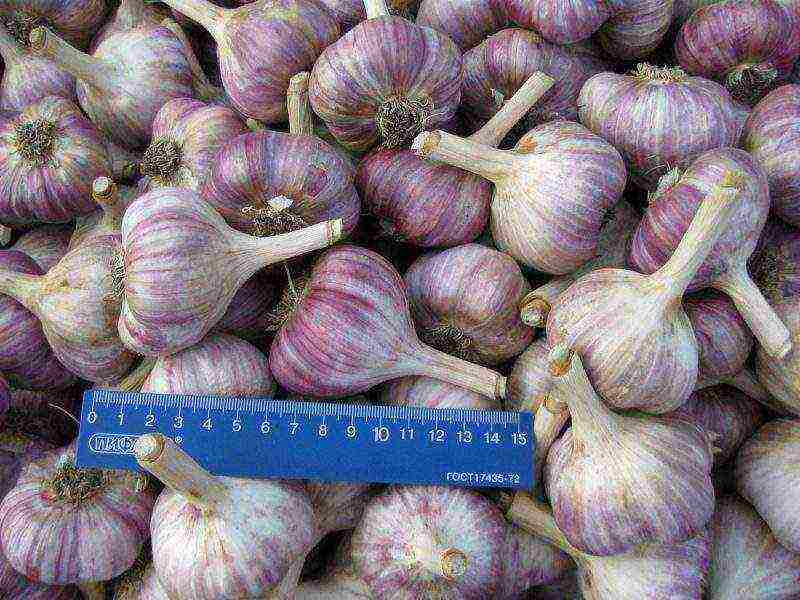

Variety of arrow-covering pink-violet covering scales. There are 7 to 11 cloves in the onion, which has a spicy taste.
Danilovsky local.

Doesn't give an arrow. In a large onion with lilac opaque scales, the number of cloves ranges from 6 to 11.
Spring varieties
Gulliver.

Produces very large bulbs weighing up to 115 g. The scales are gray, the taste is spicy, ripening later.
Yelenovsky.
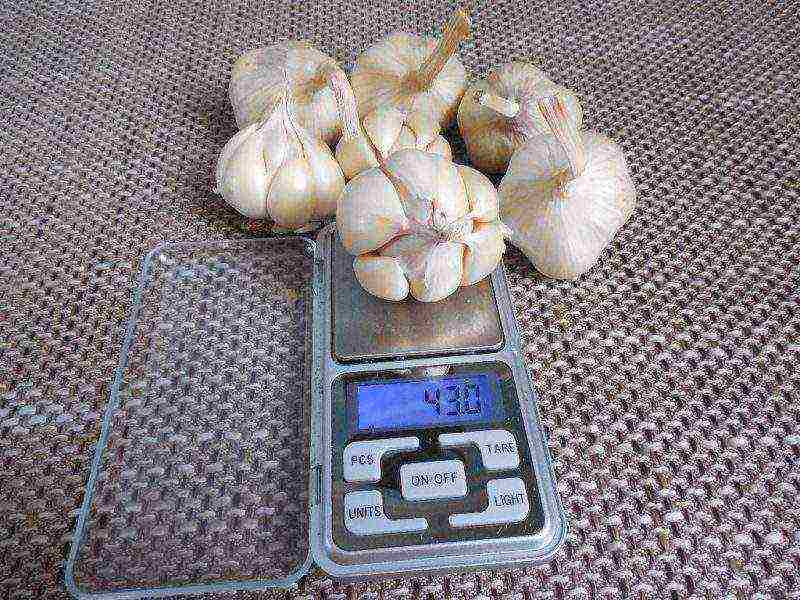

The variety is frost-resistant, the heads weigh 35 g. Ripens in medium terms. Stored up to 2 years.
Sochi.

The variety ripens early. Bulbs weighing up to 45 g with white scales, excellent taste. They can be stored for 1.5 years.
Victorio.

The taste is semi-sharp. The bulb can have up to 13 cloves, it weighs about 40 g, the shelf life is up to 8 months.
Garlic has a long tradition of use, both as a spicy seasoning that complements the taste of many dishes, and as a preventive and therapeutic agent for many diseases.


