Content
- 1 What is a vegetable
- 2 Types of celery
- 3 Planting stalked celery
- 4 How to care for celery outdoors
- 5 Growing celery at home
- 6 Diseases and pests characteristic of stalked celery
- 7 Correct harvest is a guarantee of long-term storage
- 8 Growing celery seedlings
- 9 Planting celery in the garden
- 10 Care
- 11 Trench method of growing celery
- 12 Self-bleaching varieties
- 13 Conclusion
- 14 Celery growing conditions
- 15 Growing petiole and leaf celery from seeds
- 16 When and how to plant petiole and leaf celery seedlings in the ground
- 17 How to care for leafy celery
- 18 Features of caring for stalked celery in the open field
- 19 How to grow stalked celery correctly, we look at the video:
- 20 Growing root celery through seedlings
- 21 How to care for root celery outdoors
- 22 Celery diseases and pests
- 23 Types and varieties of celery
- 24 Useful properties of celery
Celery has been known since ancient Greece. It was here that a cultivated plant was bred from a wild variety and elevated to the rank of sacred. Celery was used to make decorations for the departed, its image was minted on coins. Celery was not grown in Europe until the 16th century. At the same time, the plant appeared in Russian pharmaceutical gardens. At first, it was used for medicinal purposes and only over time was it used as a fragrant seasoning that significantly improves the smell and taste of food. Today, there are several varieties of this unique plant, among which stalked celery occupies a special place.
What is a vegetable
Petiole celery belongs to the umbelliferae family. The vegetable boasts an affinity with such popular and well-known crops as carrots, cumin, coriander, anise, etc. This is a biennial plant that is planted with seeds, and in the first year of its life cycle it forms a stem and rhizome, and in the second year it blooms and bears fruit ... As a vegetable crop, it is customary to grow stalked celery for only one season, since the stem and leaves of the plant are mainly used for food. Vegetable seeds are of more limited use.
Outwardly, celery resembles parsley: it has pinnately dissected leaves, collected in a rosette, and a core rhizome.Inflorescences are kind of umbrellas and consist of a large number of small flowers. The culture can grow up to 1 m in height, it is moisture-loving and cold-resistant.
 High-quality petioles are obtained only in the first year of the growing season of the plant.
High-quality petioles are obtained only in the first year of the growing season of the plant.
The benefits and harms of stalked celery
First of all, it must be said about the use of stalked celery in cooking. The stems of the plant are ideal for stewing and frying; they are added raw to various salads. The product goes well with meat and fish dishes. It is used to make a very healthy juice, as well as aromatic tea.
 The sap of the plant is quickly absorbed by our body, penetrating the cells through the blood and lymph
The sap of the plant is quickly absorbed by our body, penetrating the cells through the blood and lymph
One of the most remarkable properties of celery is its low, almost negative calorie content: the human body spends more calories on digesting celery products than it receives from consuming them.
In addition, celery is able to actively burn fat, so its consumption is indispensable for people who control their weight and seriously monitor their health. Experts note the following factors of the beneficial effects of celery products on our body:
- it helps to cleanse toxins;
- strengthens the immune system;
- has a beneficial effect on digestion;
- slows down the aging process and helps to cope with senile dementia;
- normalizes metabolism;
- heals burns, cuts, inflammations, hematomas and other skin disorders;
- has a calming effect;
- has a beneficial effect on the condition of the hair.
Doctors recommend celery dishes to people suffering from
- hypertension;
- obesity;
- diseases of the genitourinary system;
- rheumatism.
Such a vast area of usefulness is associated with the content in the culture of a huge amount of necessary vitamins and minerals, including:
- potassium;
- phosphorus;
- zinc;
- calcium;
- gland;
- vitamins of groups A, B, C, PP, E.
The daily consumption of two tablespoons of chopped celery greens provides the human body's daily need for carotene and vitamin C.
Contraindications
Refuse to use the plant in any form should be people suffering from gastric ulcer, varicose veins, thrombophlebitis, urolithiasis, epilepsy. The vegetable is not recommended for pregnant women and nursing mothers, since the use of spicy herbs can cause increased gas production, which will negatively affect the fetus, as well as the digestion of the baby, who will receive the product along with the mother's breast milk. Celery gives milk a specific smell and taste, due to which the baby can refuse to breast.
Video: celery - benefits, harms and contraindications
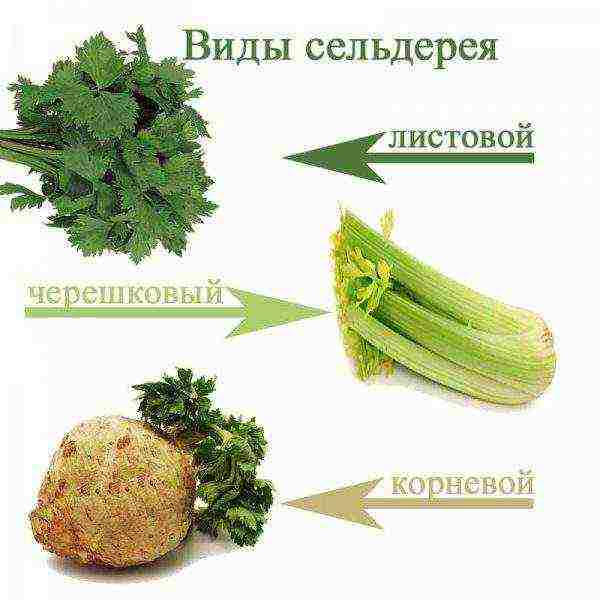
Types of celery
There are three varieties of celery: root, leaf and petiole. Root varieties are grown for a healthy and nutritious root that reaches 10 cm in diameter. Root celery can also be eaten in the aerial part, but since the variety has a long growing season (from 150 days), during which it is not recommended to cut the stems of the plant, it is not grown for greens. For this purpose, leaf celery is planted, which quickly forms a rosette with delicate leaves, and the petioles are ordinary, small.
Petiolate celery is also grown for its greens. It does not form thickenings at the root, like leafy varieties, but it has large leaves and juicy, elastic, fleshy petioles reaching four centimeters in thickness.
 When growing celery of various types, plant care has a number of features.
When growing celery of various types, plant care has a number of features.
Today the market offers a wide range of stalked celery seeds. Among gardeners, varieties of domestic selection are popular, which are adapted to our weather conditions, are not afraid of frost, are resistant to many common diseases, and give juicy petioles with good taste.
Table: varieties of stalked celery included in the State Register of Breeding Achievements of the Russian Federation
Photo gallery: stalked celery varieties of domestic selection
Golden - an early variety that allows you to grow juicy, full-bodied petioles with an excellent taste. Atlant celery stalks need bleaching. suitable not only for salad, but also for freezing or drying.The early Malachite variety provides the owner of the plot with a good harvest of juicy, rich green, tasty and fragrant petioles in a short time Pascal celery petioles have an intense dark green color and reach a length of up to 20 cm. celery of the Tango variety have excellent taste and aromatic qualities, they retain their presentation for a long time; a large plus of the Khrust celery is its cold resistance Powerful celery stalks of the Utah variety are very fragrant, retain their juiciness for a long time
Planting stalked celery
Growing stalked celery cannot be called a simple matter, but if you know the features and take into account the requirements of this plant, then success will be guaranteed. Early varieties of this variety can be planted directly from seed directly into open ground. Such sowing is carried out approximately in the second decade of April. But at the same time, the following risks must be taken into account:
- do not count on the amicability of seedlings;
- it will be difficult to care for young plants. Considering that at the initial stage of the growing season, celery develops very slowly, it will be problematic to fight weeds, as well as protect seedlings from weather disasters.
Most often, when growing stalked celery, they resort to the seedling method, which is more guaranteed to get fresh and healthy greens for the dinner table.
Seedlings can be grown in a greenhouse, since celery is a cold-resistant plant and its seedlings can easily tolerate frosts. If this is not possible, then sowing in containers that will stand on the windowsill is quite suitable.
Before sowing seeds, you need to prepare the planting container and suitable soil. As containers, you can use both special containers and trays for growing seedlings, and any available material: wooden or plastic boxes, yogurt packaging and even plastic bags. The main thing is to provide a drainage layer in them, which will not allow excess moisture to stagnate in containers.
 Growing in cassettes allows plants to form a root system that will permeate the entire substrate and not be damaged during transplantation
Growing in cassettes allows plants to form a root system that will permeate the entire substrate and not be damaged during transplantation
The soil for sowing seeds must be nutritious and always moisture and air permeable. The following composition is perfect:
- peat;
- humus;
- coarse river sand;
- turf land
in a ratio of 3: 1: 0.5: 1. Add urea (1 teaspoon) and wood ash (2 glasses) to 10 liters of prepared and thoroughly mixed soil.
For disinfection, the soil mixture is spilled with boiling water with the addition of potassium permanganate a few days before sowing (slightly pink solution).
 The soil for sowing celery should be loose, moderately moist, homogeneous
The soil for sowing celery should be loose, moderately moist, homogeneous
Seed preparation
This is a very important step in growing a crop. Stalked celery seeds have several specific features:
- their germination depends on age, but over time it does not deteriorate, but rather increases. Therefore, the most friendly seedlings will appear from seeds that have lain for 3-4 years;
- the plant contains essential oils that prevent the seeds from quickly absorbing moisture, and the germination process can take several weeks.
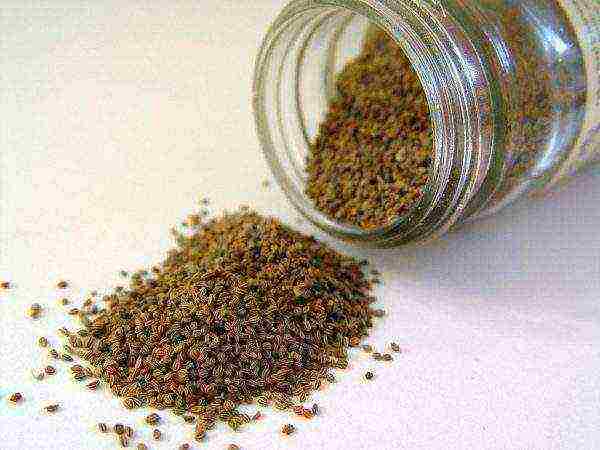 Celery seeds are very similar in appearance to parsley and carrot seeds.
Celery seeds are very similar in appearance to parsley and carrot seeds.
There are various ways to accelerate seed germination:
- The simplest preparation method is to soak the seeds for 2-3 days in room temperature water. During this time, they will be saturated with moisture, some of them will bite;
- before sowing, the seeds can be soaked for half an hour in a weak (1%) solution of potassium permanganate, and then kept for 18 hours in any growth stimulator. You can use Epin's solution: 2 drops of the substance per 100 ml of water. After soaking, the seeds are slightly dried and sowed;
 For disinfection, it is recommended to hold celery seeds in a solution of potassium permanganate, and then soak in a growth stimulator or just in water at room temperature
For disinfection, it is recommended to hold celery seeds in a solution of potassium permanganate, and then soak in a growth stimulator or just in water at room temperature - if you have an aquarium microcompressor, then the seeds can be kept for a day in oxygen-saturated water, which you get with this simple device, then pickled in the specified manganese solution.
Since celery seeds are small, after drying, they can be mixed with sand and sown into the ground in this composition.
Sowing seedlings
The timing of planting stalked celery for seedlings depends on the variety, its growing season. If it is about 120 days, then sowing should be done in the first decade of March. With proper seed preparation, seedlings will appear in 1-2 weeks. It is recommended to plant two-month-old celery seedlings in the ground.
The planting process itself is carried out in a completely standard way. It includes the following steps:
- The planting containers are filled with the prepared mixture.
- The soil is slightly moisturized.
- Seeds are evenly spread over the surface. The layout method depends on the size of the container: if space permits, then sowing can be carried out in rows located at a distance of 6-7 cm from each other. The grooves can be made in the soil mixture, or you can decompose the seeds, and then sprinkle them with wet sand, which will provide free air access, which means rapid seed germination.
 Sowing celery can be done in rows, making grooves 0.5 cm deep at a distance of 7-8 cm from each other
Sowing celery can be done in rows, making grooves 0.5 cm deep at a distance of 7-8 cm from each other - Embedding depth - no more than 0.5 cm.
- The containers are covered with a transparent material - special lids or simple plastic bags to create a greenhouse effect - and placed at a temperature of + 22-25 degrees.
- As the soil dries up, it is sprayed from a spray bottle with water at room temperature. Please note that watering with cold water can provoke the appearance of a black leg of the seedlings.
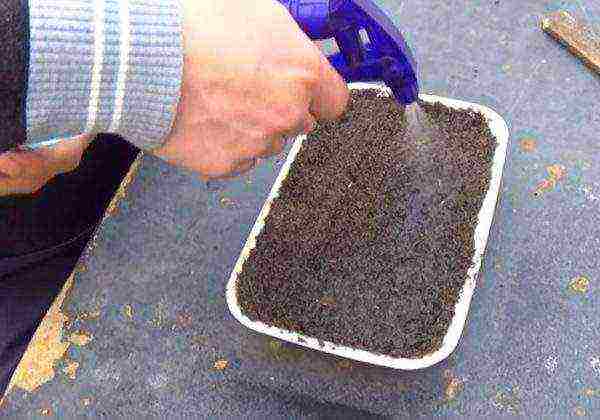 It is recommended to moisten crops with warm water using a spray bottle
It is recommended to moisten crops with warm water using a spray bottle - The covering material must be lifted daily to ventilate the mini-greenhouse.
Further care of seedlings
When the first descents appear, the seedlings need to provide good illumination and a comfortable temperature (about +16 degrees). A higher temperature regime will help to pull out the seedlings. Most often, the sprouts that appear are thin, the first month they grow very slowly. After about 30 days, they will have only 1-2 real pieces of paper each. At this time, it is necessary to carry out thinning, leaving the plants at a distance of 4–5 cm from each other, adding soil or diving the seedlings, if such a method of growing was envisaged.
 When two leaves appear on the celery seedlings, the plants can be planted so that the roots have more room to grow.
When two leaves appear on the celery seedlings, the plants can be planted so that the roots have more room to grow.
If conditions permit, then young plants can be transplanted for growing in a greenhouse. The transplant is carried out in furrows located at a distance of 5–6 cm; plants are also planted every 5–6 cm.
The pick is carried out carefully, planting seedlings in individual containers with a depth of at least 10 cm, trying not to damage the root, deepening the seedlings to the cotyledonous leaves, while not covering the central bud of growth with earth. This procedure stimulates the development of lateral roots in the seedlings, which will have a beneficial effect on the strength and endurance of the seedlings.
 When diving, the seedlings are lowered into the prepared hole, making sure that the root does not bend and remains in an upright position
When diving, the seedlings are lowered into the prepared hole, making sure that the root does not bend and remains in an upright position
After picking, the seedlings are watered and shaded from direct sunlight. The optimum temperature for seedlings during this period will be + 15-16 degrees. Finding seedlings at temperatures below +10 can lead to the fact that after transplanting to a permanent place, such plants will turn into color and do not give juicy and elastic stems.
If, during the preparation of the soil mixture, the soil was filled with nitrogen fertilizers in sufficient quantities, then the seedlings will have a rich color. With a weak color of the leaves, it can be fed with urea (1 teaspoon per 10 liters of water). Such dressings are carried out three times during the growing of seedlings (once every two weeks), always at the root.
A week before planting in open ground, you should begin to harden the plants. They are taken out into the open air, first for several hours, then for the whole day, and just before disembarkation they are left overnight.
Seedlings ready for planting should be strong, at least 10 cm high, have 4–5 true leaves and a root system that well braids with an earthen lump.
Transplanting seedlings to the garden
It is recommended to plant celery seedlings in the garden in mid-May, after stable warm weather is established, and the soil warms up well.
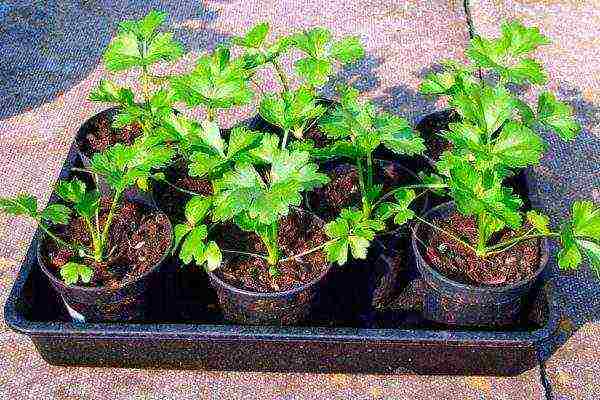 If you do not have the opportunity to grow celery seedlings, you can purchase them, but remember: good planting material is plants whose height reaches 13-15 cm, with a strong root system and four to five leaves
If you do not have the opportunity to grow celery seedlings, you can purchase them, but remember: good planting material is plants whose height reaches 13-15 cm, with a strong root system and four to five leaves
Experienced gardeners note that with favorable weather conditions and the readiness of seedlings, an earlier planting on the beds can be carried out. Plants planted at this time often produce the best yield. But with early planting, there is a risk that stalked celery will release flower stalks.
The site for planting stalked celery is selected and prepared in advance. Preference should be given to an open, sunny place with well-fertilized soil of neutral acidity. On poor, dry soil, you will get plants with thin, fibrous, possibly hollow stalks.
For autumn digging for 1 sq. meter contribute
- humus or compost (10 kg);
- ash (1 glass);
- superphosphate (1 tbsp. spoon).
If necessary, the soil is limed. A garden bed prepared in this way in the spring only needs to be loosened. Good precursors for stalked celery would be
- tomatoes;
- cabbage;
- cucumbers;
- zucchini;
- pumpkin;
- salad;
- legumes;
- spinach.
It is undesirable to plant celery after
- potatoes;
- corn;
- parsnip;
- parsley;
- carrots.
Petiole celery can be used as a compacting crop for
- tomatoes;
- legumes;
- any types of cabbage;
- Luke.
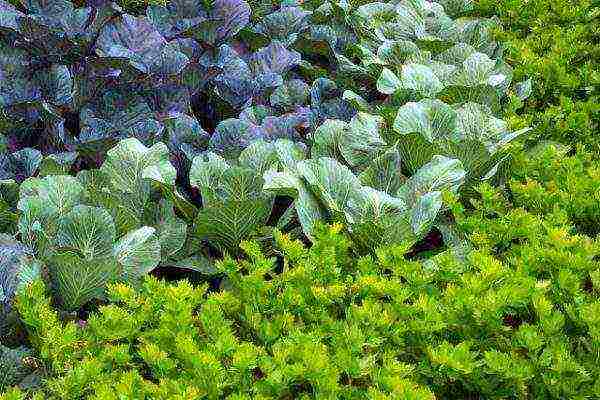 Celery perfectly coexists in the same garden with cabbage
Celery perfectly coexists in the same garden with cabbage
Such a neighborhood will benefit these vegetables, because celery has a strong smell that will scare away many pests.
The scheme for planting seedlings in open ground will depend on varietal characteristics: the height of the bush, the spreading of the rosette. The minimum distance between rows and between plants in a row will be 25 cm.For planting petiole varieties with a high spreading rosette, it is more reasonable to stop at a 50x40 cm scheme.
 Self-bleaching varieties of stalked celery must be planted in a garden so that a distance of 25 cm remains between the seedlings.The seedlings of varieties that need to be bleached are best planted in furrows at a distance of 30 cm from each other
Self-bleaching varieties of stalked celery must be planted in a garden so that a distance of 25 cm remains between the seedlings.The seedlings of varieties that need to be bleached are best planted in furrows at a distance of 30 cm from each other
The transplant is carried out as follows:
- Prepare holes corresponding to the size of the root system of the seedling together with a lump of earth.
- Humus and wood ash are added to them (one handful each).
- The seedling, as well as when diving, is buried to the cotyledonous knee.
- Lightly compact the soil around the plant.
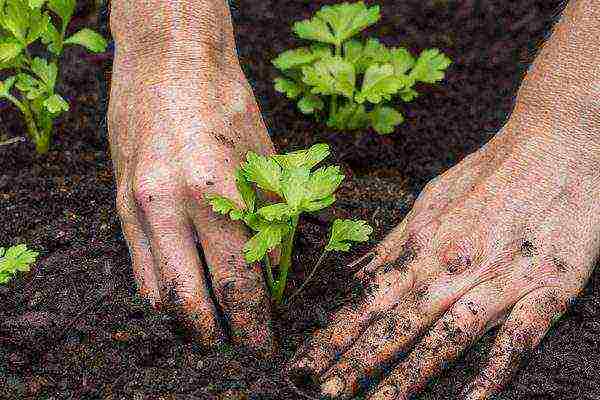 It is advisable to transplant into the ground in sufficiently dry and warm weather, preferably in the evening
It is advisable to transplant into the ground in sufficiently dry and warm weather, preferably in the evening - It is well watered and mulched with sawdust or straw.
- If the weather is hot with a bright spring sun, then it is recommended to shade the planted plants for a day or two using paper or fabric.
For weak seedlings, you can organize a mini-greenhouse right in the garden from a cut plastic bottle
How to care for celery outdoors
Further care of the plant is simple, fits into the framework of the standard rules of agricultural technology for the cultivation of any garden crop:
- watering is carried out based on the needs of the plant and weather conditions. Celery needs a lot of water to grow well. The rate of watering a plant in dry weather is about 20 liters per 1 sq. meter. But excessive waterlogging, leading to stagnation of moisture, as well as drying out of the topsoil, will adversely affect the quality and yield of the petioles. With a lack of moisture, the middle part of the stem can become fibrous, cracked and empty, and waterlogging provokes the development of fungal infections that initially affect the leaves, and then the petioles of the plant;
- the compaction of the upper soil layer must not be allowed. Its loosening is carried out after each watering or rain. The depth of loosening of the beds with young plants is 5–6 cm, the soil around the mature bushes is loosened deeper - by 15 cm.
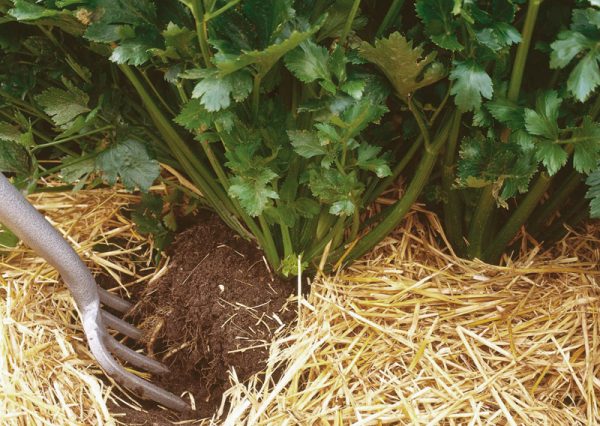 In order to prevent moisture evaporation and provide the plant roots with more oxygen, immediately after planting celery, the soil around it must be mulched with peat, sawdust, cut grass or straw
In order to prevent moisture evaporation and provide the plant roots with more oxygen, immediately after planting celery, the soil around it must be mulched with peat, sawdust, cut grass or straw
Juicy and thick celery stalks can only be obtained if the plant grows continuously throughout the growing season. Growth retardation can be caused by a lack of moisture, nutrients or compaction of the topsoil - then the plant does not receive enough oxygen.
Features of feeding stalked celery
Petiole celery responds actively to fertilization. To feed the plant, you can use humus, manure, ash, mineral complexes. A feature of feeding stalked celery is that when choosing fertilizers, they stop at compositions in which nitrogen and potassium are present in approximately equal proportions.
Table: "summer menu" for celery
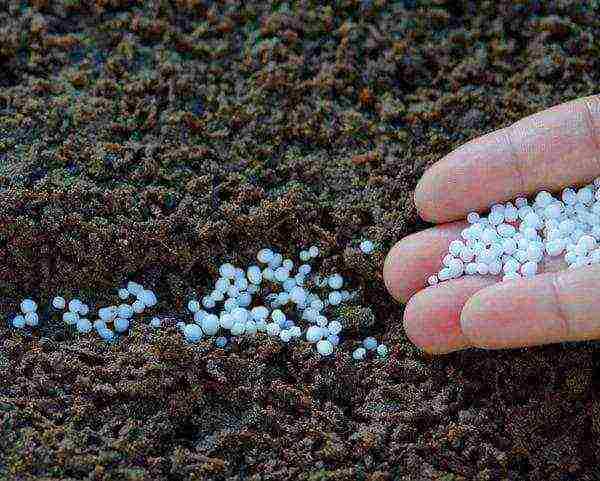 At the stage of growing leaf and stem mass, celery needs increased nitrogen feeding
At the stage of growing leaf and stem mass, celery needs increased nitrogen feeding
Petiole whitening
The main feature of petiolate celery care is the petiole bleaching procedure. As a result of its implementation, the shoots become not only lighter, but also much tastier, bitterness leaves them. This work should be done 2-3 weeks before harvesting. Whitening can be done in different ways:
- Hilling. To do this, once a month they carry out a high hilling of the bushes, the earth is poured gradually: first, the leaf rosette is fixed with soil so that it does not fall apart, then the bush is sprinkled half the height, and at the end - almost to the top, while trying not to fill the base from which it is formed foliage. Hilling is carried out only with damp soil. This method has one significant drawback - often the petioles acquire an earthy flavor.
 The first hilling is carried out when the plants reach a height of 30 cm
The first hilling is carried out when the plants reach a height of 30 cm - According to the reviews of many gardeners, the more effective way is as follows: the petioles are tied with a string, then wrapped with a layer of thick paper, cardboard and again tied with a string. Instead of paper, you can use straw, but it is necessary to overlay the plant with it tightly, without gaps.
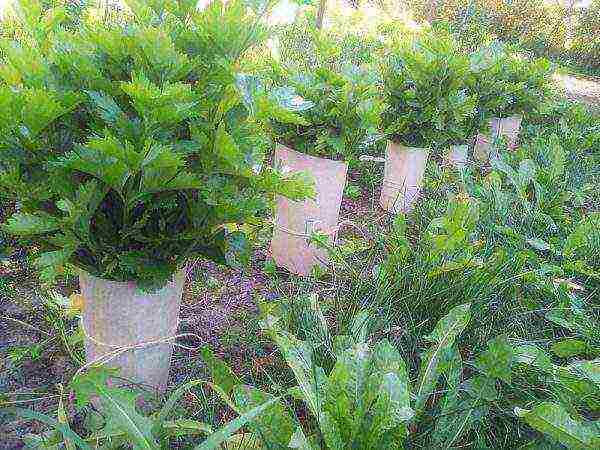 The hilling operation can be replaced by wrapping the bottom of the plant with burlap or paper
The hilling operation can be replaced by wrapping the bottom of the plant with burlap or paper
Sheet plates in both the first and second cases must remain free.
Owners of garden plots often avoid growing stalked celery precisely because high-quality petioles can only be obtained after a bleaching procedure, which for many is difficult and difficult to accomplish. Recently, self-bleaching varieties of this culture have appeared on the seed market - Golden, Malachite, Tango, which we talked about above. It should be noted that in order to achieve the self-bleaching effect, the celery bushes of these varieties must grow at a distance of no more than 25 cm from each other.
Video: we grow stalked celery correctly
Growing celery at home
Like many other herbs, stalked celery can be grown at home on a windowsill or balcony. The simplest and most easily accessible way is to obtain stalks and greens from celery stumps. In this case, celery stalks that you purchased in a store or grew on your site will serve as planting material. Celery shoots are attached to the stalk, which is usually not used for food. It should be fresh, elastic, without stains, mechanical damage and traces of rot. The stump is cut off at the base to a height of about 3-4 cm.
 Before planting, the celery stump is inspected for characteristic damage.
Before planting, the celery stump is inspected for characteristic damage.
The cut stump must be germinated. To do this, it is placed in a container with water at room temperature, immersing the bottom of the stump by about 0.5 cm in water. To accelerate germination, you can add a few drops of any rooting stimulant to the water. The container is placed in a bright place, but not in direct sunlight. The water is changed daily.
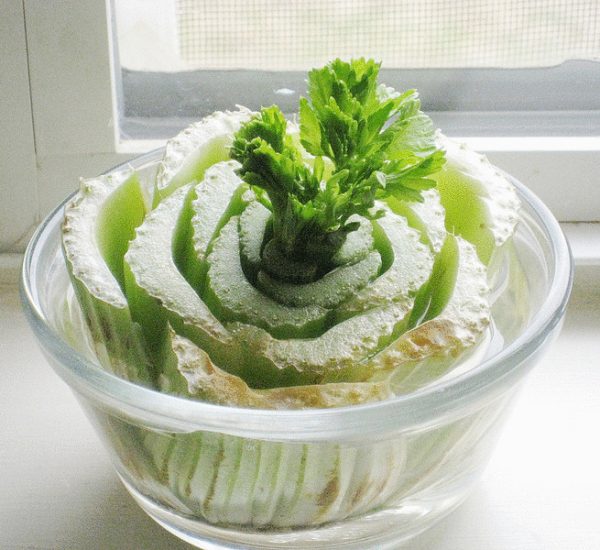 Celery stalk gives roots and new greens in 40-50% of cases
Celery stalk gives roots and new greens in 40-50% of cases
After about a week, young greens will appear from the old, dried sections. This is a signal that the plant is ready to be transplanted into the ground. The soil is prepared in the same way as for growing seedlings. An ordinary flower pot can serve as a planting container. Planting a sprouted stump is carried out as follows:
- A drainage layer is placed on the bottom of the pot. Its height must be at least 2.5 cm.
- A well-moistened soil mixture is poured over the drainage.
- A rather deep hole is prepared in which the celery stump should completely fit. When planted, only young shoots are left on the surface.
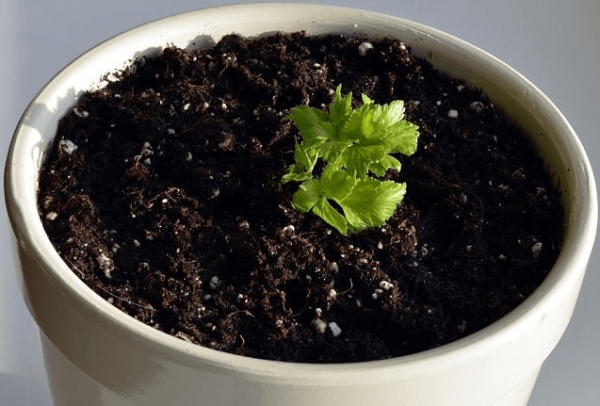 As soon as green leaves appear, and the roots reach a length of 1 cm, the stalk is planted in a small flower pot filled with nutrient soil
As soon as green leaves appear, and the roots reach a length of 1 cm, the stalk is planted in a small flower pot filled with nutrient soil - The soil is lightly squeezed and watered abundantly.
- The pot with the planted stump is placed on a warm, light windowsill.
To organize the correct and competent care of the planted plant, it is necessary to carry out the main caring activities on time:
- regularly, but moderately water the plant, avoiding stagnant moisture. This is one of the important conditions for the growth of succulent petioles;
- the top layer of the soil must be periodically loosened to provide air access to the roots of the plant;
- in late autumn and winter, you need to organize additional lighting. To do this, you can use fluorescent lamps or special phytolamps;
- every 20 days celery is fed with available fertilizers: a complex of minerals, infusion of wood ash.
In about a month, you will be able to harvest the first crop of vitamin petioles and green leaves, which will be an excellent addition to your winter diet. The petioles will most likely not be as large as when grown outdoors, but they will have enough juiciness and usefulness.
Diseases and pests characteristic of stalked celery
There is an opinion that celery is a crop that is rarely affected by diseases. If you do not comply with the basic agrotechnical requirements and ignore preventive measures, then the plant's immunity will be sharply reduced, and this will lead to the plant's defenselessness against attacks by aggressive microorganisms. So that celery does not get sick and is resistant to pathogens, it is necessary to pay due attention to elementary preventive measures, which include the following measures:
- proper preparation and mandatory disinfection of seeds, since many pathogens are transmitted through planting material;
- strict adherence to crop rotation. Celery can be returned to its old place no earlier than three years later;
- timely removal and destruction of plant residues;
- regular removal of weeds not only in the garden with celery, but also in the surrounding area, since the causative agents of a number of diseases feel great on weed grass and easily migrate to cultivated plants;
- timely liming of acidic soil;
- mandatory application of phosphorus and potash fertilizers to the site;
- avoidance of thickening of plantings;
- destruction of diseased plants.
Compliance with these measures is especially important when growing celery greens, since the use of chemicals is undesirable, they are resorted to only in cases of massive infection and strong development of the disease.
Table: diseases of stalked celery
Photo gallery: symptoms of celery diseases
Celery pests
Petiole celery can be attacked by harmful insects. To ensure a good quality harvest, it is important to identify the problem in a timely manner and develop a plan to deal with uninvited guests.
Table: celery pests
Photo gallery: the main pests of stalked celery
Celery pests are often the main vectors of pathogens. In order to prevent insects from planting celery in the garden or next to it, you can plant nasturtium, marigold or thyme. The smell of these plants repels many pests.
Correct harvest is a guarantee of long-term storage
Petiole celery can be stored for a long time, provided that the conditions are right and that the petioles are picked correctly. When harvesting, you need to pay attention to the following nuances:
- the stalked variety of celery is more sensitive to temperature drops, so it is better to harvest in September-October, before the onset of frost;
- it is not recommended to overexpose the plant in the garden for longer than specified in the recommendations for growing this variety. Otherwise, the petioles will become coarse and become fibrous;
- cleaning is carried out carefully, avoiding mechanical damage. It is in the injured places that root crops will rot and deteriorate;
- leaves must be cut off immediately after digging up the root crop;
- for root crops intended for long-term storage, you can leave the roots, and then dig them into the wet sand in the cellar.
- the harvested crop must be thoroughly dried and only then put into storage.
 The harvested crop must be thoroughly dried and only then put into storage.
The harvested crop must be thoroughly dried and only then put into storage.
How to store celery properly
If celery stalks are planned to be eaten or processed in the near future, then they are carefully wrapped in cling film and sent to the lower shelf of the refrigerator. For longer storage, gardeners use various methods:
Video: cleaning and storing stalked celery
Celery is a very healthy vegetable crop. It doesn't matter if you grow petiole, root or leaf celery in your area. The main thing is that these plants will bring you real benefits. After all, they are grown with care and love!
My name is Ludmila. Higher education, graduated from the Minsk Institute of Culture. I live in Belarus. Rate the article:
(0 votes, average: 0 out of 5)
Growing stalked celery with excellent qualities is not a very simple matter, and caring for it has its own characteristics. Due to the fact that celery seeds germinate for a long time, and the stem slowly increases in volume, seedlings are planted in open ground. It is necessary to take care of the plant regularly, without violating the technology - only then the stem will turn out to be juicy, crunchy and without a bitter aftertaste.

Growing celery seedlings
It is impossible to be late with the term for growing celery seedlings. The later the seeds sprout, the later the seedlings are planted in open ground, the thinner the cuttings will be for celery. They will not have time to increase the volume until the autumn frosts, because the ripening period for celery is long - from 90 to 150 days, depending on the variety. Sowing seeds for seedlings is carried out from late February to mid-March. In warmer regions, the best sowing time is February, in colder regions, March.
Due to the high content of essential oils, the seeds sprout slowly and not amicably. Germination can be accelerated if, before sowing, they are soaked in very warm water, the temperature of which is + 55-60 ° С. The water is changed several times - after it has cooled to room temperature. After the last soak, the seeds are washed in cool water.
Germination can be increased if the seeds are germinated. There are two ways to do this.
- Place a damp cloth on the bottom of the container. Seeds are laid out in a thin layer. To create the desired microclimate, the container is covered with glass or cling film. The place for germination should be warm, + 25 ° С. Airing is carried out regularly. The fabric is often moistened and should not be allowed to dry out.
- Well-moistened sawdust mixed with clean sand is poured into a shallow container. Seeds are scattered over the surface of the sawdust. Then, just as in the first method, cover with glass, put in a warm place, periodically ventilate and moisten.
The soil for seedlings is chosen nutritious and loose. It is poured into boxes and grooves are made 0.5 cm deep at a distance of 3 cm from each other. The seeds are laid out on the bottom of the grooves, lightly pressing them against the soil. You can not sprinkle the earth on top. Sprouted seeds must be sown carefully, taking care not to damage the sprout.
Advice
It is convenient to use a match to lay out the germinated seeds in the seed boxes. Its end is moistened, and the seeds easily adhere to the wet part. This makes sowing easier and prevents the sprouts from breaking off.
The soil must be constantly moistened, this must be monitored. Until the first leaves appear, the seedlings must be covered with cling film. After their appearance, the film is removed, and after a week the box is transferred to a cool, bright place. The optimum air temperature is + 15 ° С. Under such conditions, celery seedlings will grow strong and will not stretch out.
When 3-4 true leaves appear, the seedlings dive. It is best to place them in separate containers, and if this is not possible, then in a larger box at a distance of 4x4 cm from each other. Watering the seedlings is abundant, regular, but excess water should be drained through the drainage holes.
A week before planting in open ground, the seedlings begin to harden, taking them out into the sun.

Planting celery in the garden
You can plant stalked celery in an open field in mid-May. The garden bed is prepared in 10 days: all weeds with roots are removed, well-rotted manure is introduced, dug up and leveled.
On the day of planting, grooves are prepared with a depth of 10 cm at a distance of 30-40 cm from one another. The soil in containers with celery should be moist, this will prevent it from crumbling during transplantation. If the soil does not lag behind the walls of the cups, you can draw a thin knife between the walls and a lump of earth. Planting should be carried out a little deeper than the seedlings were in the container, but the point of growth of the leaves should not be deepened.In one row, there should be a distance of 15 cm between plants.
Celery is planted densely so that as little light as possible falls on the base of the stem - this increases its nutritional value and improves its taste. Leaves, on the contrary, should be in bright light, through them the process of photosynthesis will take place.
It is good to plant stalk celery next to cabbage, it prevents the appearance of such pests as cabbage white on it. Celery is also a desirable neighbor for tomatoes.

Care
Until the celery has grown, it is necessary to prevent the growth of weeds. For the first month, celery grows slowly and the weeds can drown it out. After the stems began to thicken, hilling must be carried out. If the plantings are thickened, then the soil for hilling should not be taken from the same beds, so as not to damage the plants growing nearby. It is better to cover the base of the stem with turf or compost. When hilling, the white color of the stem is preserved.
Before hilling, small petioles that will no longer have time to gain weight are removed. The rest are tied at the level of the leaves so that they do not break when covered with earth.
Watering should be constantly monitored. The soil should not dry out, but it should not block the base of the celery either.
Excessive dryness of the soil will cause the stem to change its characteristics:
- will cease to be juicy and elastic,
- will crack
- will acquire bitterness;
- the structure of the stem will be fibrous;
- the plant will release a peduncle arrow and begin to set seeds.
With excessive moisture, the stems can begin to rot, and this also increases the likelihood of fungal diseases.
Top dressing is important for celery. The first time is fed two to three weeks after planting. Prepare a solution of mullein (1 part of fertilizer to 10 parts of water) or bird droppings (1 part of fertilizer to 20 parts of water). The second time they are fed three weeks later with a complex mineral fertilizer, but the percentage of nitrogen in it should be minimal. With an excess of nitrogen in the soil, the petioles can crack in the same way as with a lack of watering.
At the end of July, in order to protect celery from greening, the stems must be wrapped in thick paper. You can use corrugated cardboard, paper wallpaper, craft paper. It is undesirable for the paper to contain inscriptions made with typographic ink. For wrapping, you can use agrofibre of both white and black colors of maximum density. The main thing is that air passes through the material used for wrapping.
It is necessary to protect the entire stem from the sun's rays to the point where foliage begins to grow. The paper is wrapped so that there is a small gap, but at the same time it does not dangle from the wind. The protection is not removed until the harvest itself.
Leaves can be selectively harvested from each plant during the season for use as food. They can be eaten fresh or dried for the winter.
If necessary, the petioles can be harvested at the end of summer. At the same time, the largest ones are broken off, but no more than 5 pieces from one plant. The main harvest begins in September. First, the largest plants are dug up, the rest can ripen until October.
If the dug out celery is placed in the basement, having dug the roots into wet sand, then it can be stored for up to two months. Excess stalk celery can be frozen. After defrosting, they are stewed, baked and used for the first courses.
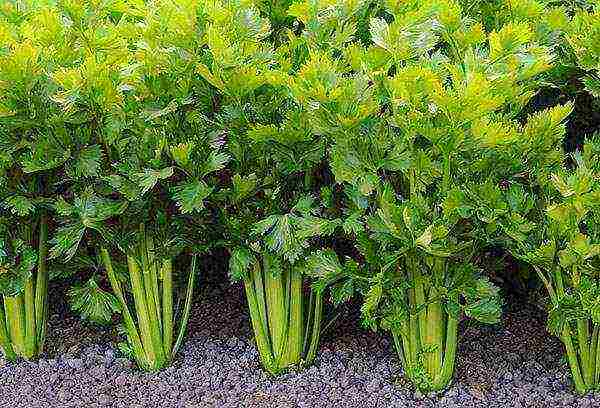

Trench method of growing celery
If there is enough space on the site, then celery can be grown by the trench method. The cultivation is carried out in stages.
- Trenches are being prepared with a depth of 30 cm, a width of 20 cm. There should be a distance of at least 70 cm between the trenches for convenience.
- When digging, all the soil is folded into a mound along the trench, on the north side. It will serve as protection from cold weather in spring and early summer.
- A mixture of earth with humus is poured at the bottom.
- Planting seedlings is carried out in the center of the trench, at a distance of 15-20 cm between the plants.
- At first, care is carried out in the same way as with a normal planting.
- After the stem begins to thicken, the first filling of the trench is carried out. The soil is taken from the mound and covered with celery to the foliage.
- Hilling is carried out several times, until all the soil dug out of the trench is used up.
- In autumn, harvesting is carried out carefully so as not to damage the stems.
When grown in this way, the stem is white, juicy, and there is no bitterness. In addition, it is not necessary to wrap the stems with this method.

Self-bleaching varieties
The stems of common varieties require bleaching, otherwise they become unusable. Currently, varieties have been bred that do not require such care - they are juicy, crunchy without much effort.
Despite this advantage, these varieties have a significant disadvantage:
- they are afraid of even light frost;
- have a short shelf life.
It is necessary to harvest immediately, without waiting for the onset of cold weather. If the weather forecast promises a drop in temperature already at the beginning of September, then all the celery should be harvested, even if the stems have not yet increased the required volume of all the plants. The collected petioles of self-bleaching celery are not stored for a long time. If they are wrapped in plastic wrap and put in the refrigerator, then the maximum shelf life is two weeks.
Conclusion
Growing quality stalked celery requires constant care. Top dressing and watering should be carried out regularly, and without bleaching, the petioles lose quality and taste. If it is impossible to spend a lot of time caring for celery, self-bleaching varieties can be grown. Due to the short shelf life, it is not necessary to plant a lot of it. It is enough to plant a few bushes so that you can use them within two to three weeks.
Celery (Apium) is a herbaceous rhizome plant of the Umbrella or Celery family. Taproot, leaf plates pinnately dissected. The flowers are small, gather in simple or complex umbellate inflorescences. The plant is biennial: in the first year it is grown for greenery and root crops, in the second year it gives seeds.
The culture is propagated by seeds. They germinate and develop for a long time, therefore, to get a good harvest, it is advisable to grow seedlings. A feature is that seeds that have lain for 3-4 years have better germination.
Celery was cultivated in ancient Greece, but it has spread widely relatively recently.
Celery growing conditions
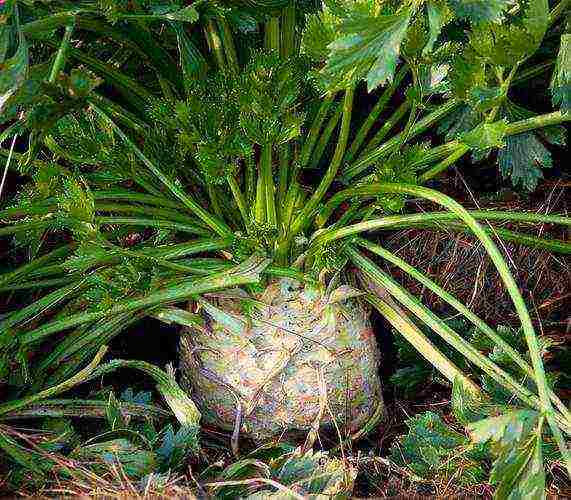

How to grow celery outdoors
Growing any kind or variety of celery is about the same, but there are some nuances.
Ground and lighting
Common to all types of celery are soil and lighting requirements:
- Celery grows well on fertile, loose soils of a neutral or slightly acidic reaction.
- The lighting is preferably bright. Slight shading is possible: the leaves will be more fragrant.
Neighbors
Tomatoes, bush beans, leeks will be good neighbors on the site. By planting next to the cabbage, you will save it from the attack of an earthen flea and cabbage whites.
Consider the features of growing for each type of celery.
Growing petiole and leaf celery from seeds

How to sow celery
The plant is cold-resistant. Seedlings will not suffer from light frosts, adult plants winter successfully.
Sowing petiole and leaf celery in the ground
Seeds of leaf celery can be sown in open ground in early spring with the appearance of the possibility of entering the site (March-April) or before winter in late autumn, at the end of October.
- The furrows are filled every 20-25 cm, very shallow, so that the sowing depth is 1-2 cm.
- You need to sow as little as possible, because densely seeded celery will be very difficult to break through.
- Break through the seedlings in three stages: first, leaving 5-7 cm, then - 10-15, in the end - 20-25 cm.
The culture is very fond of water, it should be watered abundantly at least once a week.
Growing petiole and leaf celery through seedlings

Celery petiole cultivation from seeds photo shoots
Start sowing petiole and leaf celery seeds for seedlings at home in early March. The seed should be pretreated: hold it in a weak solution of potassium permanganate for a few minutes, rinse well, then place it in a damp cloth in a solution of a growth stimulant for a day. When the seeds have swollen well, they can be sown.
- Fill crates with a mixture of peat, sand, leafy earth, and humus in equal proportions.
- Spread the seeds over the surface at a distance of 1-2 cm, helping yourself with a toothpick, sprinkle a little earth (layer about 0.5 cm).
- Spray from a spray bottle, cover the crops with foil, maintain the air temperature within 18-20 ° C.
- When using quality seeds with pre-treatment, seedlings will appear 5-6 days after sowing.
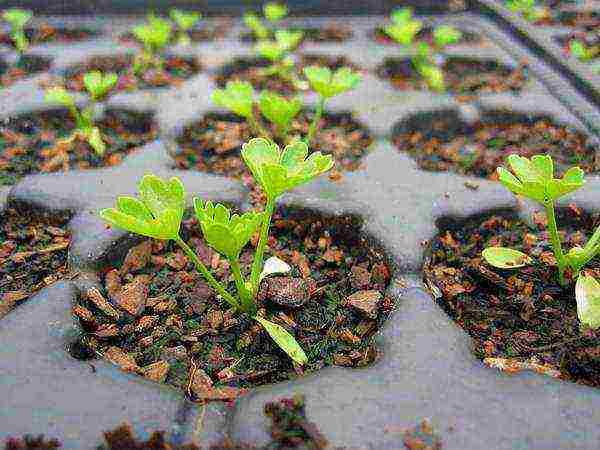

Celery seedlings need to dive photo
- When the first shoots appear, remove the shelter, lower the air temperature to 14-15 ° C.
- To prevent the seedlings from stretching, not only coolness is required, but also bright diffused lighting (arrange additional lighting if there are no southern windows in the apartment).
- Maintain moderate soil moisture.
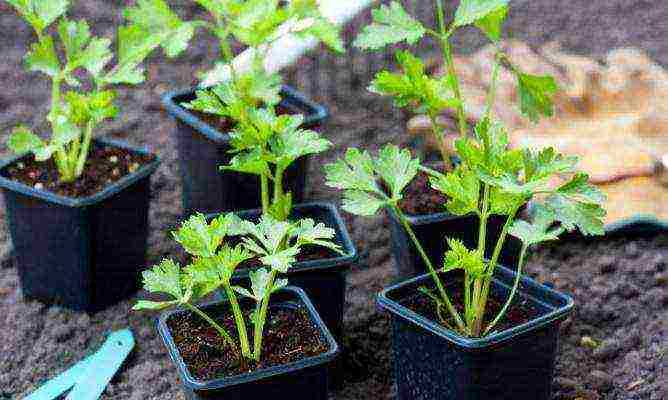

Leafy celery seedlings are ready for planting
- With the appearance of 2 true leaves, dive the seedlings - pinching the main root contributes to the further successful development of the root system.
- A week before planting, harden the seedlings: take them out into the open air for the daytime.
When and how to plant petiole and leaf celery seedlings in the ground
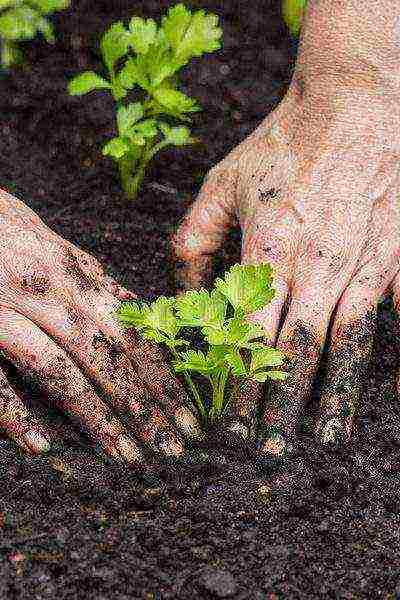

How to plant petiole and leaf celery seedlings in the ground photo
- Transplant petiole and leaf celery seedlings into open ground in late April-early May.
- When landing, use the 25x25 scheme.
- The root collar is not deepened.
How to care for leaf celery
The plant is unpretentious in care. Standard procedures should be followed: water regularly, loosen between rows, remove weeds. Mulching the soil will cut the work in half. The moisture level will last longer, it will prevent the appearance of an earthen crust, and weeds are less disturbing. Spud the bushes.
Harvest leaf celery regularly. After each cut of leaf celery, it must be watered abundantly, combining watering with top dressing. Mostly organic fertilizers are used: fermented grass, fermented manure or chicken droppings.
Features of caring for stalked celery in the open field
Cultivation of stalked celery is carried out by analogy with leaf celery. Nuances: plant seedlings in grooves 10 cm deep, the apical part cannot be sprinkled with earth.
The plant needs intensive hilling. This measure is necessary to whiten the petioles, which have a more delicate taste without bitterness. Also, a couple of weeks before harvesting, tie the leaves at the top, wrap the petioles with paper to bleach them. Harvest before frost.
How to grow stalked celery correctly, we look at the video:
Growing root celery through seedlings
Root celery has the longest growing season of 150-190 days. Growing seedlings is a must.
When to sow root celery seedlings?
Sowing should be started in 1-2 ten days of February.... The principles of planting and caring for seedlings are the same as for leaf celery. The difference is that not only picking is carried out, but also the transshipment of grown seedlings into more spacious peat cups or pots.
How to sow root celery, look at the video:
When the plants grow a little, it is imperative to make a pick.
How to dive root celery, look at the video:
The grown seedlings of root celery are transferred again into larger pots, when the plants become cramped, and are grown to planting in the ground in May, when the threat of frost has passed.

Celery root seedlings ready for planting photo
Landing in the ground
Root celery is planted in the ground at a distance of 35-40 cm, without deepening the root collar. It is useful to immediately mulch the planting with mowed grass.
How to care for root celery outdoors
- When growing root celery during the summer, you should not cut off the leaves: by mid-August, organic matter accumulated in the leaf plates passes into root crops.
- The top of the root celery sticks out of the soil - this is normal, so avoid the temptation to huddle the plant. This is contraindicated, since the active formation of lateral shoots will begin, and the main root will turn out to be flawed.
- Keep the soil slightly moist at all times between June and October.
- A couple of weeks before digging up the roots, remove the lower leaves and side shoots, partially rake off the ground.
- Root crops are harvested around the end of October.
Celery diseases and pests
Possible diseases of celery: leaf spot, mosaic virus, blackleg, white stem rot, heart rot, stem root rot.
To avoid such problems, agrotechnics should be observed (crop rotation, weeding, thinning, do not allow the soil to become waterlogged).
In case of disease, treatment with a fungicide should be carried out.
Conduct pest control. They not only damage the plant, but also carry disease. Celery can be harmed by snails, slugs, scoop larvae, carrot flies. Collect gastropods by hand, use traps, insecticide treatment will save the rest.
Types and varieties of celery
There are about 20 types of celery in the natural environment. Celery is cultivated.
There are three types of celery:
- Leafy - cultivated to produce leaves that can be cut all season (from spring to late autumn).
Popular varieties of leaf celery: Zakhar, Vodrost, Tender, Kartuli.
- Petiolate - the purpose of cultivation is juicy petioles. Harvesting takes place at the end of summer.
Sorts: Malachite, Gold, Jung, White feather.
- Root - grown to produce large root crops weighing 400-800 g. They are harvested in autumn.
Root celery varieties: Diamant, Maxim, Esaul, Gribovsky.
When choosing a variety, pay attention to the ripening period: early, medium, late. They also differ in taste. The information is indicated on the seed package.
Useful properties of celery
The plant is rich in a set of substances useful for the human body. These are vitamins (A, E, C, K, B and PP vitamins), macro- and microelements (calcium, potassium, iron, phosphorus, zinc, sodium, manganese, magnesium), amino acids (arginine, lysine, histidine), fiber , essential oils.
Also, the plant is an aphrodisiac.
Contraindications to eating are pregnancy and breastfeeding (it lowers milk levels, bloating may appear). If you have a stomach ulcer, urolithiasis, or varicose veins, you should treat celery with caution.
Depending on the type of plant, a certain part is used for food: leaves, petioles, root crops. They have a bittersweet taste and pleasant aroma. They are added to various dishes fresh, prepared side dishes, pates, and used in home canning. Leaves can be frozen. The dried and milled parts of the plant are a spice. Celery seeds are used to flavor table salt.
Celery will benefit your site too. Earthworms like to be in the roots of the plant - they contribute to the formation of humus (fertile layer of the earth).To attract them to the site in large numbers, sow or plant celery in a circle to create a "cozy house".
Caucasian cuisine cannot be imagined without celery leaves, in Russia they prefer a white root, the cultivation of stalked celery and caring for it is typical for residents of North America, Great Britain, Mediterranean countries, and it is also appreciated in Japan. In comparison with the root and leaf variety, petiole (salad) varieties are more tender, juicy, healthy. Only from them can you make juice - a drink for health and maintaining an ideal shape.

The petiolate variety of celery wins the hearts of Russian gardeners
Biological features of culture
Petiole celery is cold-resistant, so many gardeners have a question whether it can be grown as a perennial plant or not. Immediately, we note that this is a two-year culture of the Umbrella family, which in the first year gives a rosette of succulent roots and leaves, in the second - seeds. In the south, provided that the soil freezes slightly, celery is cultivated as a perennial, but only to obtain greenery. High-quality petioles, like the root, can be obtained only in the first year of the plant's growing season.
The vegetable belongs to long-growing crops - from full-fledged shoots to ripening, it takes 140-180 days, depending on the variety of stalked celery. During this period, a powerful bush will grow up to 65 cm high with a rosette of thick stems and large pinnately dissected leaves, often dark green, glossy. The petioles have a curved shape, slightly ribbed on the outside, the flesh is juicy, crispy, with a piquant aroma and light bitterness. The old varieties are more fibrous, the new ones are delicate, practically have no hard fibers. Light green, bleached or yellow-fleshy petioles are sweeter, more bitter - green or reddish.
One plant of stalked celery, with proper cultivation techniques, gives from 300 g to 1.2 kg of marketable products.
Note! Root celery also has large, thick stems, but unlike the petiolate variety, they are not fleshy, but sinewy, moreover, they are hollow inside.
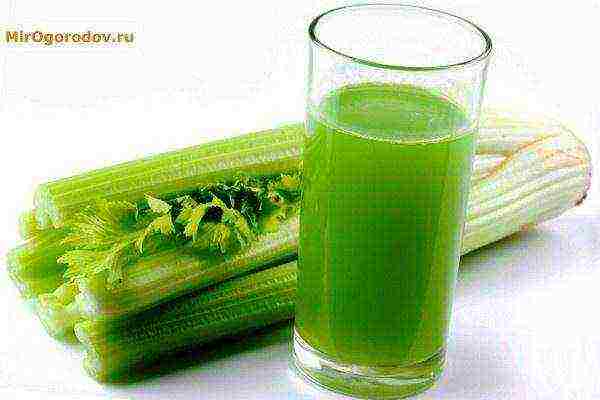

Crispy petioles are a unique product with a “negative” calorie content that burns excess fat
Successful varieties
In the garden centers there are seeds of domestic and foreign varieties of stalked celery. When choosing, pay attention to the ripening time - for regions with a cold climate, early and mid-early varieties are preferable, for greenhouses, medium-late varieties are also suitable.
Gustatory characteristics play a role. If you like a savory bitterness, plant celery with green stalks, adherents of traditional neutral flavors will love self-bleaching or yellow-fleshed plants. Here is a brief description of several of the most successful varieties.
-
Celery Utah is bred by Italian breeders. The petioles are long, light green, very tasty, practically without fibers. In terms of ripening - the variety is average, the yield of stems with leaves - up to 3.5 kg / m².
-
Malachite is one of the earliest varieties (85 days), allowing you to feast on healthy products already in the middle of summer. Productivity - 1.2 kg of petioles per plant.
-
Nughet is a variety of stalked celery of Czech selection. Among the pluses is an early ripening period, a neat, tightly closed rosette of stems, a pleasant taste and aroma.
-
Tango is a common cultivar with bluish green petioles. It ripens for a long time - the growing season is 180 days. Attracts with delicate pulp without fibers, high yield (1.0 kg per plant), excellent keeping quality.
-
Gold will appeal to lovers of self-bleaching varieties. Up to 800 g of elastic petioles with light pulp, pleasant taste and aroma are collected from one plant.

Selection of seeds and producers
How to avoid mistakes when growing?
To avoid disappointment, you need to know and follow the cultivation technique of stalked celery.It is in many ways similar to the other two varieties, but has a number of nuances. What mistakes do novice gardeners make most often?
-
The seeds are sown too late. Since the culture has a long growing season, it is recommended to plant seedlings at the age of 70–80 days. And given the fact that the seeds of celery are tough-growing, you need to sow it already in February, in extreme cases - at the beginning of March.
-
Seedlings are planted early, in cold soil and the plant goes to the arrow. The paradox of this culture is that despite its cold hardiness, it is thermophilic. Seedlings of petiolate celery will not die with early planting, but the cold oppresses it, it stops growing. In addition, the plant perceives this as a forced dormant period and moves on to the "second series" - expels the flower arrow.
-
The petioles are sinewy, with a bitter taste. This happens if the vegetable is planted in poor soil. The plant itself is large, in order to grow actively, it requires a lot of nutrition. If it is not there, it sits in place, the stems coarse. The petioles will be fibrous without watering. An important agricultural technique that allows you to remove bitterness is bleaching the stems. Many do not know about him.
Consider how to properly grow stalked celery from seeds.
Terms and technology of growing seedlings
Vegetable seeds are saturated with essential oils, so they do not germinate for a long time. To speed up this process, it is necessary to destroy the inhibitors that inhibit germination. There are several ways.
-
Soak alternately in hot (up to 50⁰C) and cool (18⁰C) water. This is done in three steps, holding the seeds in hot water for 5 minutes, 10 minutes, respectively, and the third time until the water cools down.
-
Germination for 7-10 days. To do this, they are soaked, and after swelling, they are placed on a damp cloth and placed in the refrigerator.
Prepared petiolate celery seeds are sown in shallow boxes; loose soil based on peat and humus is taken for planting. After sowing, they are not closed up, since light is needed for germination. From above, the seeds are sprayed with water from a spray bottle so that they adhere well to the substrate. You can cover them with a layer of snow, which, melting, will slightly pull them into the soil. Next, the box is covered with foam (glass) and placed in a warm, bright place, for example, on a windowsill. When thin seedlings appear, they are sprinkled with earth for half a centimeter, the film is removed.
Crops are watered carefully - from a spray bottle or through a strainer, so as not to damage fragile seedlings.
Plants dive at the stage of 2-3 true leaves, pinching off the 4th part of the central root. Plastic cups are suitable as containers. Seedlings deepen to cotyledon leaves. The cut seedlings are sheltered from direct rays of the sun for several days, after engraftment, they are returned to the windowsill.
Advice! It is recommended to start hardening the seedlings at an air temperature of at least 10⁰ C. First, they are taken out at noon, then in the morning and until 4–5 o'clock in the afternoon. A week before planting, the plants, if the weather permits, are left outside overnight.

The hardened and hardened seedlings will quickly take root after planting in the garden, begin to build up the green mass
Landing in open ground
The next stage of growing stalked celery is planting in open ground. Pay attention to the following nuances.
-
The indicator for planting seedlings is the onset of stable heat (16-18⁰C during the day).
-
The culture loves fertile, loose, slightly acidic soils (pH 5.5–6.5) with good aeration.
-
Prefers sunny places, in partial shade it turns out a vegetable with a sharper smell.
-
For stalked celery, the following planting scheme is recommended - 40 cm between rows, 20 cm in a row.
-
When planting, it is impossible to cover the heart of the seedling with earth.
Advice! The crop is suitable for compacted crops. The vegetable is planted together with cucumbers, along the borders of the beds, along the paths.
Subtleties of care
Caring for a vegetable plant consists in regular watering, top dressing, and frequent loosening.
The first feeding is recommended to be done 2 weeks after planting - 20 g of ammonium nitrate, 10–15 g of potassium salt and superphosphate are added per 1 m². This mixture can be replaced with nitroammophos or other complete fertilizer. Application form - aqueous solution. From organic matter, a solution of poultry droppings at a concentration of 1:10 is suitable, mullein - 1: 5.
They are re-fed in the middle of summer - the emphasis is on potash fertilizers, microelements are also needed, namely boron and magnesium.
The plant loves deep, abundant watering, but this must be done at the root, avoiding water getting on the stems and leaves. Waterlogging is one of the reasons for the appearance of stem rot.
An obligatory element of caring for petioled celery is frequent loosening (5–6 times per season). In addition, it needs hilling, in contrast to root celery, the fruit of which is exposed.
Petiole whitening
When the petioles become plump, a care technique such as whitening is used. The stems are collected in a bunch, the lower part is wrapped in an opaque material - paper, burlap, lutrasil, but not with a film - the plant must breathe. Some people simply spud the socket with earth - but the quality will be worse, and it is also difficult not to fill up the heart.
Reception leads to a decrease in the level of essential oils, bitterness disappears, the aroma becomes more delicate.
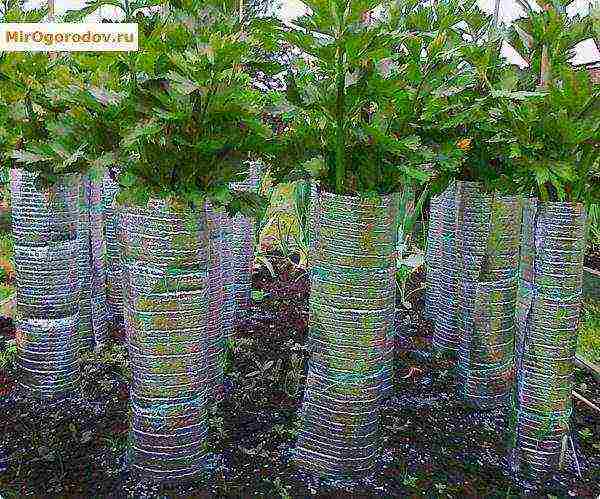

Petioles are wrapped for bleaching a few weeks before harvest
What is celery sick with?
The main causes of diseases of stalked celery are associated with improper care, waterlogged soil, poor aeration, and lack of nutrients. In a rainy summer, the aerial part of the plant can be affected by fungal infections.
-
Cercosporosis appears as spots with a light center and a reddish-brown edging on the leaves and petioles. The diseased parts of the plant dry out. For prevention, it is recommended to disinfect seeds. The affected crops should be sprayed with a fungicide solution.
-
Septoria, in contrast to cercospora, affects celery by the end of summer. This is also a spotting, but different - the spots are oblong, yellow and, as it were, depressed. Control measures are the same as with the previous disease.
-
Rust is a cold summer disease. Red-brown outgrowths begin to crumble as the spores mature. Spraying with phytosporin helps.
In addition to diseases, petiole celery also has pests, although not as many as in other crops - it scares them off with a pungent odor.
The plant can be attacked by celery and carrot flies. The pest lays eggs in the petioles and under the skin of the leaves. The larvae eat the passages in them, after which they become rough and bitter. An effective way of control is pollination of plantings with tobacco dust, wood ash, dry mustard during the summer of the fly (June, August).
Planting and caring for celery:
Moscow, Russia, on the site since 11.01.2017