Content
- 1 We select quality grain
- 2 Soak
- 3 On a note
- 4 Germination procedure
- 5 Main indicators
- 6 Eating sprouts
- 7 Sprouting for malt
- 8 Temperature and humidity
- 9 Processes inside the grain
- 10 We evaluate the result
- 11 The main difficulties
- 12 Subsequent procurement
- 13 Instead of a conclusion
- 14 How to grow barley
- 15 Barley varieties
- 16 Soil preparation and fertilization
- 17 Sowing site requirements
- 18 Barley crop care
- 19 Storing unripe barley
- 20 Barley growing conditions
- 21 Sowing barley
Few have ever done seed germination at home. And even those who decide to try it usually choose wheat as it is cheap and readily available. But it is far from the only one on the grain market. But people remember barley only in association with malt and beer. And completely in vain, because a small grain contains a huge amount of vitamins and minerals that our body needs. Today we'll talk about how to germinate barley. Perhaps for some, this will be the first step towards changing life and eating habits.

We select quality grain
Everything is very simple here. By purchasing grain from the market, you can get a spoiled product, grain with mold or treated with special compounds that do not allow germination. The latter technique is used when barley prepared for animal feed is poured. Even if the grain is damp, it will not sprout and spoil. But in our case it does not fit at all.
Any grain must be carefully examined and selected. Using low-quality grain, you get a small yield of the required product, that is, you are wasting time. So, there are a few rules to consider:
- Use barley that has been harvested no more than 2 months ago.
- It will not be superfluous to check it for germination. To do this, you need to soak about 100 grains from different batches. This gives the germination percentage. Practice shows that it is better not to use grain with an indicator of less than 90%.

Soak
It is important to carefully study the question of "how to germinate barley" before you move on to practice. At first glance, the question is not too difficult, but there are pitfalls that can deprive you of a good half of the seedlings.
So, the first secret: you must first soak the grain in water at room temperature. To do this, follow these steps:
- We put the grain in a container and fill it with water so that it completely covers it.
- We remove floating grains and debris, after which the water must be drained.
- Re-fill the grain with cool water.
- Disinfection. Since it is quite troublesome to germinate barley, you need to take care that the seedlings are not spoiled by mold. The simplest processing helps make the barley more resistant. Iodine or ordinary potassium permanganate can be used as an antiseptic. For 10 liters of water, you only need to add 30 drops. The solution must be poured into a container with grain and kept for at least 3 hours. This does not affect germination, but makes it possible for most of the grains to give strong, excellent shoots.

On a note
If you are wondering how to germinate barley, remember: correct and long-term soaking is the most important secret. It must be kept for at least 48 hours. During this time, you need to change the water every 6-12 hours and remove residual debris. Cold water is needed so that the grain does not start sprouting ahead of time. This procedure will create conditions for germination.
Germination procedure
You will need to prepare a wide drawer or tray. Its size depends on the amount of grain. Layer thickness - no more than 6 cm. The washed wet grain is carefully distributed over the bottom of the tray. Be sure to cover it with a cotton cloth on top. It will not allow water to evaporate, but it will also not interfere with ventilation. For this purpose, you can apply a stretch film, in which you need to make cuts. The first method is preferable, since it makes it possible to moisten the grain without removing the covering material and without disturbing the microclimate.
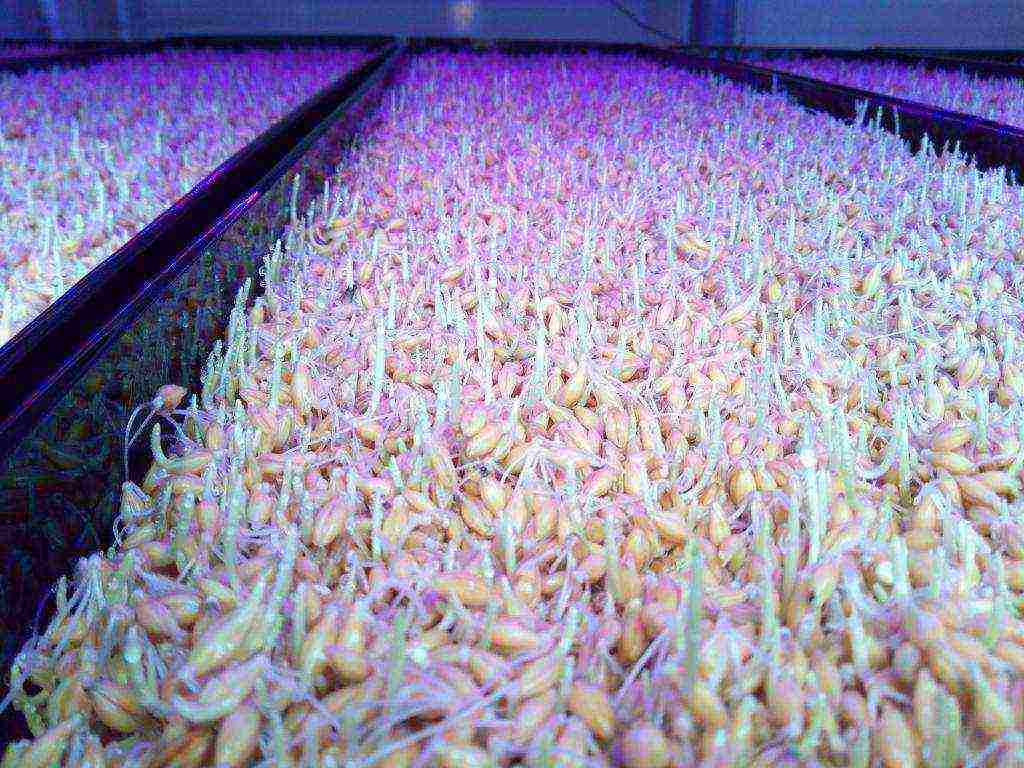

Main indicators
When talking about how to germinate barley at home, two points are important. The grain will hatch only at the optimum temperature and with sufficient moisture. The germination process should take place at a temperature of about 20 degrees. In this case, it is necessary to stir the grain every day and spray it with water from a spray bottle. Check the moisture content of the covering material and do not allow it to dry completely.
Basically, this is all you need to know about how to germinate barley at home. Usually, you can see the first shoots already on the 2-3 day. How long should the grain be aged? It depends on the goals you are pursuing.
Eating sprouts
The maximum benefit lies in sprouts that do not exceed 5 mm in size. After the barley grains have germinated, they must be rinsed in cool water. It is best if you eat them right away. If any unused sprouts remain, refrigerate them to slow growth. Strongly germinated seeds are tough and taste bitter. Be sure to rinse them before eating. Now you know how to germinate barley for food. But there are other ways to use it as well.
Sprouting for malt
In order to activate the processes that are dormant in each grain, a soaking procedure is used. In fact, it mimics spring, when melt water and sun stimulate the grain to grow. We've talked about how to properly germinate barley for food, but it's also used to make malt. In this case, the conditions need to be changed slightly.

Temperature and humidity
To start germination, low humidity is required, about 40%. That is, the grains are slightly moistened and remain in this state until the moment the embryo begins to develop. Now you need to increase the humidity to 50%. This is achieved simply, you just need to increase the frequency of spraying. This is important information for anyone looking for options on how to germinate barley for malt. In this case, it is required to control the humidity much more carefully.
The physiological processes during germination are also seriously affected by temperature. Ideally, it should be 14-15 degrees. At lower rates, development will slow down, and at higher rates, it accelerates and occurs unevenly. The duration of this process is 6-7 days. If all recommendations are followed, good malt germinates. Most believe that the warmer it is in the room where the grain is germinating, the faster it will germinate. But in order to get high-quality sprouts, you must adhere to the described rules.
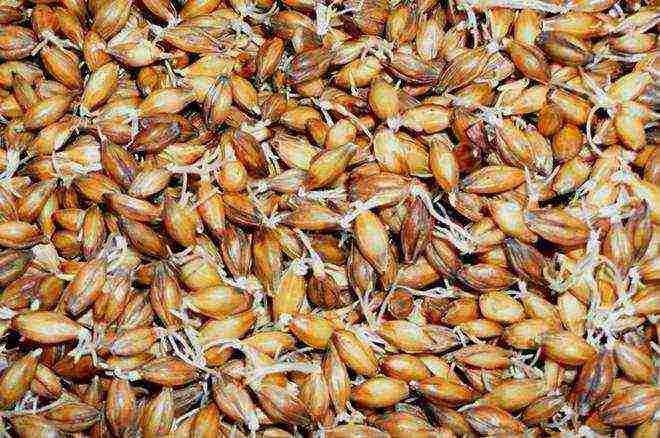

Processes inside the grain
To understand well how to germinate barley grains, you need to imagine how the embryo develops. He first breaks through the fruit and seed membranes, and then moves between them and the dorsal colored membrane. With artificial germination, the embryo develops only to a certain size. If the temperature is higher, the germ sprouts from the top of the grain, which reduces the quality of the finished malt.
We evaluate the result
At the end of the germination process, the malt can be judged by its appearance. And first of all, you can appreciate the smell. The fresh cucumber aroma suggests that everything is done correctly. But the sourish fruity one allows us to conclude that the malt sprouting was done incorrectly.Most often this is too long soaking and excessively abundant irrigation. Do not forget that for proper growth and development, grains need a little and constant moisture. If the material is overdried, life in it will cease. At the same time, one should not forget that if the moisture is excessive, then it is fraught with decay and mold growth.
The appearance of brown, wilted sprouts indicates that they are sorely lacking in moisture. The increased fragility of the sprouts is the result of unsatisfactory work of the tedder. The sprouts must be turned over several times every day.
The main difficulties
When barley germinates during the first four days, its chemical composition changes significantly. Based on this, it is necessary to control the appearance of the germinated grain and the degree of its infection with microorganisms. This can usually be assessed fairly easily by the color of the grain. Bright, green spots, black or red specks are a sign of bacterial infection. That is, you need to process the entire batch of grain, otherwise you will not get sprouts that are suitable for human consumption. The situation is similar with the batch that was intended for the production of malt.

Subsequent procurement
Since it will not be possible to germinate barley seeds at home too quickly, it is logical to make a larger batch at once. If the sprouts are intended for food, then the leftovers are put in the refrigerator, where they can be stored for much longer. And the finished malt is dried. In addition, by changing the drying phases and temperature conditions, you can get raw materials that give the drink a unique taste and color. This applies to both kvass and alcoholic beverages.
Instead of a conclusion
Today a healthy lifestyle is becoming more and more popular. And without enough vitamins and minerals, it is difficult to imagine the right diet - the basis of the basics. To do without pharmacy vitamin complexes, you can use sprouted grain. This is a real pantry of the most important trace elements. Moreover, any grain has useful properties, be it buckwheat, legumes or wheat, oats or other cereals. The principle of germination is the same for any of them, so if you master this technology, you can easily provide yourself with fresh sprouts every day. There is evidence that the daily consumption of one spoonful of fresh sprouts gives the body a full set of trace elements for a whole day.
Barley is one of the most common grain crops. If you want to grow it yourself, be sure to read our article. You will learn all about plant varieties and growing conditions.
A detailed description of the technology of sowing, care and harvesting will help to cope with the cultivation of a grain crop, and you are guaranteed to get a rich grain harvest at home.
How to grow barley
Among grain crops, barley is considered the earliest ripening, so you need to know exactly how to grow it at home to get a good harvest.
When cultivating this culture, you need to take into account some features: requirements for soil, heat, humidity and lighting.
Growing conditions
Correct seeding is key to getting a good harvest. The main condition for high seed germination is early sowing. Due to the moderate temperature regime and sufficient humidity, the culture germinates evenly and quickly gains green mass.
Due to the structure of the root system, it is demanding on soil fertility. The area for sowing must be fertilized in advance and cleared of weeds. The best predecessors of the crop are considered to be potatoes, corn, winter crops and legumes.
Growing technology
Sowing begins in the first week of spring field work. If planting is carried out later, the sprouts can be damaged by diseases and pests, and the volume of the crop will decrease. Despite the fact that the narrow-row and the row method are used for sowing, the priority should be given to the first one.
Note: With narrow-row sowing, the row spacing is only 7.5 cm. This allows seeds to sprout more closely and practically simultaneously, and the high plant density prevents weeds from growing.
Using the narrow-row method, it is necessary to strictly observe the sowing rates, since too dense plantings will negatively affect the quality and quantity of the crop. Depending on the region, the following standards are used:
- Far East and Non-Black Earth Zone - 5-6 million per hectare;
- Central strip and Chernozem zone - up to 5.5 million grains per hectare;
- Urals and the Volga region - 3.5-4 million seeds per hectare.
The sowing depth also plays an important role. If the seeds are close to the surface of the soil, they will begin to germinate unevenly, and if the seeds are placed at a greater depth, some of the sprouts will die without ever breaking through to the surface.
The average sowing depth depends on soil and climatic conditions. For arid regions, it is 6-8 cm, for sandy soils - 5-6 cm, and for heavy clay soil - no more than 4 cm.
The cultivation technology with all stages is shown in detail in the video.
Types of barley
For human consumption and the preparation of feed raw materials, only cultivated varieties are used. They are of several types (Figure 1):
- The two-row one brings only one spikelet, and the lateral shoots do not yield;
- Multi-row - a plant with multiple ears. Differs in high productivity and drought tolerance;
- The intermediate one forms from one to three ears. This species is considered a rarity for our country, as it is found only in some regions of Asia and Africa.
Figure 1. The main types of culture
In addition, a classification by species has been adopted depending on the nutritional value. Grain 1 is used for the production of cereals, and the second - for the preparation of malt and animal feed. Additionally, it is divided into winter and spring (it differs in terms of sowing, germination and yield).
Where is barley grown in Russia
It is difficult to unequivocally determine where barley is grown in Russia, since this grain crop is considered one of the most widespread in the world.
Note: In the world, it ranks fourth in terms of crop area, second only to wheat, rice and corn. In Russia, it is the crops of this plant that occupy a leading position due to the undemanding culture.
The culture is grown everywhere in Russia. The only exceptions are the northern regions (the northern border of crops passes through the latitude of the Kola Peninsula and Magadan). In general, the undemanding culture and varieties specially bred by breeders make it one of the best for cultivation in the Russian climate.
Barley varieties
Due to the wide variety, novice farmers often have the question of which plant variety to choose. In this case, you need to be guided not only by soil and climatic conditions, but also by the level of yield and the characteristics of certain varieties.
Below are the characteristic features of the best varieties of barley for cultivation in the Russian climate.
Barley variety in memory of Chepelev
The Chepelev memory variety was created by breeders by crossing several varieties. The main feature of the variety is that it was created specifically for cultivation in the climate of Siberia and the Urals (Figure 2).

Figure 2. Variety of Chepelev's memory
In addition, the crop has good acclimatization to different growing conditions and has a stable yield regardless of soil, temperature and lighting conditions. Also, the variety effectively resists drought, and although they are considered mid-season, the shoots are highly resistant to diseases and pests.
Description of the variety of barley Bogdan
This variety is one of the subspecies of grain crops. Such grain is used primarily for the manufacture of animal feed.
A characteristic feature of the variety is that it can not only be grown in the field by sowing, but also found in the wild. It is most commonly found in arid regions. The culture is valuable due to its unpretentiousness, and high yields and quality of grain make it possible to produce nutritious and fortified animal feed based on it.
Maned barley planting and care
It is rather a decorative culture that is actively used in landscape design. The plant has soft stems that end in lush tassels (Figure 3).
Note: During the flowering period, it is better to pluck the brushes in order to prevent self-seeding.
Planting and caring for the crop is very simple. Since it is unpretentious, it is enough to sow it in the garden just once. Further care only involves removing the tassels during flowering, but even if the crop spreads through the garden it will be easy to remove. The root system is shallow, so the plant is very easy to pull out from the roots.

Figure 3. Maned barley: photo
Crops can not be fed, but in the spring, after the first shoots appear, it is advisable to remove weeds, and in dry weather organize regular watering.
Soil preparation and fertilization
The soil for sowing is prepared in the fall, immediately after the harvest of the predecessor. The soil is dug up and measures are taken to keep the snow cover. This helps to saturate the soil with moisture before spring sowing.
See also: How to grow wheat at home
In the spring, immediately before the introduction of seeds into the soil, additional shallow loosening is carried out, which allows the soil to be saturated with moisture and air.
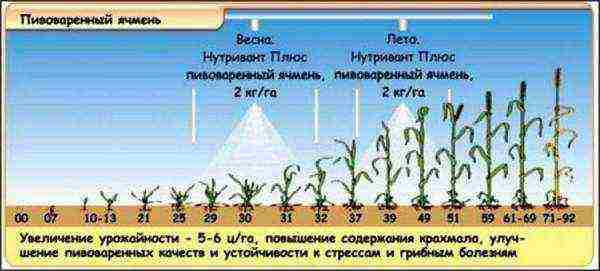
Figure 4. Fertilizing crops at home
Timely fertilization plays an important role in obtaining good yields (Figure 4). Since the culture is demanding on soil fertility, fertilizers are applied in autumn and spring (again).
Note: After the emergence of seedlings, it makes no sense to fertilize the plants, since they will not be able to fully absorb the nutrients.
To strengthen the roots and form large ears during autumn plowing and directly during sowing, phosphorus and potash fertilizers are applied. It is important that the plant responds better to mineral than to organic fertilizing.
Sowing site requirements
Despite the fact that the crop is grown in all climatic zones, it is demanding on the level of soil fertility. If the soil is acidic, young shoots may stop growing or even die, and with high humidity, the culture is affected by rot and fungal diseases.
Lighting
Plants require good lighting for normal fruiting. If the area is poorly lit, the plants will develop slowly and the ear formation will be delayed.
This condition is relevant not only for mid-ripening, but also for early varieties, therefore, the areas for sowing should be well illuminated throughout the day.
Barley: heat requirements
The culture grows well in all climatic zones, regardless of the temperature regime. Thanks to early sowing, young shoots are frost-resistant and yield high yields.
In addition, it belongs to one of the earliest grain crops, and the timing of sowing and germination allows shoots to grow stronger before the first weeds and pests appear.
Humidity
The culture tolerates drought well, and excess moisture can cause root rot and provoke fungal diseases. Plants need most of the liquid at the stage of going into the tube and at the beginning of the formation of ears.
A strong lack of moisture, like its excess, at the initial stage of plant development leads to the formation of sterile shoots or causes the death of plants.
Barley crop care
Caring for crops includes only a few activities, since this grain is considered unpretentious:
- In arid regions and in areas with light soils immediately after sowing, rolling is carried out, but if a crust appears on the surface of the soil, it is necessary to carry out surface transverse harrowing.
- In the later stages of cultivation, already in the ripening phase of the grains, a supplement is introduced, which helps to increase the amount of protein in the product.
- During the growth of culture use herbicides to control weeds, and special preparations to prevent lodging of crops.
It is also necessary to regularly inspect the field, and if pests or their larvae are found, spray it.
This video will show you how to grow crops hydroponically at home.
Storing unripe barley
The main purpose of grain storage is to preserve their nutritional value and germination ability. Small quantities of crops can be stored on the floor in barns or sheds. The main condition is that the room must be dry and clean, and the interior must be well ventilated (Figure 5).

Figure 5. Methods for storing grain
Varietal seeds intended for sowing are stored in dense fabric bags. In such a container, the seeds consume less oxygen and retain the ability to germinate.
See also: Methods of dealing with diseases and pests of barley
When storing grain, moisture and temperature are especially important. The moisture level should not exceed 12%, otherwise the raw material will start to rot and become moldy. The temperature should not exceed 10 degrees. With an increase in this indicator, microorganisms begin to develop in the storage, capable of destroying the entire crop.

One of the most effective green manures is barley. It is planted both before winter and in spring, the grains of this culture sprout quickly and well-rooted seedlings are not afraid of frosts. In addition, these are winter crops, which, after sowing in autumn, can be used in spring. Barley is undemanding to growing conditions, but it is strongly influenced by the nutritional value of the soil.
This culture perfectly structures the soil, destroys many types of weeds and quickly forms a green mass in the spring. In addition, barley has a special property - in comparison with other cereals, it perfectly withstands drought. For this reason, it is desirable to grow barley in arid regions as green manure. He develops well with early spring planting, with winter sowing, it can withstand without shelter (without snow) a drop in temperature to 5 degrees below zero. Seed consumption per 100 m2 - 1, 8-2 kilograms. You can mow the green mass of barley 1-1.5 months after sowing.
Buried roots and vegetative mass of barley inhibits the growth and development of weeds... The greens of this culture contain as many minerals as animal waste. In the soil, barley decomposes quickly and immediately supplies the plants with essential nutrients. With the help of the greenery of this culture on the site many beneficial microorganisms develop... In addition, it reduces acidity, increases the permeability and moisture content of the soil. The beneficial influence of this green manure continues for 4 years.
Barley growing conditions
Temperature. Seeds can be sown in early spring after the soil warms up to 1-2 degrees Celsius, viable shoots are formed at 4-5 degrees Celsius. But at these temperatures, the emergence of seedlings is prolonged, the most suitable growth temperature is 15-20 degrees. Barley, sown before winter, does not tolerate winters with little snow, with severe frosts, stagnant waters and sudden spring temperature changes.
Seedlings not covered with snow can withstand short-term frosts up to 8 degrees. In the later stages of growth, resistance to low temperatures decreases. Adult barley is damaged by frosts of 1-2 degrees, if grain has formed, then it is unsuitable for brewing beer.
Humidity. Barley - better than other spring crops withstands drought. But moderate temperatures and normal humidity favor the formation of many shoots. This crop requires the most moisture during booting and earing. In arid conditions, it forms more grain, but due to a weak root system, less green mass.
Pick-up locationThe most important condition for obtaining a large amount of barley is the selection of predecessors suitable for this culture. When growing winter barley, rapeseed, early potatoes, peas showed themselves well. For spring crops, crops that leave a lot of nitrogen in the soil are best. Fertilizers of organic origin are applied to the soil only when its fertility is low; most often, barley is sown after row crops that require feeding with fresh manure. Mineral fertilizers are favorable for both spring and winter barley, potash and phosphorus fertilizers are applied during autumn plowing of soils, nitrogen during pre-sowing cultivation.
Barley subspeciesVarieties of barley - multi-row, two-row and intermediate.
In a multi-row crop variety, grains are formed in all spikelets. There are two groups of this subspecies:
1. With six-row regular caryopsis;
2.With the wrong ones.
Spikelets of the first type are hexagonal, dense and hard, the second type outwardly resembles a quadrangle and are located slightly incorrectly.
Two-row barley became so called for the reason that one of the three spikelets is female, and a caryopsis is formed from it. "Male" spikelets are outwardly only scales. The cultivation of this type of barley is practiced in large areas, the appearance of an ear can be seen in the photo.

The intermediate subspecies of the culture grows 1-3 spikelets, the final number of grains also depends on this.
Most often, multi-row barley is grown.
Sowing barley
Winter barley is grown, usually in areas with a mild climate. Its main advantage is a short period from sowing to harvest, it lasts 2-4 months. For this reason, after it you can grow crops with a short growing season. Or this area will be able to "rest" more time, which will better prepare it for the next season. The timing of sowing seeds is calculated taking into account the variety and climatic conditions of the region. For him, not only the sowing site is important, but also the weather conditions of the planting area. Most often, the planting date for this culture is the second decade of September.
Barley will grow well after crops such as legumes, sunflowers and forage grasses. After growing the previous plant, the site needs to be fenced to a depth of 7-10 cm in order to process the remaining weeds and roots of the previous "owner".
Seed material is pre-sorted. Seeds intended for sowing are treated with substances that destroy pathogenic microorganisms. Sowing is carried out with seeders, after which it is necessary to roll the soil. In late autumn, if a little snow has fallen, operations are performed to exterminate rodents and retain snow. After the snow melts in the spring, the site is fertilized and sprayed with compounds intended for the extermination of weeds.

Spring barley - a cereal plant that can develop very quickly. It is classified as a crop that requires very early sowing in the spring. If the start of work is delayed by 2-3 days, you can lose a large amount of the crop. The soil is prepared for it in the same way as before sowing winter barley. Seeds are sown in a narrow-row or row method. Only for this culture, the free space between the rows is reduced.For the friendly appearance of seedlings, it is necessary to sow them in moist soil, to the same depth after sowing, the site is rolled without fail. If you do not perform this operation, then some plants will appear earlier, the pecking of others will be delayed, they can sit in the ground even before the first rain.
Before sowing, the seed is treated with compounds from diseases and pests and the seeds are sorted.
Spring barley is sown very early - this can happen even in February, so weeds do not pose a great danger to it - they simply do not have time to break through and grow. But when sowing at a later date, it is necessary to carry out work to combat weeds. During the development of barley, it is advisable to feed the crops with mineral fertilizers.
Barley is an agricultural plant that satisfies not only food and feed needs, but also technical purposes.
Barley is grown for grain, green manure and as a fodder base for livestock.
A grain of barley, a nutritious product, a cereal from which cereals, flour and even a coffee drink are obtained during processing. Barley grain is actively used in brewing, but barley flour is rarely used for the production of bakery products, due to the low level of gluten, which adversely affects the quality of bread.
The content of the article:
- Description of the plant
- Highly productive varieties of barley
- Growing barley: for grain or green manure
- Barley planting care
- Barley for grain and green mass, harvesting and storage
Description of the plant
Barley is a crop that is massively cultivated for grain. Barley grain is the basis of nutrition for the livestock and poultry industry.
Barley unites more than 35 species, wild and domesticated forms.
The culture has been known since ancient times, its age is about seven thousand years. The first was cultivated two-row cultural form of barley, the plant found wide distribution in Mesopotamia and ancient Egypt, and from these countries migrated to Europe.
 Two-row barley has two forms: spring and winter. Botanical characteristics are represented by a thin erect stem, about half a meter high, golden or brown ears of linear, flat shape, with awns diverging in different directions. Osti are represented by three-horned lobed appendages - furkat spike.
Two-row barley has two forms: spring and winter. Botanical characteristics are represented by a thin erect stem, about half a meter high, golden or brown ears of linear, flat shape, with awns diverging in different directions. Osti are represented by three-horned lobed appendages - furkat spike.
But there are ears without awns. Three ears located on the ledge of the rod are different: the middle one is one-flowered, bisexual, fertile. The grain is filmy, golden in color, is actively involved in agriculture in Europe and Asia.
Six-rowed barley, which is considered to be the homeland of Asia, is represented by a one-year spring crop. Spikelets are light yellow, brown, rarely black, differ in density, shape and size, spinous and without.
 The ledges of the stem are crowned with fertile single-flowered ears, hexagonal or tetrahedral. The grain is filmy, with a classic yellow color. The culture shows excellent qualities of resistance to weather anomalies: drought and low temperatures.
The ledges of the stem are crowned with fertile single-flowered ears, hexagonal or tetrahedral. The grain is filmy, with a classic yellow color. The culture shows excellent qualities of resistance to weather anomalies: drought and low temperatures.
For these qualities, barley has won recognition all over the world.
The productivity of barley is high, the culture is not demanding for heat, it is drought-resistant and is not afraid of cold weather, it grows on any soil, including acidic soils.
The plant is early ripening, ripens 70-90 days after sowing. After the formation of the panicle and during the ripening of the grain, it is picky about the presence of sunlight and heat.
During the ripening of the grains, barley is able to withstand temperatures up to 45 ° C. With such a hardy feature, the plant differs from other cereals, however, when pouring ears, the plant needs an additional source of moisture and nutrition.
 The most suitable soil for the cultivation of barley are neutral loams and deep-tilled chernozems.In general, barley is such a culture that calmly tolerates all the hardships associated with weedy, slightly enriched or acidic soil.
The most suitable soil for the cultivation of barley are neutral loams and deep-tilled chernozems.In general, barley is such a culture that calmly tolerates all the hardships associated with weedy, slightly enriched or acidic soil.
Selective work on improving the barley culture continues, new varieties of barley, bred by domestic and foreign breeders, have introduced completely new characteristics into the culture.
Low lodging threshold, resistance to fungal and putrefactive infections, increased productivity, breeding of new, dwarf varieties, became possible by selecting and crossing the best varieties of barley, which have proven themselves more than once.
The obtained rainfed varieties of barley are several times more productive than wheat, and the amount of harvested grain does not stop at 3.5 tons per hectare, but is constantly increasing.
Highly productive varieties of barley
The variety of varieties and forms of barley makes it possible to choose the type that will bear fruit with dignity in your region.
Priazovsky variety
 One of the most common varieties in Russia, it shows amazing vitality, is not capricious, it gives yields even on unenriched soils. Ripens in 3 months, resistant to lodging, fungal infection, cold-resistant. It is cultivated in the southern regions of Russia and in the middle lane. It is used as food raw material, as well as for livestock feed. About 65 centners of grain can be obtained from 1 hectare. arable land. The mass of 1000 grains reaches 60 grams.
One of the most common varieties in Russia, it shows amazing vitality, is not capricious, it gives yields even on unenriched soils. Ripens in 3 months, resistant to lodging, fungal infection, cold-resistant. It is cultivated in the southern regions of Russia and in the middle lane. It is used as food raw material, as well as for livestock feed. About 65 centners of grain can be obtained from 1 hectare. arable land. The mass of 1000 grains reaches 60 grams.
Variety Viscount
Hybrid variety, upright plant. Ripens in three months after sowing. The mass of 1000 grains ranges from 50 to 80 grams. The yield of feed grains is high. Viscount is used in brewing. Barley grains of this variety have a high protein content of about 12%. Shows resistance to fungal diseases and rot, temperature changes. The average yield is about 65 centners per hectare. Sowing dates begin in early spring, as soon as the snow melts. Grain consumption per hectare is approximately 4-6 million seeds; in arid regions, the density of crops increases.
Barley variety Helios
 High germination, unpretentiousness to soil. In conditions of high humidity, it gives excellent grain yields. In terms of botanical characteristics, it is similar to the Vakula variety. Ripens in 3 months, yields high quality grain. With a seeding rate of 3.5 million grains per hectare, about 88 centners can be harvested.
High germination, unpretentiousness to soil. In conditions of high humidity, it gives excellent grain yields. In terms of botanical characteristics, it is similar to the Vakula variety. Ripens in 3 months, yields high quality grain. With a seeding rate of 3.5 million grains per hectare, about 88 centners can be harvested.
Barley grade Mamluk
The variety is early maturing, productive, with high germination. Resistant to many forms of fungus, short-term drought.
It appears in the list of highly productive and valuable varieties of the country.
Grown for forage, processed into cereals. Compliance with agrotechnical measures when sowing the Mamlyuk variety excludes the development of rust and fusarium, but its tendency to lodging negatively affects the harvesting and yield of grain, therefore, it is not worth delaying the collection of barley. He achieved his popularity thanks to the high yields obtained in the Stavropol and Krasnodar regions. The yield per hectare reached 72 centners, with 4.3 million seeds sown.
Duncan variety
 The Canadian barley variety has gained its wide distribution due to high yields, with low costs of sowing material. Seedlings come together, the ears fully ripen in 2.5 months and give up to 84 centners of high-quality grain per hectare.
The Canadian barley variety has gained its wide distribution due to high yields, with low costs of sowing material. Seedlings come together, the ears fully ripen in 2.5 months and give up to 84 centners of high-quality grain per hectare.
The sowing rate of the Duncan variety is 2 million grains per hectare. In no case should the crops be too thickened, this will have a detrimental effect on the development of the ear. Duncan is unpretentious, cold-resistant, has good resistance to putrefactive infections.
Barley variety Vakula
Good yields and high adaptability to climate change. The variety is highly productive, the grain yield reaches 85 centners per hectare. The germination of grains reaches 95%, the protein content is 8%, the sowing rate is 2-4 million per hectare. It should be borne in mind that crops that are too thickened will not produce grains of high quality and caliber.
Growing barley: for grain or green manure
Barley is good because it gets along with most crops; in many subsidiary farms, it is grown with chickpeas, lentils, peas, rapeseed and wheat. When cultivating industrialists, they resort to methods of intensive farming of barley.
 It is not recommended to grow barley in the same place for more than three years in a row. Agrotechnology implies compulsory observance of crop rotation; cereals, green manures, and potatoes will become quite tolerable predecessors of barley.
It is not recommended to grow barley in the same place for more than three years in a row. Agrotechnology implies compulsory observance of crop rotation; cereals, green manures, and potatoes will become quite tolerable predecessors of barley.
Legumes can be considered as a precursor only when barley is grown for feed, but for brewing the crop obtained after legumes is not suitable, since the characteristics of the grains will decrease due to abundant tillering.
At a temperature of +1 degrees, crops begin to actively germinate.
Barley reaches its peak at a temperature of +21. A young plant can endure short-term frosts at -7 degrees. Barley becomes susceptible to climatic changes during the period of flowering and ear formation. The most resistant varieties are plants from the northern regions.
The soil for sowing is prepared in advance, first, deep plowing is carried out, then cultivation is carried out to get rid of weeds, then organic fertilizers are applied and the soil is harrowed. Before harrowing, phosphorus-potassium fertilizers, about 45 kg, are applied to enrich the scarce soil. per hectare of arable land.
Before harrowing, phosphorus-potassium fertilizers, about 45 kg, are applied to enrich the scarce soil. per hectare of arable land.
Barley sowing time is the first half of spring, as soon as the tractors can enter the field. Sowing on a personal plot is done manually. On an industrial scale, mechanized, with grain seeders, with a row spacing of 15 cm.
The method has drawbacks; at 100% germination, the crops thicken. The solution is the increased distance between the grains up to 1.2 cm, at a seeding rate of 4.5 million grains.
For sowing, use only large, seed material with high germination. Before planting, the seeds are treated with fungicides and treated with stimulants for effective growth.
Planting dates for winter barley vary depending on the region of cultivation and are carried out from September to October.
The standard seeding rate is considered to be about 165-215 kg. per ha. This is approximately 3.5-4 million grains. Varieties prone to tillering and lodging are sown in smaller volumes.
Barley planting care
Barley is an unpretentious and hardy crop, but, like all agricultural crops, it requires adherence to agricultural technology.
If the arable land after sowing is covered with a carpet of weeds or has a crust through which it is difficult for young plants to break through, it is recommended to carry out harrowing.
If the situation is different and weeds are already advancing on the seedlings, harrowing is carried out along the seedlings, it is not recommended to carry out the procedure with a low density of crops. The barley garden is cultivated by hand. Herbicides aimed at killing weeds are rarely used, as they adversely affect the germination and growth of crops.
But top dressing is welcome, and on scanty soils you cannot do without them at all. Top dressing is carried out by spraying fertilizers. At the beginning of the growing season, nitrogen fertilizers are applied, during the formation of an ear, phosphorus-potassium fertilizers.
 Barley does not need regular irrigation if it is cultivated in a temperate region; in arid regions, irrigation is established to increase yields. For example, irrigation techniques increase the germination rate, and in the process of ear formation, increase the yield by almost 47%. Agronomists still recommend watering cereals 2 times during the growing season.
Barley does not need regular irrigation if it is cultivated in a temperate region; in arid regions, irrigation is established to increase yields. For example, irrigation techniques increase the germination rate, and in the process of ear formation, increase the yield by almost 47%. Agronomists still recommend watering cereals 2 times during the growing season.
The situation is different with barley grown for brewing, these crops are watered only once, during the period of active growth, since late watering for beer varieties can cause the growth of false stems and delay the formation of high-quality grain.
Barley for grain and green mass, harvesting and storage
 Small household barley plantations are harvested by hand, the harvest begins in dry, hot weather, from August, when the grain reaches full ripeness. The harvested headers are subjected to subsequent threshing.
Small household barley plantations are harvested by hand, the harvest begins in dry, hot weather, from August, when the grain reaches full ripeness. The harvested headers are subjected to subsequent threshing.
Industrialists harvest barley using direct and two-phase harvesting. At the time of harvest, the barley grain should not exceed the moisture mark of 20%. Direct combining consists in a one-time harvesting with threshing.
Two-phase combining is used in fields with uneven grain ripening, ears are first mowed and placed in reapers, and then subjected to collection and threshing.
 Barley grown for green mass is harvested by mowing in two stages. The first stage of mowing is carried out before the flowering of barley, about 55 days after sowing, about 50% of the crops are harvested, the second stage of mowing occurs during flowering. After mowing, the green mass is sent to livestock feed.
Barley grown for green mass is harvested by mowing in two stages. The first stage of mowing is carried out before the flowering of barley, about 55 days after sowing, about 50% of the crops are harvested, the second stage of mowing occurs during flowering. After mowing, the green mass is sent to livestock feed.
After threshing, the barley is delivered to elevators for further processing for long-term storage. Wet grain is placed in grain dryers, then poured into storage in riots, granaries or sent for export.
The conditions for granaries are high, because if grain is stored improperly, losses can be up to 35%. Grain masses are thoroughly cleaned and cooled before being sent to storage. Barley can be stored for a long time both in bulk indoors and in bins.


