Content

Turnip
Published by 11.01.2015 |
Turnip vegetable has been known to many of us since childhood. It is grown in order to obtain a root vegetable, which is subsequently used for food, for a variety of salads, etc. gardeners from the north and highlands especially like to grow turnips in their backyards, because due to insufficient heat, many vegetables simply do not grow. But turnips are not afraid of temperature changes, so it is very easy to grow it. It contains a lot of vitamins, so turnip salads and soups are extremely healthy.
Turnip differs very favorably from vegetables and other root crops in that it ripens very quickly. Within a couple of months, you can collect a solid harvest, while the turnip is completely unpretentious to growing conditions. It is best to grow turnips at a temperature of 12 to 20C, but growth goes well at both lower and higher temperatures, only slightly slower. If the temperature is above 23C, growth can be severely inhibited.
Wet soil for several weeks after the turnips are sown, as well as uniform moisture in the soil during the growth process, is the key to successful growth and a rich harvest. 2 weeks after the turnip has risen, the root crop is already beginning to form and becoming thicker in the ground. That is why timely watering is so important. Turnip can grow on any soil, but light soil, which is abundantly flavored with humus, is optimal for it. To be able to harvest in the summer, turnips need to be sown in early spring, because the plant is not afraid of frosts and cold snaps. In addition, the advantage of early sowing can be called the fact that the sprouts will not be susceptible to pests, which at such a time will simply not be due to the cold. The danger of earthen fleas is very great, they can completely destroy the turnip bed, so you need to protect the plant from pests. To harvest in the fall, turnips are sown a second time in July. During this period, earthen fleas disappear again for a while.
In the first decade of June, turnips are sown for the winter storage of this vegetable. In general, the timing of sowing turnips is determined by the presence of earthen fleas in the soil, which are the main pest of these tender sprouts.
Turnip sowing rules
The optimal distance between the rows is about 20 cm. You need to sow turnips on a low bed, only 5 grams of seeds are used per 10 m2. The seeds are buried to a depth of no more than 1 centimeter; they do not need to be deeply buried. The first shoots appear on the 3rd day, after a few days they need to be thinned out in such a way as to leave the strongest plants. When 5-6 leaves are formed on the turnip, it can be thinned again to get the highest quality harvest. For sowing, it is recommended to use only fresh seeds that were grown and harvested last year. You can also use turnips as a re-culture after early-ripening vegetables sown earlier were removed from the garden in June.
Turnip must be protected from pests, make sure that there are no weeds on the breast, loosen the soil and maintain the required level of soil moisture. Growing turnips can be severely complicated by cabbage keel disease. This can be dealt with by dusting with ash or road dust. Before planting, the soil is filled with humus, if necessary, liming is carried out. The soil must be carefully dug up and leveled.When the first shoots appear, you must try to loosen the soil deep enough, since the turnip has a long root crop.
Turnip turns out to be especially tasty, if you do not forget about regular abundant watering. If there is not enough moisture, the fruits can be bitter, they have a pungent aroma, and the roots themselves grow very slowly. If the weather is too dry and hot, water the turnip bed at the rate of 30 liters per square meter of land. Particular attention should be paid to soil moistening immediately after the entrances and at the time of the formation of root crops (one and a half months before harvesting).
Harvest
It is necessary to completely remove the turnip from the site before the onset of the first frost, since the root crops themselves do not tolerate the cold well. They can become soft, lose their flavor, and become unsuitable for long-term storage. It is very easy to pull a turnip out of the ground, then the tops should be carefully trimmed from it so that the delicate skin is not damaged. After cutting the tops, you can sprinkle the tops with chalk. You can dry the roots a little in a draft before storing. The roots are placed in the box so that they do not touch each other, the free space is sprinkled with sand. The ideal temperature for storing turnips is around 0C.
It is not recommended to delay harvesting, because if the root crop sits on the garden bed, it can become completely inedible.
Our ancestors knew how to grow turnips several centuries ago. After all, this vegetable plant has been known to people for more than four millennia. Already at this time, people not only knew perfectly how to grow turnips, but also used them as one of the main food products. True, with the advent of potatoes, the importance of this root crop has somewhat decreased. It was brought to Russia around the fourteenth century from Greece.
Variety selection
For most of us, this vegetable is associated with a flattened root vegetable from old Russian fairy tales. It has a golden yellow color and a hard, smooth surface. This type is one of the most common in our country. The people called him "wax". It is important for gardeners not only to know how to grow turnips in the open field. It is equally important to choose the right variety.

Not all varieties of this root crop grow in our country. We usually grow turnips obtained by Russian breeders. This is the Petrovsky variety. Although in some garden plots, the Japanese Geisha also grows well. In addition to these two varieties recommended by the State Register, the following varieties are also cultivated in our country - May yellow green-headed, Milanese white violet-headed, Golden ball, Snow Maiden and others.
Optimal conditions for growing turnips
This root vegetable is a light-loving plant. Those interested in how to grow turnips should know that they are a long day plant. Good illumination is one of the main conditions for its normal development. It is this that contributes to the accumulation of such a useful vitamin C in the root crop. Moreover, those who know well how to grow turnips are sure that the culture presents an increased demand for illumination in the first place during the initial period of growth.
The optimum temperature for growing and growing this root crop is between fifteen and twenty degrees Celsius. For those who are interested in how to grow turnips in the open field, you need to know that a lower regime can provoke the development of vershoks. For normal growth, the plant also needs sufficient moisture in the soil and air. The culture is especially demanding on the soil during the germination period and during the formation of leaves. Experts who know well how to grow turnips in the open field believe that timely watering at this time has a positive effect not only on the harvest, but also on the taste.
Peculiarities
Turnip always needs nitrogen.It must be fed to the plant during the entire growing period. Nitrogen helps to increase the protein in fruits. However, there should be a measure in everything, since with an excess of nitrogen in the crop, the growing season increases, and in addition, the keeping quality and quality of root crops decrease. In the early stages of cultivation and growth, the plant also needs phosphorus nutrition. This trace element stimulates the development of the root system, increases resistance to adverse conditions and increases the sugar content of the root crop. Potassium contributes to the accumulation of carbohydrates, protein and ascorbic acid in the vegetable. In general, for normal growth and development, any plant needs trace elements such as boron, calcium, copper, magnesium, manganese, etc. Turnip is no exception.
Where is the culture grown?
The most suitable for this culture are sandy loam or loamy soils cultivated by peat. However, turnip also tolerates well the soil with high acidity. And varieties with flat roots can be planted in a shallow arable layer - up to eighteen centimeters.

Those who are interested in how to grow turnips in the country should know that the best predecessors of this crop are tomato, cucumber, corn, zucchini, legumes and potatoes, for which organic fertilizers have already been applied. You should not plant a crop in highly acidic areas, especially after cabbage.
Landing
Growing turnips in your garden is not too difficult. The main thing is to know some of the features. Since turnip is an early maturing crop, it can be sown several times in one season. For summer use, seeds should be sown in spring. The harvest will be ready in sixty or seventy days. For autumn, sowing in July is acceptable, and for winter storage - in early August.
When sowing in spring, the land must be prepared already in the fall. To this end, an autumn digging should be carried out and the necessary fertilizers should be applied. With the onset of spring, deep loosening is carried out at the planting site - up to twenty centimeters. Then the rest of the fertilizer is applied again. For summer sowing, the land must be dug up to a depth of twenty centimeters and water abundantly at the rate of fifteen to twenty liters per square meter before sowing.

Turnips can be planted on a flat surface in the summer, and on ridges or ridges in the spring. The row spacing must be at least thirty centimeters. Turnips can be grown as a second or third crop after composting. But if organic matter was not introduced before planting, then humus should be given under the chill at the rate of two to three kilograms per square meter.
Phosphorus or potash fertilizers are applied in the fall and under pre-sowing treatment. Nitrogen fertilizers should be applied in the spring. Approximate doses are: ten to fifteen grams of urea per square meter, the same amount of sodium chloride and thirty to forty grams of superphosphate. If necessary, liming of the soil should be carried out.
How to grow turnips from seeds?
Planting material should only be taken from last year. The freshest seeds are the key to a good harvest. Any agronomist who knows firsthand how to grow a turnip will tell about this. At home, before planting, you should prepare the seeds for sowing. This process involves sizing and soaking the planting material. For convenience and uniformity of sowing, it is better to mix the seeds with sand or its mixture with superphosphate. Along the marked rows, grooves should be made two centimeters deep, which should be moistened as necessary.
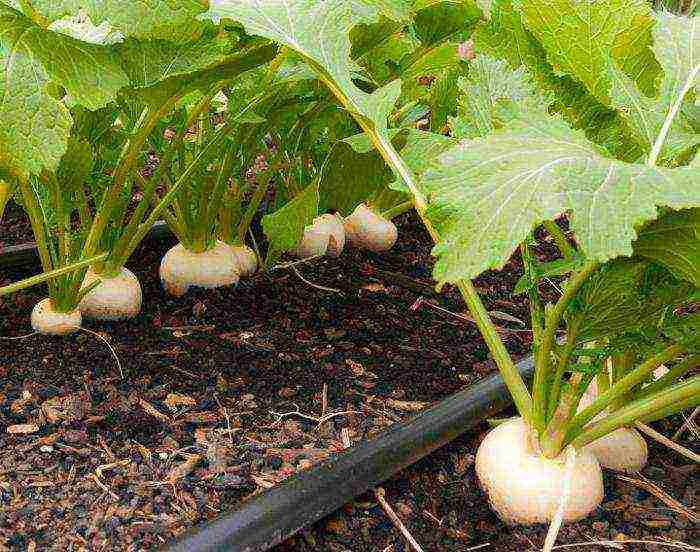

The seeding rate for turnip seeds is as follows: approximately one gram per square meter with a seeding depth of one to two centimeters. Planting material can be placed in the ground and nesting method - two or three pieces per hole, followed by thinning.
Care
Usually, seedlings appear on the fourth or seventh day after planting, depending on the temperature regime. Seedling care includes the obligatory removal of the soil crust.For this, a shallow, three to five centimeters, loosening is carried out. For the entire cultivation time, from three to five inter-row treatments are carried out. Before three true leaves are formed on the plant, thinning is carried out. The distance between bushes in a row should be from six to eight centimeters, and for summer crops - up to ten.
Thinning is most often carried out in the phase of two true leaves. This falls on about the twentieth day after germination. A distance of up to five centimeters should be left between the plants. When re-thinning is done, it increases to ten. And with the third - up to fifteen centimeters. If the sowing was carried out by the nesting method, then only the strongest plant should be left, removing all the others.
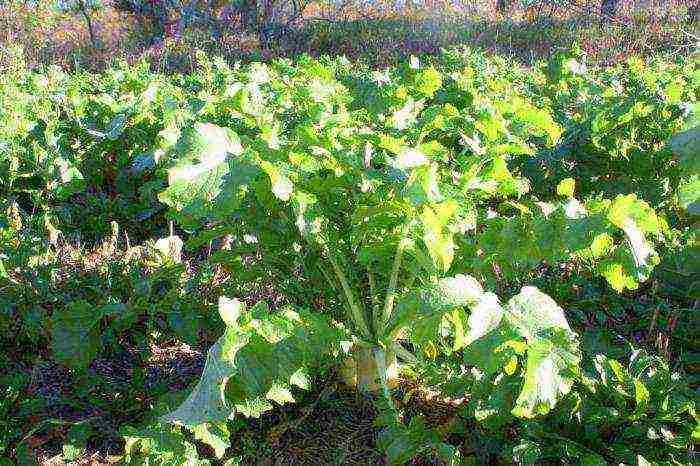

Those who know well how to grow turnips will say that weeding is very important for this crop. Weeds should not be allowed to grow on the garden bed, since the roots are deformed from this, and their quality decreases. In total, three shallow loosening should be carried out per season. In this case, it is better to slightly huddle the plants. The soil in the garden should always be moist. The rate is up to twenty liters of water for each square meter. Moreover, experts recommend alternating watering with loosening.
In general, the main steps in growing turnips are considered to ensure optimal plant density, sufficient moisture, cleanliness of the soil and pest control, especially with the cabbage fly and cruciferous flea.
Turnip harvest and storage
Root crops for summer consumption should be harvested selectively when they reach 6-8 centimeters in diameter, and for autumn and winter - at one time before the onset of frost. The plant must be pulled out of the soil and the leaves must be cut off immediately. A good yield is considered to be from two to five kilograms per square meter. Turnips keep very well in winter. The optimum temperature for storage is 0-1 degrees Celsius, and the air humidity is 90%. Root crops need to be sprinkled with wet sand or peat, although some store the crop in plastic bags.
Pest control
In the first stages of cultivation, until the formation of the first two true leaves, that is, within ten days after the emergence of sprouts, the cabbage fly and cruciferous flea are the most dangerous for the culture.

To combat the first pest, it is recommended to introduce drugs such as "Bazudin" and "Medvetox" into the soil. And from a cruciferous flea, the "Iskra" remedy will help well. If you do not take appropriate measures, then in dry and hot weather, this pest is able to completely destroy the sprouts. It is recommended that against cruciferous flea beetles, always keep the inoculated area optimally moist.
Turnip - a biennial plant of the cabbage family. Her homeland is the coast of the Atlantic Ocean and the North Sea. This ancient vegetable, which entered the culture 40 centuries ago, is grown in all regions of the humny ball. In Russia, before the introduction of potatoes, turnip was the main vegetable crop.
Turnip roots contain sugars, mineral salts, mustard oils, vitamins PP, Bi and B2, provitamin A, but it is especially rich in vitamin C. It is found in roots and turnip leaves up to 140 mg% - three times more than in cabbage. Young turnip leaves are also extremely useful. They contain compounds of potassium, magnesium, phosphorus. Of the trace elements, iron, copper, manganese, zinc are present. Turnips are eaten raw, steamed, boiled and fried, seasoned with kvass or butter. It can be fermented like cabbage.
Due to the significant amount of fiber that stimulates intestinal motility, turnips are recommended for constipation. In folk medicine, turnip juice is used to treat scurvy and kidney stones. It also has a beneficial effect on joint diseases.A decoction of turnip is recommended for colds, lung diseases, as a diuretic and pain reliever.
An infusion of leaves helps with toothache. In Tibetan medicine, turnip seeds are prescribed for all diseases. However, it should be remembered that turnip is contraindicated in inflammatory processes in the intestines, acute and chronic hepatitis and cholecystitis, diseases of the central nervous system.
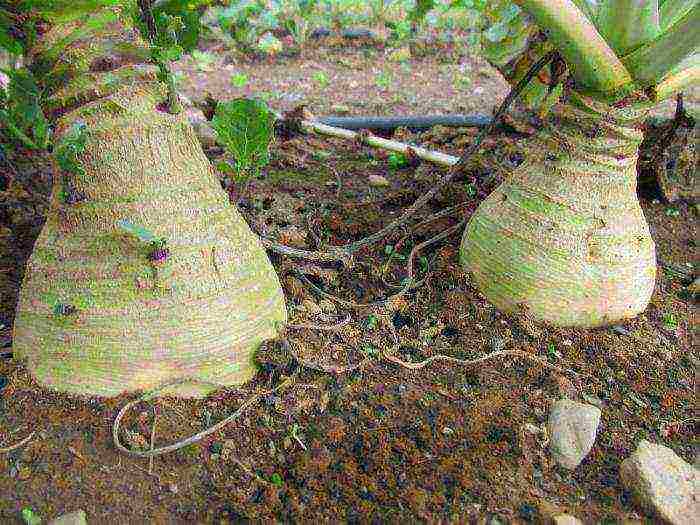
The turnip root crop is flat, flat-round, fleshy. The bark is yellow or white, smooth, yellow, green, purple, bronze in the underground part. The pulp is white, juicy, with a sweetish rare aftertaste. The seeds are very small, have a high germination capacity (85-95%) and retain it for four to five years.
Turnip is a plant of a temperate climate. It is undemanding to the soil, but it works best on light, moderately moist. On heavy soil, the taste of the root crop deteriorates. The culture is very early ripening: the period from germination to harvesting is 70-90 days, but two-month-old roots can also be eaten. Two varieties are suitable for indoor cultivation.
Turnip varieties
Geisha - early maturing, very productive variety. The root crop is round, white. The pulp is dense, the taste is excellent. Accumulates little nitrates.
Petrovskaya - an old mid-early variety. The growing season lasts 60-75 days. The root crop is flat or flat-round, with a concave bottom. Taste is good, but bitterness is sometimes encountered.
Planting and caring for turnips
At home, turnips are cultivated mainly for the sake of greenery, but if there is space, root crops are also grown (before they ripen, you can cut the leaves through a row). This technique is also safe for the harvest: two weeks before harvesting, all the leaves are cut off, leaving six to eight leaf petioles above the root crop.
Seeds are sown in February - March, earlier with additional lighting. The soil mixture for turnips is made up of garden soil and river sand (2: 1). For 5-6 kg of the mixture, one glass of ash and 20 g of nitroammophoska are added. The acidic soil is limed. Everything is thoroughly mixed and poured into seed boxes 8-10 cm high or into another container. Turnip seeds do not need germination, but before sowing they are heated in hot water for disinfection, and then mixed with sand (1: 3) for better germination and sown in rows every 5 cm to a depth of 1.5-2 cm.
The boxes are covered with foil, which is removed after germination. Thin the turnips twice. After the second thinning, the distance between the plants should be 5-6 cm. Water preferably with warm, settled water. With poor development, the plants are fed with a solution of complex ballastless fertilizers (1-2 g per 1 liter of water). Turnip is very responsive to spraying water on the leaves, the resulting greens are juicy and tender. Root crops with a diameter of 4-5 cm are harvested.
Turnip grows successfully on a loggia and balcony. In this case, very early sowing is possible. Sometimes it is carried out in the fall, the boxes are covered with rags and left for the winter. With the onset of warm days, they are heated and exposed closer to the sun.
Turnip is one of the oldest vegetable plants. Known for over 4 thousand years. In Russia, according to various sources, it has been grown since the XIV century - it was brought from Greece. As a vegetable crop, it has been a staple food for a very long time. But the emergence of potatoes diminished the importance of this root crop. This article - growing turnips in the open field - I hope will help gardeners learn more about this, unfortunately, a rare vegetable in our gardens.
Biological features of turnip as a plant
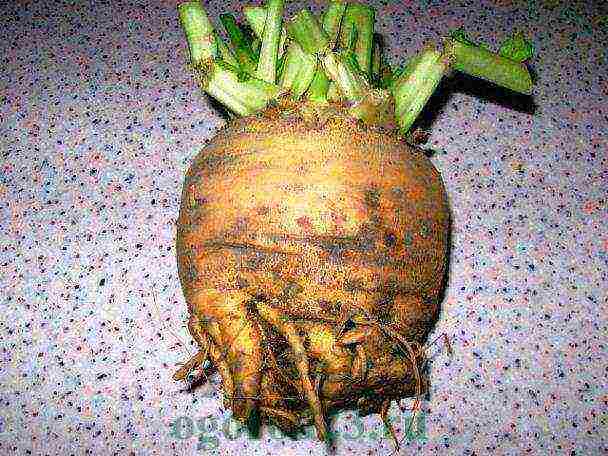

Turnip (Brassica rara L.) belongs to the cabbage family. It is a biennial plant. In the first year, root crops and a rosette of leaves are formed, in the second year the plant blooms and forms seeds. Turnip seeds are round, smooth, small, brown in color. The mass of 1 thousand seeds is 1.5-3.8 g. They remain viable for up to 5 years.
Turnip is the most cold-resistant root vegetable. Seeds begin to germinate at a temperature of 1-3 ° C. The optimum temperature for seed germination is 8-10 ° C. Young plants can withstand frosts down to -6 ° C, adults - up to -8 ° C. Early ripening varieties are less resistant to frost than late ripening ones.
↑ back to contents ↑ Subspecies of turnips
On the territory of Russia, mainly cultivated varieties of turnips of the European subspecies. The shape of their roots can be flat, round, oval and elongated. The outer color of root crops is yellow or white, the head of the root crop in some cases can be purple or green. Root pulp is yellow or white. The bark is thin, smooth. Root crops are submerged in the soil for one third or half of their length. Leaves are dissected, less often whole, pubescent, but sometimes smooth. The mass of the root crop is from 200 grams to half a kilogram.
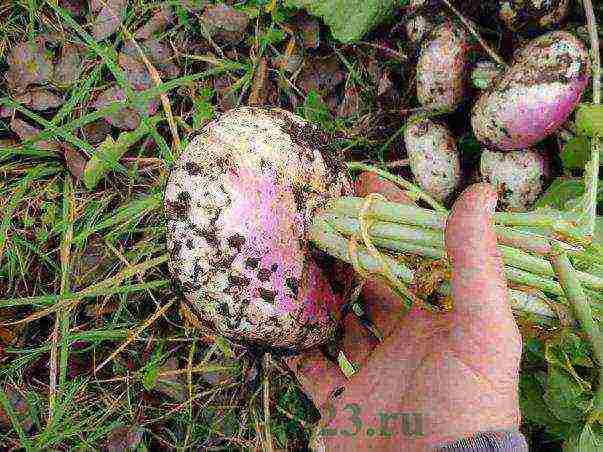

In varieties of turnips of the European subspecies, root crops are used for food, both raw and after cooking.
Recently, varieties of turnips of the Japanese subspecies have become popular. Plants form smooth, beautiful, round or flat-round roots with a diameter of 5-20 cm, white color. The leaves are whole.
The root vegetables of the Japanese turnip have a less pronounced taste inherent in the European. They accumulate up to 17 mg% of vitamin C and a number of other valuable components. They are distinguished by early maturity.
Along with root crops, many varieties of the Japanese subspecies also use leaves for food. Their leaf blades are thin and delicate, characterized by a significant content of ascorbic acid (up to 75 mg%), carotene (1.8 mg%), and minerals.
There are leafy forms of the Japanese turnip. Plants form a small root crop and a well-developed leaf rosette, consisting of large, undisturbed leaves. Such green products contain up to 75 mg% ascorbic acid, then 3.3 mg% carotene.
Local varieties of the Afghan turnip subspecies are grown in the republics of Central Asia. These roots are flat-rounded, with red or white bark.
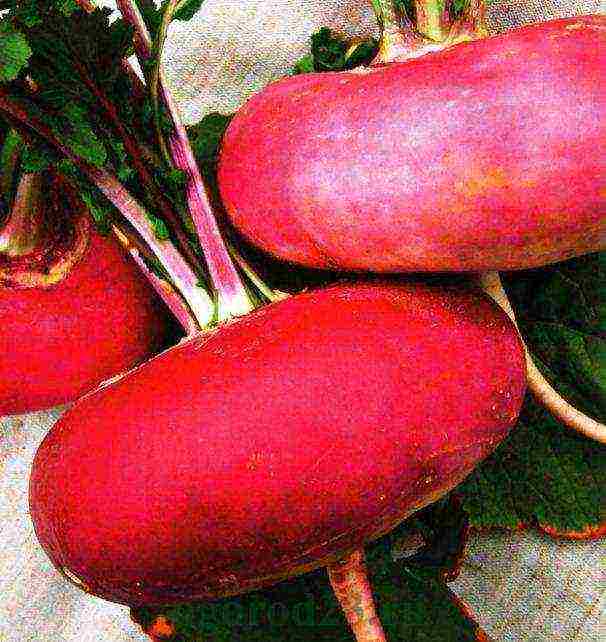
↑ to contents ↑ Choice of turnip variety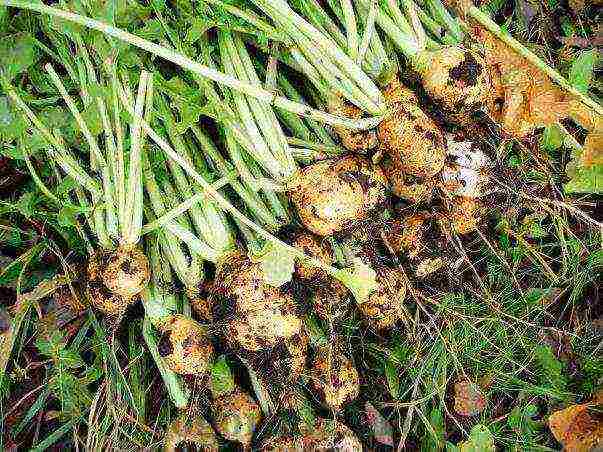 
Turnip golden ball We usually grow varieties of both the old Russian selection (Petrovskaya) and Japanese (Geisha). In addition to these varieties recommended by the State Register, the varieties Mayskaya yellow green-headed, Milanskaya white violet-headed, Golden ball, Snegurochka, and others are cultivated.
 Turnip Petrovskaya↑ to the content ↑ Growing turnips - optimal conditions
Turnip Petrovskaya↑ to the content ↑ Growing turnips - optimal conditions
Turnip is a light-loving plant. Good illumination contributes to the accumulation of vitamin C by root crops. It makes increased requirements for illumination in the initial period of growth. This is a long day plant.
The optimum temperature for cultivation, growth of a root crop is 15-20 ° C. Low positive temperatures provoke the flowering of plants.
For the normal growth of turnips, sufficient moisture in the soil and air is necessary. It is especially demanding on soil moisture during germination and the beginning of leaf formation, as well as before harvesting. Watering during these periods has a positive effect on the taste and yield of root crops.
Suitable for growing turnips are loamy and sandy loam soils, cultivated peatlands. It transfers the increased acidity of the soil. Turnip varieties with flat roots put up with a shallow arable layer (15-18 cm).
The best predecessors are crops for which organic fertilizers were applied: cucumber, zucchini, tomato, legumes, potatoes, corn. Turnips should not be grown in acidic areas, after cabbage. Turnips and other crops of the cabbage family should return to their original place no earlier than after 4 years.
Turnips have a significant need for nutrients.
Nitrogen is required throughout the growing period and contributes to an increase in the protein content of roots. With its excess, the growing season increases, keeping quality and product quality decreases. At the first stages of cultivation, growth of the crop, phosphorus nutrition is important.
Phosphorus stimulates root growth, increases plant resistance to unfavorable conditions, increases the sugar content of root crops.
Potassium contributes to the accumulation of protein, carbohydrates, ascorbic acid by the vegetable.
Calcium, magnesium, boron, copper, manganese are also important for the normal growth and development of plants.
↑ back to content ↑ Planting turnips - agricultural technology
Turnip is an early ripening crop, which allows it to be sown several times per season. Mostly it is grown in two, less often three times. For summer consumption, seeds are sown in spring - in the Kuban at the end of March-April, and in central Russia - at the end of April-beginning of May. The harvest is ready in 60-70 days.
For autumn use, July sowing is acceptable, the growing period is 50-60 days. To bookmark for winter storage, sowing is carried out in late July-early August, the crop is harvested after 70-75 days.
With spring sowing, the soil begins to be prepared in the fall. An autumn digging is carried out with the introduction of the necessary fertilizers. In the spring, deep loosening (up to 20 cm) is carried out with the introduction of the rest of the fertilizers. For summer sowing, the soil is dug to a depth of 20-22 cm, watered before sowing (15-20 liters of water per 1m2.
Turnips can be grown on a flat surface (in summer) or on ridges or ridges (in spring). The distance between the rows is 30 cm.
It is grown as a 2-3rd crop after the application of manure. If organic matter was not introduced, then 2-3 kg / m2 of humus is given under the fall. Phosphorus and potash fertilizers are applied in the fall (2/3 dose) and under pre-sowing treatment (1/3 dose). Nitrogen fertilizers are fed in the spring. Approximate doses of fertilizers: urea - 10-15 g / m2, superphosphate - 30-40 g / m2, potassium chloride - 15-20 g / m2. If necessary, liming of the soil is carried out.
Seed preparation for sowing includes calibration and soaking. For convenience, uniformity of sowing, seeds are mixed with sand or a mixture of sand with superphosphate. On the marked rows, grooves are made with a depth of 1.5-2 cm, which, if necessary, are moistened. Sowing with watering is especially important during summer and autumn growing periods.
The seeding rate is 1-0.15 g / m2. The seeding depth is 1-2 cm. You can also sow by the nest method, 2-3 seeds per nest, followed by thinning. Seedlings usually appear in 4-7 days, depending on the temperature.
Crop care includes the fight against the soil crust, for which they carry out shallow, 3-5 cm, loosening. For the entire growing period, 3-5 inter-row treatments are carried out.
Before the formation of three true leaves on the plants, they are thinned out. The distance between plants in a row is 6-8 cm (with summer crops - up to 10 cm).
About 48 plants are placed on 1 m2.
The soil should be constantly moist, the irrigation rate is 10-20 liters of oxen per 1 m2. It is recommended to alternate watering with loosening.
The main points of agrotechnology for growing turnips are:
- fighting cruciferous flea and cabbage fly;
- ensuring sufficient moisture and cleanliness of the soil;
- ensuring optimal plant density.
↑ back to content ↑ Harvesting and storage of turnips
For summer consumption, root crops are harvested selectively when the diameter reaches 6-8 cm. For autumn and winter consumption, turnips are harvested before the onset of frost in one step. Plants are pulled out of the soil, the leaves are immediately cut off. The yield is 2-5 kg / m2.

Turnip Snow Globe Turnip keeps well in winter. The optimum storage temperature is 0-1 ° C, the optimum air humidity is 90-95%. Root crops are sprinkled with wet sand or peat, they can also be stored in plastic bags. All this allows you to provide yourself with fresh root crops for the whole year.
↑ back to contents ↑ Pest and disease control of turnip
At the first stages of turnip growth - before the formation of the first pair of true leaves, which is about 10 days after germination, the cruciferous flea and cabbage flour are the most dangerous for plants. For cabbage fly, it is recommended to add Bazudin or Medvetox preparations to the soil.Iskra is a good remedy for cruciferous flea beetles (10 g tablet per 10 g water). If you do not take appropriate measures, then in hot dry weather, cruciferous fleas can completely destroy seedlings. Against the cruciferous flea, it is important to keep the crop area moist.
Of more radical measures to combat the flea and cabbage fly, it is possible to recommend dusting the area with fine lime, tobacco dust or ash.
From diseases, turnip can be affected by keel and mucous bacteriosis. To avoid this, when sowing, water the soil with a solution of colloidal sulfur, adhere to crop rotation.


