Content
- 1 Description of an ornamental shrub, use in landscape design
- 2 Outdoor planting and care
- 3 Breeding methods for Japanese quince for transplant
- 4 Chaenomeles pruning rules
- 5 Pests and diseases
- 6 Varieties for growing in the Moscow region
- 7 Harvesting in autumn, storing fruits
- 8 Jam making
- 9 Description of an ornamental shrub, use in landscape design
- 10 Is it possible to plant Japanese quince in the suburbs?
- 11 Shrub description
- 12 Landing
- 13 Spring care
- 14 Autumn care
- 15 Correct pruning
- 16 Growing methods in the Moscow region
- 17 The best varieties for the Moscow region
- 18 The choice of planting material
- 19 Preparation for planting in the ground
- 20 Landing in the ground
- 21 Watering while growing
- 22 Fertilizer
- 23 Care during growth
- 24 Pests and diseases
- 25 Harvesting and storage
If you want to decorate your site, create an original hedge and at the same time harvest healthy fruits, pay attention to the Japanese quince.
Description of an ornamental shrub, use in landscape design
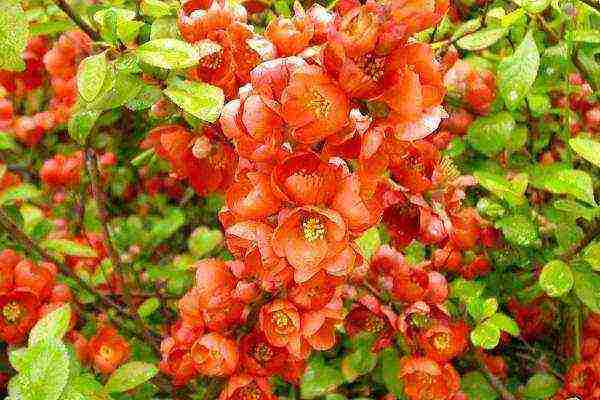
Japanese quince is a low-growing ornamental shrub. She will decorate any garden in spring, when many huge (for its small stature) orange-red flowers with a diameter of up to 4 cm, which are strewn with all the branches, are blooming on it.
In summer, the plant attracts the eye with its glossy foliage with pouring fruits. In autumn, it is strewn with medium-sized yellow fruitsresembling small apples.
Gardeners mainly plant low shrubs for decorative purposes. A group of 3-5 plants looks very good on lawns. A small bush of quince will decorate a flower bed or an alpine slide, often used in landscape design.
Shrub blooms in May and, due to the uneven opening of the buds, the bright bloom stretches for 2-3 weeks.
Spireas, forsythia and magonia will become worthy partners in garden compositions for her.
Quince has the ability to grow in breadth due to abundant root growth, and this is its quality very often used to strengthen slopes (it holds the soil).
You need to be careful with shrubs, as there are sharp thorns on some varieties.
Henomeles (Japanese quince) due to its frost resistance (withstands frosts down to -25 ° well) suitable for growing in the Moscow region... With frosts below -30 ° C, the buds may freeze, but the bush will not die.
When properly grown, the shrub grows up to 40 years old.
Japanese quince, or chaenomeles:
Outdoor planting and care
Quince is not demanding on growing conditions, but there are several conditions that must be taken into account when planting a seedling:
- the planting site should be sunny, since the shrub grows and blooms poorly in shade;
- in order to avoid freezing of bushes in severe winters, plant them in places protected from northern winds;
- the acidity of the soil should not exceed 6.5pH (slightly acidic);
- having a taproot that goes deep into the soil, the plant does not tolerate transplanting from place to place, we plant it immediately and forever;
- the distance between the bushes is 1-1.5 m, when forming a hedge 0.8-1 m.
It is preferable to plant quince in the spring; during autumn planting, the plant may not have time to take root and freeze out.
Landing rules:
- pour about a bucket of humus with wood ash (0.5 kg) and superphosphate (0.3 kg) added into the dug planting hole (60 * 60 * 50cm), mix with a shovel with a small amount of earth;
- we place the seedling in the hole in such a way that the root collar was at the level of the soil;
- we cover the roots of the plant with earth and water it well;
- it is advisable to mulch the soil around the bushes (sawdust, crushed tree bark, peat).
 It is preferable to plant quince in spring; during autumn planting, the plant may not have time to take root and freeze
It is preferable to plant quince in spring; during autumn planting, the plant may not have time to take root and freeze
Further care for a young seedling consists of watering, but waterlogging of the soil should not be allowed in order to avoid rotting of the roots, regular loosening of the soil around the bushes.
Since during landing all the necessary batteries were introduced, then no need to feed the plant for two years after planting.
Adult plants in the spring, after the snow melts, are fed with ammonium nitrate about 20 g per bush. In the summer, they give liquid fertilizing with organic matter (diluted mullein or bird droppings). Superphosphate is introduced in the fall.
The plant is winter-hardy, but young seedlings in the conditions of the Moscow region for the winter in the first years after planting are better to insulate.
To do this, you can use spruce branches or cover small plants with covering material (spandbond or lutrasil), put wooden or plastic boxes on top and sprinkle with fallen leaves.
Quince fruiting annually, starting from the third year after planting.
Chaenomeles cross-pollinated plant, therefore, for better pollination and increase yields, 2-3 bushes need to be planted nearby.
Features of planting chaenomeles:
Breeding methods for Japanese quince for transplant
There are several ways to breed Japanese quince.
Seeds
Due to the fact that varietal qualities are not preserved during seed reproduction, it is used when growing rootstocks with further grafting.
Seeds collected from fruits in autumn are stored in moist sand at a temperature of about 0 ° C throughout the winter. (thus they are stratified).
Seeds are sown in planting containers in February - March, after 1.5 months they dive into separate containers and at the end of May and beginning of June the seedlings are ready for planting in open ground.
Regular watering and feeding is carried out until autumn., for the winter, seedlings that are not yet fully strengthened are insulated with fallen leaves.
The easiest way is to plant the seeds collected in autumn immediately in prepared rows, sprinkle with earth, cover with polyethylene and cover with foliage.
The germination of such seeds is excellent., since they have undergone natural stratification, in the spring dense seedlings must be thinned out, leaving the strongest ones. By the fall, the seedlings are ready to be transplanted to a permanent place of growth.
 It is best to collect the seeds in the fall and immediately plant them in the beds, covering them with polyethylene
It is best to collect the seeds in the fall and immediately plant them in the beds, covering them with polyethylene
Cuttings
In early June, green cuttings are carried out... Annual cuttings with a "heel" (a piece of last year's wood) are cut. Slices are processed by "Kornevin" for better rooting and planted in the school at an angle.
To maintain humidity, cover the plantings with plastic wrap. By the fall, the seedlings are ready for transplanting to a permanent place, but it is better to do this in the spring.
You can cut ripe cuttings in the fall, dig under a bush at a depth of 20-30 cm, be sure to outline the place.
During the winter, callus forms at the ends of the cuttings, and with the onset of spring, the cuttings are planted immediately in a permanent place.
By dividing the bush
The easiest way to reproduce... Shoots with a well-developed root system are separated from the mother bush (root shoots) and transplanted.
Horizontal layering
Quince often grows creeping shoots, having dug in which you can get seedlings for subsequent reproduction.
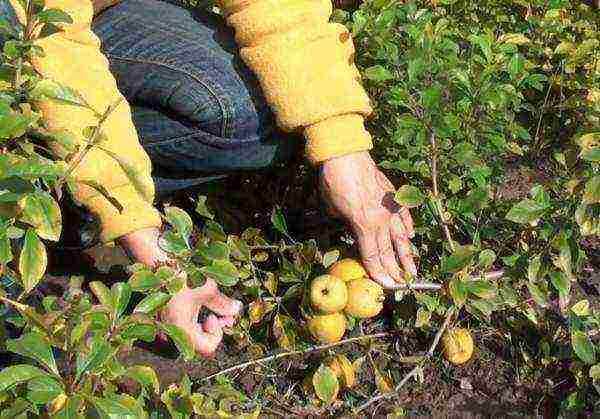 You can bend to the ground and dig in the horizontal layers of Japanese quince
You can bend to the ground and dig in the horizontal layers of Japanese quince
Chaenomeles pruning rules
The shrub tolerates pruning very well, but most gardeners, due to the thorniness of the plant, do not do it in vain. Quince pruning is necessary to improve growth and crown formation for decorative purposes.
There are three types of trimming:
- Sanitary - dry, frozen and broken branches are removed in early spring.
- Formative - they begin to do it from the age of 4, when the branches begin to branch. Shoots growing inside the bush and thickening it are cut out, excess root growth is removed, leaving no more than 2-3 young shoots annually to avoid strong expansion of the bush in breadth. Shoots creeping on the ground are also removed, they take food on themselves and thicken the bush.
- Rejuvenating - it is produced from the age of 8 in the bush, when the annual growth becomes less than 10 cm. Thin and elongated shoots are removed, leaving the strongest 10-12 in the bush. When thinning, you need to remember that the most productive are shoots at the age of 3-4 years, older branches must be removed.
In order to avoid the penetration of diseases into the plant, all sections must be treated with garden varnish.
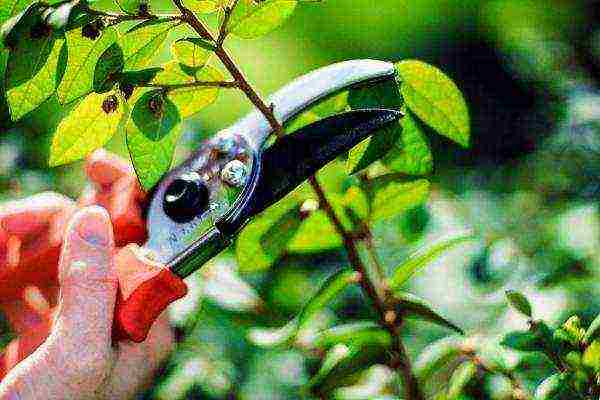 Quince pruning is necessary to improve growth and crown formation for decorative purposes.
Quince pruning is necessary to improve growth and crown formation for decorative purposes.
Pests and diseases
Chaenomeles is not damaged by pests and has great resistance to diseases, but in cool and rainy summers, diseases such as:
- leaf necrosis - the appearance of a gray bloom along the edge of the leaf with further spread over the entire surface of the leaf, the leaves dry out;
- cercosporia - manifests itself in the form of dark brown round spots that brighten over time;
- ramulariasis - the formation of brown spots on the leaves.
To combat diseases, spraying of shrubs with solutions of copper sulfate (10% concentration) or a solution of foundationol (concentration 0.2%) works effectively.
Varieties for cultivation in the Moscow region
In central Russia, low-growing varieties up to 1 m in height are grown, with arched branches and a spreading crown.
Of the domestic varieties, the most common are:
- Fragrant - bush up to 1.2 m high, winter-hardy, fruit weight 50-60 g, with a pleasant aroma;
- Nikitskaya - early ripening, medium vigor, winter hardy;
- Vitamin - winter-hardy, compact bush, with bright yellow fruits weighing up to 100 g;
- Muscat - a large-fruited variety (fruits up to 200 g), self-pollinated, winter-hardy;
- Teplovskaya - a variety of late ripening and long-term storage of fruits.
The most famous foreign varieties:
- Gaillardi - variety with large orange flowers;
- Malardi - gorgeous pink flowers with a white border;
- Papel - an interesting variety with yellow flowers and a pink border around the edge of the petal.
 In central Russia, low-growing varieties up to 1 m in height are grown, with arched branches and a spreading crown
In central Russia, low-growing varieties up to 1 m in height are grown, with arched branches and a spreading crown
Harvesting in autumn, storing fruits
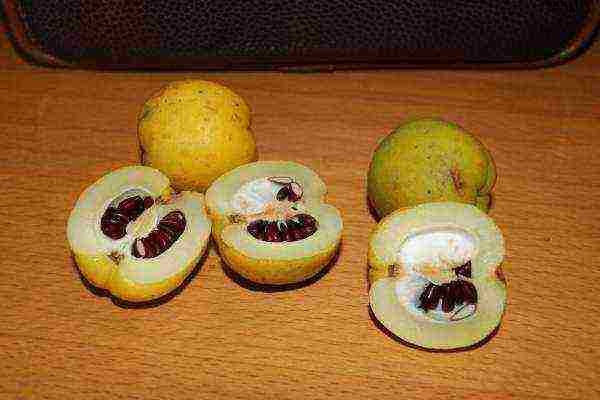
Quince fruits are small, hard and sour in taste, but very aromatic and with a high content of vitamin C. They are harvested in September - October, before the onset of frost.
They are stored at an air temperature of 1-2 ° C for 2-3 months. As a result of maturation, they become softer, the sweet aroma is enhanced.
The easiest way is to cut the quince fruits into slices or grate, sprinkle with sugar in a 1: 1 ratio and store in the refrigerator. This blank is used in the preparation of drinks and added to tea.
Jams, jams are also made from the fruits of chaenomelis, and added to compotes. Due to the high iron content, chopped fruits darken quickly.
Japanese quince. Northern lemon:
Jam making
For 1 kg of quince you need: 2 kg of sugar and 1.5 cups of water. Wash the quince, dry it, remove seeds and hard white partitions, cut into small wedges.
Put slices in boiling syrup, boil over low heat for 10 minutes, removing the foam, then remove from heat and leave for 12 hours. Boil the jam again for 10 minutes, etc. until the quince slices become transparent.
We lay out the finished jam in sterilized jars, leave it until winter. In winter, aromatic jam will remind you of the beauty of flowering shrubs and the approaching warm summer.
Japanese quince is unpretentious in cultivation, it is undemanding in attention and easy to care for, but at the same time it is beautiful in flowering and useful in application.

If you want to decorate your site, create an original hedge and at the same time harvest healthy fruits, pay attention to the Japanese quince.
Description of an ornamental shrub, use in landscape design
Japanese quince is a low-growing ornamental shrub. She will decorate any garden in spring, when many huge (for its small stature) orange-red flowers with a diameter of up to 4 cm, which are strewn with all the branches, are blooming on it.
In summer, the plant attracts the eye with its glossy foliage with pouring fruits. In autumn, it is strewn with medium-sized yellow fruitsresembling small apples.
Shrub blooms in May and, due to the uneven opening of the buds, the bright bloom stretches for 2-3 weeks.
Spiraea, forsythia and mahonia will become worthy partners in garden compositions for her.
Quince has the ability to grow in breadth due to abundant root growth, and this is its quality very often used to strengthen slopes (it holds the soil).
You need to be careful with shrubs, as there are sharp thorns on some varieties.
Henomeles (Japanese quince) due to its frost resistance (withstands frosts down to -25 ° well) suitable for growing in the Moscow region... With frosts below -30 ° C, the buds may freeze, but the bush will not die.
With proper cultivation, the shrub grows up to 40 years old.
Japanese quince, or chaenomeles:
> Quince is not demanding on growing conditions, but there are several conditions that must be taken into account when planting a seedling:
- the planting site should be sunny, since the shrub grows and blooms poorly in shade;
- in order to avoid freezing of the bushes in severe winters, plant them in places protected from northern winds;
- the acidity of the soil should not exceed 6.5pH (slightly acidic);
- having a taproot that goes deep into the soil, the plant does not tolerate transplanting from place to place, we plant it immediately and forever;
- the distance between the bushes is 1-1.5 m, when forming a hedge 0.8-1 m.
- pour about a bucket of humus with wood ash (0.5 kg) and superphosphate (0.3 kg) added into the dug planting hole (60 * 60 * 50cm), mix with a shovel with a small amount of earth;
- we place the seedling in the hole in such a way that the root collar was at the level of the soil;
- we cover the roots of the plant with earth and water it well;
- it is advisable to mulch the soil around the bushes (sawdust, crushed tree bark, peat).
 It is preferable to plant quince in spring; during autumn planting, the plant may not have time to take root and freeze
It is preferable to plant quince in spring; during autumn planting, the plant may not have time to take root and freeze
Further care for a young seedling consists of watering, but waterlogging of the soil should not be allowed in order to avoid rotting of the roots, regular loosening of the soil around the bushes.
Since during landing all the necessary batteries were introduced, then no need to feed the plant for two years after planting.
Adult plants in the spring, after the snow melts, are fed with ammonium nitrate about 20 g per bush. In the summer, they give liquid fertilizing with organic matter (diluted mullein or bird droppings). Superphosphate is introduced in the fall.
To do this, you can use spruce branches or cover small plants with covering material (spandbond or lutrasil), put wooden or plastic boxes on top and sprinkle with fallen leaves.
Quince fruiting annually, starting from the third year after planting.
Chaenomeles cross-pollinated plant, therefore, for better pollination and increase yields, 2-3 bushes need to be planted nearby.
Features of planting chaenomeles:
> There are several ways to breed Japanese quince.
Due to the fact that varietal qualities are not preserved during seed reproduction, it is used when growing rootstocks with further grafting.
Seeds collected from fruits in autumn are stored in moist sand at a temperature of about 0 ° C throughout the winter. (thus they are stratified).
Seeds are sown in planting containers in February - March, after 1.5 months they dive into separate containers and at the end of May and beginning of June the seedlings are ready for planting in open ground.
Regular watering and feeding is carried out until autumn., for the winter, seedlings that are not yet fully strengthened are insulated with fallen leaves.
The germination of such seeds is excellent., since they have undergone natural stratification, in the spring dense seedlings must be thinned out, leaving the strongest ones. By the fall, the seedlings are ready to be transplanted to a permanent place of growth.
 It is best to collect the seeds in the fall and immediately plant them in the beds, covering them with polyethylene
It is best to collect the seeds in the fall and immediately plant them in the beds, covering them with polyethylene
In early June, green cuttings are carried out... Annual cuttings with a "heel" (a piece of last year's wood) are cut. Slices are processed by "Kornevin" for better rooting and planted in the school at an angle.
To maintain humidity, cover the plantings with plastic wrap. By the fall, the seedlings are ready for transplanting to a permanent place, but it is better to do this in the spring.
You can cut ripe cuttings in the fall, dig under a bush at a depth of 20-30 cm, be sure to outline the place.
During the winter, callus forms at the ends of the cuttings, and with the onset of spring, the cuttings are planted immediately in a permanent place.
The easiest way to reproduce... Shoots with a well-developed root system are separated from the mother bush (root shoots) and transplanted.
Quince often grows creeping shoots, having dug in which you can get seedlings for subsequent reproduction.
 You can bend to the ground and dig in the horizontal layers of Japanese quince
You can bend to the ground and dig in the horizontal layers of Japanese quince
The shrub tolerates pruning very well, but most gardeners, due to the thorniness of the plant, do not do it in vain. Quince pruning is necessary to improve growth and crown formation for decorative purposes.
There are three types of trimming:
- Sanitary - dry, frozen and broken branches are removed in early spring.
- Formative - they begin to do it from the age of 4, when the branches begin to branch. Shoots growing inside the bush and thickening it are cut out, excess root growth is removed, leaving no more than 2-3 young shoots annually to avoid strong expansion of the bush in breadth. Shoots creeping on the ground are also removed, they take food on themselves and thicken the bush.
- Rejuvenating - it is produced from the age of 8 in the bush, when the annual growth becomes less than 10 cm. Thin and elongated shoots are removed, leaving the strongest 10-12 in the bush. When thinning, you need to remember that the most productive are shoots at the age of 3-4 years, older branches must be removed.
In order to avoid the penetration of diseases into the plant, all sections must be treated with garden varnish.
 Quince pruning is necessary to improve growth and crown formation for decorative purposes.
Quince pruning is necessary to improve growth and crown formation for decorative purposes.
Chaenomeles is not damaged by pests and has great resistance to diseases, but in cool and rainy summers, diseases such as:
- leaf necrosis - the appearance of a gray bloom along the edge of the leaf with further spread over the entire surface of the leaf, the leaves dry out;
- cercosporia - manifests itself in the form of dark brown round spots that brighten over time;
- ramulariasis - the formation of brown spots on the leaves.
In central Russia, low-growing varieties up to 1 m in height are grown, with arched branches and a spreading crown.
Of the domestic varieties, the most common are:
- Fragrant - bush up to 1.2 m high, winter-hardy, fruit weight 50-60 g, with a pleasant aroma;
- Nikitskaya - early ripening, medium vigor, winter hardy;
- Vitamin - winter-hardy, compact bush, with bright yellow fruits weighing up to 100 g;
- Muscat - a large-fruited variety (fruits up to 200 g), self-pollinated, winter-hardy;
- Teplovskaya - a variety of late ripening and long-term storage of fruits.
The most famous foreign varieties:
- Gaillardi - variety with large orange flowers;
- Malardi - gorgeous pink flowers with a white border;
- Papel - an interesting variety with yellow flowers and a pink border around the edge of the petal.
 In central Russia, low-growing varieties up to 1 m in height are grown, with arched branches and a spreading crown
In central Russia, low-growing varieties up to 1 m in height are grown, with arched branches and a spreading crown
Quince fruits are small, hard and sour in taste, but very aromatic and with a high content of vitamin C. They are harvested in September - October, before the onset of frost.
They are stored at an air temperature of 1-2 ° C for 2-3 months. As a result of maturation, they become softer, the sweet aroma is enhanced.
Jams, jams are also made from the fruits of chaenomelis, and added to compotes. Due to the high iron content, chopped fruits darken quickly.
Japanese quince. Northern lemon:
>For 1 kg of quince you need: 2 kg of sugar and 1.5 cups of water. Wash the quince, dry it, remove seeds and hard white partitions, cut into small wedges.
Put slices in boiling syrup, boil over low heat for 10 minutes, removing the foam, then remove from heat and leave for 12 hours. Boil the jam again for 10 minutes, etc. until the quince slices become transparent.
We lay out the finished jam in sterilized jars, leave it until winter. In winter, aromatic jam will remind you of the beauty of flowering shrubs and the approaching warm summer.
Japanese quince is unpretentious in cultivation, it is undemanding in attention and easy to care for, but at the same time it is beautiful in flowering and useful in application.
Japanese quince is a shrub from the genomelos genus of the Rosaceae family. Originally, this plant grew in countries in the east of Asia. This type of quince is very beautiful, thanks to its decorative appearance, Japanese quince has spread throughout countries around the world, including with proper care, planting is possible in the Moscow region.
Is it possible to plant Japanese quince in the suburbs?
Although this short bush came to our country from the East, but it can perfectly take root in the middle lane our country, as well as in the Moscow region and regions close to it.
Breeders have done a great job of breeding varieties of this shrub that could give good yields, would not have thorns on the shoots.
In total, there are about 480 varieties of Japanese quince in the world, but most of these varieties are not highly frost-resistant. Therefore, these varieties are not cultivated in our country.
But still there are a number of varieties that are able to withstand frost in the central regions and conditions of the Moscow region. Moreover, calling the shrub Japanese quince, in fact, buyers are faced with four completely different types of fruiting shrubs.
Shrub description
It is the Japanese quince that is Japanese Henomeles.
Bushes in height can reach 2.5 - 3 meters... The foliage changes its color with age: young trees have a bronze shade of foliage, but the older the tree, the more green the leaves become.
Quince flowers are large (about 4.5 - 5 cm), red in color, in the conditions of the Moscow region appear on the shoots before foliage. The following interesting detail should be noted: buds begin to bloom unevenly, and the bush blooms for over a month in total.
The first buds appear in Chaenomeles in the first decade of May. The fruits of the shrub are edible, their color is yellow, bright, ripe fruits reach 5.5 - 6 cm in diameter.
It is this variety that is intended for cultivation in the climatic conditions of the Moscow region, as well as in Western and Eastern Siberia, because it is distinguished by its high frost resistance.
The shoots of the bush do not cover, even if the thermometer drops to -28 -30 degrees... True, the upper buds may suffer from this cold, but the quince itself as a whole will not suffer.
Shoots of this bush grow slowly, during the season they can grow by 4 - 5 cm. The bushes are propagated by root suckers, seeds, layering or cuttings.
In landscape design, Japanese quince is used as hedges, and they are also used in single or group plantings.
The most famous varieties of this shrub are Papel, Gaillardi, Malardi, Cameo.
Landing
When to plant outdoors?
Saplings of this shrub are usually planted in spring. When the earth gets warm to a temperature of 14-16 degrees Celsius (in the conditions of the Moscow region - later than the third decade of April), it is possible to plant seedlings on the plots prepared in advance.
Landing rules
Novice gardeners often plant exotic plants and shrubs on the plot, without asking how they should be planted and how to take care of them later. Therefore, these plants do not grow well, refuse to bear fruit and bloom, and gardeners are trying to understand why the plants are withering.
The Japanese bush quince, although it is quite unpretentious, still requires a special approach for open planting and some agrotechnical measures in the years following planting.
This plant is easy to propagate, therefore, when the first planted bushes grow, further Chaenomeles will be easy to plant throughout the site, if the owners want.
 The quince root grows downward, so transplanting in the future is undesirable.
The quince root grows downward, so transplanting in the future is undesirable.
First comes choose a placewhere the quince will grow. The quince root is pivotal and gradually deepens into the soil. For this reason, replanting the shrub is undesirable.
The landing site must meet the following requirements:
- be well lit;
- protected from gusts of cold winds;
- the soil can be any, only peat and fertilizers based on it cannot stand quince;
- soil acidity - less than 6 pH.
Holes for the landing of Chaenomeles need to be dug from a distance 1.5 m apart... But you should also take into account what the volume of the crown of these bushes will be - the larger it is, the greater the distance their seedlings should be planted.
The soil
The soil for planting is usually cooked in autumn... All weeds should be removed on the site, the following components should be scattered (the norm is given per 1 m2): 1 part of sand, 10 kg of humus, 2 tbsp. tablespoons of phosphorus fertilizer. Fertilizers are scattered over the area in an even layer. Then an autumn digging of the site is carried out.
If the acidity on the site is too high, then a pound of slaked lime or the same amount of lime flour should be added to the above components that are introduced into the soil.
Selection of seedlings
 For spring planting, adult Japanese quince seedlings are used.
For spring planting, adult Japanese quince seedlings are used.
For spring planting, it is better to take mature enough seedlings (over 1.5 years old). Usually, young plants are sold with a closed root system, so when planted, their root system is practically not damaged, and the Japanese quince quickly takes root in a new place.
The dimensions of the landing hole should be as follows: in radius 25 cm, and in depth - 80 cm.
Landing in the ground
The planting process is as follows:
- Into the landing hole first fall asleep the nutrient mixtureconsisting of 10 kg of humus, 500 g of ash and 300 g of phosphate fertilizer.
- From above, the mixture is covered with a layer of earth (7 - 8 cm thick).
- The seedling is carefully placed in the hole so that the root collar is at ground level.
- Then fill the hole with soil to ground level.
- 10 liters of water should be added under each bush.
Spring care
Spring follows free the quince shoots from the shelter... For the first two seasons, the shrub does not need additional feeding, but in the third year, 1.5 tablespoons of ammonia fertilizer should be applied under each bush.
Also, until the buds begin to bloom on the shoots, the bushes are subjected to sanitary pruning - all branches that have frozen over the winter, as well as dried or broken off, are removed.
Bushes practically are not damaged by pests and do not suffer from diseases, therefore, preventive spraying of shoots is usually not carried out.
Autumn care
In the fall, after harvesting, phosphorus fertilizers should be applied under each quince. As well as prune shrubbery if necessary.
In the conditions of the Moscow region, adult quince bushes are usually not covered for the winter, but you should still take care of young seedlings - the first few years after planting at the end of autumn, the bushes are covered with spruce branches, and they are covered with wooden or plastic boxes on top. Top can be covered with foliage or sawdust.
Correct pruning
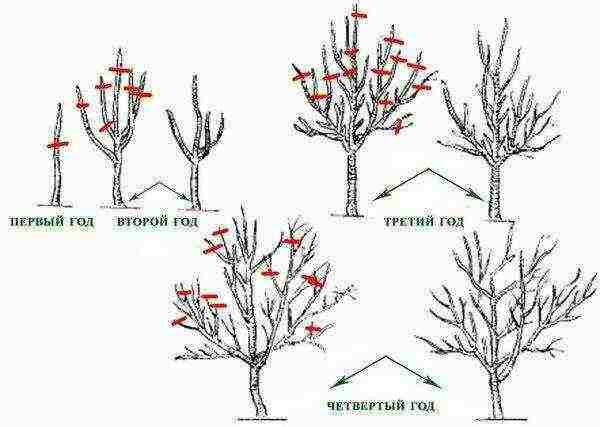 The procedure for pruning Japanese quince
The procedure for pruning Japanese quince
Formative pruning Chaenomelesa begins to be carried out from the fourth season, since only at this age the shoots of the bushes begin to branch. Shoots that grow inside the bush are cut out, excess shoots growing from the roots, leaving no more than 3 young stems annually. Stems that grow along the ground should also be pruned.
Rejuvenating pruning of quince begins to be carried out in bushes that are at least 8 - 9 years old.
Remove all weak and thin branches, leaving them in the bush no more than 10 shoots... In the process of pruning, sufficiently young branches (which are 4 years old) should be left, older shoots should be removed.
Japanese quince is a beautiful ornamental shrub that also produces tasty and healthy fruits. With proper care, it can grow in one place up to 35 - 40 years old, delighting with its flowering and good yields.
Quince is a deciduous tree or shrub with a height of 1.5 to 4 meters. Belongs to the Rosaceae family. The oldest variety, the Portuguese quince, was bred in ancient Rome.
There are three kinds of culture:
- ordinary,
- Chinese,
- Japanese.
The common quince is a large-fruited tree, while the Chinese and Japanese are shrubs with small fruits.
Ordinary, in turn, is of three varieties:
- pear-shaped,
- apple-shaped,
- portuguese.
They all differ from each other in the shape of the fruit, size, but at the same time they are very useful.
Fruits contain many minerals: potassium, calcium, iron, magnesium, phosphorus and sodium. Vitamins B3, B9, B6, B5, B2, B1, PP, K, A, E, P and C.

Ripe fruits contain sugar, fructose, tannins, organic acids, protopectins, essential oils.
Growing methods in the Moscow region
Quince reproduces:
- seeds,
- cuttings,
- root shoots,
- layering,
- vaccination.
Growing from seeds
Growing quince seeds from seeds is quite long and laborious. Because the grown tree will need to be grafted, otherwise the wild seedling will bear poor fruit, and the fruits will be small and unsuitable for food.
The largest and well-ripened seeds are selected from the ripe fruit. They are washed with water and dried. Then placed in a refrigerator for 2 months. Then they take it out and leave it for a day at room temperature in a dry place.
To increase germination, it is placed in a nutrient solution for a day, disinfected in a pink solution of potassium permanganate. Then you can plant it in the ground.
The soil is chosen moisture and air permeable. A mixture of sand and turf works well. We fill the container with soil mixture and embed the seed into it by 2.5-3 cm. We put the container on a light and warm windowsill. After about 1 month, sprouts will appear. Further care for up to a year consists in watering, loosening and fertilizing the wild sprout. After 1 year, it will be possible to plant the game with any variety of quince, pear or apple that you like best.
Propagation by cuttings
Quince can be propagated both by green cuttings and lignified. Green cuttings are harvested in June in cool or cloudy weather. The handle should have at least 2-3 whorls with dormant buds in the sinuses. At the bottom, a cut is made at a slope about 1.5 cm below the last whorl.
The cut is powdered with a growth stimulant, or put in a stimulating solution for a day. Then they are planted under a slope in a mixture of sand and peat in a ratio of 3 to 1. After 40-50 days, the cuttings will take root. Then you can transplant them into the garden. In winter, the seedlings must be insulated.
For lignified cuttings, choose the lower processes not older than two years. They are cut into lengths of 25-35 cm. At the bottom, a cut is made under the kidney and when planting, this kidney is covered with soil by 2-3 cm.They are rooted in the same way as green cuttings, but it is best to plant them in a greenhouse. After rooting, and this is about a month, level the soil, water it well and mulch with peat, sawdust or straw. Rooted seedlings are transplanted into the ground only after a year. They will begin to bear fruit only after 2-3 years.
With this type of reproduction, the seedling fully adopts the characteristics of the mother bush.
Reproduction by root shoots
Root shoots are the offspring that the tree gives. Shoots, 13-15 cm long, are separated from the mother bush, transplanted into the ground at a distance of 1.5-2 meters from each other. It is well watered and mulched around the trunk with humus or peat. Quince grown in this way may differ from the mother bush in the size of the fruit.
Reproduction by layering
This is another easy way to propagate a quince with maternal characteristics.

In the fall, the lower shoots are cut, which are no more than 2 years old. They are bent down and laid in trenches 6-9 cm deep. Attach with a clamp and buried in soil. In the spring, they already have roots, and in the fall, you can separate the seedling from the tree and transplant it at a distance of 2 meters from each other.
The best varieties for the Moscow region
Early maturing varieties (ripen in September):
- Early butter dish,
- Early ripening,
- Juicy,
- Harvest Kuban,
- Crimean Fragrant,
- Aurora,
- Scythian gold,
- Rumo,
- Anzherskaya,
- Golden,
- Nikitskaya,
- Golden ball,
- Krasnoslobodskaya,
- Gift,
- Collective.
Mid-season varieties (begin to ripen in early October):
- Kaunchi 10,
- Golotlinskaya apple-shaped,
- Kuban,
- Astrakhan,
- Trimontium,
- Beretsky,
- An excellent pupil,
- Lemon,
- Listovac,
- Persian,
- Shchuchinskaya.
Late varieties (ripen in late October - early November):
- Zubutlinskaya,
- Portuguese,
- Peace,
- Student,
- Spanish,
- Champion,
- Vraniska Denmark,
- Victoria,
- Ktyun-jum,
- Buinakskaya large-fruited.
The choice of planting material
It is best to buy ready-made seedlings from nurseries.
A one-year or two-year-old seedling must be vaccinated. This is evidenced by the ring near the root collar of the plant.
A one-year-old seedling should have at least 4-5 pairs of green leaves. The stem is light brown, straight, without damage or outgrowths. The root system is well developed, with 5-7 light roots. The container must be labeled with the name of the variety and its characteristics.
A green seedling should have 3 pairs of full-grown leaves, no more than 30 cm in height, with a green-brown trunk. The root system is well developed and has at least 3 roots. The container also contains a summary of the variety.
It is best to buy seedlings in the spring, so that before the frost comes, it has time to get stronger and take root in a new place.
Preparation for planting in the ground
If a seedling was bought in a store, it must be kept in quarantine and not planted immediately, in order to avoid contamination of other plants with diseases and pests from it. Examine well the root, trunk and foliage for the presence of parasites. If there are any, process the seedling directly in the container.
For better survival, place it in a growth regulator and leave for half an hour. After that, it can be planted in open ground.
Land preparation
The place for planting quince is chosen sunny, without drafts. In the shade, it grows poorly and bears fruit poorly. The soil for it is better to choose clay or loamy, sod or black earth. It is better not to plant on sandy soils.
Before planting, the earth is well dug on a shovel bayonet, watered and left for several days. Then they dig a hole 35-45 cm deep and 50-65 cm wide. Clay is poured at the bottom of the hole. Fertilizers mixed with soil go to the next layer. You can take humus, superphosphates, potassium salt. Then comes a layer of wood ash.
Landing in the ground
A seedling is lowered into the prepared hole, covered with soil, lightly tamped and watered to dissolve fertilizers and minerals and begin to stimulate the growth of the seedling.

It is necessary to plant trees at a distance of 1.2-1.7 m from each other, the distance between rows is 2.5-3 m.There should be a distance of 5-6 m from buildings and other trees.
Neighborhood with other cultures
Pear and apple trees are excellent neighbors for quince. They are also her additional pollinators. You cannot plant grapes and walnuts nearby.
Watering while growing
Quince is responsive to watering. In dry weather, water often. The first watering is carried out at the very beginning of flowering. This will improve the fruit set.
The second time is watered in June, this protects the fruits from shedding. Until the end of fruiting, it is watered 2-3 more times.
Watering is stopped in September so that the number of shoots does not increase and their frost resistance does not decrease.
Use water that has settled and warmed up well. Cold water can reduce the number of ovaries and cause fruit shedding.
Fertilizer
In spring, quince is fed with nitrogen and complex fertilizers. This is done by loosening the soil around the trunk. After fertilization, it must be watered well so that the feed is absorbed.
In summer, you can feed with slurry and infusion of chicken droppings. Dilute them in the ratio: on a half bucket of water 2 liters of slurry or litter infusion.
Care during growth
Quince needs to be loosened often, but not deeper than 10 cm. Otherwise, you can damage the root system. In the first year of life, it is important to remove weeds from the near-stem part of the seedling, otherwise they will suck out all trace elements from the soil.
Young and one-year-old seedlings should be covered with spruce branches for the winter, for better wintering.
It is also worth pruning the plant. Remove unnecessary and old, diseased knots. In the spring, remove all frozen and damaged branches, shorten the shoots of the last year by a third or half. The middle of the crown should not be too dense, so it is also thinned out.
Pests and diseases
Quince suffers from the same diseases as a pear with an apple tree. And they have the same pests.
Diseases:
- fruit rot,
- septoria,
- scab,
- brownish leaves,
- moliniosis,
- rust,
- powdery mildew,
- cystosporosis,
- anthracnose,
- phyllostictosis,
- tomato ring spot virus.
Pests:
- apple moth,
- leaf-dominating moth,
- round moth,
- apple blossom beetle,
- aphid,
- apple bark beetle,
- fruit mites.
Harvesting and storage
Early quince varieties are harvested in September. They are not stored for a long time, about 1.5 months. Therefore, they are most often processed into compotes, preserves, jellies and marmalade.

Medium varieties are harvested in early October. They are stored for about 3 months in a dry place at a temperature not higher than +5 degrees.
Late varieties are harvested in late October - early November. They lie up to 5 months and mature in the process. To preserve the harvest, you need to wrap each fruit in loose paper and put it in a dry place.
Quince lends itself very well to freezing, while it does not lose its useful properties. The fruits can be dried in the oven or in a special dryer. In this form, they are stored in paper or cloth bags for quite a long time.


