Content
- 1 Features of zander
- 2 Obtaining fertilized eggs
- 3 Creation of broodstock and breeding of zander in pond farms
- 4 Growing of fingerlings and their wintering
- 5 All about growing pike perch
- 6 Producer fish.
- 7 Spawning.
- 8 Incubation.
- 9 Artificial breeding of pike perch
- 10 On stimulating the maturation of milk and caviar
- 11 Equipment for cages and artificial spawning grounds
- 12 Spawning in artificial nest cages
- 13 Caviar development
- 14 Incubation of eggs
The article provides information on the cultivation of commercial pike perch, the peculiarities of obtaining and incubating zander caviar and other useful information necessary for a successful breeding zander in ponds and lakes.
Features of zander
Pike perch is a valuable commercial fish from the perch family. The body is covered with ctenoid scales. The two dorsal fins are composed of spiny and soft needles. The dorsal fin contains more than 18 branched rays. There are strong canines.
Distributed in large rivers and lakes, in the basins of the Black, Azov, Caspian and Baltic seas.
By way of life, two biological forms are distinguished: semi-anadromous and freshwater. Semi-anadromous pike perch lives in desalinated areas of the seas, and enters rivers for spawning, freshwater inhabits rivers and lakes, where it spawns. It is distributed in Ladoga, Pskov-Chudskoe, Ilmen, White and Onega lakes. In small lakes, it is found mainly in plains, rich in plankton, with a good oxygen regime. Zander is especially abundant in smelt lakes.
Juveniles very early begin to feed on fry of other fish species, but within 1-1.5 months they can completely feed on invertebrate crustaceans and overgrown forms of chironomids, growing up to 1 gram during this period.

Figure 1. Fish pike perch
Adult zander is a predatory fish. He has a narrow throat and esophagus, so he eats fish with a low back: verkhovka, minnow, char, roach, young bream, rudd, bleak, smelt. It lives and feeds not on the coast, but on the stretch, where it hunts for weed fish. It feeds most actively from May to October and weaker in winter and during spawning.
Pike perch has a high ability to use food and consumes significantly less fish per unit of growth than pike and other predators. This valuable feature of pike perch - to grow quickly and efficiently use food - can be successfully implemented in the practice of fish farms, populating reservoirs with a large number of low-value fish.
In natural reservoirs, in the first year of life, it reaches a mass of 35-37 g, in the second 190-441 g. In ponds, with an abundance of food, it grows much faster than in lakes. In lakes, pike perch of 4-5 years of age has a mass of 1-2.5 kg, old pike perch grow up to 20 kg.
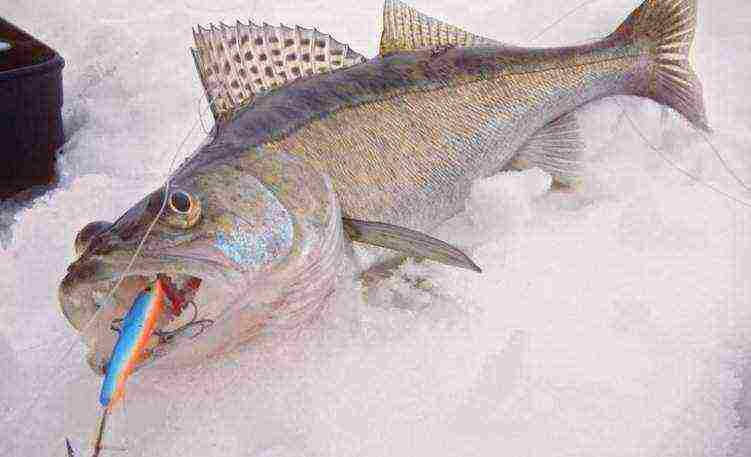
In the photo, a pike perch caught on winter fishing
Puberty in walleye occurs in the third or fourth year. During the spawning period in natural conditions, the pikeperch makes nests. To do this, he usually selects thickets of reeds or cattails in areas of a reservoir with a hard sandy bottom, in which he makes depressions with a diameter of 60-80 cm and a depth of 4-10 cm so that the bottom in these depressions is a living root system of plants. The female lays eggs on it. After spawning, males stay to guard her. They circle around the nest all the time, helping to cleanse the eggs from the settling turbidity.
In steep, washed-out shores, the pike perch does not suit nests, but chooses relatively flat areas in the ledges of such a coast, covered with the root system of plants, at a depth of 0.5 m. As in the nest, the female thickly lays her eggs on them.
Fertility ranges from 82 thousand to 1185 thousand eggs, depending on the size.Pike perch spawns in April - May when the water temperature in lakes is 8-12 ° C on the meadows, in fresh estuaries at a temperature of 12-18 ° C in non-flowing areas. Avoids silted areas. Sticky caviar in the size of 1.25-1.40 mm.
At 15 ° C, the development of eggs lasts 6-10 days, with an increase in temperature, the incubation period is reduced to 5, and often to 3-4 days. The larvae that emerged from the eggs, measuring 3.2-4.6 mm, do not leave the nest for the first 2-3 days. The resting stage alternates with a vertical upward movement and a passive sinking to the bottom, where they remain motionless.
The larvae have a fatty drop, which is consumed within 6-7 days from the beginning of external feeding. The fat droplet provides buoyancy to the larvae, which can swim away with the current for considerable distances.
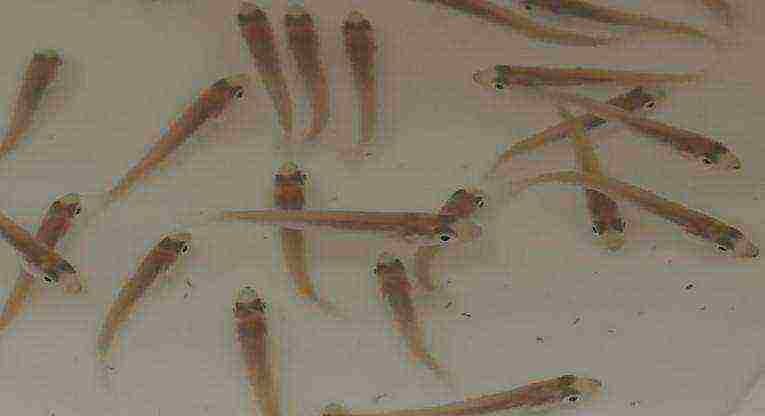
Photo of zander larva
Zander larvae are very demanding on the oxygen regime. The lethal limit for them is the dissolved oxygen content of less than 3 ml / l. Juveniles keep only in those areas where the oxygen content is not lower than 4 ml / l. The lower limit of oxygen content in water, at which pike perch breeders do not show symptoms of oxygen deficiency, is 30% of normal saturation.
The high demand of fish for oxygen regime is observed at all stages of its development. This circumstance should be taken into account when choosing ponds for breeding zander in them.
There are many small lakes and reservoirs in Russia, in which, together with carp as an additional fish, pike perch can be successfully grown in order to obtain a high-quality food product through the use of low-value and trash fish. The cultivation of a two-year-old marketable pike perch is also advisable in feeding carp ponds, in which there is a large amount of trash fish.
The best breeding results can be obtained in non-invasive reservoirs, lakes, ilmen, estuaries, which are stocked and fished once every two years. Good results are obtained with joint cultivation of pike perch with carp and crucian carp.

Photo of zander caught on spinning
The following can be used as fish stocking material for pike perch for stocking water bodies:
- larvae reared in a stocked reservoir from fertilized eggs brought from reservoirs where pike perch is found;
- fry at the age of 40-46 days, reared in spawning and nursery farms or in pond fish farms;
- underyearlings or yearlings of pike perch grown in ponds and lakes.
Obtaining fertilized eggs
Fertilized pike perch eggs can be obtained both through submerged bottom spawning grounds (nests), and by organizing spawning of pike perch in cages, on plant substrates or in nylon bristle nests. Fertilized eggs are obtained with the help of submerged bottom spawning grounds in water bodies in which there are a lot of pike-perch, during its spawning. Pike perch attracted by fresh spawning substrate spawns on them. Then the laid eggs are taken out together with the spawning substrate and transported to pond farms.
Nests for spawning pike perch are arranged round, in the form of baskets made of vines, with transverse partitions. A cord is tied to the middle of the partition, at the end of which a wooden float is fixed, which holds the nest in the bottom layers of water and is a buoy along which a spawning nest is found. To keep the nest in an upright position, weights are tied to it on three sides. Juniper branches, well-washed rhizomes of cattail, calamus, sedge, vines, willow are put as a spawning substrate. You can also use boiled bast or nylon fiber waste.
Cages for obtaining fertilized eggs are made from a brass mesh with a mesh of 10-15 mm. The frame of the cage can be metal or wood 1.2 m long, 1 m wide, 0.8 m high. In the upper part of the cage, in the middle, there is a metal mesh cover on hinges.The bottom of the cage is lined with pre-soaked branches of juniper or spruce, laid in one direction. A layer of branches is loaded with planks so that they do not float. The cage is suspended in a lake, reservoir or in a pond to the scaffold with a cable or nylon rope so that the upper part is submerged at a depth of at least 20 cm from the water surface.
To obtain fertilized eggs, you can use special spawning grounds proposed by the fish breeder P. V. Mikheev for reproduction of zander stocks in lakes and reservoirs. They are arranged in the form of two parallel stretched nylon cords tied at the ends at a distance of 1 m from one another. Nests are tied tightly to the cords every 30-40 cm.
So that the nests are distributed only in the bottom layers of water, do not lie on the bottom and do not rise high from the bottom, to the cords, in addition to the nest, they tie a float above each nest (wooden or from last year's reed), from below, every 2 m on leashes in length 40 cm - load (brick, stones). For the nest, you can use the thin roots of sedge, reed, spruce branches, juniper. Each nest should consist of two cross-linked plant bunches.
The spawning ground equipped on the shore with nests, floats and cargo, as well as seine, is taken into a boat and transported to the installation site. There, first, an anchor (stone 8-10 kg), tied with an anchor rope, is thrown into the water, and then, sailing in a boat, all the spawning grounds are dismissed. At the second end of a well-stretched spawning ground, a second anchor is dropped. At the same time, they make sure that all nests, after getting wet, sink into the bottom layers of water. If they swim on the surface of the water even after getting wet, an additional load is tied to the cords.
The length of the spawning grounds should be 30 m. It is best to establish spawning grounds for zander along the paths of the approach of zander to natural spawning grounds. Such places are usually used by fishermen for commercial fishing for pike perch with fenders. The depth of the spawning grounds is 2-5 m.
In lakes, spawning of farmed pike perch can be carried out in areas fenced off by a palisade with a sandy bottom, where it spawns on mats made of juniper branches. After laying the eggs, these mats are taken out, and the eggs are used for stocking. If lakes, ilmeni, estuaries are stocked with fertilized eggs, it must be pre-incubated. Fertilized eggs are usually transported in May.
The caviar brought in for pre-incubation, after removing the lid and ice from the transport utensils, is sprayed with water from the reservoir for 30 minutes. First, spray it a little, intermittently, and after 10 minutes with a full stream. Spraying is carried out in the shade, in places protected from the wind. Then the caviar, observing all the precautions, is transferred into incubation baskets lined with moist moss, 10-20 thousand eggs each. So that the upper branches with caviar do not press on the eggs lying under them, they should be shifted with special circles.
Incubation baskets, on the bottom of which stones are placed under the moss for the purpose of loading, are hung on laces in pre-selected places so that the bottom of the basket is at a distance of 0.5 m from the bottom of the reservoir, and the upper part is at a distance of 0.5 m from the water surface ... The place where the hatching baskets are placed should be protected from the wind and have a hard pebble or sandy bottom.
The baskets are hung on a stainless wire or nylon cord. The caviar placed in this way is washed from all sides and does not silt. In silted reservoirs, mats with a load should be lowered to the bottom of the site, on which baskets with caviar are suspended, so that the larvae have the opportunity to hide in the first days of life. On a muddy bottom, the larvae will inevitably die.

In the photo, milking of pike perch caviar
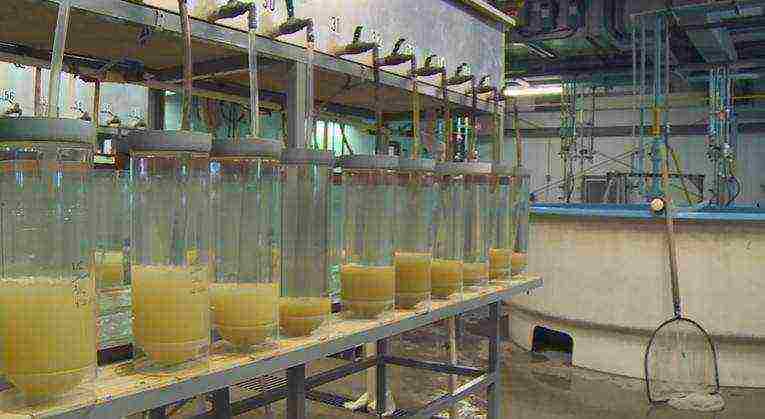

Photo incubation of pike perch eggs with its artificial breeding
Creation of broodstock and breeding of pike perch in pond farms
To create your own broodstock of pike perch, it is necessary to grow from the eggs to the sexually mature state. Zander grown in ponds from the earliest stages of development adapt to the relatively unfavorable oxygen regime of the ponds.
The recruitment of broodstock in such fish farms is carried out by selection of two-year-olds that stand out in growth, weight and exterior from feeding ponds and reservoirs with their planting in a brood pond, in which replacement young animals and pike perch producers are kept in summer and winter.
A brood pond for fish - zander is made at a depth of 2-2.5 m at the dam, the bed is well planned. The pond is lowered only once a year - in early spring to trap broodstock in order to obtain offspring from them. When the pond is lowered, the replacement young growth is temporarily kept in the cages of a pond, followed by replanting it after catching the broodstock.
During the capture, the broodstock are assembled into nests and immediately planted for spawning. The nest consists of one female weighing 2-2.5 kg and two males weighing 1-1.5 kg. Breeders caught from a reservoir or located in wintering ponds or cages are seated in early spring (females separately from males). In the spring, the sex of the producers is distinguished by the following characteristics: the males are narrower, mobile, their abdomen is straight, the color is light, with a golden sheen, with light pressure, the male secretes milk. In females, the abdominal part of the body is swollen, convex, the body color is less light, with a silvery sheen. Older males are selected for spawning. In this case, more fertilized eggs are obtained in comparison with the same-age composition of broodstock.
When breeding under artificial conditions, the injected spawners should be planted for spawning at a stable temperature of 7.5-8 ° C. Where spawning nests are established, one female pike perch and two males are planted for spawning. If the fish has not spawned within 3 days, the producers must be caught, branches replaced and put back for spawning. Such a measure is necessary in case of siltation of branches. Therefore, the cages should be installed in calm places with pebble or sandy, in extreme cases with a clay bottom. On the second day after laying and fertilization, the eggs of the producers are caught and transplanted into ponds.
Spawning of farmed pike perch can be carried out directly in cage ponds with an area of 200-400 m², with a depth of up to 2 m, with a sandy or pebble bottom. The cage is drained in early spring, disinfected with quicklime at the rate of 200 g per 1 m², after which it is filled with water, washed and installed in the pond 2-3 spawning chairs of a square shape on four legs 0.5 m high. The frame is intertwined with spruce branches around the circumference, are loaded with stones so that the armchair does not float, they are filled with water and the producers are released for spawning.
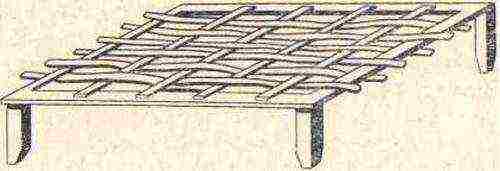
Figure 2. Frame of a spawning chair for zander
During the incubation of eggs, a slight flow of water can be allowed. After the larvae emerge from the eggs, the flow is stopped to prevent them from leaving the pond. For this, a metal brass mesh with a mesh of 0.5 mm is stuffed on the grating of the bottom drain. After 2-3 weeks, when juveniles of pike perch reach 2-3 cm in length, they are caught behind the bed of the drain with the help of a trap. It is built from boards or galvanized iron, the upper part is made of a brass mesh with a mesh of 2 mm.
The trap is installed at the end of the drain bed so that its bottom is 2 cm higher than the bottom of the net. This prevents pike perch fry from returning to the bed. It is necessary to tightly connect the trap to the bed, otherwise the fry may escape through the cracks. Water is lowered gradually and not through the upper flaps, since the fry, falling from a height, will die, but through a gap 2-3 cm high, formed by the rise of the lower flaps above the grate. In this case, the trap must be cleaned with a brush, and the fry must be caught with a racket.
Counting of fry caught from spawning ponds is carried out by sampling or a standard method.
Growing of fingerlings and their wintering
Pike perch underyearlings are raised in nursery ponds. Ponds for growing them should be well planned, before the bottom drainage there should not be a deepening or a fish-collecting pit, so that water does not remain during the descent, since juvenile zander will remain with it. The pond bed is made hard, sandy or clayey with an admixture of pebbles.
To keep pike and perch out of the pond, water is passed through a trash trap or glass-gravel filter. In flowing ponds, pike perch can leave with water; therefore, the spillways in the bottom drainages are covered with a net.
| On a note. Pike perch underyearlings can be reared together with carp underyearlings or 2-year-olds (preferably 2-year-olds). In addition to carp, the planting of pike perch can be no more than 10 thousand pieces when breeding with underyearlings, and up to 15 thousand pieces when growing with two-year-old carp. per 1 hectare. The yield of underyearlings is about 50% by the time of landing. By autumn, they grow to 12-15 g. |
In late autumn, young of the year from ponds are caught using various traps installed behind the bed of the bottom drain. The caught fish is concentrated in a storage cage, and then transported to wintering ponds.
Wintering of pike perch underyearlings is possible in wintering flowing ponds with a depth of at least 2 m, with a landing of up to 200 thousand pieces. per 1 hectare. In winter, water is continuously supplied to the ponds. The usual maintenance and control over the oxygen regime of the water is carried out.
In early spring, overwintered yearlings are planted in feeding ponds for growing commercial two-year-olds. When stocking natural reservoirs for breeding marketable pike perch, one of the types of planting material can be used in the following amount per one commercial two-year-old pike perch (in pcs.):
- Live caviar 50
- Larvae at the age of 7-10 days 40
- Fry, 45 days old 20
- Fingerlings 1.6
- Years 1,2
When stocking non-drained lakes, in which pike perch fish are grown up to four years of age, the amount of planting material should be increased by 20% to the marketable yield.
During fish farming, the usual care of the reservoirs is carried out. Catching pike perch at a young age is not allowed.
When breeding pike perch in a RAS, it gains 350 grams of weight in 12 months.


Photo of zander in the water column
All about growing pike perch

Pike perch is a fish picky about habitat, but its value is a definite "plus" when choosing a type of fish for breeding. Therefore, if you decide to breed pike perch in the lake, a few tips will be valuable to you.
- Fertilized eggs from reservoirs and larvae obtained from it in a stocked reservoir;
- Fry raised in fish farms;
- Underyearlings and two-year-olds grown in ponds;
- Producers taken from natural reservoirs and raised in pond farms.
Since pike perch is a capricious fish, you should carefully approach preparation of the reservoir, in which it will be grown or bred. The optimal size of the winter mother pond should not exceed an area of 0.1 hectare, and the proportion should be observed in which the width to the length of the pond is 1: 3, and the depth is 1.5-2 m. For summer mother ponds, the area should be identical, but the ratio of the width the length of the valleys is 1: 4, the depth is 1.5 m.To grow juveniles, the area of the pond should be 25-50 hectares, the depth is 1.5-1.8 m.Pond with clean running water, hard sandy bottom, good gas regime with moderate vegetation and "weedy" fish (roach, bleak, bitterness, rudd, gustira and carp fry) - the best place for growing pike perch.
Producer fish.
Producers are procured in September-October at fish bases. An equal number of males and females, 40-50 cm long, are selected for transportation.Since zander has spiky fins and can be injured, breeders are placed in a stretcher of four sections, placing one fish per section, and then the stretcher with zander is delivered to the slots, into which up to 1000 individuals are placed. The slot is moved to the farm and the fish are transplanted into the brood pond in an amount of no more than 1000 individuals. Culling of injured individuals is carried out twice - during selection at the fish base and after transporting them to the farm, before settling in brood ponds. The exchange of water in such a pond should take place within 10 days, the content of dissolved oxygen should be 5 mg / l, and the pike perch should be fed with small fish. Since March, the fish are moved to summer brood ponds, with a density of 15 individuals per 10 m2 and separating females and males - at this time it is very easy to recognize them: males have a faint blue-blue color on their abdomen; females have a white abdomen with barely noticeable yellowness, it is thickened, and the genital opening turns slightly red.
 Spawning.
Spawning.
Males of pike perch become sexually mature in two years, females in three years, when they give 200,000 eggs weighing 1 kg. Pike perch breeders are planted for spawning when the water temperature is 8 ° C. For this, spawning ponds are used with an area of no more than 0.5 hectares (length 40 m, width 10 m) and a depth of 1.5 m, without vegetation in the bed and slopes of the pond. In such ponds, nests are installed in a checkerboard pattern - artificial spawning grounds, which are a wooden frame with a circle of aluminum wire 1 m in diameter, intertwined with nylon threads, with bundles of nylon threads laid on this grid. One such nest is intended for one pair, that is, 500 pairs of producers are placed in the spawning pond. After spawning, the eggs laid on artificial nests, together with the substrate, are transferred to the incubation room.
Another version of the nest can be made from hard plant fibers, heather, hard polymer sponge. On frames with a facet length of 75 cm, 25 such nests are attached, and the frame itself is attached to the cables passing through the piles (the piles have rings), which makes it possible, if necessary, to remove the frames on the cables from the water. Such piles are installed every 8 meters into dams, at the edge of the slope; two more piles are installed in front of the support: one at the foot of the slope, the second 3 m from it.
Incubation.
Pike perch eggs are incubated in a freezer. This room has a size of 5x2.5x2.5m, on the side walls of which, at a height of 2m, water pipes with water nozzles are installed at a distance of every 0.5m - this creates the necessary humidity of the environment. A drain should be installed in the center of the floor, so it should have a slope towards the center of the chamber, in addition, transverse racks 1.5 m long and 1.8 m high are installed in its middle, where nests with caviar should be hung. The passage along the walls of the chamber should be 0.5 m. The nests with eggs should be transferred to the reservoir for pre-incubation several hours before the start of hatching of the embryos.
It is possible to carry out incubation in the reservoir itself, for which they use incubation devices made of transparent polymeric material with perforated holes. The size of such holes has a diameter that allows water and hatched young pike perch to pass freely, but does not allow predators to enter the apparatus. The upper side of the apparatus has the shape of an inverted cuvette for air to enter the apparatus. An anchor is attached to such an apparatus, and it is carefully immersed in water in an upright position, without tilting it, so that its arch (space filled with air) is 40 cm below the water level in the reservoir. To move the apparatus, boxes are used, pouring polymer sponges with pieces of ice between the walls of the box and the apparatus, and upon delivery to the installation site, the apparatus is immediately placed in a cool place. For stocking a reservoir with caviar deposited on underwater vegetation, it is recommended to place 2-6 thousand fertilized eggs per hectare of the reservoir.Good pike perch caviar is transparent with a yellowish tinge, diseased or unfertilized caviar is cloudy, dirty white, some eggs may be burst. In a clutch of eggs, the eggs are evenly spaced, therefore, to count them, you can cut off a small piece of substrate with caviar, carefully calculate the number of eggs, and multiply the resulting amount by the entire area of the clutch.
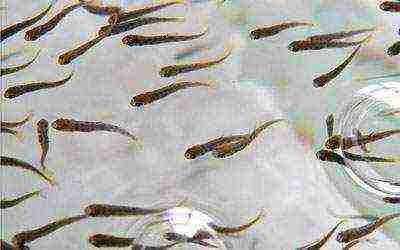 Growing young animals.
Growing young animals.
In a pond with an area of 25-50 hectares and a depth of 1.5-1.8 m, 4-5 nests with caviar are placed for each hectare of the reservoir. They constantly monitor the adequacy of the water level in the pond and maintain a favorable gas regime. After 3-4 days, the prelarvae become larvae and begin to feed on small zooplankton organisms; and after 40 days, juvenile zander weighs 1.5 g. After the release of zander from the breeding ponds, water is released from them; this process must be completed by mid-June.
Interesting Facts.
Underyearlings of pike perch reach a length of 8-15cm and weigh 10-15g, while two-year-olds grow up to 20-30 cm and weigh 500-1000g. The first 48 hours after spawning, parent pike perch guard the nest, attacking all enemies, and keep it clean. Young zander can swim immediately after hatching, since it has a fat bladder, and the density of fish is equal to the density of water. After the first year of life in natural conditions, 0.5-1% of fish survive, with artificial breeding - 10%.

One of the problems of fish farming in ponds is the presence of low-value and weedy fish species, which, with a slow growth rate, consume food resources of commercial fish.
Belarusian fish farms are engaged in the cultivation of carp, crucian carp, herbivorous fish, pike. Polyculture on the basis of some farms is partially represented by variegated silver carp, grass carp. Growing only such an assortment of commercial fish farming objects leads to the fact that feed is not fully used, which is also trash fish. It is known that among predatory fish there are differences in habitats. Thus, the pike assimilates the coastal zone and the outskirts of thickets, the catfish - the deeper part, and the pike perch prefers the open area of the reservoir without vegetation.
The joint keeping of pike perch and other fish is absolutely safe, while the introduction of pike and catfish with a small number of weedy small fish in ponds and a small excess of the size of these predators in the size of peaceful fish can lead to the consumption of the main fish species of pond polyculture. It is known that pike and catfish can consume fish of almost equal size, while pike perch can only consume prey much smaller than their own.
It is known that German fish farms have mastered the technology of growing pike perch in mono- and polyculture. In Hungary, since 1900, work has been underway to develop pike perch as an object of fish farming. Pike perch underyearlings are reared in this country on zooplankton and benthos. In Russia, a technology has been developed for growing pike perch underyearlings and feeding it with trash fish.
In Belarus, it is still impossible to call pike perch a well-developed object of commercial fish farming, since fish farms do not have the appropriate technologies for its cultivation.
At the same time, in recent years, the cost of walleye, in some countries exceeding the cost of sturgeon fish. The high cost of pike perch is explained by the taste and dietary qualities of meat, its low calorie content.
The introduction of pike perch into the polyculture of fish species grown in fish farms in Belarus will expand the range of products obtained from marketable fish, increase the productivity of feeding ponds in comparison with pike farming by about 15 kg / ha. Farmed fish will help restore natural populations that are rapidly decreasing due to pollution of water bodies.
Artificial breeding of pike perch
Trapping producers
Pike perch is very sensitive to mechanical damage, so spawners should be caught very carefully. A fish taken in hand, at a water temperature exceeding 10 degrees, may die in three to four days. Breeders caught in the spring do not adapt well to spawning in artificial conditions and their maturation has to be stimulated with pituitary injections. Therefore, for artificial breeding, it is better for producers to stock up on autumn or winter. Zander is less injured when fishing with a seine.
Keeping producers
For artificial breeding, manufacturers weighing one and a half kilos are most suitable. Larger individuals adapt less well to living conditions in ponds and to spawning in artificial conditions. If possible, it is advisable in fish farms to have their own breeding stock of pike perch. In summer, producers are kept in feeding ponds and fed with live fish. The daily requirement of pike perch for forage fish in summer is usually two percent of its weight. For keeping producers in winter, a flowing wintering pond is most suitable. In such a reservoir, forage fish is required - 20% of the total mass of the predator. Crucian carp, young of the year carp, perch, ruff, roach weighing 10-30 g are the food supply for pike perch breeders.

The abundance of food in winter guarantees a successful spawning of these fish in the spring. In the event of a shortage of food, spawning is prolonged, and the percentage of fertilization and fertility of females decreases.
In the spring, 10-12 days before spawning, at a temperature of about 8 degrees. (most often at the beginning of the third decade of April), zander breeders are sorted and males are separated from females. At this time, sexual dimorphism is more pronounced in fish. In females, the abdomen is taut and swollen, lighter. Males and females are kept in different cages.
Zander has very sensitive skin, so thick rubber gloves are recommended when sorting fish.
At a water temperature of 10 degrees. preparation for spawning of pike perch begins.
On stimulating the maturation of milk and caviar
Females are given pituitary injections. It is better to use the pituitary glands of pike perch, but the pituitary glands and other fish - bream, carp are suitable.
Harvesting of the pituitary glands is carried out in winter or in the pre-spawning period. After extraction, the glands are stored in a tightly closed glass jar with anhydrous acetone until use. The volume of the latter is two dozen times greater than that of the pituitary glands. After 12 hours, the acetone is replaced with a pure one, in which the glands are kept for another week. After that, they are laid out between two sheets of clean paper and dried in a warm room. When dry, they are placed in clean, sterilized dry tubes and sealed. The weight of one dried pituitary gland is 3-4 mg.

Before injection, the pituitary glands are removed from the test tubes, ground into powder, and 0.5% saline solution (5 g of NaCl dissolved in 1 ml of distilled water) is added at the rate of 1 ml of solution per 4 ml of dry matter. Everything is well mixed and with the help of a medical syringe the suspension is injected into the spinal muscle of the pike perch (milliliter per kilo of live weight of the fish). After injection, the eggs in females fully mature within two days.
Recently, human chorionic gonadotropin has been increasingly used to inject fish.
In the process of work, larger specimens of manufacturers, in order to avoid damage, are put to sleep with the help of anesthetics. For this, baths of a solution of phenoxyethanol at a concentration of 1: 5000 are used. At the same time, it is necessary to observe the gill covers of the fish so that they constantly, albeit slowly, open. After injections, the pike perch are immediately placed in clean water.
Equipment for cages and artificial spawning grounds
For spawning of zander, artificial spawning grounds (nests) of various designs, shapes, with different types of substrates are made.The basis of the spawning ground is a frame made of a metal square, which submerges the artificial substrate. Two or three wooden or metal frames are attached to it, covered with a fine-mesh mesh material, which can be easily removed at any time. The spawning substrate is attached to these frames.
Artificial nests are sized to fit in spawning cages. Cages, measuring 1 x 1 x 2 m, are sewn from Delhi with a mesh of 10 mm. Before the spawning cages are planted, spawning cages are lowered from bridges or other floating structures to a depth of 1.5 m so that the bottom is no closer than 20 cm from the bottom of the reservoir.
Spawning in artificial nest cages
Pike perch are planted for spawning when the water temperature reaches 10 degrees. In one cage, one injected or naturally matured male and one flowing male are planted. After a day, a control examination is made, carefully lifting artificial nests together with the case and examining them. When eggs are found, the female is removed from the cage, and the male remains to aerate the eggs. The second inspection of spawning cages, where spawning has not occurred, is carried out two days later. If the producers do not show signs of the disease (saprolegniosis) and the secondary sexual characteristics of puberty are not lost, they are left in the cage for another three days, but the artificial nests are replaced with new ones. During this time, spawning occurs in almost all artificial nests. Fertility of a kilogram female is 200 thousand. eggs.
Caviar development
Spawning in cages must be carried out in five to six days (maximum 8 days), so that the incubation of eggs occurs at the most favorable water temperature - 15 degrees. At a higher water temperature, the development of eggs is accelerated, but most of the hatched prelarvae die in the first days of their life.

Pike perch eggs develop at about 110 degree days. At a temperature of 15 degrees, the incubation of eggs lasts five to six days. To determine the time of mass release of prelarvae, a sample of eggs from the spawning nest is taken. Several eggs are placed in a shallow bowl of water. If all prelarvae hatch within a few minutes, this means that in three to four hours a mass emergence will begin in the nests.
At the indicated temperature, usually on the fourth day after fertilization (ocellation stage), the nests with eggs are removed from the cages and transferred to ponds intended for rearing fry. The nests are placed on pre-slaughtered stakes, at a depth of 0.5 m. It is believed that there are about 200 thousand pieces in one spawning nest. eggs. If several nests are placed in a pond, then they are placed at a distance of two meters from each other.
Incubation of eggs
Before selection of eggs, milk, females and males of spawners are kept separately. In tanks with a volume of 8 m3, the water must be changed every 8 hours. In addition, the water must be saturated with sufficient oxygen. If manufacturers are to be used next year, they are put to sleep with anesthetics before harvesting the genital products.
Strain about 150 ml of caviar into a 2.5 ml dish. A liter contains about 1.5 million pieces. not swollen eggs.
The male is laid on one side, lightly pressed on the abdomen, with the help of a long pipette, the secreted sperm is collected, which is sprayed on the eggs. The caviar and semen are mixed with a feather. For better fertilization, caviar is poured with Voinarovich's solution - 40 g of sodium chloride NaCl and 30 g of carbamide CO (NH2) 2 are dissolved in 10 liters of water. After 10 minutes of stirring, the caviar is washed with clean water and filled with a solution of tannin (0.8 g of tannin is dissolved in 10 l of water) to remove stickiness. Once again, everything is well mixed and washed with clean water. De-glued caviar is placed in Weiss apparatus. After three to four days of incubation, the prelarvae hatch and they are planted in ponds, natural reservoirs or grown in fish tanks of various types.

Tweet


