Content
- 1 Dig lilies of the valley in your area
- 2 Planting lilies of the valley in a pot for subsequent distillation
- 3 Forcing lilies of the valley in a warm room
- 4 How to care at home
- 5 Lilies of the valley in the open field
- 6 Growing features
- 7 Problems and diseases of the convali
- 8 Influence of lilies of the valley
- 9 Breeding technology
- 10 How to stimulate flowering
- 11 How to choose a conval
- 12 What do lilies of the valley love and dislike?
- 13 The wisdom of planting and breeding features
- 14 What kind of care will the flowers need?
- 15 Protection from pests and diseases
- 16 Collection and distillation at home
- 17 Use in medicine and landscape design
There was a time, let's say, 125 years ago, when the idea of growing a fragile lily of the valley in a pot on a window did not seem like something remarkable. But now very few people repeat this experiment. We are used to growing plants outdoors and have forgotten the flower magic of indoor plants. In this article, we'll show you how to grow your own window lilies of the valley. But you have to act quickly before the ground is frozen.
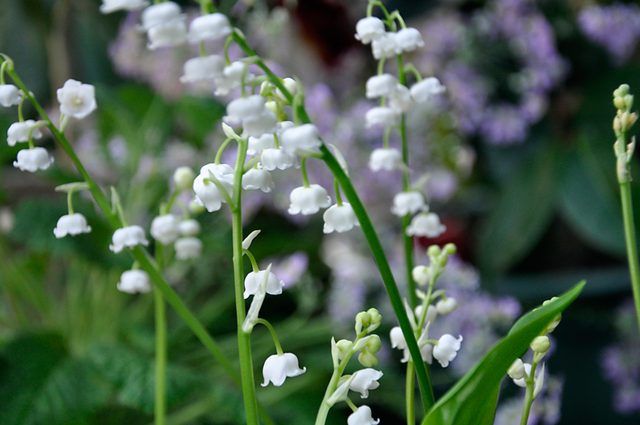

Lily of the valley sprouts used to be applied to a gardening magazine in the 1940-1970s. Now they are hard to find and expensive. The finest quality sprouts are imported from France, but until you are familiar with a French florist you have little chance. Fortunately, the lily of the valley cannot be called a "timid" inhabitant of the garden. 2 years ago we decided to grow our own plant and we succeeded

If you are not planning a trip to Paris this winter, you can still enjoy the scent of lily of the valley in January or February. It looks like a fairy tale, believe me! Below we will tell you how to bring the subtle scent of lily of the valley into your home.
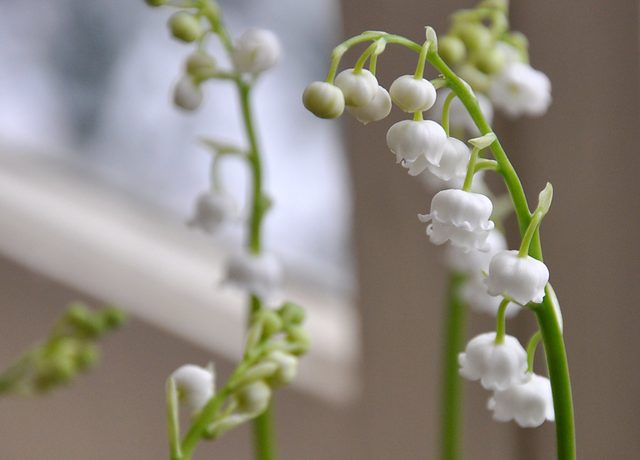

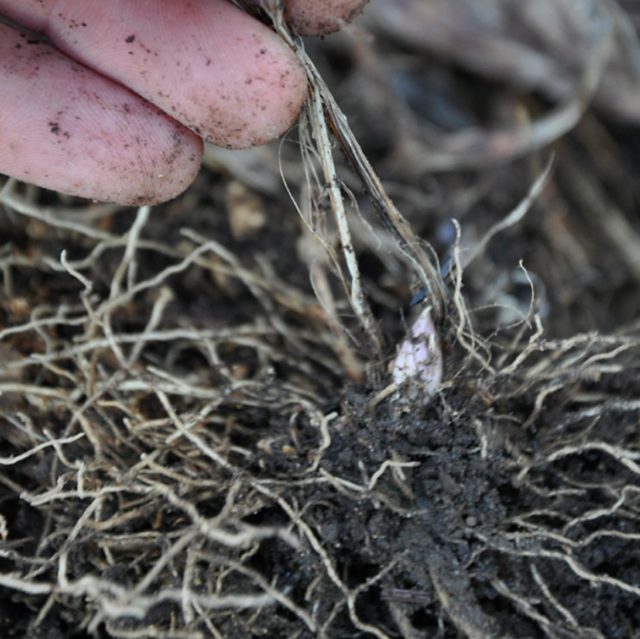
Dig lilies of the valley in your area
If lilies of the valley are already growing in your garden, you will not lose anything if you dig up a square meter of roots in the fall. Lilies of the valley reproduce so well that even neighbors will willingly share the roots with you. Dig up the roots in late fall, just before the first severe frosts. Separate the shoots and roots from each other with your hands (do not worry that a clod of earth is crumbling, then you will plant the lilies of the valley in a pot in new soil) Save as many shoots as fit into the pot. Each sprout must end with a root. Choose pots made of thin plastic. 2 square meters of spines is enough for at least 4 pots.
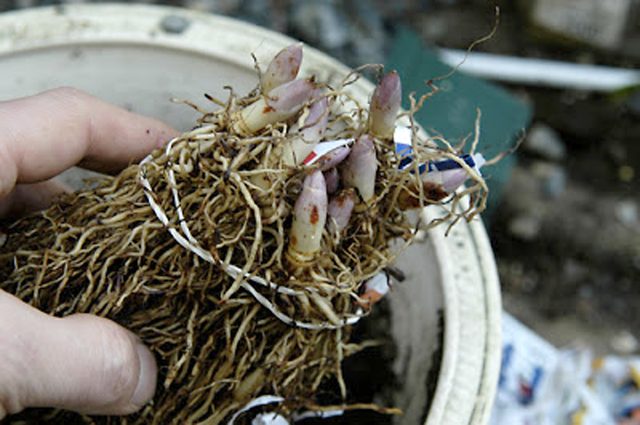

Planting lilies of the valley in a pot for subsequent distillation
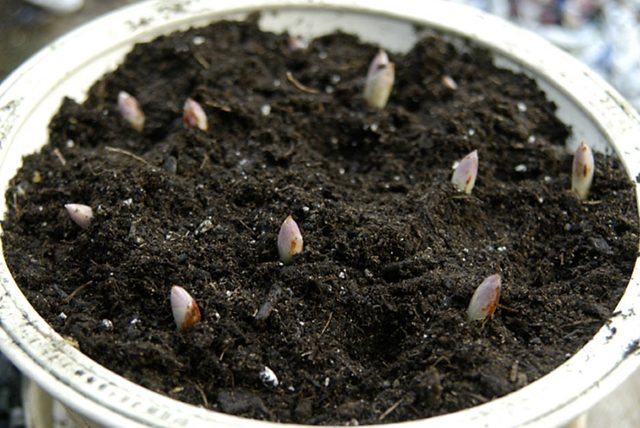
Lilies of the valley are not very whimsical, ordinary mixed soil will suit them. When the sprouts are already planted in the pot, let them sit for a few weeks before distilling. You can store the pots outside or in a barn, at freezing temperatures. It is advisable to store them until December or January.
Commercial lily of the valley sprouts start to appear in December and are ready to be forced as soon as you receive them. Soak all the roots in water at room temperature for a couple of hours, and then plant them in a pot at least 8 cm deep.The tips of the shoots should rise above the surface of the soil; in nature, lilies of the valley grow close to the surface of the earth
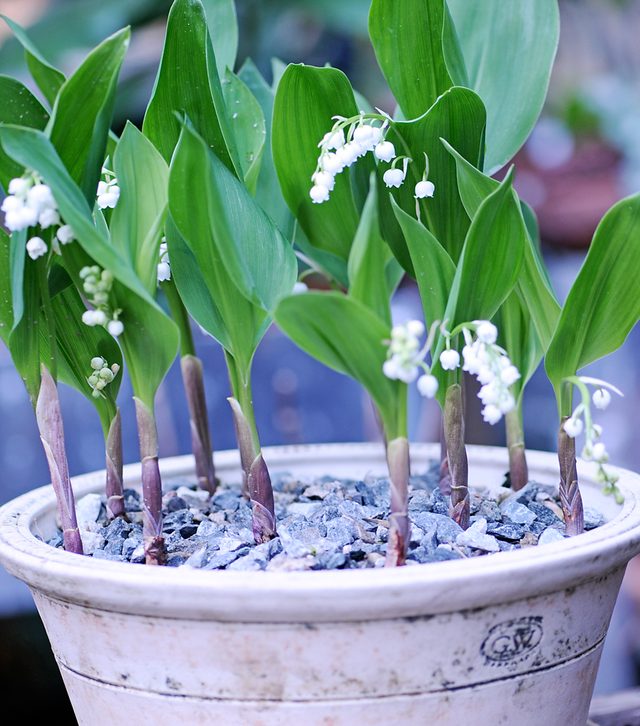

Scions dug up in the garden will emerge better if stored at near zero temperatures for at least 5 weeks. You can start distilling in late December or early January if the cuttings have been kept cold before. If it snows, move the pots to a shed, garage, or shelter out of the way. And although lilies of the valley are considered frost-resistant flowers, avoid freezing the soil in pots.

Forcing lilies of the valley in a warm room
Lilies of the valley are best kept warm. Imagine what the weather is like in May.Frequent precipitation is interspersed with warm and sunny days. If the "climate" in the room is colder at night, the lilies of the valley will appreciate it. If you want to start forcing as soon as possible, without waiting for December, the plants will not die, but they will grow slower than those that have been in the cold for the allotted time. Let's just say that the result will not be earlier than the middle, or even the end of winter. The closer to spring, the faster the lilies of the valley begin to grow.


Plants driven out in the very first winter can produce an arrow with a flower even before the foliage appears. Thus, the pot will have an incomplete look. Plants driven out later (in February and March) will produce foliage and flowers at the same time. Either way, in both cases, you will get beautiful fragrant flowers in your pot! You can use moss to cover the soil to add a decorative touch to the composition.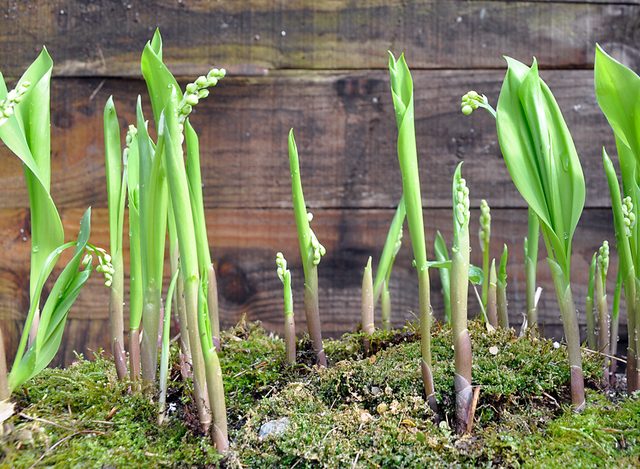
Another way to get lilies of the valley in a pot is to order them in our store. We received these lilies of the valley from Holland right from the roots, transplanted ready-made flowering plants into the ground. Therefore, the life of such compositions is no more than 10 days. However, you can try to keep the roots until spring and plant them in open ground.
Article author: Matt mattus
Translation and revision: Kanunnikova Natasha
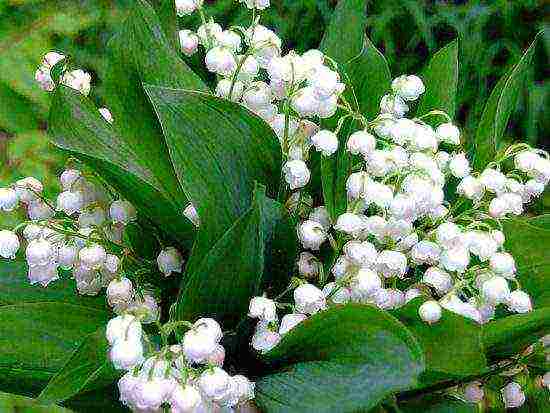
 Recently, this humble flower has become very popular in landscape design. Several garden species of lilies of the valley have been bred, distinguished by their size and color. For growing in a summer cottage or at home in a pot, it is not necessary to have a cultivar, the plant can be dug up in the late autumn in the forest or you can try to plant seeds. Of course, you have to tinker, but the snow-white beauty of spring lilies of the valley (pictured) is worth the effort.
Recently, this humble flower has become very popular in landscape design. Several garden species of lilies of the valley have been bred, distinguished by their size and color. For growing in a summer cottage or at home in a pot, it is not necessary to have a cultivar, the plant can be dug up in the late autumn in the forest or you can try to plant seeds. Of course, you have to tinker, but the snow-white beauty of spring lilies of the valley (pictured) is worth the effort.
Lily of the valley taxonomy and being in nature
Lily of the valley, oddly enough, comes from the asparagus family. In the botanical classification, it is represented by the only species - May lily of the valley, but geographical subspecies are also distinguished:
- Far Eastern (Keiske);
- mountain;
- transcaucasian.
There are no significant differences in morphology between them, the only thing is that these subspecies are territorially separated from the main one. In the wild, lily of the valley is distributed throughout the European part of the Russian Federation, in the Far East and Transbaikalia. The halo of the population covers Asia Minor and North America. The plant is classified as a protective species, as its number is actively decreasing.

May lily of the valley
The Latin name for lily of the valley sounds like "lily of the valleys", which well reflects the favorite places of settlement. You can meet lily of the valley thickets in forests on clearings and glades, in lowlands near water. Lily of the valley is very recognizable by its bright green oblong leaves and peduncles with white fragrant bells. In the middle lane, flowering occurs in May and lasts about twenty days. This happens at different times in each region.
Lily of the valley is a plant of the lower tier, it loves diffused light and light partial shade. Its stems reach a height of about 30 cm. After flowering, fruits are formed - round berries, which contain seeds.
Attention! All parts of the lily of the valley are poisonous, as they contain a large amount of convallatoxin.
Material procurement and artificial forcing of lilies of the valley
The easiest way to get new plants is from rhizomes with flower buds. It is easy to distinguish them from leafy ones by their rounded tops. In the fall (no later than October), the rhizomes are dug up, tied in bundles of several pieces and placed vertically in washed river sand.
Advice. Instead of sand for storage, you can use wet sphagnum moss.
The containers are left to winter in a cool place: a cellar, a compartment for vegetables in the refrigerator (no more than + 2 ° C). Only with early distillation (December, early January) are lilies of the valley frozen three weeks before planting (-3 ... -5 ° C). Thawing is carried out gradually, thereby imitating the spring thaw. To do this, prepare a bath (+ 30 ° C), the water in which is changed several times.

Lily of the valley root
The best month for forcing lilies of the valley is the last calendar month of winter.By this time, the rhizomes have already woken up and are ready for planting in a nutritious soil. The sprouts in containers are placed tightly to each other, watered abundantly and, covered with a transparent pact, are placed in a warm, bright place. Greenhouses shade from direct sunlight. When the first green leaf appears, the shelter is removed and the temperature of the containment is lowered.
Attention! Watering is carried out only with water heated to + 25 ° C.
Late forcing takes place in March. Usually these plants do not bloom profusely. To prevent the peduncles from getting lost among the foliage, remove the unopened leaves with nail scissors.
It is necessary to look after lilies of the valley in a pot: water, spray, mulch the top layer with peat. Flowering occurs in less than a month. With the appearance of the first buds, lilies of the valley are provided with an air temperature of no more than + 18 ° C. It is not advisable to propagate lily of the valley by seeds by seeds.
Lilies of the valley at their summer cottage
The forest flower loves well-hydrated nutritious soils. It is better to choose a place in the shade of large trees or bushes. Since the plant has a creeping root system, it will grow throughout the garden without assistance. To limit growth, plastic curbs from specialty stores are used.
A place for planting a lily of the valley is prepared in advance. Fertilizers are applied:
- Deciduous humus or peat (10 kg per 1 sq. M).
- Mineral additives (superphosphate 100 g and potassium salt 40 g per 1 sq. M).
Planting grooves or holes are made, the depth of which depends on the size of the rhizomes. The sprouts are covered with a layer of soil 1–2 cm. About 10 cm are placed between the plants.

Lilies of the valley feel good in the shade of trees
Planted in autumn, lilies of the valley will delight you with flowers in the first spring. Some people prefer to plant rhizomes "before winter". Lilies of the valley perfectly tolerate the most severe frosts - up to -40 ° C and do not need shelter.
Attention! For varietal lilies of the valley, some care features are possible.
Lilies of the valley are very fond of organic fertilizing, they can be applied immediately after rooting. Plants will need minerals only after a year. In one place, May lilies of the valley can grow and bloom for more than 10 years.
At first, the planting will have to be weeded and loosened, the overgrown meadow of lilies of the valley does not need this.
Lilies of the valley in landscape design
There are many interesting varieties of lily of the valley that will decorate a spring flower bed. Plants were obtained not only with traditional white flowers, but also with pink, double bells. There are differences in the color of the leaf, the size of the inflorescences. The most famous varieties:
- Aurea (yellow foliage);
- Flore Pleno (white double flowers);
- Grandiflora (white flowers, large wide leaf);
- Green Tapestry (yellow-green foliage);
- Rosea (pale pink flowers, abundant variety).

Lilies of the valley in landscape design
Even after flowering is complete, lilies of the valley do not lose their attractiveness. Therefore, you can decorate with lush green bushes garden paths, empty spaces near gazebos and benches in the yard. They combine lilies of the valley with the same shade-loving and moisture-loving plants, for example, forget-me-nots, hosts, veronica. The main thing is that the root system of the "neighbors" is not very extensive and deep.
At the summer cottage, you can create your own corner of untouched nature. Plant lilies of the valley between coniferous or deciduous trees. You can add ferns, low ornamental shrubs to the composition.
Delicate lilies of the valley in the garden or in pots on the window will impress even the most sophisticated gardeners.
What you need to know about lilies of the valley: video
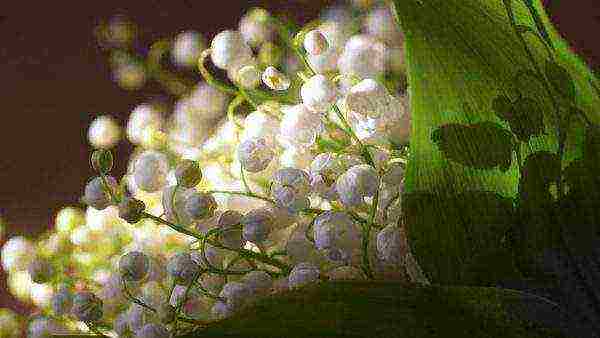
The lily of the valley flower (also known as the silversmith, the convalia, the rejuvenator, the tongue of the forest, the lapushnik, the soapy grass, the hare's ears and the raven) belongs to the herbaceous perennial plants of the genus Lily of the Valley. The culture reaches about 30 cm in length. Lily of the valley (lat. Convallaria) prefers shaded areas. The leaves of the plant are distinguished by an oblong structure.The inflorescences include about 15 bright white water lilies. The flowering period lasts from May to June. Lily of the valley has a pronounced delicate aroma. In its natural environment, the plant can be found in clearings, in ravines and forest edges. It is widely used by gardeners for decorating plots. The plant is also known for its healing properties.
How to care at home

Bell-shaped inflorescences of lilies of the valley.
Lighting
The young lapushnik needs protection from solar radiation for the first month after planting. It is recommended to cover the plant in an open area. Indoors, move the container further away from an open window.
Fortified lily of the valley needs to be provided with full lighting. Direct sunlight has a detrimental effect on the development of culture.
Temperature regime
It is possible to stimulate growth and abundant flowering by stratification (exposure to temperature). The rhizome of the convalia should be refrigerated for several days.
The optimum temperature of the environment for plant development should be in the range from + 20 to + 24 degrees.
A temperature regime of the order of + 27 degrees will help to reduce the forcing time.
Proper watering

Lilies of the valley at all stages of development require regular moisture of the substrate.
It is necessary to constantly maintain the moisture content of the substrate. The amount of watering depends on the weather conditions. In the hot season, it is necessary to moisten the soil at least 3 times a week. In calm cloudy weather, the number of irrigations can be reduced to one time.
Humidity
Lily of the valley is a moisture-loving plant. It is necessary to periodically spray water at room temperature on the flower. It is important to maintain the humidity level within 55-70%.
Transfer
For transplantation, rhizomes are used, on which there are rudiments of leaves and buds. Before planting, the soil must be thoroughly loosened. It is advisable to add humus to the soil.
You need to gently straighten the bent tips of the roots. It is advisable to cover the buds of lilies of the valley with a thin layer of soil - no more than 1.5 cm.

Lilies of the valley are very difficult to tolerate a transplant.
The convali should be replanted in September or early October. The plant is difficult to tolerate the change of soil and container. It is recommended to initially choose a suitable place for breeding lily of the valley.
Pruning
You will need to periodically clean the culture of damaged areas.
Lily of the valley perfectly tolerates sudden changes in temperature and severe frosts. In the spring, after the snow melts, you need to collect the leaves with the help of a small garden rake.
Restraining growth
Lilies of the valley are capable of covering a large area. A fragile rejuvenator with graceful inflorescences has "punchy" qualities. The plant is capable of destroying large shrubs and trees. A powerful root system wraps around the surface of the substrate.
In an open area, the convoys are capable of capturing a large territory.
To prevent the capture of a large area, it is recommended to limit the area with slate leaves or iron material. The depth of the fence should be about 50 centimeters.
Lilies of the valley in the open field
To grow the convali outdoors, you need to choose a suitable place. Lily of the valley garden prefers uniform moisture and shade. It is advisable to plant the plant in the shade of other shrubs or trees. A miniature plant will need protection from wind and drafts.
In neutral soil, lily of the valley can actively develop for more than 10 years. Lime must be added to slightly acidic soil. It is advisable to periodically fertilize the soil with manure and peat compost. Superphosphate and potassium sulfate are available.

To grow a conval, it is necessary to prepare the landing site in advance.
For planting, you must prepare the site in advance. A year before planting, the soil should be dug up at a depth of 35 cm. The site should be covered with agrofibre and constantly cleaned of weeds. You can also plant legumes.
Lilies of the valley should be planted in October or mid-April. For the conval it is necessary to make small holes.In the pits, sprouts of silversmith with parts of the rhizome should be placed. The length of the rhizome should be about 7 cm. You should choose a planting material with two buds in the apical part. The rounded top of the sprout, more than half a centimeter in size, guarantees flowering in the current year.
It is necessary to close the soil up to 3 cm deep. The spacing between the grooves should be at least 20 cm. Densely planted shoots are often affected by gray rot. Lilies of the valley must be watered abundantly with warm, settled water.
A month later, when the lilies of the valley take root, you need to feed the plant with organic matter. During the dry period, the plant will not lose its decorative appearance. The formation of new inflorescences may completely stop. It is necessary to thin out the conval once every 3 years.
You can find out all the features of a flower from the video:
Growing features
Substrate
Lilies of the valley prefer loose soil with high air permeability. It is advisable to prepare a loamy, well-drained soil.
For indoor plants, a peat mixture from garden nurseries is ideal.

For container lilies of the valley, you can purchase a ready-made soil mixture.
Top dressing
The soil for the convali must be fed periodically. Depleted soil adversely affects the development and flowering of lilies of the valley.
Indoor plants can be watered with a solution of a water-based complex mineral fertilizer.

Minerals should be used for feeding.
In the open air, a mixture of rotted manure and leaf humus should be used for the top layer of soil. Compost tends to retain moisture.
Konwalia in a flower pot
Lilies of the valley can also be grown in a container. A container should be prepared taking into account the size of the rhizome. In the fall, it is necessary to plant lilies of the valley in a pot of nutritious soil. Place the container in a cool and dark place. The average air temperature should be between + 2 and + 4 degrees.
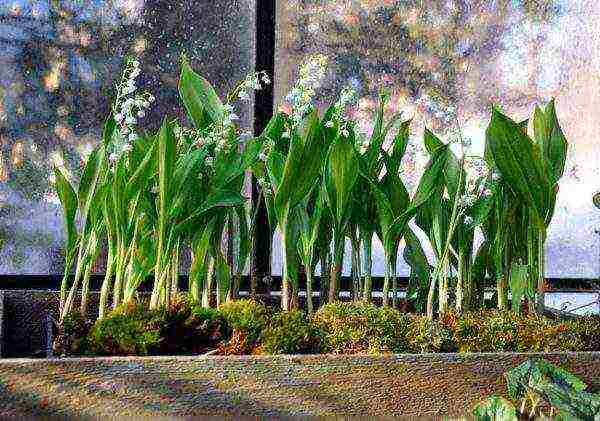

Lilies of the valley in a container.
In mid-January, it is necessary to take the lilies of the valley to the windowsill. It is advisable to choose the side of the building with diffused sunlight.
When the plant forms green foliage, you can start feeding. Application of mineral fertilizers about 3 times a month will prolong the abundant flowering of lilies of the valley.
After the inflorescence wilting, it is necessary to transfer the conval to a cool room. At the first sign of yellowing of the leaves, it is necessary to reduce watering.
Problems and diseases of the convali
The plant is most often affected by vegetable rot. For treatment, you will need fungicides.
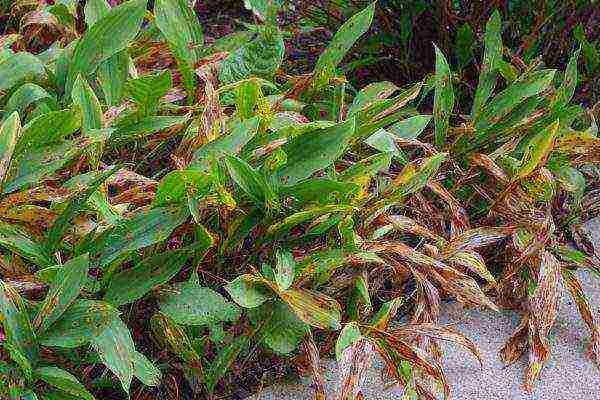

Damage to lilies of the valley with vegetable rot.
Several insects can cause damage. Nematodes, sawflies and onion crackers are especially dangerous. You can get rid of onion crackers and sawflies using insecticides. Plants affected by nematodes must be destroyed. The lilies of the valley, the top layer of the substrate and the container should be burned. All neighboring cultures must be examined. The parasites spread quickly.
As a preventive measure, good drainage of the soil should be ensured. It is necessary to constantly clear the area of weeds. You need to thin out the culture as needed.
Influence of lilies of the valley
The fragile plant is very poisonous. At first glance, harmless miniature inflorescences can lead to serious consequences. Blooming convalia in the bedroom can cause migraines, shortness of breath, rhinitis, swelling and other allergic manifestations. It is not recommended to grow the plant in a house with children.
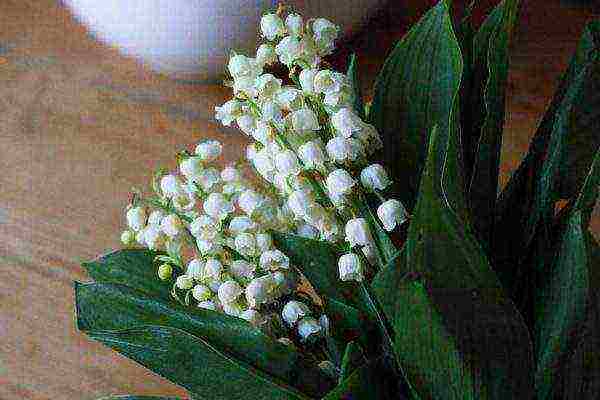

The aroma of the convalia can cause poisoning.
Lily of the valley berries contain a high concentration of toxic substances. Eating the fruit causes poisoning. It is necessary to rinse the stomach, take a sorbent and seek help from a medical center.
Breeding technology
Lilies of the valley can be spread by seeds and vegetatively (cut off rhizomes).
Convalia from seeds is able to form the first inflorescences only after 7 years. The seeds are sometimes sown in the fall. The planting material gives a low germination rate.You can plant seeds in a container. The resulting sprouts must be carefully protected from exposure to sunlight. It is recommended to constantly moisten the soil. During the first two years, transplanting a young convalia can destroy immature shoots.
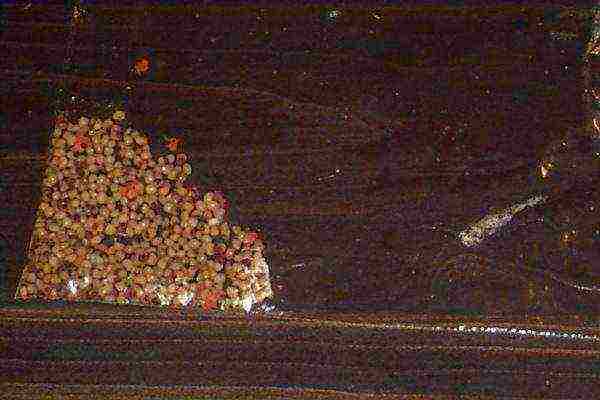

Lily of the valley seeds.
For vegetative propagation, you will need to split the root. The procedure should be carried out in the fall (before the first cold snap) or early spring. In the first year of the life cycle, only two leaves will form. Flowering will come on average in 3 years.
To breed lily of the valley, you will need to plant the top of the rhizome in the prepared substrate. The mixture must include clean sand and clay soil. The soil should be loosened thoroughly. When planting, it is advisable to feed the earth with leaf humus. It is necessary to maintain a distance between seedlings of the order of 15-20 cm.

Division of the rhizome.
With the help of distillation, you can get blooming convalues even in winter. Large-colored representatives of the culture should be prepared for the procedure. In the fall, you need to cut off the top of the rhizome. Cuttings should be placed in large containers. At least ten lilies of the valley should be planted in one container.
The pot must be transferred to the greenhouse. You need to bury the container in the sand and cover it with moss on top. The temperature of the medium should remain between + 30 and + 35 degrees. Moss moisture must be constantly monitored. If all conditions are met, the first inflorescences will form in 3 weeks.
How to stimulate flowering
In a closed room, convali often do not form inflorescences. For reproduction, the culture needs insect pollination. It is advisable to transfer the flowerpot to an open balcony, terrace or loggia in the summer.
For a lush flowering garden lily of the valley and a plant brought from natural conditions, it is necessary to provide darkened conditions, uniform moisture and loamy neutral soil.

For the formation of inflorescences, lilies of the valley need to create favorable conditions.
In natural conditions, convalia can bloom only in the seventh year of its life cycle. After twelve years, grown-up crops stop producing buds.
In a home environment, lilies of the valley form inflorescences on average after 5 years. An abundant bloom will help preserve humus and minerals.
How to choose a conval
Package of seeds of lily of the valley "Brilliant" weighing 0.05 gr. can be purchased for 46 rubles. A container with 3 rosea lilies of the valley, 20 cm high, is sold for 490 rubles.
Foreword
This perennial plant has white flowers with a shade of pink and a rich, pleasant aroma. Of course, we are talking about garden lilies of the valley. What does their planting require, what is their care? Where to start for an inexperienced florist?
What do lilies of the valley love and dislike?
These flowers are common in the forest in clearings and forest edges, they grow well on moist, neutral soils. The garden lily of the valley differs from its forest counterpart in large leaves and flowers, the height of the plant is no more than 30 cm. It has fibrous roots and large basal leaves of an oval shape. The dark green leaves are over ten centimeters long and about five centimeters wide. In autumn, they turn yellow and fall off. The main bud is located on the rhizome. White flowers resemble bells, after ripening red berries form. The main types of this lily of the valley: May, mountain, Keiske, Transcaucasian. The differences are insignificant: Keiske blooms late, long flowers are characteristic of the mountain, and wider in the Transcaucasian inflorescence.

Lilies of the valley at their summer cottage
Flowers can be white, pink, cream, and foliage - green, yellow, striped, speckled. So it is worth trying to enrich your site and plant a garden lily of the valley. Experienced flower growers draw the attention of all novice lily of the valley lovers to the following factors. The rejuvenator captures the territory, and in order to control the increase in crops, limit the plantation, install a fence with a height and depth of 25 centimeters.The root grows rapidly in width and depth. Lilies of the valley prefer a humid and darkened environment. Flowers require the same conditions as in a forest in a clearing, they need a temperate climate.
Solid darkening interferes with flowering, and oversaturation with moisture and stagnant water negatively affects the sprouts. The species is frost-resistant, therefore it tolerates frost well. In the garden, they select a place near the terraces and paths. This is the most suitable option to feel the bright aroma. But for successful flowering, you need to choose the right neighbors. Bushes of currants, gooseberries, raspberries, deciduous trees will provide protection from overheating and drying out. Better to plant next to plants with roots at the surface of the earth. Species that breed with whiskers are suitable. Flowers do not overwhelm species with small root systems. Neighborhood with them will give the territory a beautiful aesthetic appearance. Also, lilies of the valley do not tolerate strong winds, they will not bloom in a blown area. Will shelter a house, buildings or a fence from the wind.
The wisdom of planting and breeding features
What can be done to improve soil properties?
- if there is a lot of clay, add sand;
- mix sandy soil with clay;
- for sour - prepare lime four months before planting;
- humus or peat compost is useful for the soil;
- for nutritional value, use superphosphate (100 g / m2) and potassium sulfate (40 g / m2).
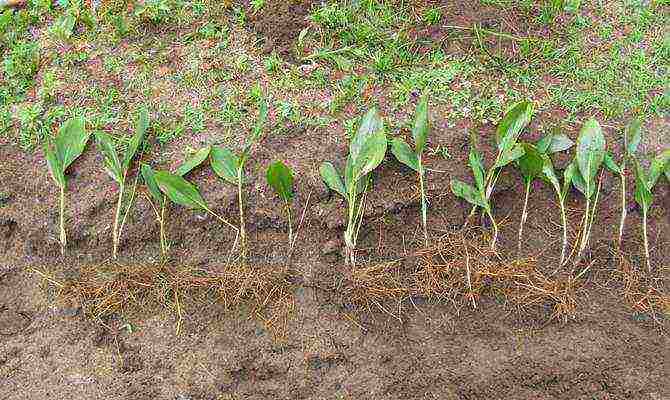

Planting lilies of the valley
Wet, slightly acidic and neutral soils will provide good growth. Expect to prepare the soil a year before planting flowers. To normalize the environment in the previous season, you can plant legumes, peas, lupines. In addition to creating a good chemical balance in the soil, the tops of legumes will serve as a good material for mulching, because they retain the moisture necessary for life.
Rhizomes are planted and transplanted in September, since heavy rains that begin at this time have a beneficial effect on the microclimate near the garden. After planting, in order to prevent dryness of the land, if nature does not help with precipitation, it is required to water several times and loosen a little. Water and air easily penetrate into such a substrate. You can pre-mix the soil with deciduous humus, this will be an unobtrusive replenishment of nutrients, or you can throw a little on top of a new plantation. Lilies of the valley are planted at a distance of 100 mm, and 250 mm are measured between the rows.
The best way to reproduce is by dividing the rhizome. At the end of summer, the sprouts are sorted. It is necessary to select separately those that are going to bloom next year and in two years. To understand this, you should look at the buds: large, rounded 0.6 cm in diameter will give color in the next season, and thin and sharp at the top - in another year. They mainly use separate roots with unblown buds. But you should not plant it right away in the soil, you need a little preparation. First, the roots are soaked in water at room temperature for four hours. Then the roots are spread, planted with a large handful of earth in the hole, and rows are formed. Then the roots and buds are covered with earth. If the latter are swollen enough, they are left outside. It remains to press down on the soil, water it, cover it with compost-mulch.
Alternative planting - using seeds. Red small fruits in lilies of the valley are formed after flowering, in which the seed is formed. These seeds are prostrated, i.e. wrapped in a damp cloth, placed in a closed container and placed in a freezer with a temperature within 3-5 degrees. In this case, they can be stored for a month. Then the container is filled with earth and the workpieces are planted to a depth of 1.5–2 cm in the holes. Sow them in rows. The distance between flowers should not be less than 12 cm. If necessary, the rows are then thinned out.
Many seeds are sown in autumn immediately into loose soil. But this landing will not be effective. In general, it is difficult to grow a flowering lily of the valley using seeds. In spring sprouts develop slowly to adult form, form 2-3 leaflets.The next year, another leaflet appears. Flowering will begin only after 5-6 years. The seeds are characterized by poor germination, and besides, they are unsuitable for storage. You should also expect that a lot of material will be required for sowing, because only 1/5 part will rise.
What kind of care will the flowers need?
Naturally, plants need compost and organic fertilizers. Humus is applied in August, and mineral fertilizers are not applied at all in the first year, but they do it later. Otherwise, the flowers do not require special care in terms of feeding. In the spring, fertilizers are usually applied in liquid form, and once is enough. As a result, large leaves and flowers will appear very quickly, and flower buds will form in a larger size.
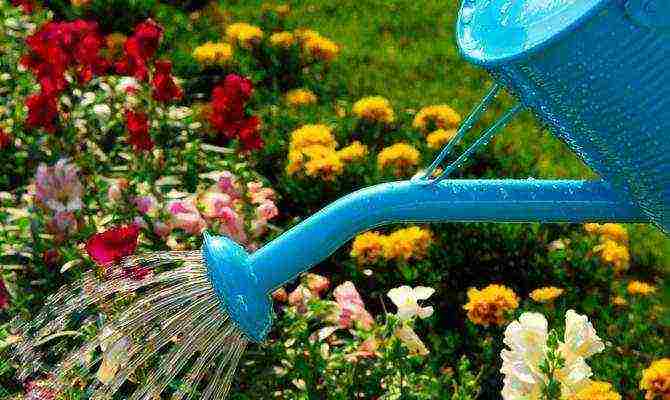

Watering flowers on the site
It is important to monitor soil moisture. Its excessive dryness will lead to the death of the roots. Stagnant water and high humidity are also detrimental. Therefore, water the plant throughout the summer when required. Large flowers require a lot of water to appear, but there should be no puddles. With good care, the bush blooms 3-4 times a year. It is also necessary to restrain the growth of weeds and remove them in a timely manner, therefore, it is advisable to remove the grass after watering. Initially, the plants need to be weeded every time after this operation, and when they grow, they will be able to displace the weeds on their own. They pull out the excess near the flowers, as a rule, with your hands, carefully, protecting the root system. During such care, there is no need to loosen the soil, if the weeds do not have time to grow, then, by taking them out every time, you will already create good channels for air exchange.
When the lilies of the valley have matured a little, there is no need to clean them after each watering, weed twice a month during the year. After all, not only weeds, but even the most common grass significantly harms growth with their roots. Watch the temperature as the flowers take root well and grow in cool weather. If it's hot, create a shade, when watering it is better to take colder water, but do not try to put it in the refrigerator. The health of the plantation will also be improved by transplanting, they are engaged in it after five years of flowering. Usually in the spring, the overgrown rhizome is divided and the bed is formed again. The roots are selected in such a way that the buds and leaves have not yet blossomed.
On average, lilies of the valley are usually grown for about 10 years, then they stop blooming. To prolong flowering, the beds are periodically renewed in a natural way. Part of the bed is dug, leaving an empty space, they are monitored in the same way as for a regular bed. The vacated plot is overgrown again, but with young growth. This is best done every three years. For the health of the garden, it is important to periodically induce cosmetic beauty by removing wilted and broken bushes and leaves. This helps to maintain plant growth, cleanliness, and a beautiful appearance of the flower bed.
Protection from pests and diseases
An important part of grooming is to look after the health of the flowers. The main enemies of the lily of the valley are crackers (onion and linear), as well as sawflies. These bugs eat leaves, stems and flowers. Their thick brownish mucus-covered larvae need to be removed from the beds, usually carefully collected under the leaves, this is their favorite place. Preparations Aktara and Confidor will help to destroy the larvae of these insects. Still not a very pleasant guest - nematode worms. They affect the stems and roots, diseased plants cannot be saved, they must be removed from the site. Marigolds as neighbors will help get rid of this worm, or you can cultivate the land with nematicides.

Aktara drug
Diseases can be different too, even if the care seems ideal. The appearance of a gray bloom on the leaves indicates excessive overgrowth of plantings and soil moisture. We need a flower transplant, and it is also necessary to reduce the number of watering. The reddish border is gleosporia. In case of slight damage, Topaz and Alarin-B will help, in case of serious damage, the plantings must be eliminated in order to preserve at least part of the plantation.Treatment with fungicidal preparations will also help.
From the defeat of gray rot, they get rid of with the help of fungicides. This is a fungal disease that spreads very quickly on both vegetables and flowers. Sick plants are dug up. Otherwise, the disease will spread to other bushes.
Collection and distillation at home
Flowers, as a rule, are not cut, but are plucked by hands, just gently pulled up. Moreover, it is desirable to collect them, as this accelerates the growth of the plantation. Dorien and Grandiflora varieties look beautiful in a bouquet, usually 20–25 sprouts are enough. It is better to collect the bouquet before the flowers have fully opened. They are not placed in water with other flowers, because their strong aroma will overwhelm the neighbor's, and even worse, if you get an unpleasant smell from mixing them. At home, bells are arranged on one side so that the bouquet does not look loose and careless, they are placed in filtered water and activated carbon is added - three tablets.
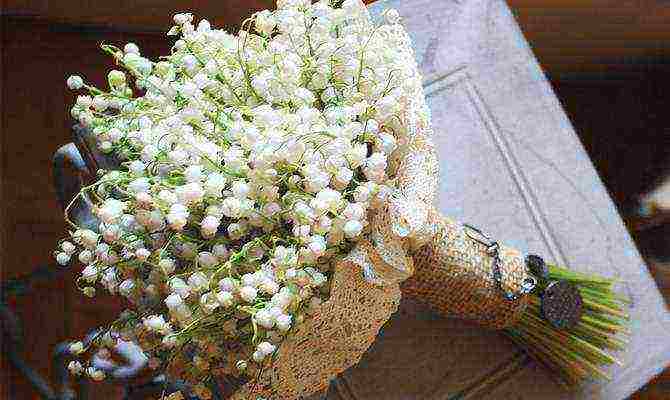

Beautiful bouquet of lilies of the valley
When the plantings have grown in the country, it will be possible to admire the flowers in winter, but at home. This can be achieved by distillation - by creating the necessary conditions for the species in apartment conditions. What do I need to do? In the summer - standard care, the beds are weeded, loosened and watered. And in the fall, with the first frosts, they dig out strong plants, they will be planted in another place. Sprouts with large buds are transplanted into pots. Those that do not fit are transferred to a new bed. Next year they can be used again for forcing. The rest of the weak shoots are left in their original place. In the future, they will grow and strengthen. A pot for household residents is filled with earth with humus, sand is added, roots are planted there. Small boxes, containers, and other containers are also suitable.
The sprouts are distributed in rows, measuring 40 mm between them, watered, covered with sand or moss with a layer of about 100 mm. The container is placed in a cool place - basement or loggia. The room temperature should be only 5 degrees, this retains the necessary substances. We begin further care in two weeks, when the containers return to a warm room - we water the flowers with warm water, this will promote germination. The pot can be transferred to the battery, but covered with something so that the moisture does not evaporate at great speed. After two to three weeks, the flower will begin to grow. Then remove the extra layer of sand. Gradually, the sprouts will begin to get used to the light, the boxes need to be placed on the windowsill and watch out for the draft. To speed up the distillation, the pot is sometimes covered with snow a little and left overnight, they say that after such a frost, the flowers will bloom earlier.
Use in medicine and landscape design
Lily of the valley is widely used in decorating parks and gardens. This plant is not suitable for a round small isolated flower bed, but rather finds application for a continuous soil cover. Looks good with ferns and aquilegia. The plant is popular with perfumers, but it is difficult to get a natural smell from flowers, therefore chemical compounds are actively used to recreate the scent of a flower.
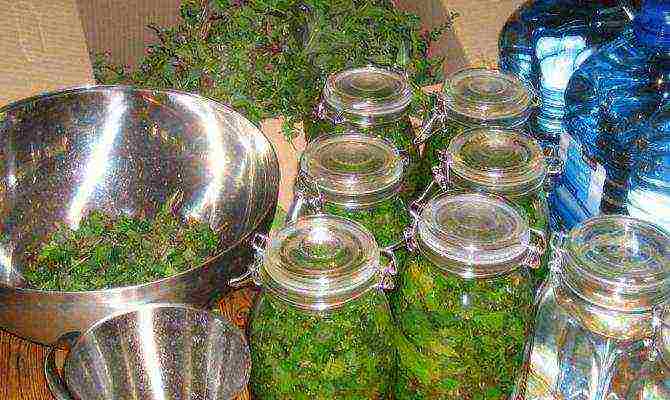

Lily of the valley tincture
In medicine, cardiac drugs, choleretic drugs are made from herbs and flowers, they are used for cholecystitis, cholangitis. The tincture is used as a sleeping pill. Zelenin drops soothe with neuroses, Korglikon is needed for injections. The drugs normalize the work of the heart, relieve pain, swelling. All recommendations on the use of drugs should be obtained from a doctor and be careful, since the substances in the composition of such drugs can provoke poisoning due to one feature - convallatoxin.
It is a poison found in plants, it is present in the lily of the valley and makes it poisonous. Hands should be washed after touching flowers. Children should be warned about the danger, not allowed to eat or put red berries in their mouths. Planting and caring for lilies of the valley does not require much effort.They can breed for several years in abandoned areas, but the above rules should be followed to obtain bright large flowers. Then, in the garden every spring, the lily of the valley will delight you with beautiful bell flowers and an extraordinary aroma.
Rate the article:
(1 vote, average: 2 out of 5)


