Content
- 1 Live food for fish at home - which one to choose?
- 2 Live fish food - benefits
- 3 Types of live food for aquarium fish
- 4 Which aquarium fish need live food?
- 5 How to store live food for aquarium fish?
- 6 DIY live food for aquarium fish
- 7 Live food tubifix and tubifex
- 8 Live food Cyclops and Daphnia
- 9 Harvesting live food Daphnia for the winter
- 10 Live food Gammarus
- 11 Live food Coretra
- 12 Live food Infusoria
- 13 Live food Artemia
Dear colleagues! In today's article, we will talk about food for aquarium fish, or rather, how to prepare it yourself. If your fish feed only on gammarus, cereals, or dry daphnia, then keep in mind that this diet is far from the best. As a rule, fish grow poorly from such food, problems with reproduction appear or may even die.
Trouble can overtake you even if you feed the fish with live food. They can go bad, as a result of which the fish gets sick and dies. To avoid problems with feeding in the future, every novice aquarist should know how to feed their pets, how to get this very food and how to store it.
Pipe worker
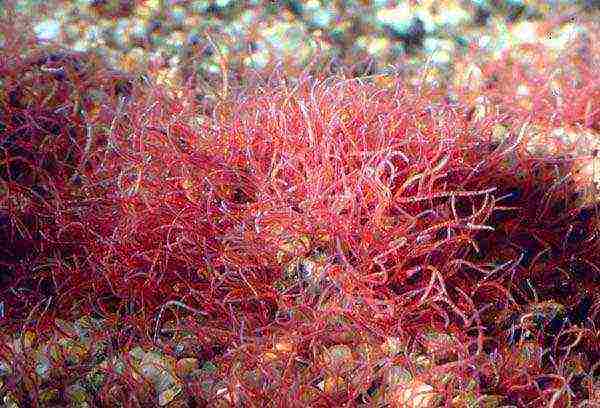

We will probably start with the pipe maker, as it is extremely popular among aquarists of all stripes. This dish is an annelid worm, 20 to 40 millimeters long. The body color of the worms is dirty red. They get it in the bottom silt of a natural reservoir, where it gathers in lumps. It so happened that the pipe maker is very common in our country. It can be found in particularly polluted bodies of water and in places where wastewater flows into these very bodies of water.
As a rule, the tubifex is found in huge amounts of the upper layers of silt accumulations and forms a fluffy carpet that disappears from view if this rug is disturbed. The head of the worms is submerged in silt, while the rest of the body hovers in over the bottom. The worm passes soil saturated with bacteria and other organic impurities through its digestive system. There are places where a huge amount of organic waste accumulates, and there, in turn, the bottom is literally strewn with a pipe-maker and it is red in color. If you plan to feed your aquarium pets with a tubule, always remember, as it can accumulate various toxic substances in itself, which can provoke the death of all your fish.
In aquarium practice, there are several ways to collect annelids. If you need a little pipe maker, then it is enough to lower the net to the bottom of the reservoir, on which spoiled fruits, corn cobs and boiled potatoes are spread. A few days later, these baits will be covered with a pipe maker.
But if you need a lot of pipe maker, then you will have to scoop the worms together with the silt with a shovel and pour it all into a bucket. You can also use a shallow landing net, where the top layer of silt, rich in worms, is collected. When the sludge has settled in the bucket, the remaining water can be drained off. Then, cheesecloth is spread on the remaining silt or sprinkled with washed river sand. Next, the bucket must be placed in a basin filled with hot water or put on fire. As a result, due to the heat, the poor tubifex cannot find a place for himself and begins to crawl to the surface, where he is carefully collected by a caring aquarist. After the tubule is assembled, it must be rinsed from the remnants of silt and sand.
To bring the pipe maker home safely and intact, it is best to use a special suitcase equipped with wooden pull-out frames covered with mesh. If the frames are made of wood, then they need to be impregnated with hot linseed oil. If the substrate is kept in a humid environment, the worms will live for several hours.
At home, you can store the tubifex in flat cuvettes filled with water. The water level should be such that after tapping on the cuvette, the tubule begins to protrude out of the water. Just make sure that a bacterial film does not accumulate on the surface of the water. The water in the cuvette must be changed several times a day, while the tubule must be transplanted into a clean cuvette in the meantime. It is best to store the worms in a cool place, but never freeze it.
In view of the fact that the tubifex is obtained in dirty waters, it is possible to feed the fish with it only after a week of aging in clean water. If during the holding time in the cuvette the water has not deteriorated and dirt does not accumulate, then the lump can be safely used. If you keep a ball of worms in a cool place, then in this state it can live up to three months.
If you feed the fish with a pipe maker, take into account the fact that it burrows very quickly into the aquarium soil, where it quickly dies accordingly. This, subsequently, leads to deterioration of the aquarium water. To prevent this, it is better to use a bottom or floating feeder. If you need to feed the fry, then the tubifex is finely chopped with scissors and washed in a nylon net.
Earthworms

For such aquarium fish as viviparous (mollies, swordtails, platies and guppies) or haracin (red and blue neons, minors, ornatus, rhodostomuses), such food is not suitable, but for large fish (cichlids, tetragonopterus and goldfish) this is ... In our country, you can count more than 50 species of earthworms. These guys are hermaphrodites and they reproduce by cross fertilization. The earthworm lays a cocoon, from which about 10 embryos emerge. They feed, as a rule, on fallen leaves, humus and other organic compounds in the soil. You can find them in damp places that they leave after rain. They can also be obtained in vegetable gardens and orchards, and especially where the land is fertilized with manure.
The harvested worms can be safely stored for more than one month in a cool place by placing a container with livestock in a wet canvas bag or in a wooden box, which is filled with turf, moss, wet sand and shavings from a deciduous tree. Worms are also perfectly preserved in humus with fallen leaves. You can feed the worms with cornmeal or milk. Before feeding the fish with worms, the latter are allowed to live for several days without food, so that their intestines will be freed from all the contents. You can also place worms in a container of water for a couple of hours. Then they are rinsed from mucus, cut or given whole to their fish.
Bloodworm

The mosquito larvae of the families Tendipedidae and Chironomidae are called bloodworms. The larvae are harvested in reservoirs with a large amount of silt, which is collected from the bottom and washed in a sieve to remove various small particles and sand. When only bloodworms and various debris remain in the used sieve, the sieve needs to be dried a little and lowered into water. As a result, the bloodworm will begin to float to the surface and can be collected with a net. This procedure continues until you have removed all the bloodworms from the sieve.
In order to finally clean the bloodworm from various debris, it is laid out on a sieve or gauze, and placed in a basin of water. The bloodworm will sink to the bottom, and any remaining debris will remain on the gauze or sieve. In this way, live and dead larvae can be sorted. Live bloodworms can be safely stored in the refrigerator on the bottom shelf for two to three weeks.To preserve it for your fish, the larvae are wrapped in a damp and well-wrung cloth and placed in a plastic jar with tiny holes. You can also mix bloodworms with used tea leaves. The larvae of mosquitoes are also perfectly preserved in a basin with running water, at the bottom of which sifted and washed sand is laid. The larvae will burrow in the sand, and you will not wash them out of the basin when you change the water in it. Bloodworms are removed from the sand with the same net with which you sifted the sand when you caught the larvae. Bloodworms are also successfully stored in a fabric bag, which is placed in a flush tank.
To feed the fish, mosquito larvae can be placed in a floating plastic feeder that has holes at the bottom through which they enter the aquarium. In no case do not allow bloodworms to fall into the ground, since in large quantities it will greatly spoil the water, slowly decomposing in the substrate. If you want to arrange a mini-breeding of bloodworms on your personal plot, then a small pit breaks out, which is filled with water. To attract mosquitoes and provoke mosquitoes to lay larvae, a lantern can be installed above the water, and hay can be spread on the surface of the water. You can feed the larvae with yeast.
Coretra
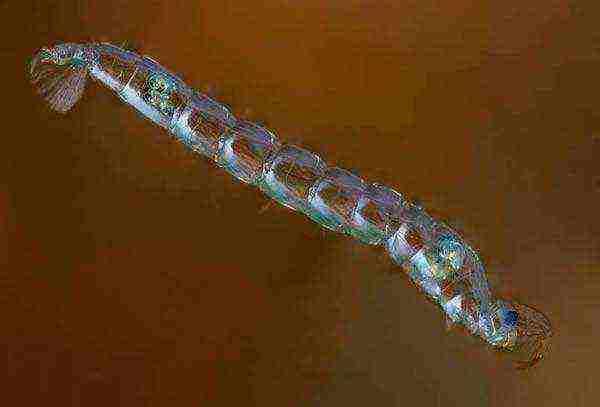
Coretra is also a mosquito larva, but of a different species (Chaoborus), the length of which is 10-12 millimeters. If bloodworms are mined at the bottom of the reservoir, then the coretra floats in the water column and is not buried in the ground. From natural reservoirs, it is caught with nets in the cold season. If it gets warm outside, the core becomes a pupa, and then a mosquito. You can store the larvae in a wet rag, which is placed in a vessel with cold water. The best option is to put it in the bottom of the refrigerator. When feeding the fish to the coretra, be aware that these larvae are predators and they can harm the young.
That is, in principle, all the main types of live food that are used in aquaristics today. Of course, you can experiment with various bugs and worms, but at your own peril and risk. In the article, I have cited the most popular and most affordable ones.
Thank you for your attention!
Hello to all readers of my blog!
It is known that only experienced aquarists breed live fish food at home. Aquarists who truly understand the essential need for live food. And what is this importance? Live food for fish is, first of all, food created for them by nature, and it cannot be deleted from the fish instinct.
Live food contains essential amino acids that are not present in artificial food, and without these amino acids, the fish will be sick and stunted. Without live food there will be the lowest rates in fish farming, because without live food it is impossible to grow good producers and raise fry of most aquarium fish.
Live food for fish at home - which one to choose?
There are several types of living organisms that can be bred as live food at home. These can be: nematode worms, enchitreus pot worms, drosophila flies, aulophorus water snakes, daphnia cladocerans. And all these organisms are divided not only by nutritional value, but also by the complexity of their cultivation.
As you can see, the list is rather big. Well, what to choose so that the fish are happy, and the most less fuss and hassle? I would advise you to make a choice in two directions, that is, to breed live food that could be used as starter food for fry, as well as food for adult fish. Daphnia is great for breeding such live food at home.

Breeding daphnia is not difficult at all. All fish adore these crustaceans., and the versatility of Daphnia can hardly be overestimated, when the newly spawned small fry of Daphnia is excellent asstarter feed for fry, for example, barbs, and the same small fry of daphnia, which is rapidly growing on the second or third day, is already well suited for feeding adult fish.
It is especially important to note that the floating fry receive not some kind of chopped aulophorus, but plankton, where the way of feeding and development of fry in the aquarium actually becomes similar to the natural one.
You need to know that not all types of daphnia are equally suitable for breeding at home. I breed daphnia moin and in winter I easily raised barbus fry. This type of daphnia, as I think, is the most unpretentious.
Moins reproduce well and do without a heater, and I only turn on the blowdown for a few minutes, when I need to stir the tremors in the aquarium cultivator or remove the appeared film from the water surface.
This daphnia species is considered the smallest and is well suited as a starter food for fry. This is the best option to always have live fish food on hand at home.
To learn more about breeding this type of live food at home, you can follow this link. You can also prescribe daphnia by mail, so that you can then breed them as live food for fish at home.

Live food for aquarium fish is that “delicacy”, the presence of which in the aquarium causes revival among its inhabitants. This variety has an increased nutritional value, but when choosing it, you should take into account both positive and negative aspects.
Live fish food - benefits
Live food for fish is not only a useful and necessary element, but also the maintenance of natural instincts in the inhabitants of a home aquarium. The activity of the fish increases if live food appears in the aquarium. Certain species of pets are in danger of dying, deprived of the opportunity to hunt for living creatures, if their daily diet consists only of dry food ("motionless food").
Live food for aquarium fish for predatory subspecies is required, without it they will not be able to give birth to healthy offspring. The rational use of living substances helps to keep the water in the aquarium clean for a long period of time. The remains of dry waste, not eaten by the fish, begin to rot, contribute to the rapid deterioration of water, its clouding.
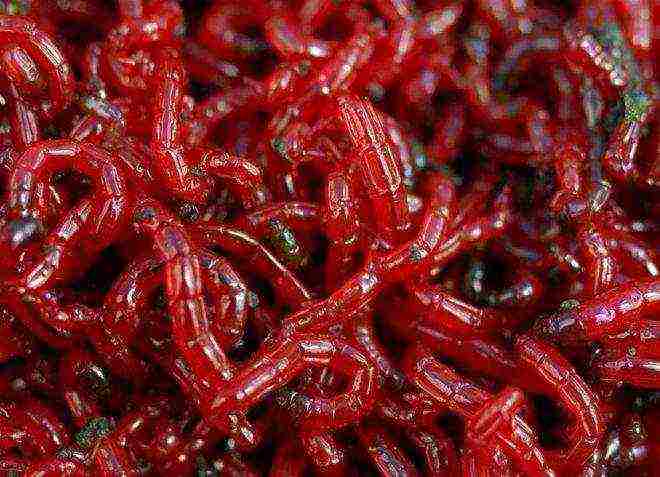

Types of live food for aquarium fish
The organization of food serving in the form of live food for aquarium fish is a good option: it is natural, not subject to processing, devoid of any harmful ingredients, saturated with protein, it has a harmonious ratio of all incoming elements. There are several types of live food for aquarium fish:
- Bloodworm (mosquito larvae), healthy food, contains up to 60% protein.
- Pipe worker (annelid worm), has the greatest nutritional value.
- Daphnia (freshwater crustacean), recommended for feeding juveniles.
- Artemia (a crustacean living in salt water) is able to reproduce quickly.
What live food is best for fish?
Choose food based on the preferences of the inhabitants of your aquarium, focusing on its quality and nutritional characteristics. It is advisable to provide pets with a variety of species, the amount of nutrients and elements necessary for the formation of skeletal and muscular systems, they differ. Aquarium lovers prefer live food for bloodworm fish, attributing to its advantages the presence of a large percentage of protein and hemoglobin.
Which aquarium fish need live food?
Live food for aquarium fish is necessary for fry, it helps them to grow viable, with well-developed immunity, and prevents the occurrence of diseases in the future. Various combinations of living organisms are used to feed carnivorous predators and omnivorous fish, they are especially recommended for pets weakened after illness and during the spawning period. There is a list of breeds of aquarium fish that cannot live without natural food:
When choosing different fish species for living in an aquarium, consider their needs for different types of food, ensuring the kind that is characteristic of these representatives of the aquatic world. Don't expect the fish you choose to adapt to the food you offer them. Some types of aquarium pets do not accept dry types of food as food, so the aquarist, when deciding on the choice of individuals inhabiting the aquarium, must be sure that the animals are provided with live prey all year round.
How to feed your fish with live food?
It is interesting and funny to watch the feeding process, you just need to familiarize yourself with how often you can feed fish with live food without harming them. Pour this type of food to pets every other day, dividing the daily portion by 2-3 times. During the first falling asleep, the fish actively absorbs the offered food, if you see that the appetite has noticeably decreased, you can finish feeding.
All living organisms tend to bring infected bacteria with them into the aquatic environment, this is facilitated by the natural environment in which they are obtained. The best way to keep the aquarium dwellers from the possibility of contamination is to freeze the food before consumption, this method helps to kill a number of harmful bacteria. Pet stores sell frozen briquettes, consisting of mixes of several types of living organisms.
How to store live food for aquarium fish?
The positive points when choosing natural food crops are undeniable, but you need to know how to store live food for fish, protecting it from loss of quality and useful properties. Storage conditions directly depend on the type of living elements used, the initial state and the number of stored living cultures. Aquarists procure these feeds in three well-known ways:
- Freezing. Feed in this form can be purchased in ready-made briquettes or frozen independently, nutritional qualities are preserved in them for up to 6 months. The inconvenience of storage can be attributed to the need to keep them in the freezer, next to the food, not all people like it.
- Drying. This method is durable, but some nutrients lose their value during processing. Self-drying is carried out in the oven, such food can be stored for up to 15-18 months.
- The natural way. It needs containers, a little water is poured into them and the purchased food is placed, storage is possible for a short time (3-7 days) in the refrigerator. So you can store bloodworms and tubifex, their useful properties will remain maximum, but not for long.
DIY live food for aquarium fish
Grown live food for fish with your own hands takes time and effort, but it is justified by the safety that disappears when purchasing this product in a pet store. At home, they resort to the following methods of growing "live food":
- Farmed live plantations cannot be oversaturated with nutritional supplements; rapid reproduction will have a disastrous effect due to a lack of oxygen and an overabundance of waste products.
- Frequent replacement of water in vessels is required.
- Divide the cultivated culture into several containers, if you fail, there is a high probability of recovering the loss.

How to grow live fish food?
It is not difficult to breed live food for fish at home, serious and enthusiastic aquarists know that the efforts made will provide their pets with good health, activity and an attractive appearance. Experts advise growing the following creatures at home:
- Daphnia. These crustaceans breed in settled water with a temperature regime of 22-26 ° C; an aerator is also needed to produce oxygen.To feed them, add yeast, water with blood from the washed meat, vegetable juice (cabbage, beetroot, carrot are suitable).
- Nematode worms. For breeding, they can be collected in humus or last year's foliage, then placed in a container filled with milk mixed with flour, and a piece of wood placed in the same place, on which worms will begin to multiply in 4-5 days.
- Drosophila flies. Place the fruit puree in a closed container, add the oatmeal and yeast and wait for the flies to appear. After a week, their number will reach a volume capable of feeding the entire school of fish.
Very often, in rather heavily polluted reservoirs, the surface of the silt is covered with a multitude of red and thin worms like a crimson carpet. If the aquarium is kept untidy and not well-lit, then similar worms in the world of science, called tubifix or tubifex, also start and breed in it. The tubifex is a type of live food for aquarium fish that is bred at home. But about everything in order below.
Live food tubifix and tubifex
Of course, both tubifix and tubifex are excellent food for aquarium fish after bloodworms. It is recommended to store it in the same way as bloodworm larvae in a saucer of water. It is recommended to change the water at least twice a day. Tubes live for months under such storage conditions. Before feeding, the worm must be cut, otherwise it will immediately burrow into the ground of the aquarium.

When washing tubifix, if the sludge turns out to be dense enough and it is not possible to wash the worm, then the sludge, together with the worms, is placed in a galvanized bucket and poured with cold water. The bucket is placed on a gas stove and heated slowly. Thus, the tubifexes, escaping, float to the surface of the water, where you can easily catch them.
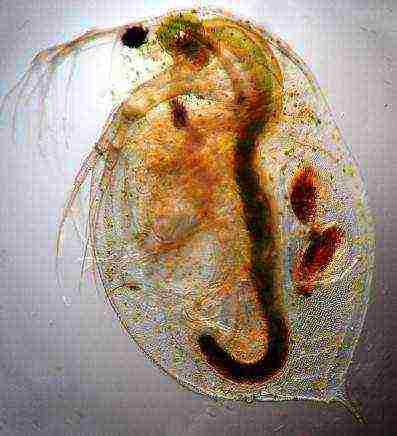
Live food Cyclops and Daphnia
In moderately flowing and stagnant water bodies there is an excellent food for small adult fish and fry - these are various swimming cyclops of crustaceans and daphnia. Translucent and small, they move in the water column, rowing with their antennae-oars. Daphnia cyclops and crustaceans are irreplaceable food for juveniles. The more neglected and dirtier the reservoir, the more and better the food lives in it.
For catching crustaceans, a landing net on a long stick is fitted. For this purpose, it is recommended to make a net bag from nylon silk or perlon. Also, the net can be made in a combined way, namely, its lower part is made of dense calico fabric attached to the hoop. The upper part of the net is sewn from a material that allows water to pass through well, or a nylon stocking is used. For catching large daphnia or cyclops, a gauze net is used.

It is recommended to make the shaft for the net similar to a spinning rod, that is, folding. A stick can be made from duralumin tubes, joints are made on a thread. To transport the caught feed, a can bucket or can is used. If you plan to stock up on dry daphnia or cyclops for future use, then transportation will help you dry them, if you lay the food in a thin layer on a dense cloth, so you will bring more dry food to your home.
Brought live cyclops and daphnia are placed in an enamel basin, changing the water in it from time to time. To do this, it is necessary to strain the upper layer of water through the net, and the dead and settled crustaceans are thrown away. When overconsolidated, cyclops die, thereby becoming unsuitable for feeding aquarium fish. Daphnia and Cyclops should be put into the aquarium as many as the fish are able to eat with one feeding.
The abundant catch of daphnia or cyclops depends on the illumination of the season and time of day, the direction of the wind, the oxygen amount and temperature. Under certain conditions, crustaceans begin to move closer to the shores and surface of the water.
Harvesting live food Daphnia for the winter
If you decide to breed daphnia or other live food at home, then here are some secrets of breeding and harvesting for the winter.
A little dry cow dung is placed in a barrel of soft water and the crustaceans are launched. They are fed with ordinary yeast, while the water is kept in a state of slight turbidity. By drying, daphnia is harvested for future use; at the beginning of summer, large crustaceans are selected for this purpose.
Aquarium fish reproduce and grow poorly if they are constantly fed with dry food, therefore it is recommended to mix vitamin "D" with dry daphnia. No more than two drops of oily solution "D" of vitamin is mixed with one matchbox of dry daphnia. Also, instead of vitamin "D", you can add fish oil to dry daphnia.
Food from powdered dry daphnia is poured into a feeder made of glass tubes floating on the surface of the aquarium. Cyclops and daphnia, as well as bloodworms, can be harvested by freezing for future use.
It is very good to feed aquarium fish with dry food, mixing it with chopped lettuce leaves. Fresh lettuce leaves are also nutritious for fish, but lettuce leaves should be scalded with hot water and cooled before being put into the aquarium.
Live food Gammarus
Gammarus or otherwise amphipod crustacean is considered a tasty food for fish, people also call gammarus mormyshkoy. When dry, gammarus is quite tough and must be ground into powder for fish. In terms of nutritional content, gammarus is rated higher than food consisting of daphnia and, of course, is inferior to live food.

Live food Coretra
Also, along with gammarus daphnia and cyclops, the coretra is nutritious food for fish. Coretra-long, unlike bloodworms, does not bury itself in the sand. These larvae endure all unfavorable conditions. If you catch a carriage and put it in a bundle of ordinary newspaper, then in this form it will live without water for about two hours. It is recommended to store the carriage at a low temperature.

Live food Infusoria
When fishing for cyclops and daphnia, barely noticeable larvae of rotifers and ciliates often fall into the net. They are also called "living dust". "Live dust" is an excellent food for newly hatched fry. It is recommended to feed fish fry with “live dust” no more than two or three times a day. The most important thing when feeding juveniles is to monitor the state of the water.
Live food Artemia
Artemia lives in salt water and in most cases you will not be able to catch it yourself. But you can easily independently obtain brine shrimp nauplii from brine shrimp cysts or eggs. How? Read more about this in the article. Live food. Breeding brine shrimp at home.


