Content
- 1 White mushroom: description
- 2 Varieties of porcini mushrooms
- 3 We grow mushrooms in the country
- 4 White mushrooms at home
- 5 Requirements for planting material
- 6 Mushroom growing technology
- 7 Growing methods in the garden
- 8 Sowing forest mycelium
- 9 How to prepare seed yourself
- 10 Buying ready-made mycelium
- 11 Selection and preparation of the substrate
- 12 Growing features
- 13 Mushroom picker tips
- 14 Video "Self-cultivation of porcini mushrooms"
- 15 Cultivation of porcini mushrooms (boletus)
- 16 Growing boletus (redheads)
- 17 How to grow boletus
- 18 Granular butter dish - growing on the site
- 19 Cultivation of saffron milk caps in the country
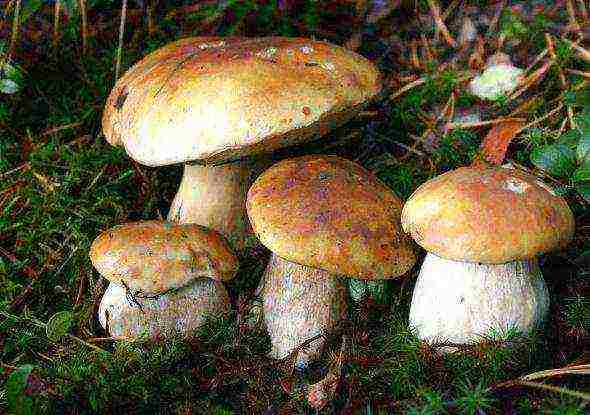
White mushroom is deservedly and rightfully considered the standard for other mushrooms. He also looks attractive - with a fleshy brown hat on a white pot-bellied leg, and his taste is excellent. When fried, porcini mushrooms emit a special, nutty aroma. The mushroom got its name - white - because its incision does not darken during drying and cooking, while maintaining a juicy, appetizing structure. And today we will consider the cultivation of porcini mushrooms at home and not only.
White mushroom: description
Almost everywhere white mushroom is also called boletus. And also it is called a bear, a white-grouse, a wood grouse. No matter how else this forest handsome man is called in numerous corners of Russia, he always looks distinctive:
- The boletus cap is brown. It changes its bulge with the age of the fungus. From a semi-cylindrical shape in a small mushroom, it gradually makes a transition to an almost flat, about 20 cm in diameter, hat of an adult mushroom.
- The stem is always whitish, with characteristic brownish vertical veins. At first it has the shape of a barrel, and as it grows, it stretches into a dense, powerful cylinder.
Now you can visually distinguish the porcini mushroom (you received the description) from other forest mushrooms.
Varieties of porcini mushrooms
The porcini mushroom has many forms, and their varieties depend on the trees under which the mushroom grows and in symbiosis with which it enters:
- The pine shape is perhaps the most colorful of the porcini mushrooms. It has a beautiful brown hat and a slightly purple-tinged leg, slightly thickened at the bottom.
- The spruce form is the most common in central Russia. The hat has a brownish-reddish color, with spots and a rim along the edge. The leg is barrel-shaped, covered to the middle with a fine mesh.
- Oak form - strong porcini mushrooms with elastic brown caps with a grayish tint.
- Dark bronze shape - the name speaks for itself. Hats are dark, wrinkled; legs are brownish.
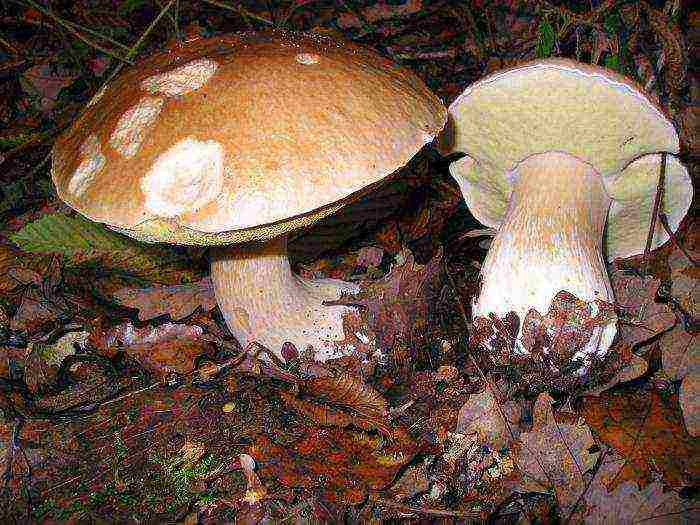 Boletus growing in shaded areas has a lighter color of the cap. And their fellows, who grew up in the sun, have a rich brown top. The mushroom absolutely does not tolerate strongly shaded and mossy places. For example, it will not grow in a dense forest. And he will choose comfortable, slightly shaded or sunny places.
Boletus growing in shaded areas has a lighter color of the cap. And their fellows, who grew up in the sun, have a rich brown top. The mushroom absolutely does not tolerate strongly shaded and mossy places. For example, it will not grow in a dense forest. And he will choose comfortable, slightly shaded or sunny places.
We grow mushrooms in the country
If a mushroom picker returns from the forest with a basket full of boletus, it means that he did not go mushrooming in vain. Many people wonder if it is possible to grow mushrooms in the country in order to admire the beautiful landscape, and, of course, it is guaranteed to have a rare product on the table. Yes, growing a king of mushrooms in a garden is quite possible, although not an easy task. You need to know the intricacies and peculiarities of breeding this fastidious forest sturdy fellow, but as a result of hard work, the first white mushrooms will grow near your country house.
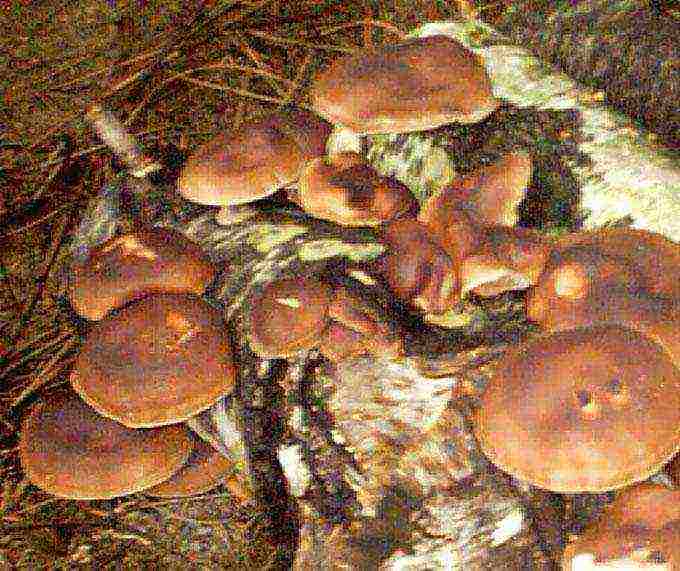 So, growing mushrooms in the country.It will not be easy to achieve results because the porcini mushroom belongs to the mycorrhizal group, which indicates their duty and very difficult intergrowth and interlacing with the roots of the trees under which they live. This is a very complex and vital symbiosis for fungi. Without a tree, or rather its roots, the so-called fungus root cannot form and the fruit growing on the surface cannot develop. Therefore, alas, it will not work to grow porcini mushrooms in a bare area.
So, growing mushrooms in the country.It will not be easy to achieve results because the porcini mushroom belongs to the mycorrhizal group, which indicates their duty and very difficult intergrowth and interlacing with the roots of the trees under which they live. This is a very complex and vital symbiosis for fungi. Without a tree, or rather its roots, the so-called fungus root cannot form and the fruit growing on the surface cannot develop. Therefore, alas, it will not work to grow porcini mushrooms in a bare area.
A long-standing and well-proven method of cultivation is in an area where trees between ten and thirty years old grow. White mushroom settles under pine, spruce, oak, birch, beech. Matching tree species when replanting mycelium is necessary. The more similar the conditions of a summer cottage plantation of boletus mushrooms with their forest location, the more chances that they will successfully take root.
White mushrooms at home
If you wish, you can master the cultivation of mushrooms at home, having studied the accumulated experience of scientists from Holland. With the help of the technologies they recommend, you can start growing the product in greenhouses and dug cellars.
 The cultivation of a plantation with an intensive method, namely, it is taken into service at home, has its own difficulties. One of them is a considerable investment, the purchase of equipment to ensure the required temperature and humidity in the room. But the advantages of this growing method are considerable - fertility throughout the season and a good ripening rate. For effective indoor breeding, it is recommended to use mycelium cultivation.
The cultivation of a plantation with an intensive method, namely, it is taken into service at home, has its own difficulties. One of them is a considerable investment, the purchase of equipment to ensure the required temperature and humidity in the room. But the advantages of this growing method are considerable - fertility throughout the season and a good ripening rate. For effective indoor breeding, it is recommended to use mycelium cultivation.
Requirements for planting material
It is advisable to purchase planting material from suppliers with recommendations, carefully study all the initial data of the mycelium indicated on the label. It is very important to pay attention to the smell and color of the mycelium. If there is a weak ammonia smell, immediately reject the batch of planting material - it was overheated and is now unviable. The color of a healthy exudate is orange with a slight yellowness.
Having brought home the packages with the purchased mycelium, you need to cool them, ventilate and only then start preparing before laying. The contents of the bags are crushed without tearing the packaging. Thus, they maintain a gentle and adaptive temperature regime for the future mycelium. When laying, sterility is very important:
- it is necessary to work with gloves;
- premises for growing porcini mushrooms and laying mycelium should be separate;
- opening the package, it is necessary to process it with a disinfectant solution.
Mushroom growing technology
To complete the topic of the previous paragraph, let's start with the method of germinating a crop at home. So, growing mushrooms at home. Here are the main stages of indoor work:
- Boiling in bags for 1-1.5 hours and subsequent cooling of the substrate. (Hole water drainage bags).
- Mixing mycelium and substrate on disinfected tables. The availability of domestic material should be at the level of 5%, and imported - 2.5%.
- Putting the mixture into bags. Tamp the grafted substrate tightly into bags, flatten one side and make several cuts for the mushrooms to germinate.
- Place the bags vertically on the shelves. Watering is normal, without strong waterlogging. Ventilation of the room is required.
- If the care was correct, the crop of mushrooms can be harvested for at least six months.
This is how porcini mushrooms are grown at home. Yes, quite difficult, but worth it.
Growing methods in the garden
Growing porcini mushrooms at home is strikingly different from growing in a personal plot. But first things first.
 For cultivation of porcini mushrooms on the site, first prepare the place for laying the mycelium. On the top layer of soil previously removed with a shovel, compost or soil with peat is laid. Lay the planting material, cover it with a layer of turf removed earlier.
For cultivation of porcini mushrooms on the site, first prepare the place for laying the mycelium. On the top layer of soil previously removed with a shovel, compost or soil with peat is laid. Lay the planting material, cover it with a layer of turf removed earlier.
The most effective options for harvesting seed is to bring several pieces of mycelium the size of a chicken egg from the forest. Such blanks are planted in the soil without processing, it is only important to observe at least two conditions:
- The trees under which the boletus grew in nature should be of the same species with the plants at the new planting site.
- It is necessary to dig out the material very carefully - porcini mushrooms are hard to grow together with the roots and restore communication with the satellite tree.
Sowing forest mycelium
How to grow porcini mushrooms if there is no way to purchase high-quality planting material?
A very good effect is given by the method of sowing mycelium using the cap and the tubular part of the porcini mushroom. 5-6 mature caps are taken, it is possible even with wormholes, and soaked for a day in a bucket of water. Then the contents are kneaded with your hands. The thick is separated into another container. The thick mass is the body of the mushroom, and it comes in handy too. The bare roots of the tree are spilled with the remaining liquid with a large number of spores, then everything is covered with a layer of thick mushroom substance and sprinkled on top with the soil removed earlier. It is necessary to carefully water the planted mycelium and carry out subsequent watering once a week in the absence of rain.
Now you are familiar with the cultivation of porcini mushrooms at home, and in the garden, where, with the correct observance of all technologies, you can get a harvest of boletus the first time in a year or two. Good luck!
Plant mushrooms. "Who will plant them, these are mushrooms." But you can plant them, I checked in practice. The fact is that mushrooms reproduce in two ways. With the help of mycelium (here we are powerless, the main thing is not to harm). And yet - by spores that ripen in the hat.
Everyone knows the "witch's rings" when mushrooms grow like a ring. The explanation is simple. The hat is round, not far from the ground, spores are poured out “for themselves”. The next year, the fungi grow in a small, dense ring. And again, everyone is dusting for themselves. And after 10-15 years, the ring reaches a diameter of 1-2 meters. This effect should be used, especially for the propagation of mushrooms in the forest, at their summer cottage, on an alpine hill.

This is done simply. As a rule, a mushroom picker, finding an old flabby or wormy mushroom, simply leaves it on the ground, and even turns the cap upside down. There is absolutely no sense from this. I do this. I take the hat and put it on a spruce branch, or prick it on a dry one. This kills two birds with one stone.
Firstly, the cap does not rot, but dries, the spores ripen and grow dusty over a large area. You look, and several new foci of myceliums are tied. Secondly, the mushroom dries up. And in winter, in the most hungry time for animals, you look, and will please any hare, squirrel or bird.
You work - 5 seconds, and the benefits are great. If every mushroom picker “picks up” at least 20-30 mushrooms per trip, then the number of mushrooms will become more and more, not less and less. Leave the mushrooms to your descendants, do not deprive them of this pleasure. Source - magazine "Do it yourself"
Mushrooms on the site
Believe it or not, up to 30 species of a wide variety of mushrooms can be grown on the garden plot. Of course, some of them settle in our gardens on their own, but we simply do not notice some of them, we kick others with our feet, considering them to be toadstools. However, despite the strong adherence of compatriots to porcini mushrooms, milk mushrooms and similar gifts of the forest, it will not hurt to reconsider our attitude to some of them, growing literally under our feet, edible and tasty, but unfamiliar.
So, in Europe, the lilac-footed ryadovka is considered one of the most delicious mushrooms. On our site, it grows on potato ridges. The dissonant name dung beetle does not detract from the value of this mushroom, which can grow on a lawn, in a shady place on manured garden soil. When fried, to taste, the shaggy white dung leaves behind the most delicious mushrooms. Umbrella mushrooms, ring mushrooms, and several types of champignons willingly grow on composts.One hat of a variegated umbrella is enough for a whole frying pan. And what to say about shiitake - legends are made about the healing properties of this mushroom with the Japanese name.
My own practical experience confirms that it is possible to grow forest mushrooms on the garden plot - boletus, boletus, oil cans and others.
Very often, field or forest mushrooms appear on garden plots by self-seeding. The slender pig is often found in the beds with cucumbers, if they grow nearby: birches. On our lawn, fertilized with a fertile substrate, two species of edible spit fungus grow by self-seeding. Sometimes in the gardens, milk lovers are found in abundance. violins, morels and other mushrooms.
In addition to forest and field mushrooms, tree mushrooms - various types of oyster mushrooms - successfully grow in the open-air garden. mushrooms are summer, autumn and winter, and it is hard to believe. - shiitake. On compost beds, you can successfully grow mushrooms and ringworms. And now let's take a closer look at the mentioned mushrooms and the methods of growing them in the garden.
Macorizic mushrooms
These are mushrooms that live in symbiosis with trees, that is, their fruiting bodies are formed only after the mycelium is introduced into the roots of trees and the formation of mycorrhiza, or. in other words, fungus root. This is why many cap mushrooms grow only in the forest. Moreover, often a certain mushroom is confined to a certain tree species, as evidenced by the popular names of these mushrooms: boletus, boletus, oak, etc. Different mushrooms have different preferences for soil fertility and its acidity.
The relationship between the tree and the fungus, in general terms, is as follows: the host tree stimulates the growth of mycelium only if it lacks mineral substances. obtained from the soil. Then the branched hyphae of the fungus begin to supply the tree with mineral salts and water from the topsoil in exchange for carbohydrate nutrition in the form of tree sap with sugars. Therefore, porcini mushrooms are more likely to appear under a birch on poor sandy soil than on fertile soil. The question arises, how to make forest mushrooms grow in the garden?
White mushroom
White mushroom, or boletus (Boletus edulis). - the tubular mushroom is without a doubt the most welcome guest, both in the kitchen and in the garden. Its nutritional value and taste can hardly be overestimated. For a person who grew up in Russia, no mushrooms smell as pleasant as dried porcini.
It makes no sense to describe the appearance of the porcini mushroom, it is not familiar, perhaps, to newborns. But the fact that porcini mushrooms growing under different trees differ from each other in appearance is interesting.
Those. that grow under birches, the cap is light, the flesh is tender and, according to some mushroom pickers, the most delicious. Porcini mushrooms, shade under the spruce, darker. And the most beautiful porcini mushroom, with a red-brown cap, grows under a pine tree. It is believed that each of these varieties of white fungus forms mycorrhiza only with its own tree species.
The porcini mushroom on a dry matter basis contains 41% protein, which is more than in any other mushroom, and significantly more than in meat (31%).
Porcini mushrooms prefer sandy soils if they grow under birch trees; on fertile soils with a high nitrogen content, their fruiting bodies are formed worse. Although under oak trees, which are much more demanding on soil fertility, porcini mushrooms are more likely to grow in rich soil.
The birch form of the porcini mushroom is more common, since there are birches in almost every forest. The porcini mushroom prefers to grow under mature enough trees - twenty years and older. If they are not there, then it is best to bring young birch trees from the forest, but those that grew near an adult birch, where porcini mushrooms were seen.
In this case, one can hope that the roots of the trees already have mycorrhiza.
It is easier to breed porcini mushrooms in the garden if there are adult birches there. I have tried two methods.The first method is simple, but not effective enough. It consists in the usual laying out of pieces of a mature mushroom under a leaf litter within a radius of 1.5 m from the trunks of birch trees. The second method turned out to be more productive, it is based on the preparation of a suspension of spores isolated from old mushrooms and their sowing.

Making a spore suspension at home
From the caps of large mature (and even overripe) porcini mushrooms collected in the forest under birches, it is necessary to separate the tubular layer (hymenophore), where spores form, pass this mass through a meat grinder, transfer to a container with water (1-2 kg of mushroom mass per 10 l of water) and mix thoroughly. Then add 15 g of dry baker's yeast to the mixture, mix again and leave everything to infuse (for convenience, the mixture can be poured into three-liter cans) at room temperature for two weeks. Soon, foam with pulp particles and small debris forms on the surface of the liquid.
In the middle of the container there will be a clear liquid, and at the bottom the spores will collect in a layer of several centimeters.
The addition of baker's yeast spores to the spore suspension is very effective in stimulating their germination. Yeast is a nutrient substrate, and also helps to mix the crushed mass of mushroom pulp and release spores.
Sunlight falling on the plantation in the morning and in the evening stimulates the fruiting of the porcini mushroom.
The foam must be carefully removed from the surface with a spoon, the water must be carefully drained, and the sediment with spores from different containers must be combined into one jar and allowed to stand for another week. After that, drain the supernatant once more, and pour the remaining suspension with spores into plastic liter bottles and store in the refrigerator.
The finished spore suspension sometimes acquires a not very pleasant smell, but remains viable for a year.
It is advisable to use a suspension of spores within a month after preparation, since during long-term storage the activity of spores decreases.
Sowing spores and caring for a mushroom plantation
Before sowing, the suspension with spores must be diluted with water in a ratio of 1: 100. evenly pour the liquid under the birches (you can use a watering can with a strainer) and wait for the harvest. With good care of the plantation, the fruiting bodies of the porcini mushroom may appear as early as next year. What is this care?
As you know, all mushrooms love high soil and air humidity. Therefore, in the dry season, crops must be watered and protected from the hot midday sun. In the area where porcini mushrooms are cultivated, under the trees, it is advisable to plant shrubs or other plants that create a light shade and protect the area from the sun on the south side.
Watering is needed not only during the development of the mycelium in the soil, but also after the appearance of full bodies. In the second half of the day, when the sun's rays no longer fall on the plantation due to the crowns of trees and shrubs, it is advisable to arrange a slight "mushroom rain". that is, watering with a fine spray with water heated during the day.
After the night, the caps of the mushrooms are moistened with morning dew, then the moisture evaporates, and at this time the mushroom grows, since along with the evaporation of moisture, nutrients from the mycelium come into it. Then watering and drying out the caps in the evening also stimulates the growth of the fruiting body.
The introduction of mineral fertilizers into the soil can have a negative effect on the development of mycelium, therefore, they should not be used on a mushroom plantation.
Growing porcini mushrooms in garden plots with different conditions
In 2006, two different sites were "seeded" with a suspension of spores of porcini mushrooms collected in the forest and prepared according to the technology described above: one in the Moscow region, the other in the Tver region. On a plot of two hundred square meters near Moscow, sparsely growing birches of various ages were present; in the second plot, young birches grew. Previously, porcini mushrooms were not found in both garden plots. In previous years, pigs, russula and boletus were found on a site in the Tver region.In addition to the different ages of the birches in different plots, the differences in conditions were as follows: in 2007, which is considered non-fungal due to the dry summer, the plot outside Moscow was regularly watered, while the plot in the Tver region was not. Probably, these reasons led to different results, namely: in the first section, my work was rewarded with 20 porcini mushrooms for three waves of fruiting in August, in the second - porcini mushrooms never appeared.
Porcini and boletus mushrooms are in a competitive relationship, so it is better to sow their spores in different, isolated areas with birches.
Obviously, the presence of old birches and regular watering have a beneficial effect on the growth of porcini mushrooms. One of the possible reasons for the absence of mushrooms in the second site, in my opinion, is the presence of the boletus mycelium, which is in competition with the porcini mushroom and suppresses the development of its mycelium.
Boletus and boletus
Both of these tubular fungi are widespread in our forests, including those near Moscow. They are. undoubtedly popular with their compatriots and very tasty.
The boletus (Leccinum) is represented by two species. In common with aspen, the boletus L. aurantiacum grows - a beautiful mushroom with a red cap and a leg covered with red scales.
Unfortunately, aspen is a rare tree species in the garden.
Another species of boletus, L. vulpinum, is found under the pines. He has a darker cap and black scales on the stem. Gardeners, especially in recent years, willingly plant pines and other conifers on their plots.
Aspen mushrooms grow better on poor sandy soils than on rich ones.
Fruit bodies of both species have a bright taste and a strong pleasant smell that is different from other mushrooms. Boletus boletuses are little affected by insect larvae and are well stored. It is the perfect mushroom for stir-fry. The mushroom pieces, which partially retain their shape when fried, form a tasty crust. Fried boletus has a slightly sour taste. Mahra (tubular layer), as a rule, is also suitable for soup and roast. The broth turns out to be dark, but thin slices of boletus caps with terry become a decoration of mushroom soup.
Many gourmets put boletus to taste in fried and boiled form in the first place.
Boletus mushrooms have an undeniable advantage over porcini and aspen mushrooms: the likelihood of their appearance on the garden plot after sowing is much higher.
Boletus, or common boletus (Lec-cinuni scabrum). the taste is closest to porcini mushroom. At a young age, it has dense flesh and a beautiful velvety cap; in middle-aged boletus boletuses, the terry becomes loose. This mushroom is in many ways inferior to porcini and orange-cap boletus in consistency. Its less dense fruiting body contains more water and is poorly stored. The boletus legs quickly become stiff and fibrous. To make boletus boletus more attractive in dishes, remove the terry and pre-blanch them to remove some of the excess water.
With proper care of the boletus plantation, its yields are more frequent and higher than those of the porcini mushroom. With regular moistening of the earth, they can appear under the birches by themselves. On the garden plot, where the growth of mushrooms is under constant supervision, boletus mushrooms do not have time to worm, they can be collected in a timely manner, although under natural conditions these mushrooms are strongly affected by insect larvae and quickly deteriorate.
Sowing spores and caring for a mushroom plantation in a garden plot
A joint suspension of boletus and boletus was prepared in the same way as in the case of porcini mushroom. Boletus spores, when standing in jars, settled in the form of a dark layer. The boletus spores mostly remained in the mixture with the pulp, poorly precipitating, so it was necessary to use a suspension of spores together with the pulp.
Sowing of boletus and aspen mushrooms was carried out in August 2006 on a garden plot in the Moscow region throughout its entire territory, except for two acres allocated for the porcini mushroom.
In dry weather, the soil was regularly moistened, as on a plantation with porcini mushrooms. The mushroom site was protected from direct sunlight in the daytime by planting plants, but was illuminated by the morning and evening sun. When fruiting bodies appeared, watering was daily.
Mushroom harvest
Sowing spores, we hoped that the boletus would take root on the roots of the pine trees, and the boletus - on the roots of the birch trees. In 2006, one boletus grew on this site, and in 2007 there were none. The boletus boletus yielded large yields. For the sake of fairness, I must say that boletus boletus came across in this garden area in 2006 before our sowing. But in the non-mushroom 2007 they grew several times more than in the wet mushroom 2006.
However, we do not lose hope for good "harvests" of aspen mushrooms in the future: the appearance of even a single mushroom inspires confidence.
Chanterelles and dry milk mushrooms
Chanterelles and milk mushrooms are also mycorrhizal fungi. These mushrooms have gnmenophores. where the spores ripen, in the form of plates, therefore they are called lamellar. The chanterelle is in symbiosis with conifers, although it is also found in deciduous forests, and dry milk mushrooms form mycorrhiza with birches. Both mushrooms prefer calcareous soil. Chanterelle (Cantharellus cibarius) grows steadily from June until frost, constantly and everywhere, even in a dry year.
In Europe, and in Russia, many people prefer chanterelles to other mushrooms. There are reasons for this. They are bright yellow so they are easy to find. They often come across in groups, so you can collect a lot of them. Even those who are not particularly versed in mushrooms know that chanterelles are not poisonous. Chanterelles often spontaneously appear in garden plots if there are conifers there.
As for the taste of chanterelles, their taste and smell, though mushroom, are weak. They are good in frying, as they are a little fried, but it is better to cook them together with other, more aromatic mushrooms. published
Thanks to its rich taste and delicate aroma, the porcini mushroom is considered the most valuable trophy from the "quiet hunt". However, not all gourmets like to wander through the forests in search of prey, but this delicacy is not cheap. However, there is a way out! Let's find out how to grow porcini mushrooms on your own plot.
How to prepare seed yourself
To grow mushrooms at home, you need to stock up on seed. To cook it yourself, you need to find overripe boletus in the forest (dried and wormy ones will do).
To obtain seed, you need about 10 caps. At home, separate them from the stalks and prepare a container of water. Alcohol (3 tablespoons per 10 liters), potassium permanganate (1 g per bucket) and granulated sugar (50 g) can be added to the water. Knead the caps in your hands and add them to the water to make a homogeneous mass. It should be infused for about 10 hours. Then strain it. Spores of fungi are contained in water, cake is not needed. Use the caps collected in the forest within a few hours, otherwise they will deteriorate. You cannot freeze them.
To grow boletus at home, you can use the mycelium brought from the forest: having found an adult mushroom in the forest, cut off a layer of earth around it about 25x25 cm. At home, you can completely lay the mycelium in the prepared soil, or divide it into 8–20 pieces.
Buying ready-made mycelium
Growing porcini mushrooms at home is possible with the help of a purchased mycelium. The mycelium of the porcini mushroom can be either dry or already germinated, placed in a substrate. If you intend to purchase it online, choose a trusted and reliable supplier. When buying directly, pay attention: the sprouted mycelium of porcini mushrooms should be red in color with small yellow blotches.The presence of black and green areas, as well as a strong smell of ammonia, indicate that the product is spoiled.
In open areas, planting the mycelium of porcini mushrooms should be carried out under a forest tree. The first harvest can be expected next year. Fruiting from the mycelium lasts on average 3-4 years, but if useful microorganisms (for example, "Baikal EM-1") are added to the water for irrigation, this period can be increased to seven years and, moreover, the yield can be increased.
Selection and preparation of the substrate
To grow mushrooms in the garden, you can use a purchased substrate or cook it yourself. To do this, you need to mix straw, sawdust of deciduous trees, sunflower husks. Other sources recommend alternating layers: one from a mixture of dead leaves with sawdust, the second from the same mixture with the addition of soil. It is important that none of the components contain rot and mold. Before planting mushrooms, the substrate must be properly moistened, and it is recommended to use boiling water or steam - this will kill harmful bacteria at the same time.
Growing features
First, decide where you will grow your crop: in the basement, greenhouse or on the site. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages.
First, let's look at how to grow a porcini mushroom on the site.
The cultivation of porcini mushrooms in a personal plot assumes the presence of coniferous or deciduous forest trees there. Fruit mushrooms will not work - you need to plant porcini mushrooms in the country away from any cultivated plants, be it trees, shrubs or vegetables.
Remove the top layer of earth (about 15 cm) around the selected tree. It is desirable that the roots are exposed at the same time, but in no case should they be damaged. If using a spore infusion, pour it on the ground (approximately 350 ml per 25 cm2). Then cover again with earth and water abundantly - either along the trunk or with shallow irrigation. In this way, you can plant a porcini mushroom in the country in August-September.
To plant mycelium, make a 1.5 sq. m in diameter and 30 cm deep. Place the substrate in it, alternating it with the ground in 10 cm layers. The height of such a bed should be 20 cm above ground level. Plant the mycelium in the substrate in a checkerboard pattern at a distance of 30 cm between the bags. Carefully water the garden bed, cover it with a layer of fallen leaves.
Planting mycelium can be carried out from May to September.
Caring for planted mushrooms consists mainly of abundant watering. For the winter, it is recommended to cover them with a thick layer of foliage, spruce branches or straw.
When growing mushrooms indoors, it must first be sterilized with a 1% chlorine solution, otherwise pests may start, including various types of mold and parasitic insects.
Growing mushrooms in a greenhouse or in a basement implies creating a warm and humid microclimate, since it will not work to grow many porcini mushrooms in dry air. In order for the greenhouse atmosphere to meet these requirements, it is recommended to install several barrels of water or wet sawdust there.
The substrate for the premises is the same as for open areas. In the basement, bags with small incisions are filled with them. Sowing is recommended with mycelium. The bags should be placed no closer than 5 cm from each other.
During the incubation period (until the caps appear), the temperature should be maintained at + 23–25 ° C; a temperature of +30 ° C will destroy most of the myceliums of the grown crop.
Lighting is not required at this time. In the greenhouse, it is advisable to muffle it as much as possible, in the basement it is simply not to turn it on. Airing is not necessary, but the humidity should not be more than 90%, so that mold does not start. Also, for its prevention, disinfection is periodically done with a chlorine solution.
Growing mushrooms need different care: when the caps appear, the temperature is lowered to +10 ° C. Now the greenhouse or cellar should be well ventilated - oxygen is necessary for the normal development of boletus.Lighting is required for 5-6 hours a day. To grow porcini mushrooms in a greenhouse, it must be muted, without direct sunlight. It is advisable to spray mushrooms from a spray bottle 2 times a day: this will make their structure denser. The first crop can usually be taken in 20-25 days.
Moldy bags must be removed from the premises immediately. Mushrooms cannot be grown on them, but they can become a good fertilizer.
Please note: boletus can hardly take root without trees, and the first attempts to grow in the basement may be unsuccessful. But if you intend to start breeding porcini mushrooms in this way, choose the Dutch mycelium: in Holland, a boletus variety was bred, which grows most easily "in captivity".
But having mastered all the subtleties, indoors you can get a harvest of mushrooms all year round or even start growing porcini mushrooms on an industrial scale: since growing boletus is more difficult than champignon or oyster mushroom, it is much more appreciated.
Mushroom picker tips
Finally - small secrets of mushroom growing.
When self-collecting the seed, the boletus that grew near the type of tree that is on your site will take root better. When physically transferring mycelium, their appearance must necessarily match.
It is recommended to disinfect the substrate or soil with a solution of tannins 2-3 hours before planting. It can be made from cheap black tea: 50-100 g is poured into 1 liter of boiling water and brewed until it cools completely. Another option is oak bark. It will need 30 g per 1 liter of water. The bark should be boiled for an hour, adding water to the original volume as it boils. Each "mushroom" tree needs 2-3 liters of one of these solutions.
Video "Self-cultivation of porcini mushrooms"
From this video you will learn how to grow porcini mushrooms on your site.
Do you love mushrooms, but you have no time to pick them? Don't be scared, start growing mushrooms in the country yourself. The main thing is to know how to do it correctly in order to get a guaranteed harvest.
Growing mushrooms in the country is convenient because you can control this process, creating the most favorable conditions for their growth. And what about the forest: it was a dry summer, and then early frosts of the soil and that's it - there will be no harvest of forest mushrooms! If you do not want to depend on the vagaries of nature, feel free to try to grow mushroom plantations on your site.
Cultivation of porcini mushrooms (boletus)
This handsome man, the king of all mushrooms, can be safely relocated from the forest to your site, and with a favorable outcome, you will get an impressive harvest next year.
There are several ways to breed forest boletus.
Mycelium transplant
Few resort to this method, since the outcome of the operation depends on careful adherence to the technology. Judge for yourself, it is quite difficult to dig out the mycelium and transfer it to your site, while not damaging it. Nevertheless, many have succeeded, you should try it too.
The transferred mycelium should interact with the roots of shrubs and trees, so choose a place on the site where deciduous or coniferous trees and bushes grow! It is extremely important to plant a porcini mushroom under the same tree from under which the mycelium was dug.
So, choose a suitable place on your site and prepare the ground next to the desired tree. To do this, remove 20-30 cm of the topsoil at a distance of 0.5 m from the tree trunk. At the bottom of the formed hole, lay the prepared compost from fallen leaves and tree dust, and sprinkle it on top with a small layer of earth. Now you can lay a layer of earth with mycelium, water and sprinkle with a layer of leaves. If the weather is dry in the first 14 days after planting, periodically water the mycelium.
Growing mushrooms from mycelium
One of the most popular methods among mushroom pickers. Ready-made mycelium can be purchased - it is readily available in many garden stores.Before proceeding with this method, prepare the site and soil. Choose a location in the shade of trees where the soil is moist. At a distance of 0.5 m from the tree trunk, remove the top layer of earth to a depth of 0.5 m. Calculate the area of the fossa in advance, based on the amount of acquired mycelium.
This is what mushroom mycelium looks like.
Prepare a substrate from dust, sawdust and leaves. Lay it on the bottom of the hole in a layer of about 20 cm. Sprinkle with soil on top (about 10 cm). Next, lay a mixed layer of soil and compost. Now, on top of this, you can put mycelium mixed with the ground. Spread it out by hand, tamping evenly. Sprinkle on top with soil and water, cover with fallen leaves.
Ready-made substrates for planting porcini mushrooms, as well as mycelium, are sold in specialized stores. These mixtures are a great alternative to forest mushrooms.
After planting the mycelium, the area must be watered regularly. If the planting of the mycelium is successful, then the harvest will appear as early as next year. Such mycelium can bear fruit from 2 to 5 years.
Mushroom seedlings
The easiest way to grow porcini mushrooms is from mushroom seedlings. To do this, it is enough to finely chop or pass the mushroom caps through a meat grinder. Then pour the resulting substance with water and leave for 24 hours. During this time, you can start preparing the site. Dig up the soil under your chosen tree and fertilize it generously with compost (same as above). Pour the mushroom infusion over the prepared place, and sprinkle with leaves on top.
If there are no forest trees on your site, do not despair - try planting mushrooms near wooden buildings on the shady side. And remember that the porcini mushroom does not like fruit trees, so try to avoid such a neighborhood.
In cold winters, do not forget to sprinkle the mycelium with compost, and, if necessary, cover with polyethylene or roofing material.
The optimal time for planting porcini mushrooms is from May to September. Mushrooms should be planted in the ground at dusk.
Growing boletus (redheads)
As you may have guessed from the name, this mushroom mainly grows in aspen groves. Sometimes it can also be found in a mixed forest. If you undertake to grow a mushroom in the country, then the issue of choosing a site should be approached as carefully as in the case of a porcini mushroom.
Boletus, like many other forest mushrooms, belongs to mycorrhizal fungi. This means that it forms symbiosis with the roots of trees, i.e. mutually beneficial cohabitation. Therefore, the site must be aspen, birch or oak. In the shade of these trees and plant your future plantation.
Boletus boletus can be bred using:
- Spore (mushroom seedlings)
Spores form on the underside of the caps of overgrown mushrooms. Here you should prepare them: pour water and leave for several hours. With the resulting infusion of spores in water, pour the area you have chosen for growing mushrooms. Also, the caps can be dried and used as seed. Germinating spores form the mycelium (mycelium).
- Fruit bodies
Collect young aspen boletus in the forest, chop and bury in your area in the upper soil layer in the shade of trees.
- Mycelium
Wild Mycelium can be harvested from the forest by digging up with soil and trees. Thus, you will move the mycelium to your site, just as in the case of boletus. Alternatively, you can buy ready-made mycelium from the store.
Mushroom plantation and care
Prepare compost. Spread a plastic wrap on the ground, lay on it in layers, leaves and wood dust with manure, taken in a ratio of 9: 1. Pour warm water over a bunch and let it sit for a week. During this time, it should warm up to a temperature of 35-40 ° C. Now it can be shoveled until smooth and left for another 5 days.
Redheads can be planted from mid-May to September (in warmer regions - from early May).
In the selected area around the tree, dig a hole 30 cm deep and 2 square meters in area. If the roots of the tree are on or close to the surface of the soil, remove only the top layer.
Fill the pit with compost. If it is deep, then put the compost to ground level, in a shallow one - spread in layers, alternating between compost (10-12 cm) and soil (5-6 cm), until the height of the layers reaches 50 cm above ground level.
Then, at a distance of 25-30 cm, make holes 20 cm deep. Dip pieces of boletus mycelium in them and cover them with soil. Immediately water the plantation with 20 liters of water per square meter and cover with a layer of fallen leaves or forest floor.
Do not forget to insulate the mycelium for the winter.
In order for the mycelium to take root, it is useful to feed it with a sugar solution: 10 g of sugar per 10 liters of water. Keep the soil slightly moist in the summer. Water the area periodically, especially during dry periods. For the winter, cover it with a layer of fallen leaves, moss or spruce branches, and do not forget to remove them in the spring.
Under favorable conditions, the fruiting of boletus begins the next year after the establishment of the plantation. The yield is 5-15 mushrooms per sq.m. With proper care, a mushroom meadow will delight you with a harvest for 4-5 years. After this period, the mycelium of the mushrooms must be planted again using the same method.
How to grow boletus
The next “forest dweller”, beloved by many mushroom pickers, is boletus, which is also easy to grow on your own.
Boletus, like any forest mushroom, needs not a stump, but a living tree for normal life and growth. From its root system, the mycelium absorbs carbohydrates and amino acids, giving the tree moisture, mineral compounds and natural antibiotics that protect it from pests and diseases. Therefore, it is extremely important that the mushroom zone is as close as possible to the natural habitat of the mushroom.
As for the cultivation methods, they are the same as for boletus and boletus.
Reproduction by spores
Finely chop the overripe mushrooms, mix with one spoonful of flour and gelatin powder. Pour the mixture into moist soil under mature trees. The spores will germinate and form a fungus root. The first harvest can be expected in a few seasons.
Growing from fruit bodies
Select young boletus boletus, chop and bury in the topsoil next to the root system of the tree. Fruit bodies form mycelium, and after a year with good soil moisture, you can get a small crop of 2-3 mushrooms.
Alternatively, in rainy weather, you can scatter small pieces of young mushrooms under the trees and cover them with fallen leaves. Mycelium formation will be no less effective.
Mycelium transplant
This is a laborious and not always effective process. Find a young tree in the forest with boletus under it. Dig up the mycelium carefully and transfer it to your site. Place it under a deciduous or coniferous tree.
Do not place mushroom plantings next to fruit crops, as mushrooms form mycorrhiza and grow in symbiosis only with forest trees. Many mushrooms are even named after the trees next to which they live (boletus, boletus).
Granular butter dish - growing on the site
This mushroom is just very convenient to breed by transplanting mycelium.
If you notice a couple of small pines with a constant harvest of oil, you can safely transplant mushrooms to your site. Remember, boletus plants prefer lime-rich soils and indirect sunlight. The mycelium tolerates transplantation quite comfortably and takes root well. With regular watering (especially abundant watering in dry weather), the first mushrooms will appear in 3-4 years and will delight you with abundant fruiting throughout the season - every three weeks, starting from mid-May.
Summer boletus is almost not susceptible to attacks by worms, and the size of their caps can reach 10 cm.
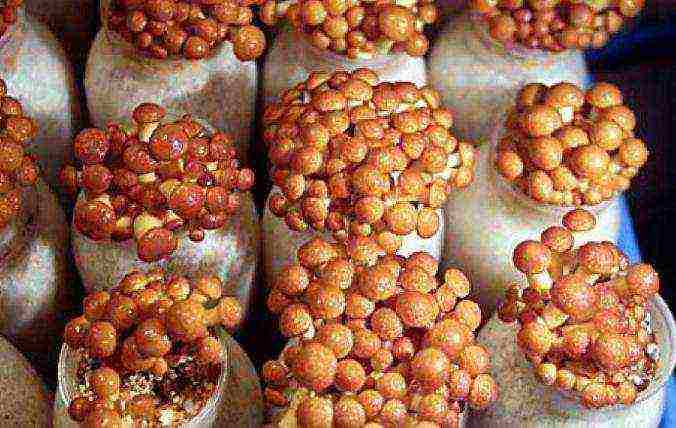
Cultivation of saffron milk caps in the country
Another wonderful mushroom that is so easy to "domesticate" is the mushroom!
For him, as for his forest brothers, it is also important to create the right conditions, as close to natural as possible. The mushrooms prefer to grow in the shade with good air circulation. The soil should be moist and contain decaying leaves and needles. It is important to ensure that with the onset of spring, the site is not flooded with water, otherwise the mushrooms will die.
You can breed a camelina plantation in several ways.
Sowing mycelium
As in the previous cases, collect the caps, but this time the old mushrooms. Chop them finely and, after drying on a cloth, gently lay them out on damp ground. Tamp it well, cover it with moss and pour it over with warm water. After 2 weeks, lift the moss: if greenish-purple threads are visible under it, similar to ordinary mold, and the caps have disappeared, then the mycelium has taken root.
Spruce mushrooms should be placed under spruces, and pine mushrooms - under pines.
Transfer of mycelium
This method is also very effective in the case of sowing saffron milk caps. Carefully dig out the mycelium with a layer thickness of at least 25 cm, being careful not to damage it. Plant the mycelium as soon as possible so that it does not dry out, and do not forget to regularly moisten the soil.
The first mushrooms will germinate only the next year after you have planted the mycelium or transferred the mycelium. You need to collect them, carefully cutting the leg and trying not to damage the root. If you do not follow this rule, then the number of mushrooms will only decrease every year.
Of course, not every summer resident can grow the harvest of forest mushrooms on their own the first time. However, do not despair. Try to tame different "forest dwellers", look for optimal breeding methods, and very soon this laborious process will be rewarded with the first harvest of domestic mushrooms.