Content [show]
Many people love mushrooms for their taste and dietary properties. Someone even tries to organize mushroom farms on their own, producing oyster mushrooms or champignons. Is it possible to organize the cultivation of forest oil, for example, in your country house? Fortunately, self-cultivation of boletus is not so difficult today.

The appearance of the butterflies is easily recognizable thanks to the brown oily cap covered with a sticky layer
Back to content
Distribution in nature
The oiler chooses places in forest zones of a temperate climate, preferring sandy soils with a light structure and a high content of limestone, rich in organic matter. The geography of its distribution is extensive - Europe, North America, Asia and Australia. In Russia, all kinds of butter oil are found everywhere: from the forest-steppe zones of the Saratov and Voronezh regions to the Far East and Siberia.
Belonging to mycorrhizal fungi, boletus mainly grow at the roots of young conifers and bear fruit up to 15 years.

Back to content
Growing methods
Industrial cultivation is limited by the lack of highly profitable technologies that allow the use of intensive cultivation methods in indoor conditions. Growing oil on industrial plots requires coniferous planting of large areas. Therefore, only amateur breeding of boletus has become widespread. The use of extensive methods, as close as possible to natural ones, makes it possible to obtain myceliums of high fertility and excellent quality mushrooms.
There are several ways to grow wild mushrooms at home.
Taking into account the characteristic feature of oleagus to form mycorrhiza only with the roots of young coniferous trees, the plantation for cultivation is selected based on the presence of at least several young pines, cedars, larches or spruces on the site. The exact species of trees are determined by the type of oil taken in the cultivation and the immediate growing conditions of the mycelium from which the mycelium was taken.
At home, the most suitable age for trees is about 10, maximum - 15 years. Young trees take a minimum of nutrients from the soil and water, leaving more food for the mushrooms. This neighborhood allows the mycelium to develop as actively as possible, therefore, the process of growing mushrooms will be the most effective.

Butterlets will not be able to live on their own, without a patron tree
Back to content
Soil preparation
The optimal soil for the development of mycelium is prepared as follows. In the selected area (preferably in partial shade, however, sunny areas are also suitable for boletus), the upper soil layer is removed. Since the correct cultivation technology requires the formation of several layers of soil, plant materials are placed in the first layer, for example, chopped wood, grass, foliage, needles. For the second layer, it is advisable to use the soil collected in the places where mushrooms grow, then it will have an acid-base balance that corresponds to the optimal one as much as possible. You can take the usual garden land in the country. If necessary, humus can be added to it. The mycelium is sown on the soil prepared in this way.
Back to content
Sowing mycelium
Although today it is not difficult to purchase oil mycelium obtained in the conditions of specialized laboratories, mushroom growers prefer to collect spores of overripe mushrooms in the forest. The reason for this lies in the nature of the mushroom's nutrition, in which it receives most of the necessary organic matter from the patron tree. Consequently, successful cultivation requires a specific soil composition and tree species to form symbiosis. For independent cultivation of boletus, these conditions are of paramount importance, otherwise the fruiting bodies may not form, despite the successful development of the mycelium.
It is not difficult to get mycelium oil from spores at home. To do this, the collected mushrooms should be mixed with a substrate prepared on the basis of a mixture of coniferous sawdust and peat and helping to create a nutrient medium close to natural. It is better if the wood species favorable for the cultivation of oil is used for sawdust. Ideally, if these are the breeds next to which the mushrooms grew, collected for the preparation of mycelium.
Growing mycelium is as follows. The dried substrate is up to half laid out in three-liter jars, lightly tamped and poured into 1.5 liters of a special nutrient solution for the mycelium. It is prepared from sugar syrup and yeast suspension (for 1 liter of water - 1 tsp sugar and the same amount of yeast). The solution is brought to a boil and poured into peat packed in jars. Fill the remaining volume of the jar with dried sawdust and close it with a tight lid. It will take about 5 hours for the substrate to be fully saturated with nutrients. The remaining water should be drained, the substrate should be mixed and the pieces of mushrooms with spores should be placed in the puncture holes made with a stick. The jar is closed with a lid with a hole (about 1.5 cm), covered with a foam rubber stopper. The development of hyphae takes about 3 months at a room temperature of 23-25 ° C. The substrate with mycelium matured for cultivation is stored before sowing in a cold (about 6 ° C) and dark room.

Back to content
Sowing mycelium, leaving and harvesting
In spring, the substrate, filled with multiplied mycelium, is evenly distributed in a thin layer on trees, covered with a layer of leaves or grass, sprinkled on top with garden or forest soil (with subsequent moistening of the upper soil layer). To protect the soil from drying out, the area can be covered with a thin layer of grass or leaves and periodically moistened.
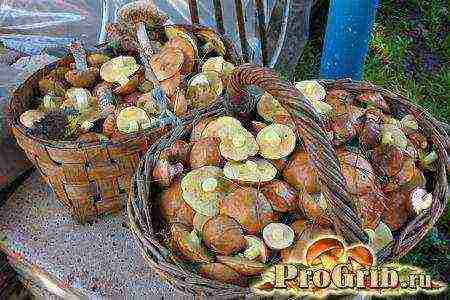
Fruiting of home-grown butter plants (in the garden or in the country) begins a year after the mycelium is planted and lasts about 15 years. Although in the first years one should not count on a significant harvest (the mycelium develops for about 5–7 years), in subsequent years the volume of harvesting of fruit bodies will increase significantly.
Many people love mushrooms for their taste and dietary properties. Someone even independently tries to arrange mushroom farms, producing oyster mushrooms or
Champignon
... Is it possible to organize the cultivation of forest oil, for example, in your country house? Fortunately, self-cultivation of boletus is not so difficult today. The appearance of the butterflies is easily recognizable thanks to the brown oily cap covered with a sticky layer
Distribution in nature
The oiler chooses places in forest zones of a temperate climate, preferring sandy soils with a light structure and a high content of limestone, rich in organic matter. The geography of its distribution is extensive - Europe, North America, Asia and Australia. In Russia, all kinds of butter oil are found everywhere: from the forest-steppe zones of the Saratov and Voronezh regions to the Far East and Siberia.
Belonging to mycorrhizal fungi, boletus mainly grow at the roots of young conifers and bear fruit up to 15 years.
Growing methods
Industrial cultivation is limited by the lack of highly profitable technologies that allow the use of intensive cultivation methods in indoor conditions. Growing oil on industrial plots requires coniferous planting of large areas. Therefore, only amateur breeding of boletus has become widespread. The use of extensive methods, as close as possible to natural ones, makes it possible to obtain myceliums of high fertility and excellent quality mushrooms.
There are several ways to grow wild mushrooms at home. Taking into account the characteristic feature of oleagus to form mycorrhiza only with the roots of young coniferous trees, the plantation for cultivation is selected based on the presence of at least several young pines, cedars, larches or spruces on the site. The exact species of trees are determined by the type of oil taken in the cultivation and the immediate growing conditions of the mycelium from which the mycelium was taken.
At home, the most suitable age for trees is about 10, maximum - 15 years. Young trees take a minimum of nutrients from the soil and water, leaving more food for the mushrooms. This neighborhood allows the mycelium to develop as actively as possible, therefore, the process of growing mushrooms will be the most effective.
Methods for growing boletus
Butterlets will not be able to live on their own, without a patron tree
Soil preparation
The optimal soil for the development of mycelium is prepared as follows. In the selected area (preferably in partial shade, however, sunny areas are also suitable for boletus), the upper soil layer is removed. Since the correct cultivation technology requires the formation of several layers of soil, plant materials are placed in the first layer, for example, chopped wood, grass, foliage, needles. For the second layer, it is advisable to use the soil collected in the places of growth.
mushrooms
, then it will have an acid-base balance that corresponds to the optimal one as much as possible. You can take the usual garden land in the country. If necessary, humus can be added to it. The mycelium is sown on the soil prepared in this way.
Sowing mycelium Although today it is not difficult to purchase oil mycelium obtained in the conditions of specialized laboratories, mushroom growers prefer to collect spores of overripe mushrooms in the forest. The reason for this lies in the nature of the mushroom's nutrition, in which it receives most of the necessary organic matter from the patron tree. Consequently, successful cultivation requires a specific soil composition and tree species to form symbiosis. For independent cultivation of boletus, these conditions are of paramount importance, otherwise the fruiting bodies may not form, despite the successful development of the mycelium.
It is not difficult to get mycelium oil from spores at home. To do this, the collected mushrooms should be mixed with a substrate prepared on the basis of a mixture of coniferous sawdust and peat and helping to create a nutrient medium close to natural. It is better if the wood species favorable for the cultivation of oil is used for sawdust. Ideally, if these are the breeds next to which the mushrooms grew, collected for the preparation of mycelium.
Growing mycelium is as follows. The dried substrate is up to half laid out in three-liter jars, lightly tamped and poured into 1.5 liters of a special nutrient solution for the mycelium. It is prepared from sugar syrup and yeast suspension (for 1 liter of water - 1 tsp sugar and the same amount of yeast). The solution is brought to a boil and poured into peat packed in jars. Fill the remaining volume of the jar with dried sawdust and close it with a tight lid. It will take about 5 hours for the substrate to be fully saturated with nutrients.The remaining water should be drained, the substrate should be mixed and the pieces of mushrooms with spores should be placed in the puncture holes made with a stick. The jar is closed with a lid with a hole (about 1.5 cm), covered with a foam rubber stopper. The development of hyphae takes about 3 months at a room temperature of 23-25 ° C. The substrate with mycelium matured for cultivation is stored before sowing in a cold (about 6 ° C) and dark room.
Sowing mycelium, leaving and harvesting In spring, the substrate, filled with multiplied mycelium, is evenly distributed in a thin layer on trees, covered with a layer of leaves or grass, sprinkled on top with garden or forest soil (with subsequent moistening of the upper soil layer). To protect the soil from drying out, the area can be covered with a thin layer of grass or leaves and periodically moistened.
Harvesting butter
Fruiting of home-grown butter plants (in the garden or in the country) begins a year after the mycelium is planted and lasts about 15 years. Although in the first years one should not count on a significant harvest (the mycelium develops for about 5–7 years), in subsequent years the volume of harvesting of fruit bodies will increase significantly.

We all know what you can grow mushrooms, oyster mushrooms, mushrooms for personal use and for sale. What about forest mushrooms: white, chanterelle, boletus and others? After all, they are mycorrhizal, that is, they cannot live and develop independently, without cooperation with the patron tree. To the credit of amateur gardeners, at present, several methods have been developed for growing forest mushrooms in a private courtyard and a garden plot. In our article we will talk about the subtleties of self-cultivation of butter - delicious mushrooms suitable for pickling, frying and making soups.
Butterlets belong to the Bolet family, which includes about 250 different types of hat mushrooms (Fig. 17). In nature, several types of oil are common, of which the most common are late, or real, larch oil can, soft oil can, yellow-brown oil can and granular oil can. All these species can be cultivated on personal plots or on specially organized mushroom farms, depending on the conditions created, the composition of the soil and the presence of host trees with which these types of fungi form mycorrhiza.

Butterlets description:
In the wild, it grows mainly in the forest zone with a temperate climate on the edges and clearings of coniferous forests, along roadsides, in young plantings of pines and spruces; larch oiler is found in larch trees. Oiler is widespread in Europe and North America, inhabits Asia and Australia. In Russia, the butter dish lives everywhere: from Arkhangelsk and Vologda in the north to the forest-steppe zone of the Saratov and Voronezh regions in the European part of the country; it is typical for the Urals, Siberia and the Far East. Butter mushrooms are traditionally considered summer mushrooms; they grow in coniferous forests from June to October, and in warm autumn in the southern regions they are found until early November.
By the nature of nutrition, boletus belongs to the category of mycorrhizal fungi, or fungi-symbionts, forming mycorrhiza with the roots of young coniferous trees. In nature, the mycelium develops until its maximum fruiting about KZ-15 years, prefers light sandy soils with a high content of limestone and rich in organic matter, grows mainly on coniferous litter.
Outwardly, boletus is difficult to confuse with any other mushroom due to its characteristic oily cap, covered with a sticky layer on top, and yellowish flesh. In most species, the oily film separates easily from the pulp. The color of the cap is brown; depending on their type and soil characteristics, it can vary from yellowish-brown to red-brown or brown-olive.
The cap of the mushroom reaches an average of 5–6 cm in diameter, but often you can find mushrooms with a cap of 8–12 cm in diameter. At the initial stage of development of the fruiting body, the cap is either hemispherical or convex, and as the fungus grows, it straightens and becomes flatter. The height of the fungus is on average 6-10 cm, the stem is often cylindrical, in some species it can be clavate.
Oils application and useful properties:The mushroom has a harmonious taste, high nutritional value, and can be subjected to any processing method: from drying to boiling, roasting or pickling. Some types of oil, such as larch and graceful, contain medicinal substances that can bring relief from severe headaches and soothe an attack of gout. These properties of butter oil are widely used in folk medicine.
Growing oil:
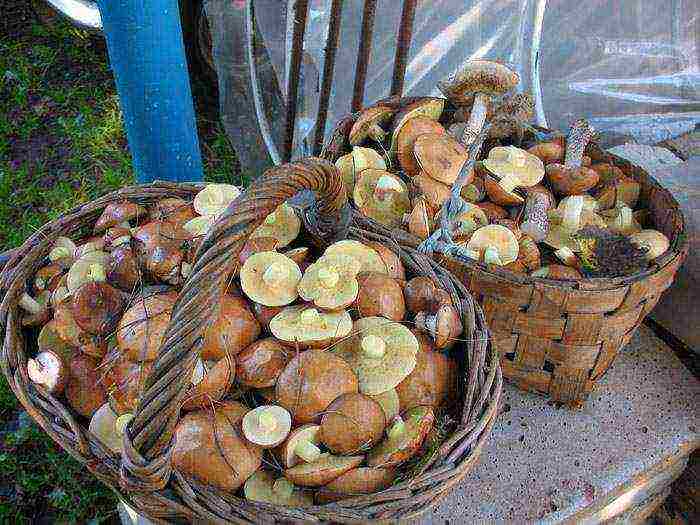
There are two ways of breeding oil:
1. In the first case, pine trees should already grow in your garden. To prepare planting material, you need to bring freshly picked boletus from the forest. The butter dish should be well ripe, even overripe. And then experienced mushroom pickers offer several options to choose from: in the fall, break the caps into small pieces and scatter them into well-moistened soil around the tree, covering them with fallen needles on top, if the latter are few, a week before sowing the spores, you can prepare a "pillow" of pre-scalded or boiled straw ; as an option, you can water the soil around the tree with a liquid suspension of ground mushrooms with the addition of food flour and gelatin (1 tablespoon per bucket); the third method of preparing the suspension is the most laborious, but also the most effective.
First, you need to separate the granular layer with spores, grind it and put it in a bowl with water (1-2 liters of the mixture per 10 liters of water); secondly, add 15 grams of dry yeast as a growth stimulant, and then leave to infuse for two weeks. Disputes during this time will settle to the bottom. Then you need to drain the water with garbage, and pour the sediment into the container. The life-giving mushroom mixture is ready for sowing within a year from the moment of preparation. Before pouring the liquid with spores under the trees, it must be diluted 1: 100 with water. Then gently and evenly, through a watering can, water the well-moistened soil under the pine trees, ideally during the rainy season.
2. If you do not have suitable trees on the site, look after several two-year-old pines (about a meter in size) in the forest with boletus growing around (there should be no competing weed fungi of the yellow-bearing weed around) and in the fall transfer them along with the mycelium. In order for the fungus root to form or take root in a new place, you need to create optimal conditions for the mycelium. Regular watering is essential if you are growing mushrooms such as boletus. The oiler grows naturally among the grass, so try to recreate a natural-like area under your pine trees. You may need to sow some herbs and plant shrubs.
Mushrooms should start bearing fruit in the second year after planting.: amicably and efficiently, and more than once a season they will delight you with boletus. Oiler in artificial plantings practically does not worm, which is especially pleasant. The area with mycelium should be fenced off from trampling. Mushrooms grow better during rainy periods, so when fruiting bodies appear, natural precipitation can be imitated by scattered irrigation with cold water. Of course, growing boletus in the garden is 100% justified by the fact that they regularly replenish the owners' table with fresh mushrooms. Therefore, if the size of the garden area allows, start growing forest mushrooms - you will not regret it!
In industrial mushroom growing, oil cans are bred to a limited extent due to the lack of a highly profitable technology for intensive cultivation in enclosed spaces, and therefore large areas with coniferous plantings are required to create production plots.However, the cultivation of boletus is typical for amateur mushroom growing due to the excellent qualities of the mushrooms, as well as the high fertility of the mycelium. Today, in the culture of boletus, they are grown by amateur mushroom growers according to an extensive method, as close as possible to natural
Due to the characteristic feature of fungi, to form mycorrhiza with the roots of young coniferous trees, for plantations of boletus, a site with several young pines, cedars, larch or spruces is selected, depending on the type of oiler and the growing conditions of the mycelium from which the mycelium was obtained. The desired age of trees is from 10 to 15 years, it is with such a neighborhood that the mycelium of oily mushrooms develops as actively as possible, since young trees take less nutrients from the soil and water, leaving more nutrition for the mushrooms. Some types of boletus, taken from mixed forests, can be grown under deciduous trees with which they are able to create symbiosis. Butterflies love light partial shade, but they can grow in sunny areas, prefer acidic soils, and are able to grow on enriched peatlands.
To create an optimal soil for the development of mycelium, the top layer of the soil in the selected area is removed to a depth of 20 cm. The soil nutritious for oily soil is formed from several layers. The first, lower layer is made from plant materials - it can be cut grass, fallen leaves, chopped wood, needles. It is desirable to create the second layer from the soil collected at the place where the mushrooms grow - in this case, its acid-base balance will be as close as possible to the optimal one, but you can replace it with ordinary garden soil. Depleted garden soil must be enriched with humus. The mycelium of fungi is sown on the prepared soil.
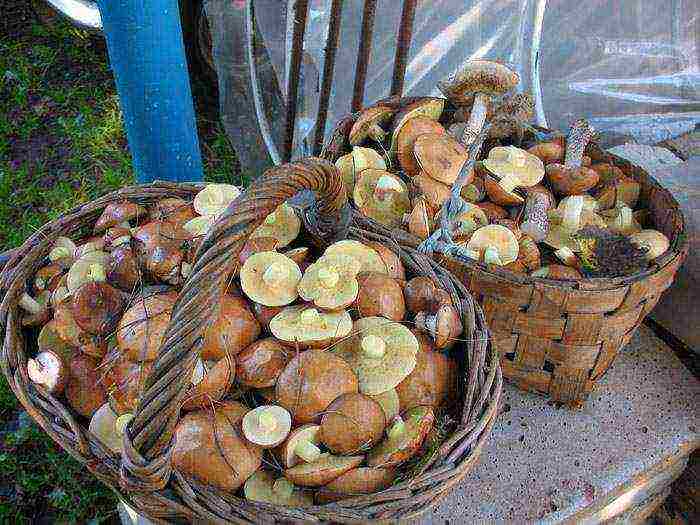
Sowing mycelium oil:
Today, most mushroom growers prefer to use spores of overripe mushrooms collected in the forest for planting, despite the fact that oil mycelium obtained in laboratory conditions is now presented in specialized online stores. This is primarily due to the nature of the nutrition of the fungus, which receives most of the organic matter from the tree, with which it forms a symbiosis. With such a diet, the composition of the soil, as well as the type of trees with which the oiler forms a symbiosis, are of paramount importance. As a rule, in conditions that are very different from natural ones, in which the mycelium developed earlier, fruiting bodies are not formed, despite its successful development.
Obtaining mycelium from spores can be done at home, for which the collected mushrooms must be mixed with a specially selected substrate. The substrate for the development of mycelium is prepared on the basis of peat and coniferous sawdust, which help to create a nutrient medium close to natural. To obtain sawdust, it is advisable to use those tree species near which the mushrooms collected for cultivation grew. For the reproduction of mycelium, ordinary three-liter jars are better suited. Thoroughly dried substrate is laid out in a jar, lightly tamped until the container is about half full. Additional nutrition for the mycelium is provided by a special nutrient solution, which is prepared on the basis of sugar syrup with the addition of yeast suspension at the rate of: 1 tsp for each liter of water. sugar and the same amount of yeast. For each three-liter jar, it is necessary to prepare 1.5 liters of nutrient solution. It is brought to a boil, after which the peat laid out in jars is poured into it. Then add dried sawdust until the entire volume of the jar is filled, close the lid tightly and leave for 5 hours to saturate the substrate with nutrients. Then the remaining water is drained, the substrate is thoroughly mixed, punctures are made in several places with a thin stick and pieces of mushrooms with spores are placed in the holes made.The jar is tightly covered with a lid with a 1.5 cm hole made in it, which is plugged with a foam rubber stopper and left for 3 months, keeping the room temperature at 23–25 ° C. After the development of the hyphae, the substrate with the mycelium is removed before sowing in a cold, dark room with a temperature of about 6 ° C.
Butter care and harvesting:The propagated mycelium is added to the trees in the spring. The substrate, filled with mycelium, is evenly distributed in a thin layer over the prepared area, after which it is covered with a layer of plant material from leaves or grass, and a layer of garden or forest soil is added on top. The sown area is watered from sprinklers with fine spraying or by the drip method until the upper soil layer is moistened. From above, the site can also be covered with a thin layer of leaves to protect the soil from drying out. As it dries, the soil must be moistened.
Fruiting occurs a year after sowing, continues in one place up to 15 years. In the fall, it is advisable to cover the beds sown with mycelium with straw, grass, leaves. In the spring, the protective layer is removed, leaving a thin layer of plant material. Unlike forest oil, garden ones are almost never wormy, since in the garden soil there are no natural pests of fungi characteristic of the forest.

As a rule, the harvest is insignificant in the first years, since the mycelium continues to develop for another 5–7 years, after which the number of fruiting bodies will begin to increase significantly. Collect the boletus by hand, twisting the mushrooms or cutting them at the root. After 10-15 years, with a decrease in fruiting, the mycelium can be replaced. To obtain stable yields, several plots with different ages of myceliums are created on plantations, which makes it possible to collect abundant harvests of mushrooms annually. After cutting, the butter oil can be used both for cooking and for preparing for future use - the mushrooms need to be dried or pickled.
Fresh butter soup
At the weekend, we went out with friends to the forest to pick mushrooms. We had a rest in nature, took a walk and came across a huge clearing with boletus. A real find! Today we have fresh butter soup for lunch!
Cooking description:Butterlets are just asking for soup, let's not torment them and let's get down to it. First chop and sauté the onions, carrots and celery, then add the mushrooms, salt and pepper to taste and fry together for 10 minutes. At this time, your potatoes, which have been boiled in broth, are almost ready. Add vegetables and mushrooms, bay leaf to it and let it boil. Set aside the prepared soup from the heat and serve with sour cream. Bon Appetit!
Ingredients: Butterlets - 300 Grams
Onion - 1 Piece
Carrots - 1 Piece
Celery stalk - 1 Piece
Potatoes - 3 Pieces
Black peppercorns - 2 Pieces
Bay leaf - 1 piece
Vegetable oil - To taste
Salt - To taste
Servings: 4
How to make "Fresh Butter Soup"Chop onions, carrots, celery and sauté them in olive oil. Boil the chopped potatoes.
Then add mushrooms, salt, pepper to vegetables and fry together for 8-10 minutes.
Add peppercorns to the broth with half-cooked potatoes and cook until tender.
Then add the mushrooms and vegetables from the pan to the pan, add the bay leaf and let it boil for literally 1 minute. Set aside from heat and serve with sour cream.
Discuss this article on the forum
- Butterlets and their counterparts
- Oil and their benefits
- Types of butter
- Chanterelle species
- The healing properties of chanterelles
Butterlets belong to the Bolet family, which includes about 250 different types of hat mushrooms (Fig. 17). In nature, there are several types of oil, of which the most common are late, or real, larch oil can, soft oil can, yellow-brown oil can and granular oil can.All these species can be cultivated on personal plots or on specially organized mushroom farms, depending on the conditions created, the composition of the soil and the presence of host trees, with which these types of fungi form mycorrhiza.
Butter description:
In the wild, it grows mainly in the forest zone with a temperate climate on the edges and clearings of coniferous forests, along roadsides, in young plantings of pines and spruces; larch oiler is found in larch trees. Oiler is widespread in Europe and North America, inhabits Asia and Australia. In Russia, the butter dish lives everywhere: from Arkhangelsk and Vologda in the north to the forest-steppe zone of the Saratov and Voronezh regions in the European part of the country; it is typical for the Urals, Siberia and the Far East. Butter mushrooms are traditionally considered summer mushrooms; they grow in coniferous forests from June to October, and in warm autumn in the southern regions they are found until early November.
By the nature of nutrition, boletus belongs to the category of mycorrhizal fungi, or fungi-symbionts, forming mycorrhiza with the roots of young coniferous trees. In nature, the mycelium develops until its maximum fruiting about KZ-15 years, prefers light sandy soils with a high content of limestone and rich in organic matter, grows mainly on coniferous litter.
Outwardly, boletus is difficult to confuse with any other mushroom due to its characteristic oily cap, covered with a sticky layer on top, and yellowish flesh. In most species, the oily film separates easily from the pulp. The color of the cap is brown; depending on their type and soil characteristics, it can vary from yellowish-brown to red-brown or brown-olive.
The cap of the mushroom reaches an average of 5–6 cm in diameter, but often you can find mushrooms with a cap of 8–12 cm in diameter. At the initial stage of development of the fruiting body, the cap is either hemispherical or convex, and as the fungus grows, it straightens and becomes flatter. The height of the fungus is on average 6-10 cm, the stem is often cylindrical, in some species it can be clavate.
Oils application and beneficial properties:
The mushroom has a harmonious taste, high nutritional value, and can be subjected to any processing method: from drying to boiling, roasting or pickling. Some types of oil, such as larch and graceful, contain medicinal substances that can bring relief from severe headaches and soothe an attack of gout. These properties of butter oil are widely used in folk medicine.
Butterlets growing:
In industrial mushroom growing, oil cans are bred to a limited extent due to the lack of a highly profitable technology for intensive cultivation in enclosed spaces, and therefore large areas with coniferous plantings are required to create production plots. However, the cultivation of boletus is typical for amateur mushroom growing due to the excellent qualities of the mushrooms, as well as the high fertility of the mycelium. Today, in the culture of boletus, they are grown by amateur mushroom growers according to an extensive method, as close as possible to natural
Due to the characteristic feature of fungi, to form mycorrhiza with the roots of young coniferous trees, for plantations of boletus, a site with several young pines, cedars, larch or spruces is selected, depending on the type of oiler and the growing conditions of the mycelium from which the mycelium was obtained. The desired age of trees is from 10 to 15 years, it is with such a neighborhood that the mycelium of oily mushrooms develops as actively as possible, since young trees take less nutrients from the soil and water, leaving more nutrition for the mushrooms. Some types of boletus, taken from mixed forests, can be grown under deciduous trees with which they are able to create symbiosis.Butterflies love light partial shade, but they can grow in sunny areas, prefer acidic soils, and are able to grow on enriched peatlands.
To create an optimal soil for the development of mycelium, the top layer of the soil in the selected area is removed to a depth of 20 cm. The soil nutritious for oily soil is formed from several layers. The first, lower layer is made from plant materials - it can be cut grass, fallen leaves, chopped wood, needles. It is desirable to create the second layer from the soil collected at the place where the mushrooms grow - in this case, its acid-base balance will be as close as possible to the optimal one, but you can replace it with ordinary garden soil. Depleted garden soil must be enriched with humus. The mycelium of fungi is sown on the prepared soil.
Sowing mycelium oil:
Today, most mushroom growers prefer to use spores of overripe mushrooms collected in the forest for planting, despite the fact that oil mycelium obtained in laboratory conditions is now presented in specialized online stores. This is primarily due to the nature of the nutrition of the fungus, which receives most of the organic matter from the tree, with which it forms a symbiosis. With such a diet, the composition of the soil, as well as the type of trees with which the oiler forms a symbiosis, are of paramount importance. As a rule, in conditions that are very different from natural ones, in which the mycelium developed earlier, fruiting bodies are not formed, despite its successful development.
Obtaining mycelium from spores can be done at home, for which the collected mushrooms must be mixed with a specially selected substrate. The substrate for the development of mycelium is prepared on the basis of peat and coniferous sawdust, which help to create a nutrient medium close to natural. To obtain sawdust, it is advisable to use those tree species near which the mushrooms collected for cultivation grew. For the reproduction of mycelium, ordinary three-liter jars are better suited. Thoroughly dried substrate is laid out in a jar, lightly tamped until the container is about half full. Additional nutrition for the mycelium is provided by a special nutrient solution, which is prepared on the basis of sugar syrup with the addition of yeast suspension at the rate of: 1 tsp for each liter of water. sugar and the same amount of yeast. For each three-liter jar, prepare 1.5 liters of nutrient solution. It is brought to a boil, after which the peat laid out in jars is poured into it. Then add dried sawdust until the entire volume of the jar is filled, close the lid tightly and leave for 5 hours to saturate the substrate with nutrients. Then the remaining water is drained, the substrate is thoroughly mixed, punctures are made in several places with a thin stick and pieces of mushrooms with spores are placed in the holes made. The jar is tightly covered with a lid with a 1.5 cm hole made in it, which is plugged with a foam rubber stopper and left for 3 months, keeping the room temperature at 23–25 ° C. After the development of the hyphae, the substrate with the mycelium is removed before sowing in a cold, dark room with a temperature of about 6 ° C.
Butter care and harvesting:
The propagated mycelium is added to the trees in the spring. The substrate, filled with mycelium, is evenly distributed in a thin layer over the prepared area, after which it is covered with a layer of plant material from leaves or grass, and a layer of garden or forest soil is added on top. The sown area is watered from sprinklers with fine spraying or by the drip method until the upper soil layer is moistened. From above, the site can also be covered with a thin layer of leaves to protect the soil from drying out. As it dries, the soil must be moistened.
Fruiting occurs a year after sowing, continues in one place up to 15 years.In the fall, it is advisable to cover the beds sown with mycelium with straw, grass, leaves. In the spring, the protective layer is removed, leaving a thin layer of plant material. Unlike forest oil, garden ones are almost never wormy, since in the garden soil there are no natural pests of fungi characteristic of the forest.
As a rule, the harvest is insignificant in the first years, since the mycelium continues to develop for another 5–7 years, after which the number of fruiting bodies will begin to increase significantly. Collect the boletus by hand, twisting the mushrooms or cutting them at the root. After 10-15 years, with a decrease in fruiting, the mycelium can be replaced. To obtain stable yields, several plots with different ages of myceliums are created on plantations, which makes it possible to collect abundant harvests of mushrooms annually. After cutting, the butter oil can be used both for cooking and for preparing for future use - the mushrooms need to be dried or pickled.


