Content
- 1 What do you need
- 2 Tips
- 3 Warnings
- 4 Description of the plant
- 5 Sundew care at home
- 6 Sundew reproduction
- 7 Diseases and pests
- 8 The healing properties and use of sundew
- 9 Sundew is a carnivorous plant-predator for insects (video)
- 10 How to recognize sundew, plant photos
- 11 Sundew care at home
- 12 Flowering, reproduction and wintering of sundew
- 13 Diseases, pests of sundew and control methods
- 14 The use of the plant in medicine
- 15 Sundew plant: species, varieties and description
- 16 Where does the sundew grow
- 17 Features of growing a predator plant
- 18 Sundew care at home
- 19 Sundew plant: reproduction
- 20 Diseases, pests and control methods
3 parts: Buying an adult plant Growing the seeds Caring for the plant
The sundew (Latin Drosera), also known as the flycatcher, is a plant from the genus of carnivores. They are considered one of the easiest carnivores to breed at home. Much of this is due to their way of catching insects: they secrete a sticky substance from their tentacle leaves. Thus, it is very easy to feed them. You can buy sundew seeds from any major nursery or online stores. If you decide to grow a sundew at home, there is nothing difficult about it.
Part 1 Buying an adult plant
-
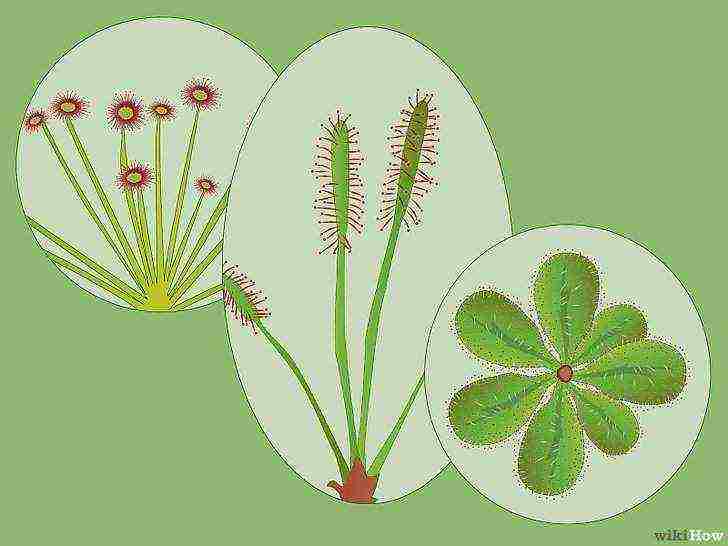 Learn about sundew.
Learn about sundew.
If you do some research, you will have an idea of what kind of plant it is and whether it is possible to grow it in the area where you live. All over the world there are about 194 species of sundews of all sizes and shapes from round to oblong. Rosyanka can live for 50 years if they are in good conditions. In some cases, they can be used for medical purposes. Some of the most common types of sundews for growing at home are presented below:
-
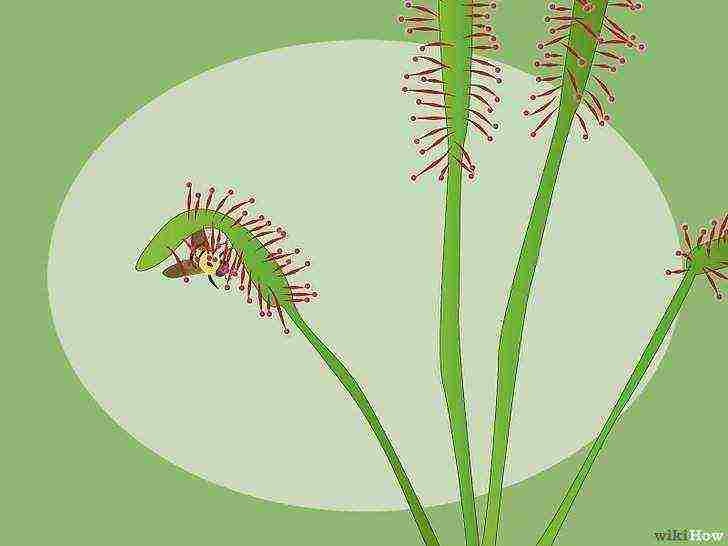

Learn how the sundew catches its prey. When an insect sits on sticky tentacles on the leaves, it most often sticks to them, and then the sundew folds its tentacles around the victim and begins to digest it.
-
 Buy a plant.
Buy a plant.
Dewdrop is rarely sold in regular flower shops. You need to look for it in really large nurseries or order it online. With this option, the plant is usually supplied in seed or in very small seedlings.
- Ask the nursery consultant to give you as much information and advice as possible on how to properly care for your sundew at home. But remember that the grooming requirements vary from species to species, so make sure you know how to care for the sundew you are about to buy.
- Ask the nursery consultant to give you as much information and advice as possible on how to properly care for your sundew at home. But remember that the grooming requirements vary from species to species, so make sure you know how to care for the sundew you are about to buy.
Part 2 Growing seeds
-
In a pot 10 cm high, add either regular sphagnum moss or long staple moss. Also, instead of moss, you can add a mixture of peat and sand or peat and expanded clay. Wet or dry soil should be 70% peat and 30% sand or expanded clay. But be sure to take into account the specific soil requirements that you learned about in the nursery or during your research. The pot should be at least 10 cm because the roots of the sundew are extremely long, and if they do not have enough space to grow, then the plant itself will not be able to reach its maximum height. Most often, sundews do well in humid conditions. Usually the roots of this plant are very weak and practically useless for absorbing nutrients from the soil.
- Spread the seeds over the surface into small indentations in the soil.
Make sure you plant enough seeds in one pot to increase your chances of sprouting.
- Water the seeds with a little rain or distilled water (approximately 1.5-2.5 cm). It is preferable to water in a pan to avoid damaging small seeds.
- Keep an eye on the sprouts every day, as the sundew is a very sensitive plant!
-

Wait for the sundew to grow, get bigger and wider, and it will have more branches. This period may take a month or more.
Part 3 Plant care
-
 Keep the sundew at a temperature of +7 to +32 C or create subtropical conditions for it.
Keep the sundew at a temperature of +7 to +32 C or create subtropical conditions for it.
The more light hits the plant, the better. Place it next to a window so that there is enough sunlight. High humidity is not needed, so keep the room relative humidity up to 50%.
- The sundew should be in a well-lit place. She should receive direct sunlight for at least half a day. Also note that the sticky substance on the leaves can dry out.

- The sundew should be in a well-lit place. She should receive direct sunlight for at least half a day. Also note that the sticky substance on the leaves can dry out.
-
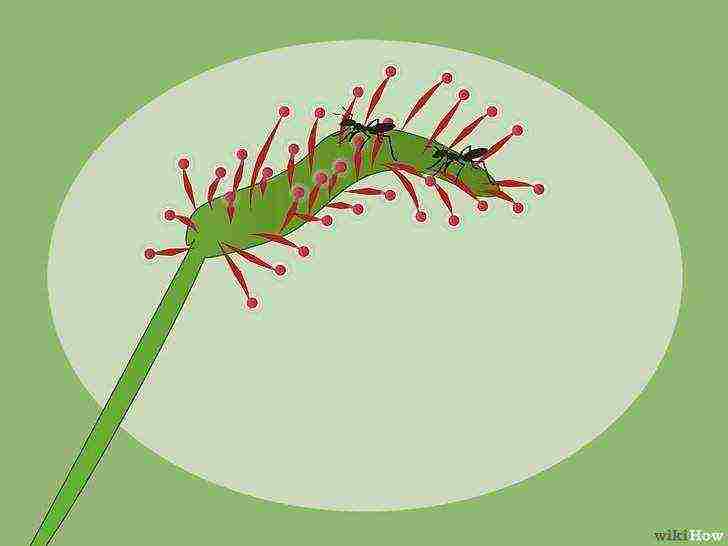 Feed the plant every two weeks.
Feed the plant every two weeks.
If your sundew is indoors, then you need to do it yourself. Give her live or dead insects such as ants; they must be fresh.
- Dewdrop cannot digest meat, so there is no need to feed it to the plant.
- Do not feed the plant with insects that are larger than the tentacles on the leaves. Because either the insect will be able to break out of them (and you will have to catch it), or the plant will simply not be able to digest it.
- Do not overfeed your sundew if it is kept in a high humidity environment. Otherwise, it can provoke the growth of mold, which will destroy the leaves.
- If you keep the plant outdoors, then most likely it will be able to feed itself, so additional feeding is not required.
-
 During summer or late spring, the 5-petalled flower may begin to bloom.
During summer or late spring, the 5-petalled flower may begin to bloom.
You will most likely notice that the sundew will become less active as it will take a lot of energy to create the flower. Once the flower has formed, you can move the plant outside so that a bee or other insect can carry pollen from plant to plant. The flowers are usually red, pink, or white, and can self-pollinate if no insect does.
- Seeds may form after flowering. To aid this process, you can do cross-pollination by rubbing pollen from one plant on the stigma of a pistil on a flower on another.
-
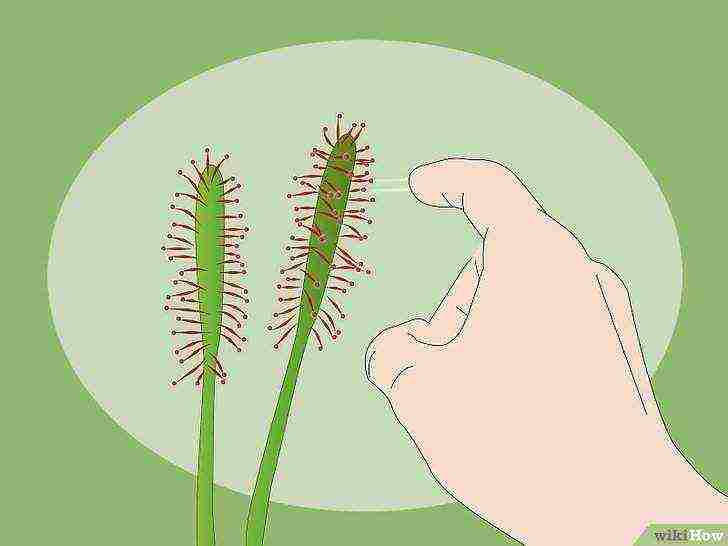
 Spray the plant.
Spray the plant.
Usually the roots of the sundew are poorly developed, and most of the water enters through the leaves. Therefore, spray the plant from a distance of 4-5 cm with clean water without any admixtures of any minerals or with distilled water at all. This should be done once a week. Do not forget that you do not need to water the soil, as too much moisture can provoke root rot.
- Do not use any water other than the one described above (for example, tap water), as there may be an excess of minerals that will deposit in the soil and destroy the plant. If you do flood the plant, turn the plant pot over and press down on the soil a little to drain the excess water.
-
 If you decide to grow a plant in a room (although it will grow better outdoors), do not forget that you need to feed it.
If you decide to grow a plant in a room (although it will grow better outdoors), do not forget that you need to feed it.
Since the room is a closed space, and few insects can enter there, you will be the only breadwinner for the sundew.
- You can control the intensity of the light if the plant is indoors. This is definitely a plus in keeping the sundew indoors.
-
If the sundew is outside, remember to watch it every day to make sure no one has attacked it. Also check the plant for diseases. Place the plant in a location where it will receive direct sunlight during part of the day, but at the same time it will have shade at times.
What do you need
- Pot height 10 cm
- Pure water without minerals
- Sundew seeds
- Live or recently killed insects
Tips
- The sundews digest food for a long time, so you shouldn't try to see the whole process. Just trust it to happen. After all, the plant knows what to do and how to digest food.
- Remember that the sundew can be bred and planted in a different location using a cut leaf or part of the root.
Warnings
- Spray the sundew with mineral-free water only. The deposition of minerals in the soil most often ruins the plant. Standing water over the course of the day will also result in an even greater concentration of minerals in the remaining water.
- During winter, you may notice that the leaves wilt or die off completely. This is due to the transition of the sundew into hibernation. Remove dead leaves carefully. During this period, do not stimulate the sundew with excessive sunlight or water. Just make sure the soil is dark brown. With the arrival of spring, you can increase the amount of sunlight.

- Leaf dying off usually stops as soon as daylight hours begin to increase and spring approaches.
- If your sundew is white and looks very weak or its leaves are not as sticky as usual, do not add mineral fertilizers. The result from this will be the same as from watering from the tap, or even worse. The deposition of minerals and chemicals puts your plant at risk. Since sundew health does not depend on fertilizers, pay attention to watering, nutrition, sunlight (some of this may be in excess or in deficiency). See a professional gardener to determine the problem.
Article Information
This page has been viewed 18,934 times.
Was this helpful?
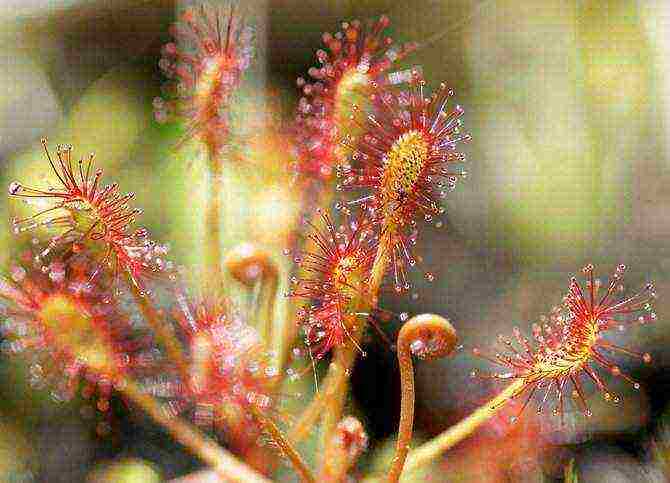

Plants of the genus carnivores number almost two hundred different species all over the world, among which is the carnivorous plant sundew (drosera). She, thanks to her special structure and ability to survive, is able to grow in almost any conditions and on any continent. The only exception is Antarctica. The sundew can grow even on swampy soils in which nutrients are almost completely absent, since it gets them from insects. Dewdrop because of this is called a trap plant.
Description of the plant
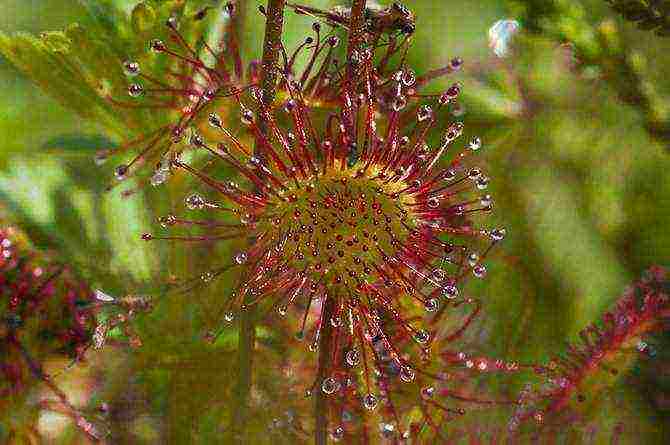

The appearance of the sundew does not at all resemble an insect trap. Plants of different species differ only in the shape and size of the leaves, but they have in common - thin soft villi with droplets of sticky liquid, very similar to ordinary dew. When an insect sits on a leaf to quench its thirst with "dew", it immediately sticks and becomes as if paralyzed. With weak attempts to get out of the sticky captivity, the insect creates vibrations that give a kind of signal to the plant and the leaf curls up along with the prey.
Having received the necessary nutrition, the sundew in a few days again unfolds its leaves in anticipation of a new victim. True, if small debris or a raindrop gets on the sticky leaf, then the plants will not react. This natural specimen can grow not only in the wild, but also feels great at home.
Dewdrop is a flowering plant that blooms in the spring months with pink or white flowers that later turn into seed pods. Some varieties are capable of self-pollination.
Sundew care at home
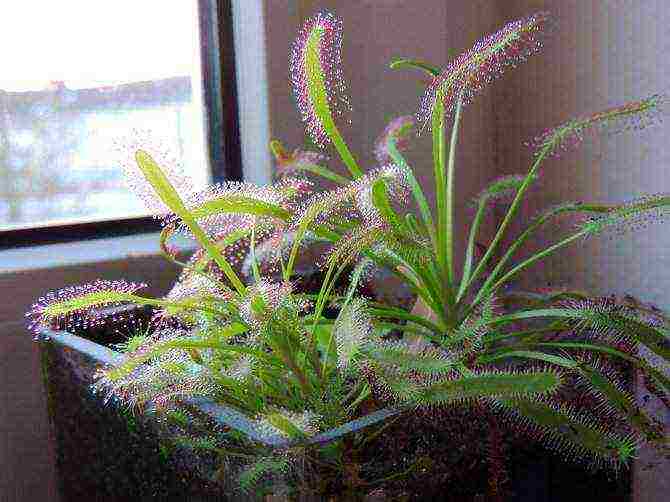

Location and lighting
Rosyanka needs long-term lighting for many hours - about 14 hours in summer and about 8 hours in winter. Direct sunlight is not recommended for the sundew, so it is advisable to grow the plant on a windowsill on the east or west side of the house. In the cold season with short daylight hours, plants can be supplemented with a fluorescent lamp.
Temperature
The sundew is excellent and can easily endure a cold snap and even small frosts. In winter, the sundew can be at a temperature of 5 to 12 degrees Celsius, but in the summer, the temperature regime depends on its type. For example, 18 degrees are enough for European varieties, but for African varieties it is about 30 degrees Celsius to create complete comfort.
Air humidity
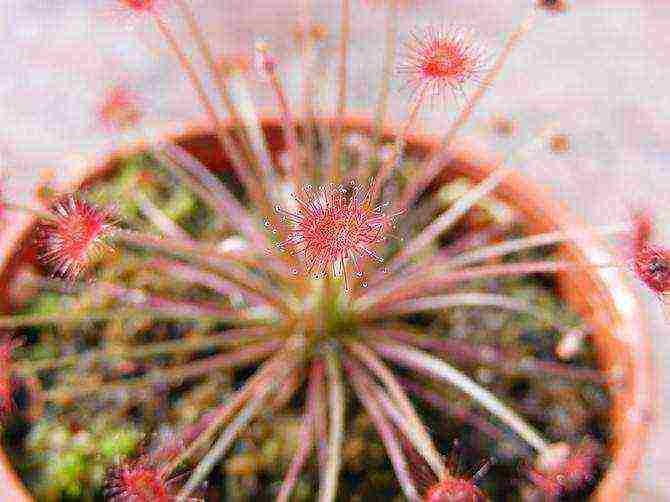

In the room where the sundew is kept, it is necessary to maintain a high level of humidity (about 70%). This can also be done using a terrarium in which a potted plant is placed. The plant will receive the necessary moisture if the terrarium is covered with a lid or by regularly spraying the sundew, but with the lid open. To keep the moisture in the container for a long time, its bottom is covered with moistened moss.
Watering
The soil in the flower pot must be moistened daily with a sprinkler, and the sundew should be watered once a week. A lack or excess of moisture in the soil should not be allowed. When dry, the plant will begin to wither, and with excessive moisture, the roots will rot.
As irrigation water, you need to use rain, thawed, purified or distilled water, but in no case tap water.
The soil

Since the sundew in the wild grows on poor soils, in which there are practically no nutrients, its root part is very poorly developed. For home cultivation, you will need a low flower capacity (about 10 centimeters) and a sand-peat soil mixture with a small amount of moss, which will help to retain moisture.
Top dressing and fertilizers
The sundew does not require additional feeding, since it receives its main food from insects. The main thing is that insects in the form of flies or mosquitoes sometimes sit on the leaves of the sundew.
Sundew maintenance in winter
From November to February, the plant is dormant. During this time, the sundew sheds its foliage and becomes inactive towards insects. It is recommended to keep the flower in a cool place with high levels of humidity and away from heating appliances.
Before the start of the active phase of plant development (approximately in the last week of February), you can transplant and update the soil.
Sundew reproduction
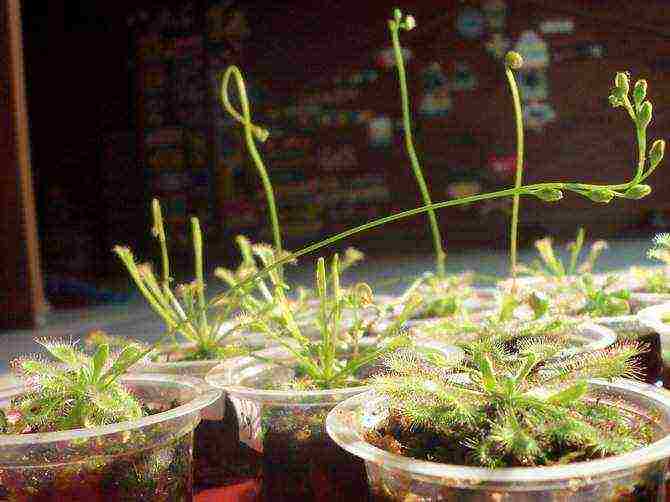

Seed propagation
The seeds are planted in a well-moistened sphagnum moss and kept in a well-lit place covered with a film at a temperature of more than 25 degrees Celsius. Seedlings will appear in about 25-30 days. Plants with 3-4 full leaves are suitable for transplanting into soil. The sundew will reach maturity in 3-4 months.
Reproduction by dividing the bush
The bush of the plant can be divided into several parts along with the root and transplanted into separate containers. Daughter rosettes are also planted in individual flower pots. In the new place, young shoots and separated parts quickly take root.
Propagation by cuttings
The cuttings can be placed in water for root formation, or they can be immediately planted in moist soil, which will be sphagnum moss. For good rooting in the soil, the plant needs a lot of moisture and the creation of greenhouse conditions.
Diseases and pests
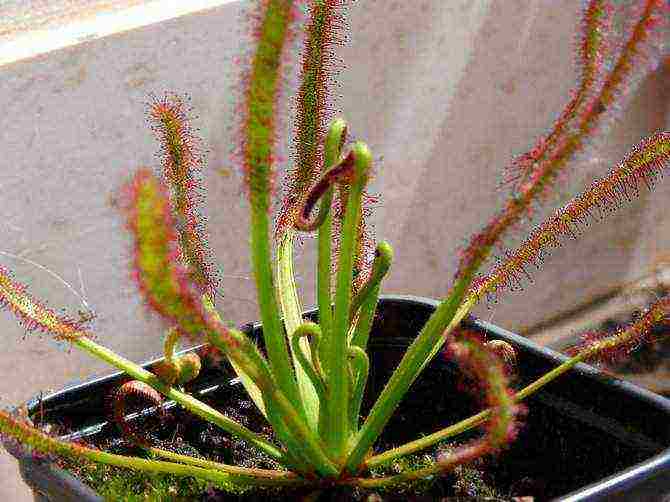

Since the sundew feeds on insects, it is almost never disturbed by pests. The only harmful insect for this plant is aphids. You can get rid of it by spraying with special parasite agents for flowering indoor plants.
The flower is sick in most cases due to improper care of it. Basically, this is a lack or excess of moisture in the soil and indoors. With insufficient watering and dry air, sticky drops on the leaves of the sundew may dry out. It is urgent to spray and raise the moisture level by keeping the plant in the terrarium.
With an excess of moisture, the process of decay begins in the root part.This comes from the stagnation of excess water in the plant pot. In this case, it is better to transplant the sundew into a new soil and, having examined the roots, remove their damaged and rotten parts. In the future, it is recommended to use only soft water in moderate volumes for irrigation.
If the disease has caught the plant during the period of active flowering, then removing the peduncles will help to save its strength and redirect them to the fight against the disease.
The healing properties and use of sundew

Dewdrop belongs to poisonous plants, and you need to handle it with extreme caution, but at the same time it has a lot of healing qualities. It is used in folk and official medicine. At home, sundew can be treated, but after consultation with a specialist and at a strictly indicated dosage. Choosing a treatment yourself is dangerous to health.
The plant contains a large amount of useful substances that help in the treatment of many diseases and their consequences. Both fresh plants and dry raw materials are used. On the basis of sundew, tinctures and ointments, decoctions and solutions for compresses are made. The list of diseases that sundew can cure include diarrhea, asthma, dysentery, tuberculosis, bronchitis, dropsy, whooping cough, fever and many skin diseases.
In folk medicine, all parts of the plant are used, as well as its juice.
Dewdrop is used:
- To relieve spasms and inflammation.
- For the treatment of the nervous system.
- As a diaphoretic and diuretic.
- To normalize body temperature.
- In the treatment of atherosclerosis.
- For the treatment of the gastrointestinal tract.
- In complex therapy in the treatment of colds, including cough and ENT organs.
- For the destruction of calluses and warts.
Despite the fact that the sundew is a very exotic plant, caring for it is quite simple and even a beginner grower can do it.
Sundew is a carnivorous plant-predator for insects (video)
Sundew is one of the most common plants in the genus of carnivores. There are about 200 species of this plant in the world, which can be found on all continents of our planet except Antarctica. It owes its vitality to a special structure that allows it to grow even in bogs poor in minerals.
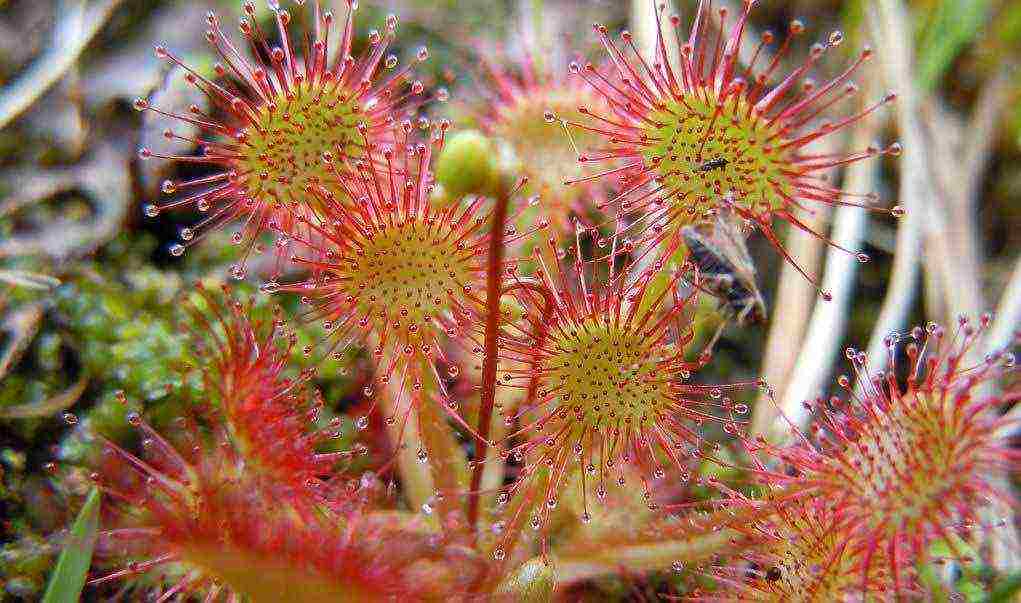

Dewdrop extracts nutrients from insects that fall into its trap. This mechanism has attracted the attention of many peoples and is even described in fairy tales, for example, "Rosyanka - mosquito death" by V.V.
How to recognize sundew, plant photos
There are many species of this plant in various forms. Its leaves can be small and round, long and wide, or generally thin, fern-like. But there will always be one feature that gave the name to this plant: the leaf will be covered with villi with drops of liquid that imitate dew. It is a food trap.
The insect, trying to quench its thirst, will sit on a leaf. However, these shiny drops are not dew, but glue with the addition of digestive enzymes and a substance called the alkaloid coniine that paralyzes the insect. While trying to get out, the prisoner will create vibrations that will feel the leaf and begin to curl up. After a few days, he will turn around again, completely digesting food. It is noteworthy that sundew leaves do not react to raindrops or debris.
Sundew care at home

The main condition in the care of a sundew is to create similar natural growing conditions
This carnivorous plant is not difficult to buy in a pot at many flower shops, mostly online. In order for the sundew to grow well at home, you need to create a climate for it similar to the natural conditions of a swampy area. Caring for this flower includes such components as:
- lighting;
- temperature;
- the soil;
- air humidity;
- watering.
The sundew should receive a lot of light: in the summer - 14 hours, in the winter - about 8.But direct sunlight can cause burns, so it is best to place the pot on a west or east window, or in the shade of a garden. You can use additional lighting in the form of a fluorescent lamp.
It is a cold-resistant plant. European species prefer temperatures around 18 ° C even in summer. African sundew species can live comfortably at +30 ° C. The plant likes to hibernate in the cold 5-12 ° C. It can even tolerate slight frosts.
The sundew has a poorly developed root system, because she is not used to using it in soil poor in minerals. Equally taken peat with sand will do. It is a good idea to add sphagnum moss, which is able to retain moisture in the soil. A small pot is suitable, no more than 10 cm. Mineral fertilizers are not required due to a special method of nutrition: the sundew takes all the necessary substances from insects. But if they do not penetrate the premises, buy a couple of flies a week for the predator.
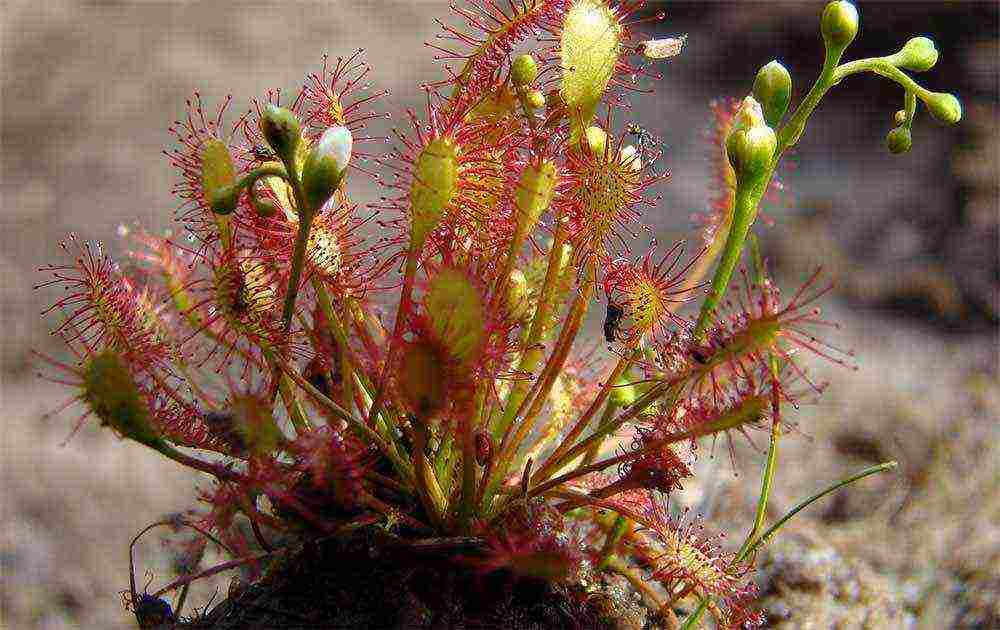

Dewdrop needs a couple of flies a week
Air humidity should be high enough: 50-70%... If the indoor air is dry, it is recommended to place the flower pot in a terrarium, where it can be covered with a lid to maintain moisture. You do not need to cover the terrarium, but then the sundew must be regularly sprayed with water, and to retain moisture, cover its bottom with moist moss.
Watering is enough to carry out once a week, but do not dry out. At the same time, if the flower is too flooded, it can cause rotting of the roots. You can put a pot of sundew in a high pan, and regularly add water to it so that it is at the level of 2 cm. Spray the soil regularly with a spray bottle until it becomes moist.
ATTENTION: Do not use tap water because it contains excessive amounts of minerals. Rain, distilled or, in extreme cases, filtered water will do.
Flowering, reproduction and wintering of sundew

Sundew propagates by seeds, cuttings and dividing the bush
In spring, the sundew actively blooms, so it does not waste energy on the growth of leaves. Long stems with white or pink flowers appear, which attract insects for pollination, but keep them away from traps. Some types of sundew self-pollinate, others need help. To do this, you need to take the pot out into the garden, or gently rub the flowers against each other with your own hands. You can also use a brush or cotton ball. After a month, a box of seeds is formed, which you can collect and plant.
If you want to share the sundew with your friends, there are three ways to breed it:
- seeds;
- dividing the bush;
- cuttings.
Plant sundew seeds in moist moss, cover and keep under plenty of light. They will rise within a month. When the sprouts have three or four leaves, they can be planted in the soil. Within 2-4 months they will develop into an adult plant.
Sundew leaves are usually collected at the root in a rosette. It can be divided and planted. Sometimes a daughter outlet can branch off from the main plant. It can also be placed in a personal pot.
And finally, it is quite possible to propagate a sundew by cutting off the stalk. Just like seeds, greenhouse conditions and a lot of moisture are required. Wet sphagnum is best for soil, although some growers put cuttings in water.
Dewdrop is active from spring to autumn. In winter, it is inactive, so the plant needs a dormant state. We need to give her a rest. A cool, damp place, such as a balcony greenhouse, garage, or windowsill, away from the battery will work. Many leaves die, food consumption and insect catching are significantly reduced. Hibernation ends around February when daylight hours increase again. Around this time, once a year, it is recommended to replant the plant so that the soil does not cake.
Diseases, pests of sundew and control methods

The only pest that can be found on a sundew is aphid.
If sticky drops dry out from a plant, this indicates insufficient moisture. Spray the leaves with water, cover the flower in the cage, and she will most likely return to her previous healthy appearance.
There is always a danger of oversaturation of the soil with improper watering. You need fresh soft water without fertilizers and minerals. If there is water in the pot all the time, the plant may rot its roots. The presence of water is allowed only in the sump. From the pot itself, it must be drained, gently holding the soil. If the process of decay has begun, it is better to remove the infected roots, and transplant the sundew itself.
Pests practically do not bother her, because they themselves often become her food. Sometimes aphids can start. In this case, you need to purchase a parasite remedy at a flower shop and spray the plant.
If the plant gets sick during flowering, you can remove the peduncles. It takes a lot of energy to form a flower, and this method will allow you to save it and direct all your efforts towards recovery.
The use of the plant in medicine
Before attempting to treat any disease with any part of the sundew, consult your doctor. Self-medication is dangerous. The plant is poisonous, therefore, non-compliance with the dosage can threaten with poisoning.
Sunflower contains many substances that have different effects on the human body. For example, plumbagon is an antibiotic that helps in the fight against microbes and pathogenic fungi: streptococci, staphylococci, etc.
One of the uses is the treatment of diseases of the upper respiratory tract: cough, bronchitis and especially whooping cough. It can be used with great care for the treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis. Antispasmodic, anti-inflammatory, diaphoretic, sedative, antipyretic and diuretic properties of this plant are also noted.
In folk medicine, it is used as an antiemetic, although in excessive amounts, sundew itself can cause nausea and vomiting. Sundew infusions are recommended for atherosclerosis, asthma, fever, dropsy, diarrhea, dysentery, pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, etc.
Fresh sundew is not used internally. For this purpose, dry raw materials are procured. However, sundew juice can be applied topically to get rid of warts or old calluses.
We recommend watching a short documentary on the sundew, we wish you a pleasant viewing.
Exotic lovers will be delighted with this plant. The sundew is a charming insect-eating predator that always shines and shimmers in the sun's rays thanks to the droplets of moisture on the leaves. This indoor flower requires special care conditions.
Sundew plant: species, varieties and description
Rosyanka is a predatory, carnivorous plant that belongs to the extensive genus Droseraceae. This perennial herb has medicinal properties and is harvested during flowering to treat coughs, fever and eye diseases. It is found on all continents except Antarctica, and a total of 187 plant species are known.
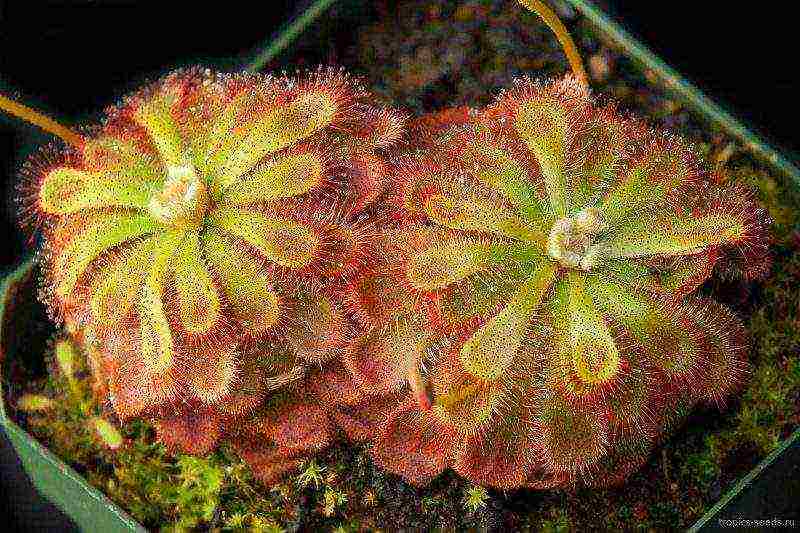

Here are some of them:
- Round-leaved sundew - its rounded leaves with a diameter of about 2 cm grow on long petioles. Above and along the edges, they are covered with red glandular hairs that secrete a sticky liquid. The leaves are spread over the soil surface. It blooms in summer with small white flowers that grow on long peduncles.
- The English sundew has a height of no more than 25 cm. Its linear-oblong leaves on petioles are collected in a basal rosette.
- The intermediate sundew is a small plant, up to 8 cm high. The leaves are arched, lanceolate and have glandular hairs.
- A filamentous sundew - it grows up to half a meter, its beautiful thin leaves, shimmering in the rays of the sun.
- Rosyanka Adel is an unpretentious large plant with lanceolate leaves. Does not tolerate frost, but loves coolness.
In indoor conditions, the Cape sundew (Drosera capensis) is most often grown, which is unpretentious in care and is a long-liver.
The plant got its name from the droplets of sticky liquid that are always covered with its leaves. In appearance, they resemble dew, but in fact, it is something similar to gastric juice. This sticky liquid contains special enzymes that attract gullible insects, which paralyze them and then digest them.
An insect stuck to the leaf, trying to free itself, breaks out. In response to this, the sheet is folded, covering the victim from all sides. A medium-sized insect is digested by the plant for several days, and its chitinous shell, legs and antennae remain intact. Then the sheet unfolds again and waits for a new victim.
Where does the sundew grow
The habitat of predatory plants is wetlands, sandstones or mountains. They prefer lean soil, since all nutrients are obtained from captured insects. Many species are listed in the red books of the states in which they grow.
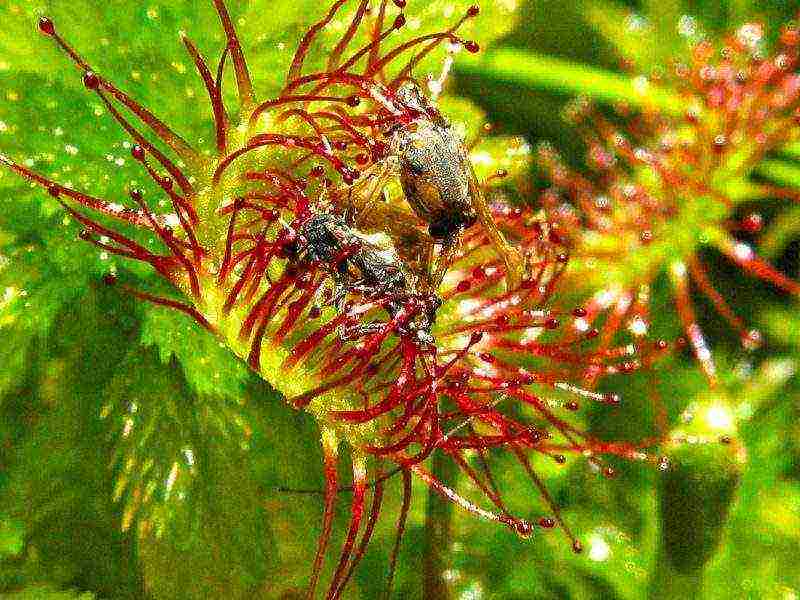

- In Russia, there are only four types of sundews: round-leaved, English, obovate and intermediate.
- There are known Australian sundews that live in the tropical forests of Queensland, among them there are interesting dwarf species.
- The representative of the forests of South Africa is the royal sundew. Of all the varieties, it has the largest leaves, which sometimes reach more than half a meter in length.
- In the USA, the filamentous sundew is growing.
Features of growing a predator plant
Growing sundews has nothing to do with caring for other plants. Special requirements are placed on soil, watering, lighting and even a flower pot.
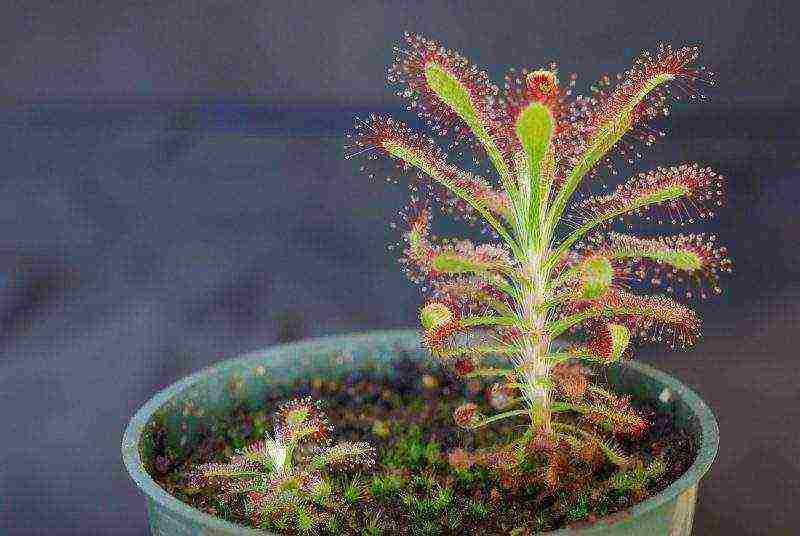

An important point is the lack of dressing. Only on very poor soil will a sundew have its natural look of a predator plant. An ordinary weed will grow on fertile soil.
The plant obtains all the substances necessary for growth on its own from the caught insects, but it can easily exist for several months and generally without nutrition. Flies are a favorite food, but other insects will do as well. They must be alive, just caught, for the green predator to agree to eat them.
Sundew care at home
If the plant is properly cared for, it can live more than 10 years in indoor conditions. Features of care are associated with the natural habitat of sundews.

- If the variety is native to the tropics, then it does not have a dormant period and in winter it needs additional lighting and high humidity.
- In tuberous sundews, with the onset of summer, a dormant period begins. They shed their leaves and only with a decrease in air temperature in the autumn do they grow again. Plants do not tolerate frost, but for normal growth, the air in the room where they grow must be cool. It is forbidden to water such sundews during sleep, otherwise the tuber will begin to rot and the plant will not survive.
- Some species, on the contrary, fall asleep in winter. Basically, these are representatives of a temperate climate, which are adapted to the changing seasons. In winter, they can shed all or some of the leaves, leaving a wintering bud on the soil surface. Watering such sundews is reduced to a minimum in cold weather. Fresh, young leaves will begin to grow in the spring.
Lighting and temperature
The sundews need bright lighting for normal development. The requirements for the amount of consumed rays of the sun depend on the type of plant. For most members of the genus, you need about five hours of exposure to direct sunlight, and the rest of the time - under bright, diffused lighting.
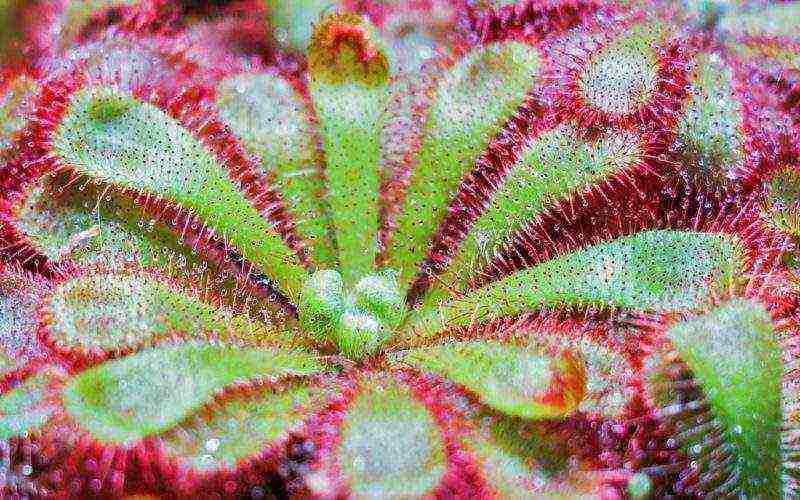

In the hot summer period, direct rays are needed only in the morning and in the evening, while in the afternoon, diffused light is preferable. The recommended total daylight hours are 12 to 16 hours.In winter, you can use fluorescent lighting.
Ground requirement
Marsh dewdrop prefers poor soil. For cultivation, a mixture of high-moor peat and perlite in equal parts is used. Instead of perlite, you can take sand. Perlite should be soaked in distilled water for several days before being added to peat. After that, the soil is prepared for planting. The finished substrate or its components are bought in flower shops.
Watering and humidity
Watering the predator plant is necessary only with distilled or rainwater. It should not contain any mineral salts. If this condition is not observed, the sticky liquid that attracts insects will cease to be produced.

To form droplets of liquid, the sundew needs increased air humidity, which is rather difficult to create, because you cannot spray the leaves with water.
It is impossible to water the soil from above, this is done through the pallet. In winter, when the soil dries slowly, the plant is watered once every one and a half or 2 weeks, in summer - almost every day.
How to transplant a sundew
To grow sundew, a mixture of peat and sand is prepared in equal proportions (acidic soil is needed). Transplanted in the spring when the old pot becomes too small or immediately after purchase from the store. The plant does not need frequent transplants.
The flower pot must be plastic. A ceramic container can interact with acidic peat and release salts, which are very harmful to the plant.
Plant the plant in moist soil to reduce stress on it and prevent dry soil particles from sticking to the leaves.
Sundew plant: reproduction
The plant propagates by seeds and root processes. Old leaves can also take root.
- A greenhouse with high air humidity is made for seeds.
- You need to sow seeds in a nutrient-poor substrate so that a common weed does not grow.
- After sowing on the soil surface, the seed is covered with glass until shoots appear. Maintains high humidity and good lighting.
But the easiest way to breed a sundew is to seat the offspring. The offspring sundew forms new plants on the peduncle at the point of contact with the ground.
Diseases, pests and control methods
Sundews get sick most often due to mistakes in care. Insufficient moisture can lead to drying of the leaves, they do not form "dew".

The plant is sick from lack of lighting, too high an air temperature and improper watering. Lighting should be bright, watering should be done only with distilled water in a tray. It is necessary to take into account the dormant periods of the plant and reduce watering when it sheds the leaves so that the root does not rot.


